Cell Homeostasis (Cell transport)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
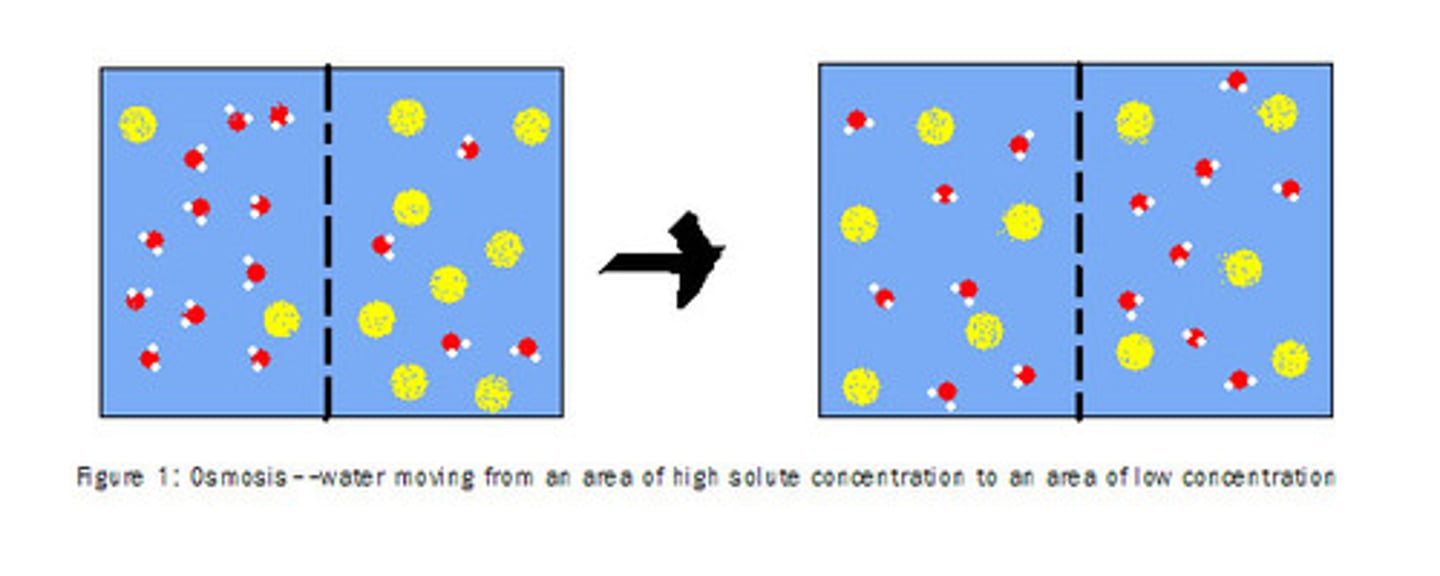
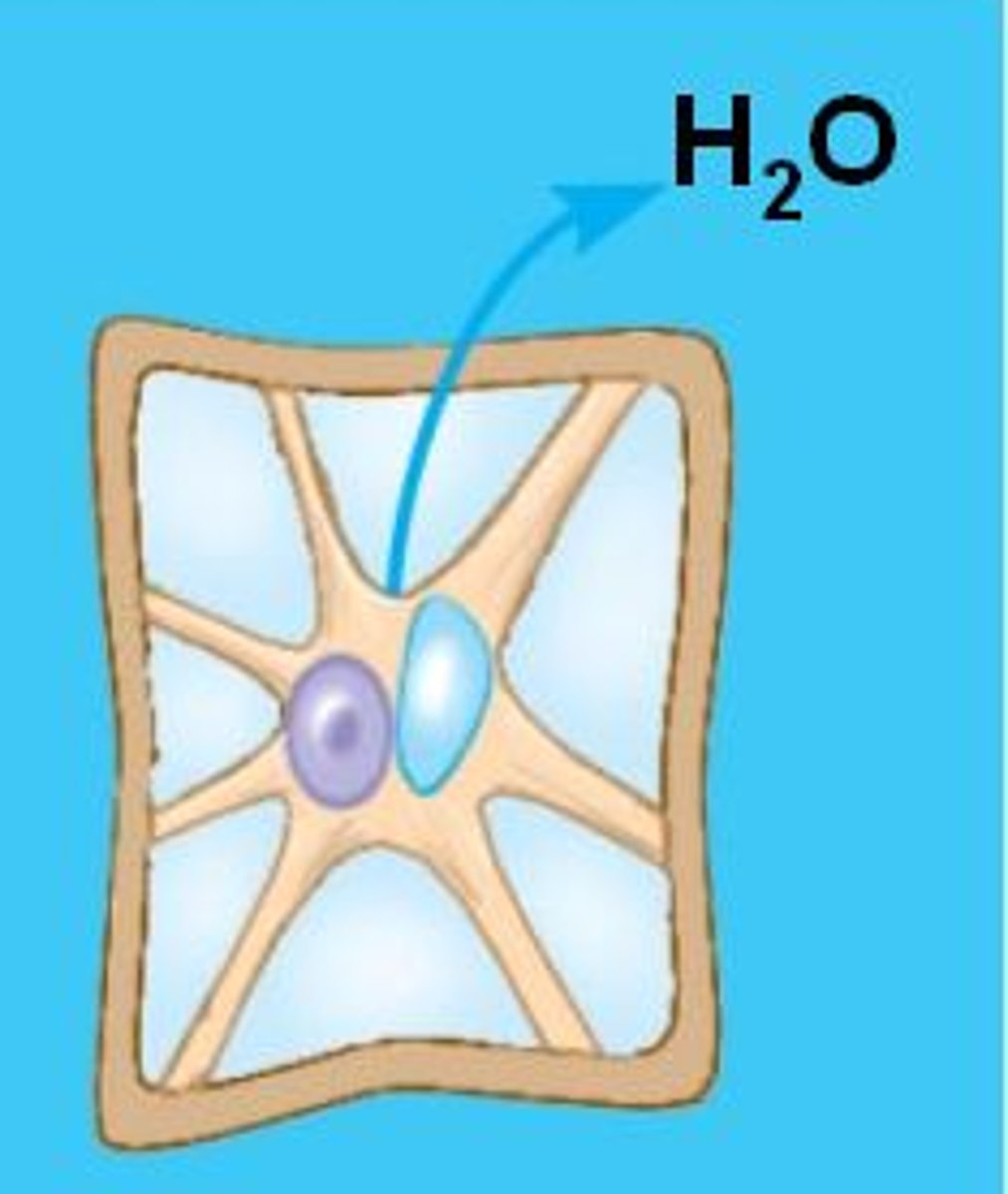
osmosis
movement of water across a membrane from an