science chapter 2 lesson 1/2/3
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
nucleus
Contains the cell’s DNA & is the control center of the cell
lysosmes
Digests wastes, worn out cell parts, and foreign invaders; trash can of the cell
a ribosomes
Site where amino acids are hooked together to make proteins; the factory
cell membrane
Controls the movement of nutrients into the cell and waste products out of the cell
cell walls
Supports and protects the cell while still letting materials pass through it; only in plant cells
vacuole
Store water, nutrients and even waste.
cloroplast
Converts the sun’s energy into high – energy sugars through the process of photosynthesis.
mitochondria
Uses cellular respiration to convert food energy into a chemical energy called ATP that can be used by the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
System of tubes through the cytoplasm that allow proteins & other materials to pass from one place to another.
cytoplasm
Fluid-like material inside the cell that contains all of the cell’s organelles
golgi apparatus
ite where proteins are further processed for shipment out of the cell.
true
The microscope led to the discovery of cells.
true
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells.
false
Animal and plant cells have the same structures and look identical.
true
Cell theory has 3 core ideas.
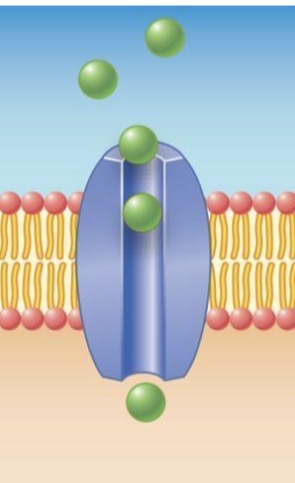
channel proteins
receptor protiens
recognition proteins
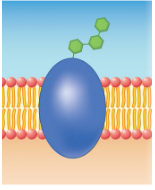
what sits on the surface.
peripheral proteins
