Bones, Joints, and Synovial Fluid
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Skeletal function
Structure, organ protection, locomotion, mineral storage, hematopoiesis, and adaptation
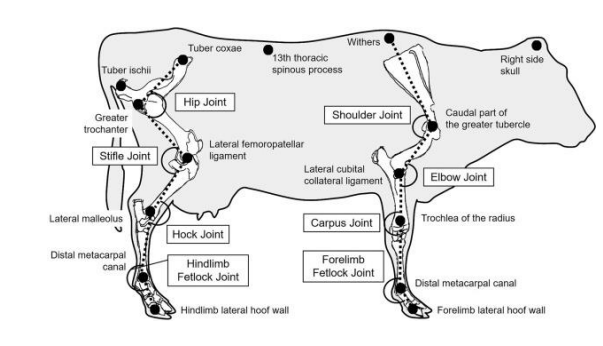
Bones Labeled

Axial skeleton
lies on the long axis (midline) of the body and includes the skull, vertebrae, and those bones attached to the vertebrae (ribs, ventral connections of the ribs, and sternum)
Nucleus pulposus
acts as a gel-like shock absorber that distributes pressure within the intervertebral disc, while the anulus fibrosus provides structural support, containing the nucleus and resisting excessive movement
Appendicular skeleton
made up of the bones of the front (thoracic) and hind (pelvic) limbs and their respective pectoral girdle (shoulder) and pelvic girdle (pelvis)
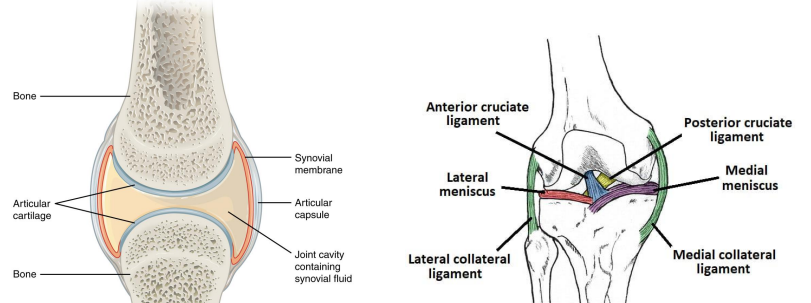
a specialized type of connective tissue that covers the ends of bones in joints; reduces friction and absorbs shock in joints
a porous bone tissue that houses red marrow for blood cell production and provides lightweight support
Cavity that stores fat (yellow marrow) or produces blood cells (red marrow)
a dense layer of vascular connective tissue enveloping the bones except at the surfaces of the joints that supports bone growth, repair, and nutrient supply
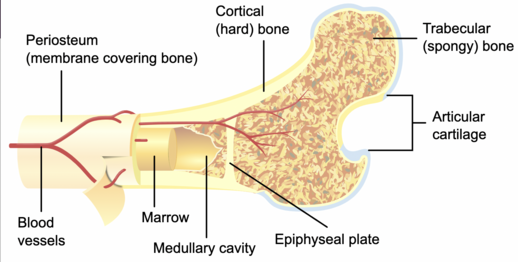
dense, hard outer layer of bones that provides strength and structural support
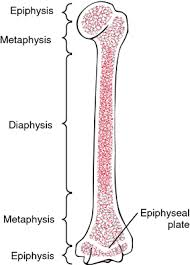
the end part of a long bone that forms joints and contains spongy bone with marrow
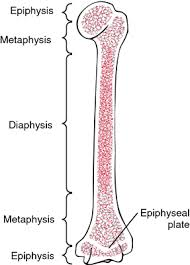
The shaft of the bone, providing leverage and strength
minute tubes which form a network in bone; contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels to supply nutrients and oxygen to bone cells
Concentric rings of calcified matrix inside the bone that provide bone strength
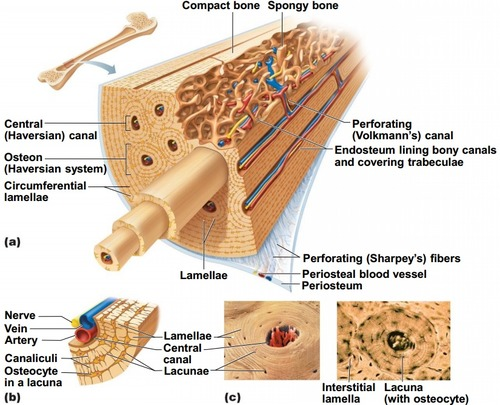
lamellae that house osteocytes (bone
cells)
Tiny channels in the bone connecting lacunae, allowing osteocytes to exchange nutrients and waste
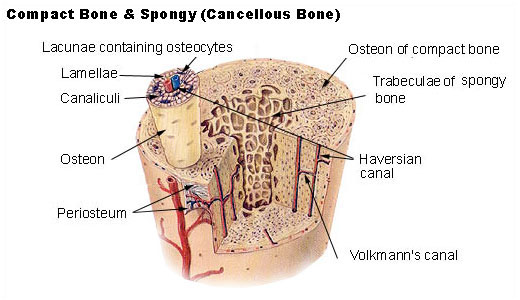
Perpendicular canals in bone that connect Haversian canals, facilitating blood flow between osteons
Build bone by producing and mineralizing bone matrix
Mature bone cells; maintain bone structure and regulate nutrients
Break down bone for remodeling and calcium release.
Stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts for bone growth and repair.
starts as hyaline cartilage
the diaphysis
epiphyses after birth
replaced by bone in distinct
zones
The thin layer of cartilage near the ends of long bones ossifies into the epiphyseal line, stopping growth in adulthood
Bone remodeling
Osteoclasts reshape the bone, restoring strength and structure; a continuous process of renewal: 1) Activation (Osteoclasts are recruited), 2) Reabsorption (Osteoclasts break down the old bone), 3) Reversal (Osteoclasts die and osteoblasts arrive), 4) Formation (Osteoblasts build new bone); ARRF
Joints Labeled