area of high concentration to lower concentration
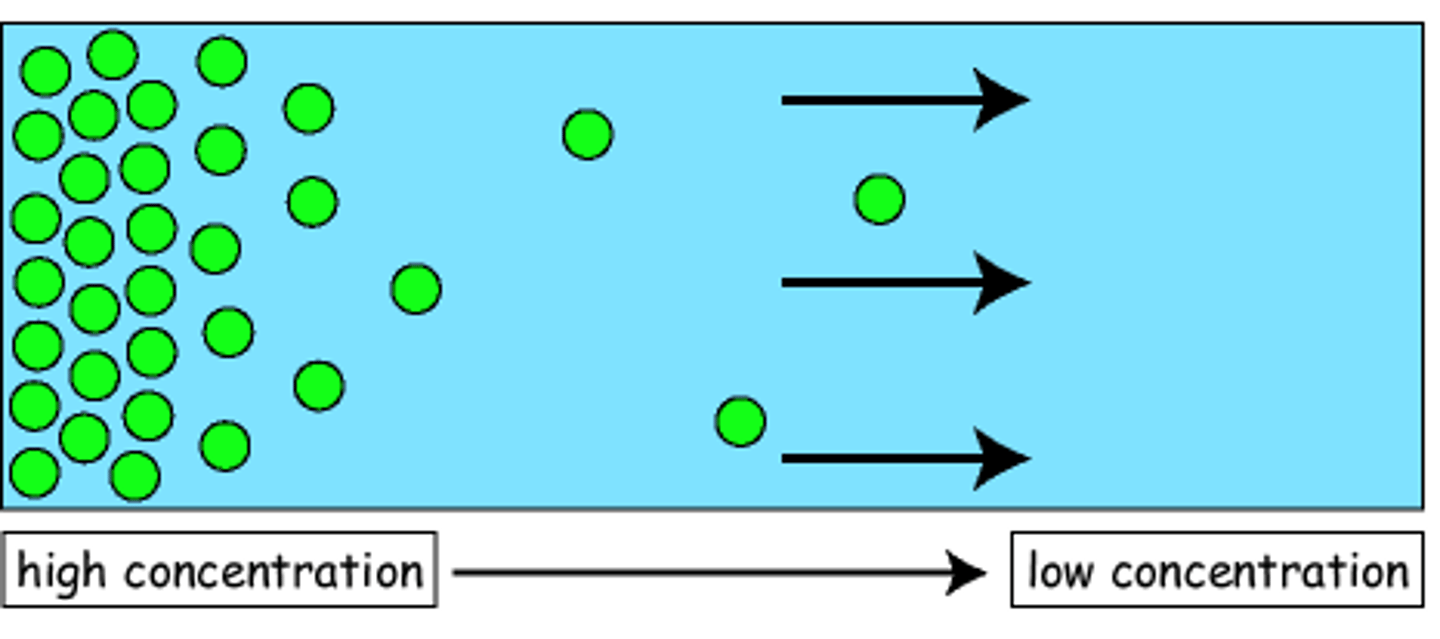
diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration
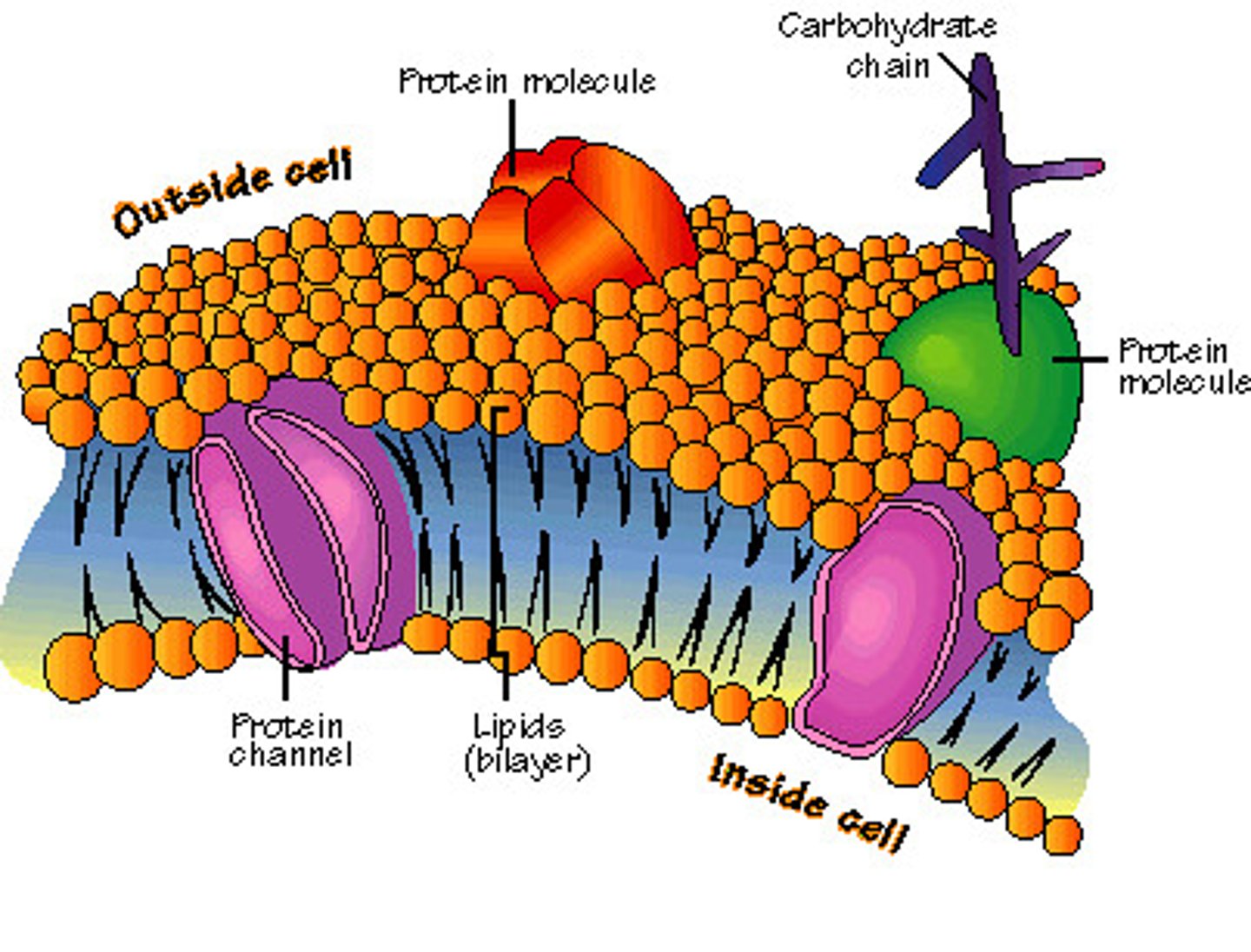
phospholipid bilayer