what goes through the membrane;
integral proteins
what transport moves molecules without energy.
passive transport
what transport uses energy to move molecules
Active transport
Tell me one structure that a plant cell that an animal cell does not have
cell wall
explain why a plant cell needs this structure but an animal cell does not.
(Cell wall)
they provide support and protection while animals don’t need this because they can move and get support from their bones
what is the movement of other molecules other than water from high to low concentration
Diffusion
What is the diffusion of water across a membrane
Osmosis
What are the three core ideas of cell theory?
All living things are made of cells.
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
All cells come from preexisting cells.
The invention of this scientific instrument led to the discovery of cells:
Microscope
The cell theory states that all cells come from where?
Preexisting cells
Describe the role of a Lysosome
Digests waste and worn out cell parts
Explain the primary difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell:
Prokaryotic cells are simpler While eukaryotic cells is more complex
True or False: The cell membrane is also referred to as the Fluid Mosaic Model
True
What is the primary molecule that makes up the cell membrane
Phospholipids
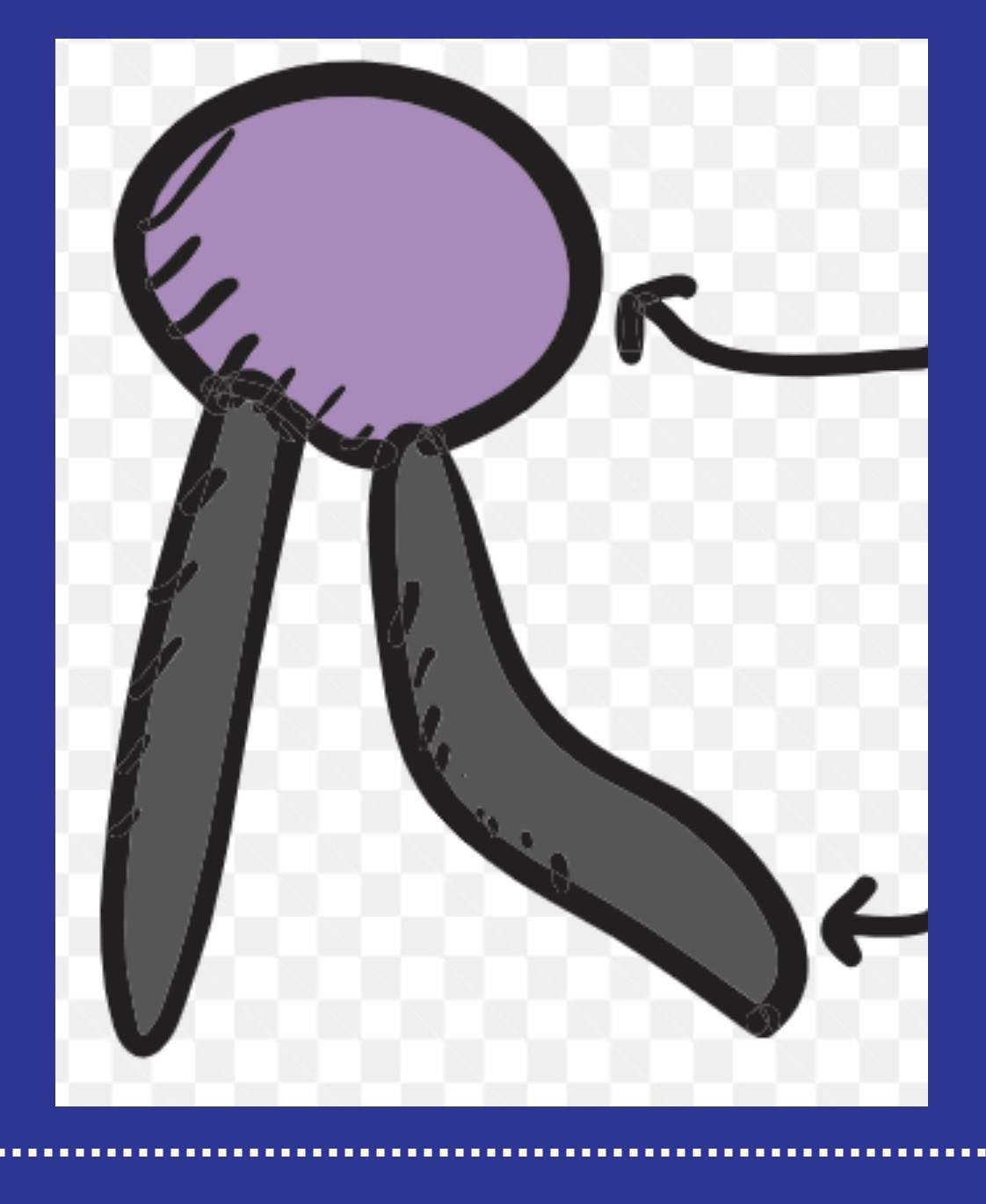

Looking at the image of the phospholipid, which part is polar (hydrophilic) and which part is nonpolar (hydrophobic
The head (purple circle) is polar and the tails (black lines) are nonpolar

