Midterm Exam Review
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
____ amputations are 11x more common than ____
LE>UE
The leading cause of amputation is ________
Dyvascular disease
What are the risk factors for amputations as a consequence of disease?
CCVD
HTN
High cholesterol
Smoking
Amputations due to trauma are most common among which population?
Young adult men
Amputations due to cancer are most common in ages ____
12-20
Amputations due to cancer are most often a result of ___________
Osteosarcoma
The “name” of the amputation is always based on…
The main bone amputated or the joint disarticulated
T/F: Most amputations occur proximally
FALSE
What are the 4 main categories of surgical consideraitions for an amputation?
Nerves [pulled distally to avoid neuromas in scar tissue]
Bone
Healing
Post-op dressing
Smokers have a ____ rate of infections and re-amputation
2.5x
What is the MOST important factor that can affect rehab success?
The activity level AT (before) the time of amputation
______ preservation is key for ambulation success
Knee
Main risk factors for diabetic foot:
Sensory loss
Abnormal mechanical stresses
Poor circulation
What are the areas tested in the Semmes-Westein Monofilament testing?
1,3,5 Met heads
Medial & lateral midfoot
Heel
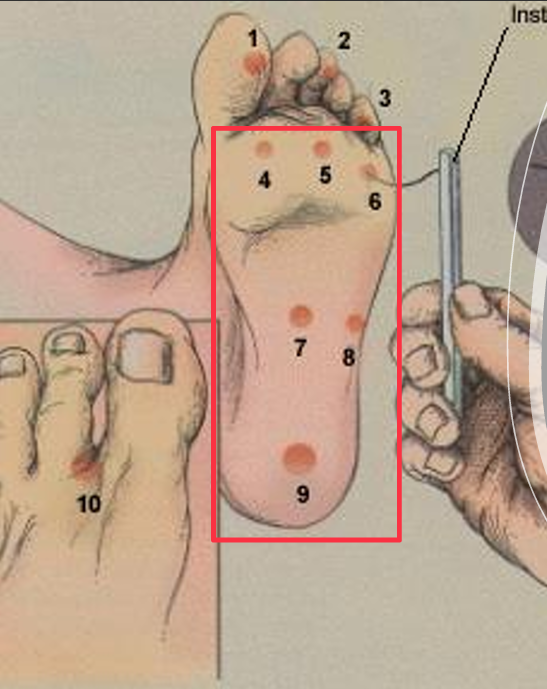
____ = BEST # for protective sensation assessment
5.07
Vascular risk factors:
Ankle Brachial Index < 0.9
Toe systolic pressure < 30mmHg
Transcutaneous oxygen tension < 26 mm/Hg
Prevention risk categories:
0 = No loss of protective sensation
1 = Loss of protective sensation
2 = Loss of protective sensation with high pressure (callus/deformity) or poor circulation
3 = PMHx of ulceration
Follow up schedule based on prevention (0-3):
Education; 6 mo F/U for foot/shoe screening; protective footwear; nail/callus/skin care as needed
Education; molded/modified footwear; 3 mo F/U for foot/shoe screening; protective footwear; nail/callus/skin care as needed
Education; monthly F/U for foot/shoe screening; appropriated footwear; nail/callus/skin care as needed
An ABI of <.45 means…
Wound healing is unlikley
When is an amputation necessary?
Presence of necrosis because of vascular impairment or trauma (with or without infection)
What are the 3 main factors that determine the level of amputation?
1. Ability to heal at the incision
2. Removal of nonviable tissues
3. Ability to achieve a long-term functional residual limb (to avoid revisions)
During the post-op stage, dressings are worn for about _________
2 weeks
During the post-op stage, after removing dressings, patients get for a preparatory prosthesis that they will wear for ________
3-12 months during the residual limb shrinkage (this is NOT standard practice anymore)
The standard length of a transtibial amputation (measured from tibial plateau) is ____
5-6 inches
If the residual limb is ______, pt will have difficulty with prosthetic control
3 in or less
For a TT circumference residual limb measurement, you should start at _________________
Tibial plateau or tibial tuberosity
For a TF circumference residual limb measurement, you should start at _________________
Ischial tuberosity or greater trochanter
Desired shape of residual limb: TT vs TF
TT: Cylindrical shape — within ¼ inch of the proximal circumference
TF: Conical shape — distal should be less than proximal
ACE Wraps: Pros and Cons
Disadvantages: Requires skill and experience for proper application
Can slip and form a tourniquet effect
Advantages: Inexpensive, Light Weight, Readily Available
Shrinkers: Pros and Cons
Advantages: Easy to don, no special skill needed to don, easy to control amount of pressure
Pressure is constant
Disadvantages: More expensive than ace wrap, often painful to apply and wear immediately after surgery
IPOP: Pros and Cons
Advantages: Immediate ambulation with limited weight bearing (will be connected to prosthetic foot!)
↓ psychological traumatic period when limb is absent
Less pain, mobilize faster,
Disadvantages: Possibly injurious effects, particularly in weight bearing and its effects on wound healing
Limits access to the surgical site, potential tissue damage and wound breakdown