description of the cell membrane which has a double layer of lipids
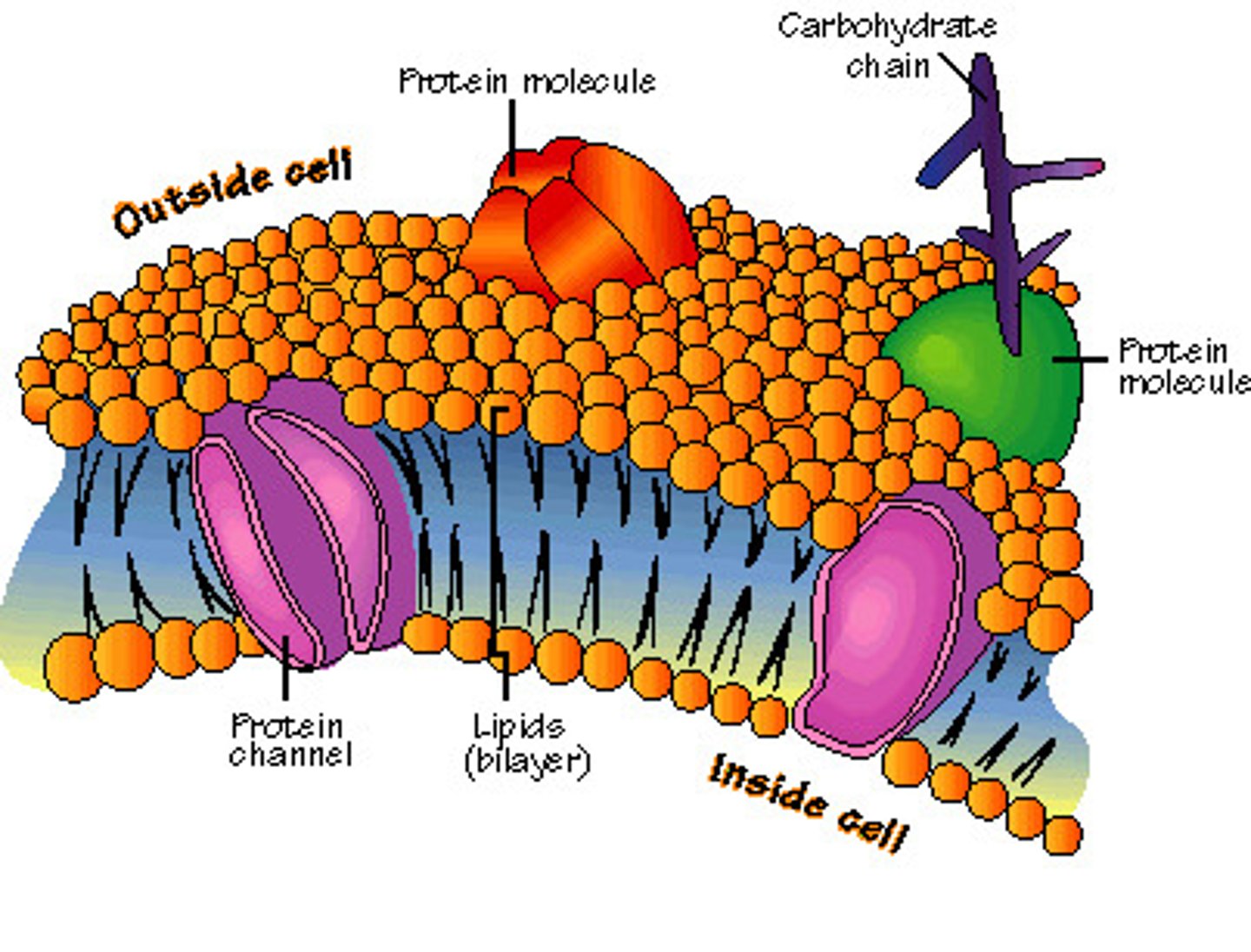
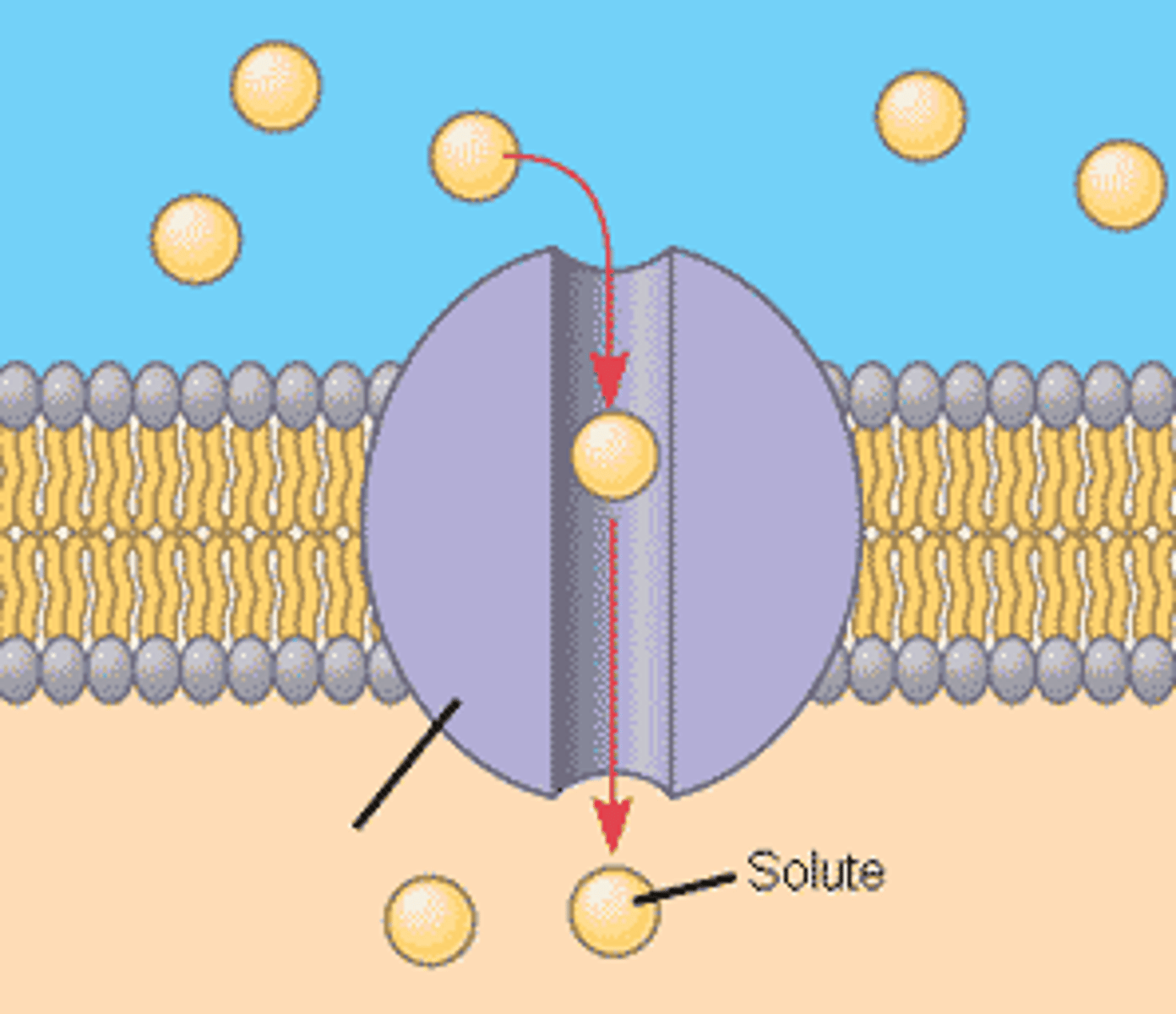
channel proteins
proteins embedded in the cell membrane's lipid bilayer