Where is channel protein
J
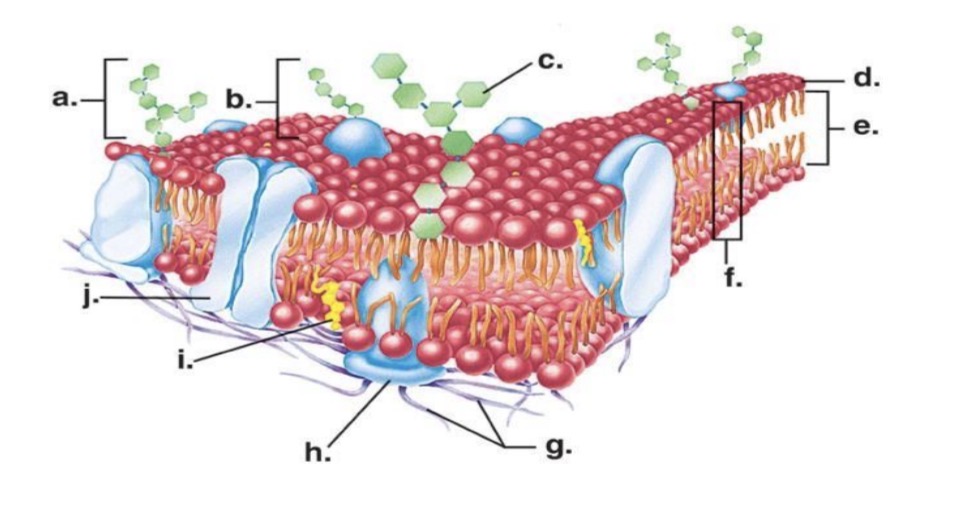
Where is carbohydrate chain
A

Where is recognition protein
B
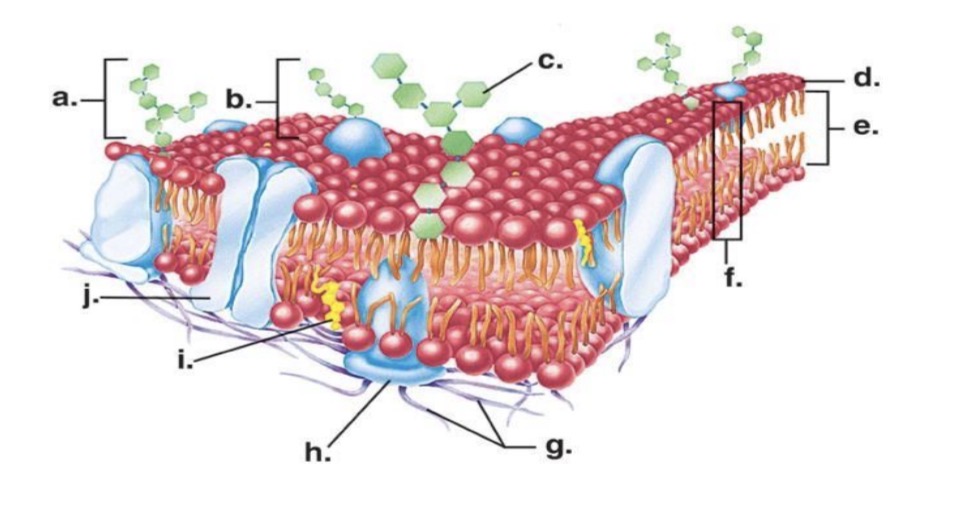
Where is hydrophobic tail
E
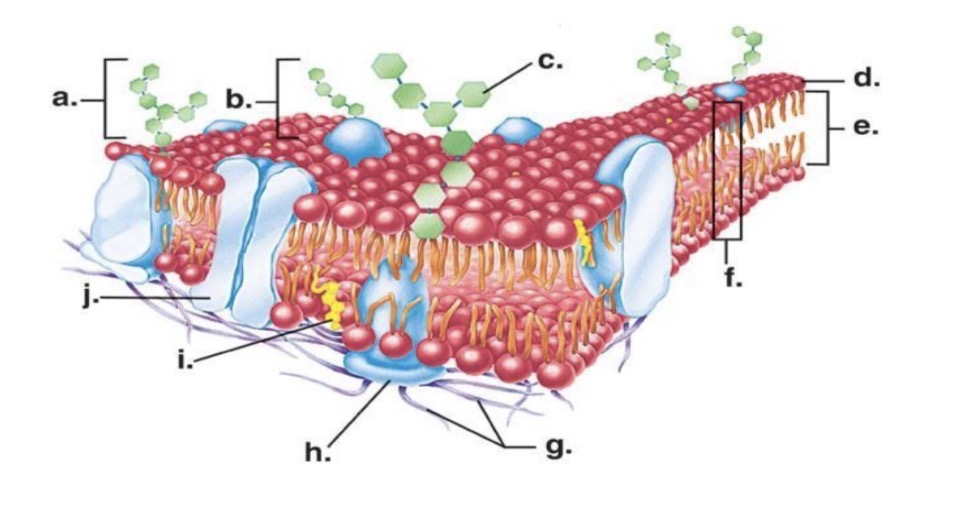
Where is hydrophilic head
D
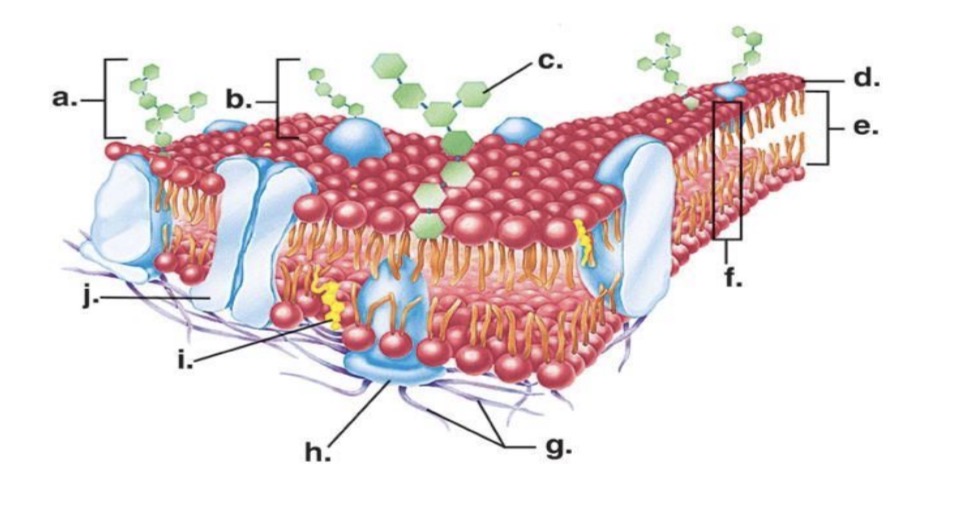
Cholesterol
I
True or False: The cell membrane allows all substances to pass through it, regardless of size and polarity
False
This process moves molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration and does not require energy
Passive transport
Define facilitated diffusion
is molecules other than water of other higher to low concentration
Why might some molecules need a channel protein to get into the cell even if they are moving with a concentration gradient?
Some molecules are too big or have a charge
What are the major differences between passive transport and active transport?
Passive transport does not use energy while transport
While active uses energy to transport
Define Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water from high to low concentration
Fill in the blank:
Water moves from an area of ________ concentration to an area of ________ concentration
High and low
What specific evidence in the celery lab supported the claim that water moved into the celery stalk?
The water was red and it was visible in part of the celery that wasn’t exposed to water
Integral proteins
Proteins that inside the membrane and go from one side to the other
Peripheral proteins
Protein’s that stay on one side of the cell membrane