RRD: Pros and Cons
Advantages: Provides excellent protection, improved wound healing environment (not connected to prosthetic foot)
Allows some weight-bearing exercises
Disadvantages: Does not prevent flexion contractures
Messy and requires skill/practice

What are the TWO essential things that determine when a patient is ready for their prosthetic?
When the wound is healed (#1), and when the best shape for the residual limb is achieved
Main forms of contractures:
TT: Knee flexion
TF: Hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation (bad for ambulation)
Delaying weight bearing at least ______ may reduce complications
2 weeks
Functional demands of the foot during the stance phase:
1. Shock absorption
2. Maintain balance during single limb support
3. Propulsion
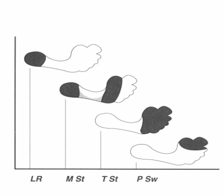
____ of all partial foot amputees ultimately require revision to a higher amputation level
1/3
Standard treatment for a transphalyngeal amputation
Diabetic shoe
Standard treatment for a ray resection amputation
Toe filler
Resection of the _____ ray is most common due to ulceration
5th
Transverse Metatarsal Amputation (TMA): Main complications
Balance and gait are affected: ↓ WB area, ↓ lever arm
Muscle imbalances: DF is often limited due to the loss of attachment points for the DF muscles
Skin breakdown and ulcer due to sheer friction and pointed pressure
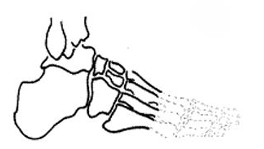
For a TMA, why is the risk of EV+PF contracture so high?
PF is unopposed by DF since attachment points were removed (Some DF are also inverters, which follow this same relationship)
What is a Lisfranc amputation? What are the main complications?
Tarsal-metatarsal disarticulation
Same risks as TMA + Higher risk for plantar flexion contracture
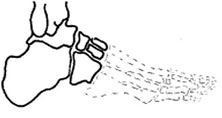
Which type of amputation has the HIGHEST risk for PF ccontracture?
Chopart (mid-tarsal disarticulation)
What is a Chopart amputation? What are the main complications?
MID-tarsal disarticulation
Talo-navicular + Cuneiform-calcaneus disarticulation
Same concerns as Lisfranc and TMA + Highest risk of contracture
Functional deficits with Midfoot PFA
↓ lever arm & ↓ step length (with sound leg)
Shoe fillers should allow toe break/extension by ___ degrees
15

Ss the length of the foot decreases, there is a greater need for additional _______ control
Proximal
What is a Boyd amputation? What are the advantages?
Horizontal resection of calcaneus followed by arthrodesis to distal tibia
Allows end weight bearing without a prosthesis
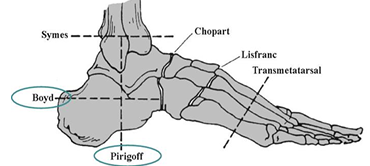
What is a Pirogoff amputation? What are the advantages?
Vertical resection of calcaneus rotated 90 degrees then arthrodesis to distal tibia
Allows end weight bearing without a prosthesis
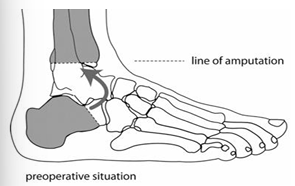
What is a Symes amputation? What are the PROS and CONS?
Ankle disarticulation
Pros
Self-suspension over malleoli
Maintains limb length + clearance
End weight bearing within socket
Cons
Bulbous distal end → limited suspension and prosthetic foot options
Requires a healthy calcaneal fat pad
Requires application of volume management socks.
Identify K Level: Does not have the ability or potential to ambulate or transfer safely
K0
Identify K Level: Has the ability or potential to use a prosthesis for transfer or ambulation on level surfaces at constant cadence
K1
Identify K Level: Has the ability or potential for ambulation with the ability to traverse low level environmental barriers such as curbs, stairs, or uneven surfaces
K2
Identify K Level: Has the ability or potential for ambulation for ambulation with variable cadence
K3
Has the ability or potential for prosthetic ambulation that exceeds basic ambulation skills, exhibiting high impact, stress or energy levels
K4
When does insurance cover a lower limb prosthesis?
If pt will reach or maintain a defined functional state within a reasonable period of time
SACH contraindications
When inversion/eversion is required
K3-K4 patients (active individuals)
Disadvantages: Limited plantar flexion/dorsiflexion adjustability
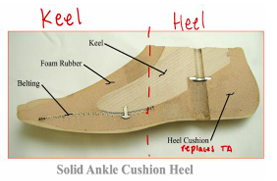
Flexible Keel contraindications
When inversion/eversion is required
K3-K4 patients (active individuals)