which allow larger molecules, such as glucose, to diffuse into the cell
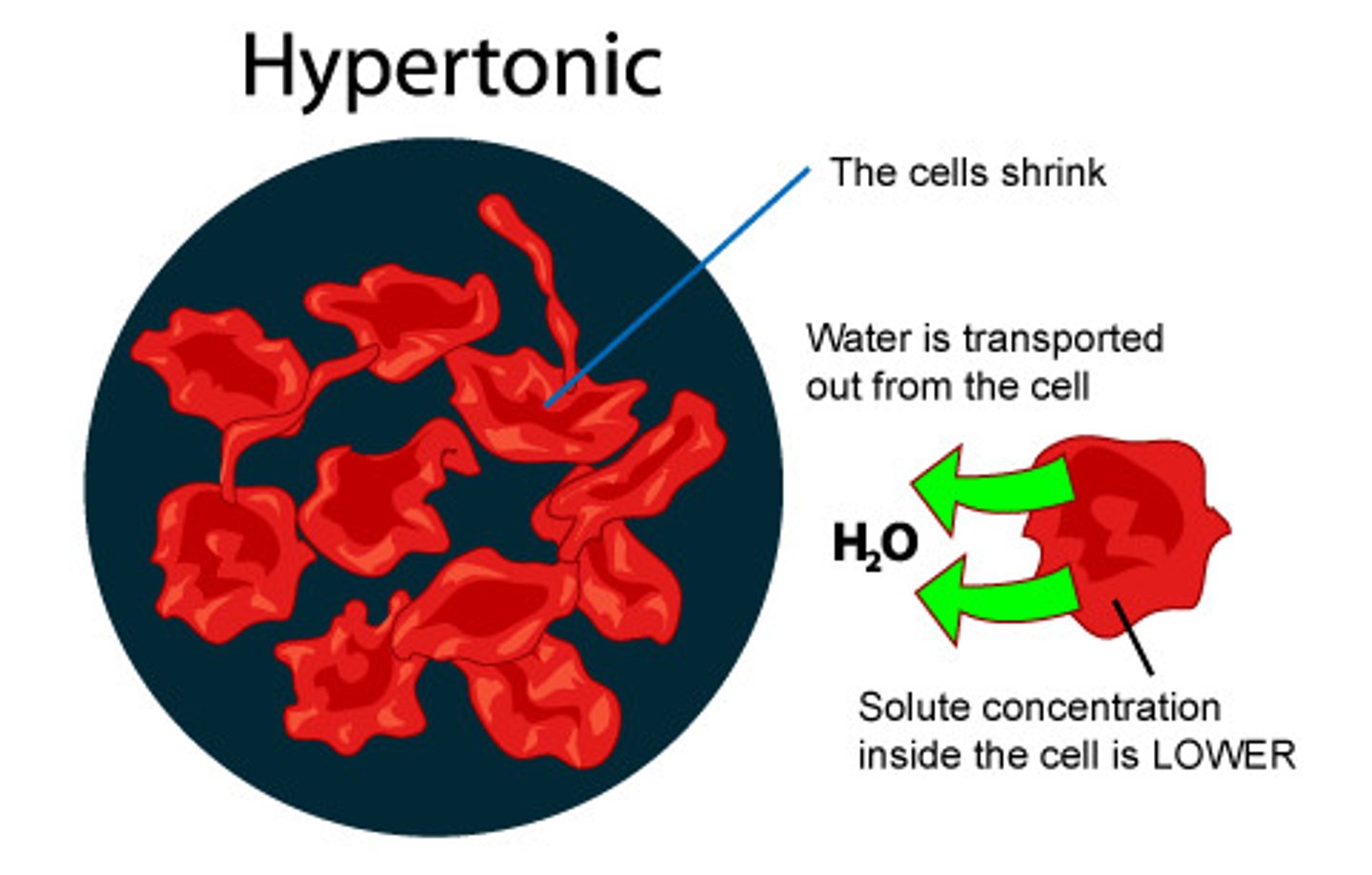
hypertonic solution
solution around the outside of the cell that has MORE solute and LESS water than inside the cell; water moves out of the cell and it shrinks
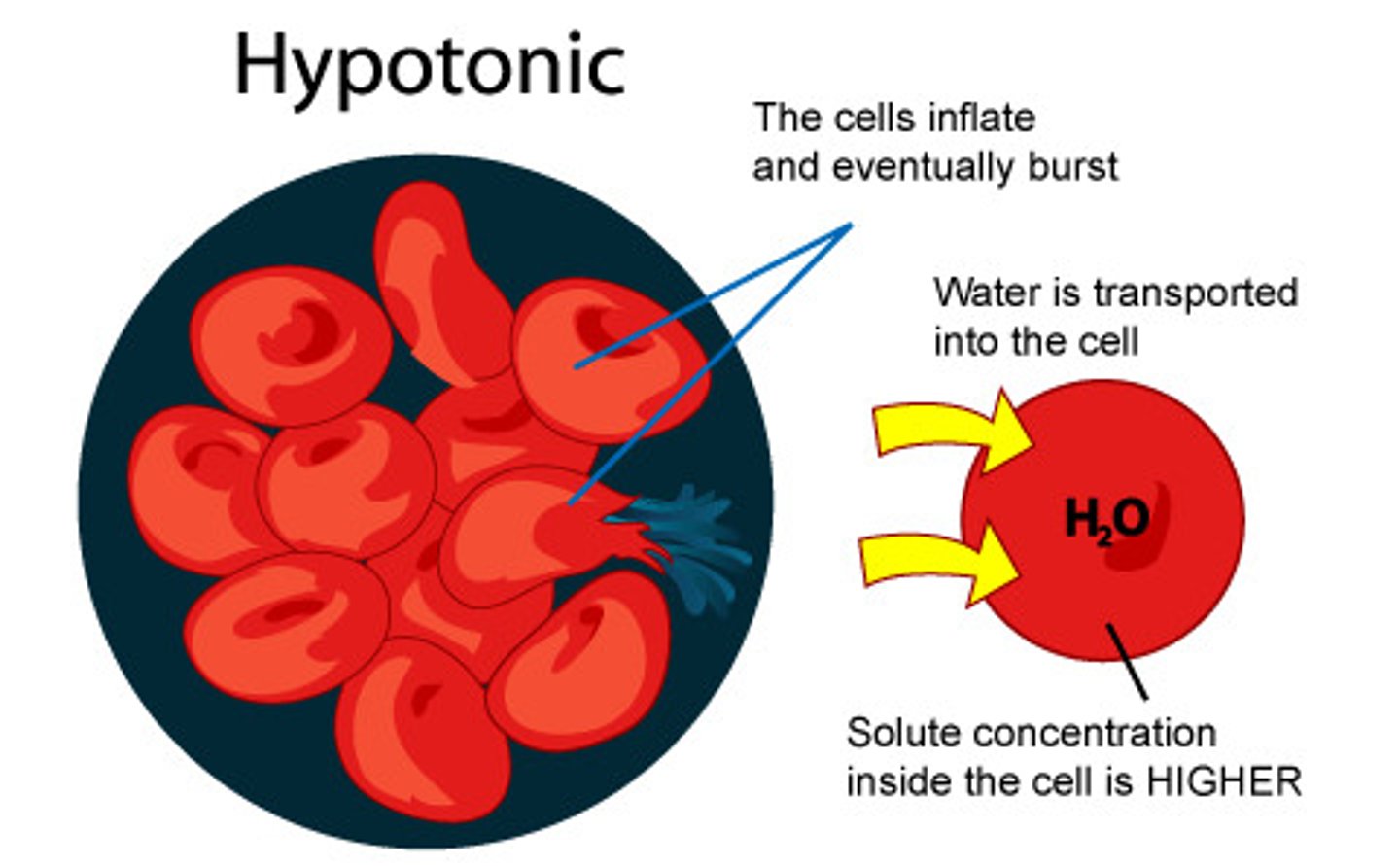
hypotonic solution
solution around the outside of the cell that has LESS solute and MORE water than inside the cell; water moves into the cell and it swells
receptor proteins
a type of protein imbedded in the cell membrane which receives chemical (hormone) messages

marker proteins
proteins in the cell membrane that identify the type of cell.