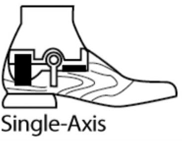
What are the main indications for a single axis foot prescription?
Need for ↑ knee stability (controls compression)
Very short TT residual limb
Hip disarticulation
Patients whose knees “buckle” – as this induces knee EXTENSION moment
Single axis foot contraindications
When inversion/eversion is required
K3-K4 patients (active individuals)
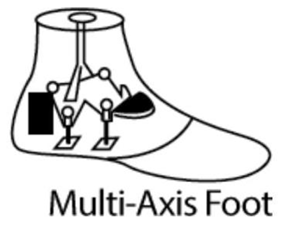
What are the main indications for a Multiaxial foot prescription?
Ambulation on varying terrain
↑ knee stability at heel strike, bumpers can be varied
simulates inversion/eversion AND reduces torque on residual limb
K2???
What are the main indications for a dynamic response foot prescription?
Variable cadence** (K3-K4)
Ambulators + unlimited community ambulators
Active individuals (NOT FOR K2-1)

What are the main indications for a multiaxial dynamic response foot prescription?
Variable cadence** (K3-K4)
Ambulators + unlimited community ambulators
Suitable for uneven terrain
Active individuals (NOT FOR K2-1)

Why would you use a knee immobilizer over a RRD or any other dressings?
Prevents Flexion Contracture + Protection & Compression
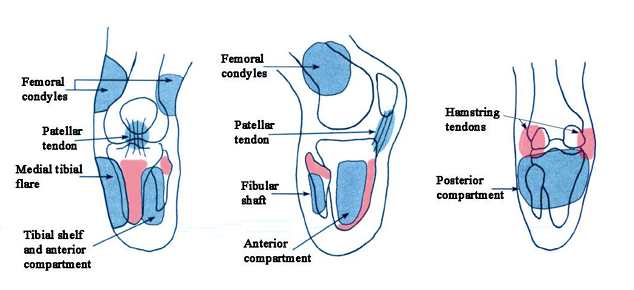
What are the most pressure-sensitive areas in a PTB socket?
Tibial tuberosity, fibular head, and hamstring tendons
After ___ ply socks, the pateint will need a new socket
10
In a PTB-SC, the prostheris ssuspends from the _______
Femoral condyles

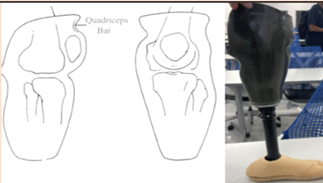
What are the main advantages of a PTB-SCSP socket?
Controls Knee extension using the Quadriceps Bar
Good for those that tend to hyperextend
Good for those with short residual limbs
What are the main advantages of a TSB socket?
Equal distribution of loads across the entire surface of the residual limb
Improved Suspension
Decreased shear on the residual limb
Anatomical suspensions are mainly prescribed for which population?
Pediatric patients and disarticulation amputees

Suction suspensions are contrainidicated when…
excessive volume fluctuations or inability to complete donning
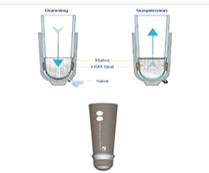
Suspension sleeve advantages
Allow unrestricted knee motion but does control for rotational component
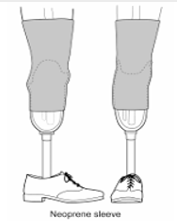
A supracondylar cuff mainly restricts knee ______ and does NOT provide _____ stability
flexion, M/L
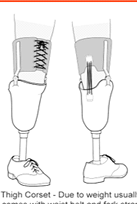
Which suspension mechanism provides the MAXIMAL M/L stability as well as prevention of recurvatum?
Thigh corset
Redistributes some weight-bearing and torque forces to the thigh
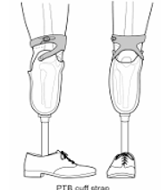
A supracondylar cuff mechanism does not provide even suspension through ________ _______
Swing phase
AMPnoPRO scoring
(Out of 43)
K0 = 0-8
K1 = 9-20
K2 = 21-28
K3 = 29-36
K4 = 37-43
AMPro Scoring
(Out of 47)
K1 = 15-26
K2 = 27-36
K3 = 37-42
K4 = 43-47
TT bilateral amputation patients have _______ energy expenditure than TF unilateral amputation patients
LESS, remember the importance of the knee joint in energy preservation!
Traumatic TT bilateral amputees experience a _____ increase in EE
41%
Traumatic TF unilateral amputees experience a _____ increase in EE
60-70%
Quiet standing is “a natural stance is achieved when the ______ is balanced with the _______ at the foot.”
CoG, CoP
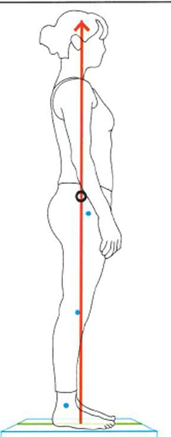
Plumbline alignment
Hip – slightly ________
Knee – slightly _______
Ankle – slightly _______
Hip – slightly POSTERIOR (EXT moment)
Knee – slightly ANTERIOR (EXT moment)
Ankle – slightly ANTERIOR (DF moment)