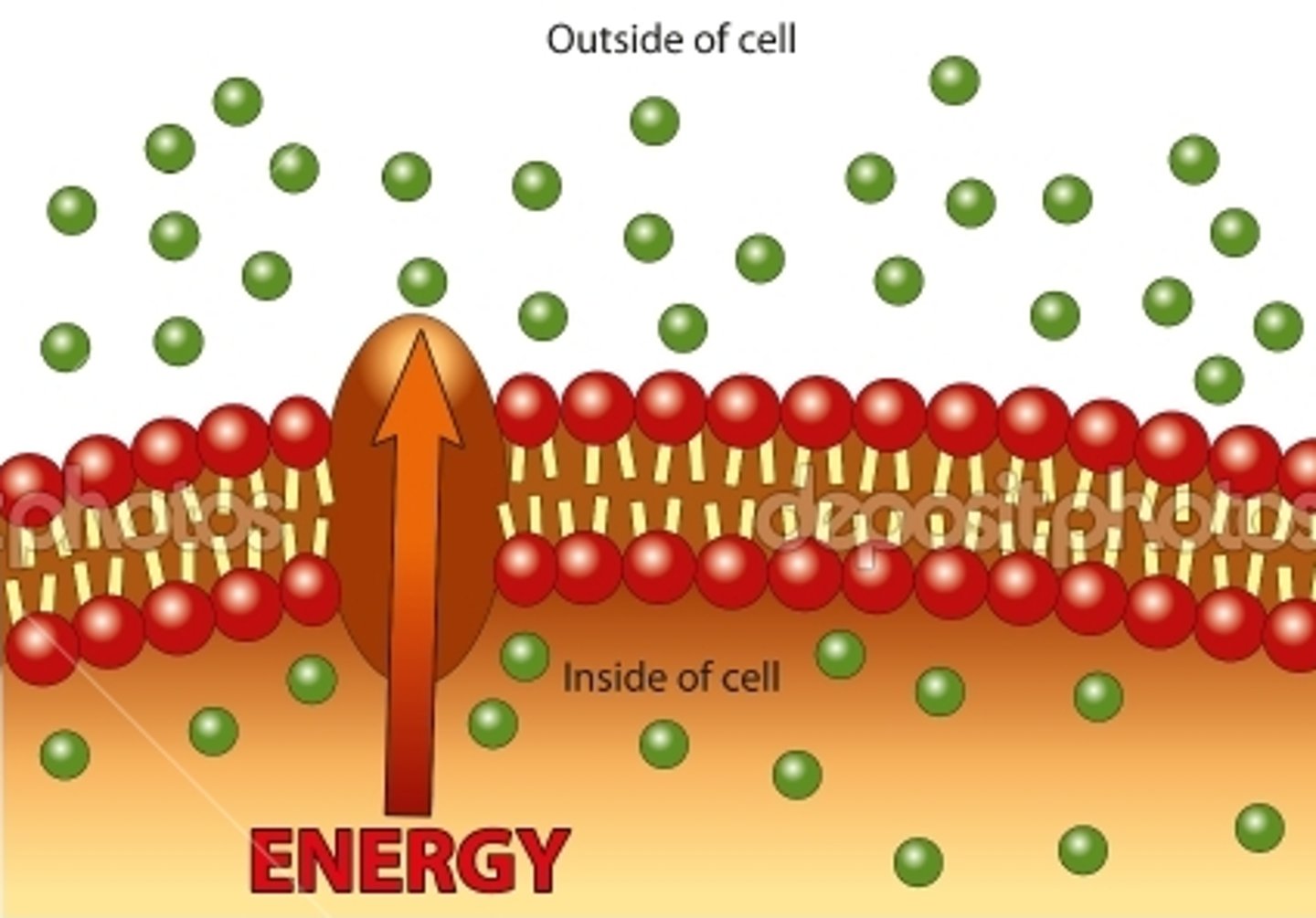
active transport
movement of molecules across the cell membrane that REQUIRES energy; molecules move from LOW to HIGH concentration
phagocytosis
a type of active transport in which large, solid objects are brought into the cell
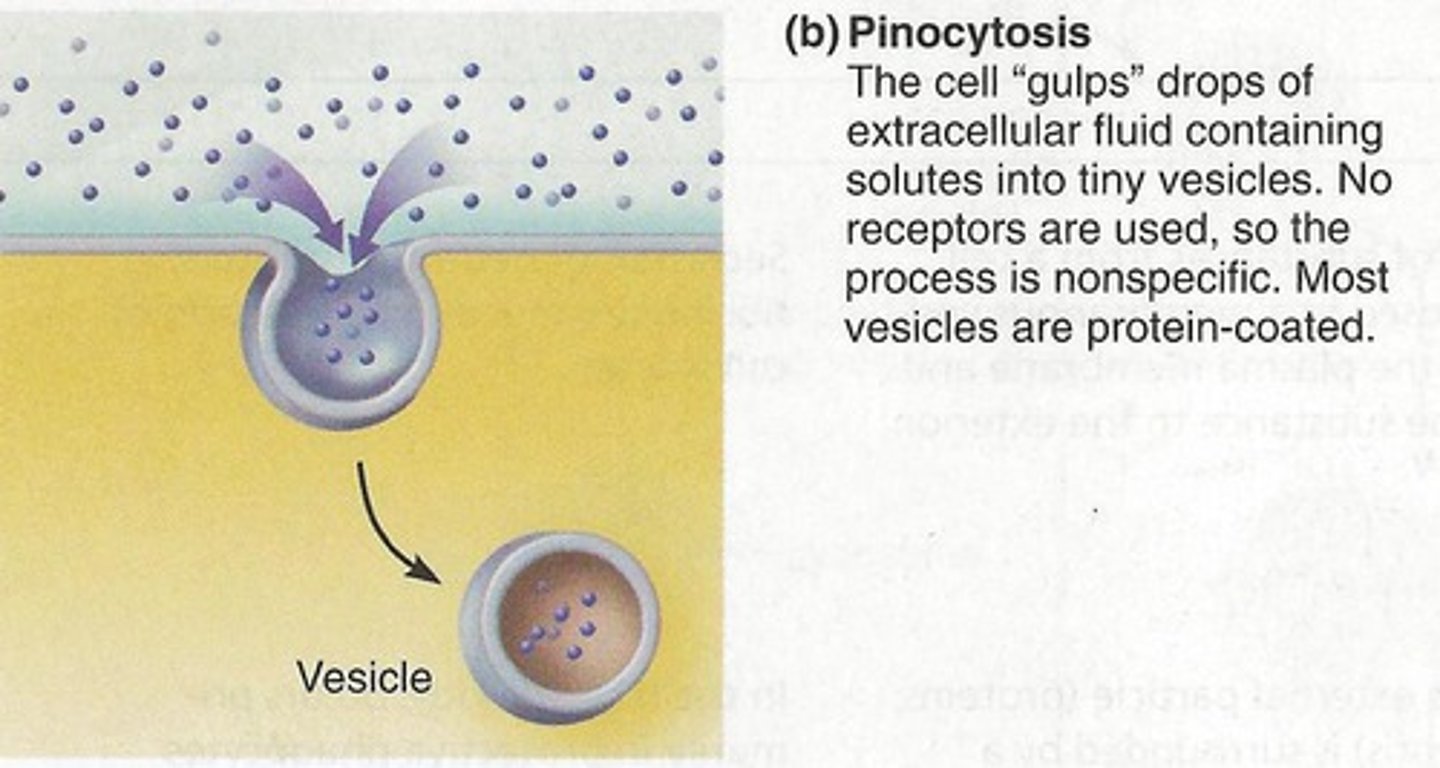
pinocytosis
"cell drinking"; a type of active transport in which large amounts of liquid is brought into the cell
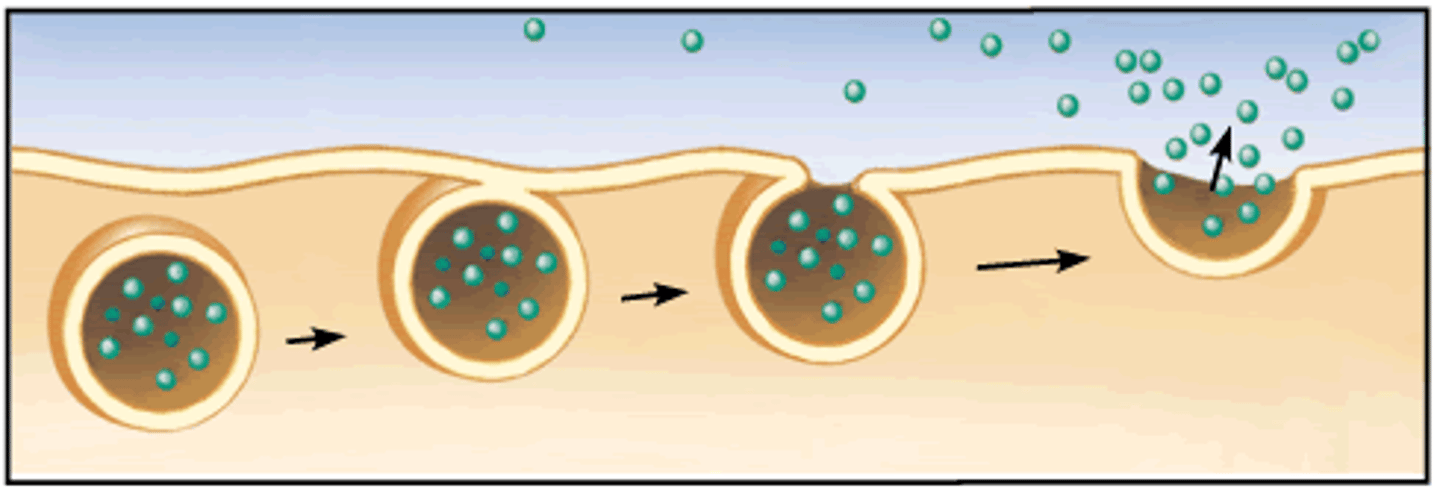
exocytosis
a form of active transport in which the cell expels or gets rid of large amounts of molecules at once
osmotic or turgor pressure
the pressure created when large amounts of water diffuses into a plant cell and causes the central vacuole to expand and push up against the cell wall
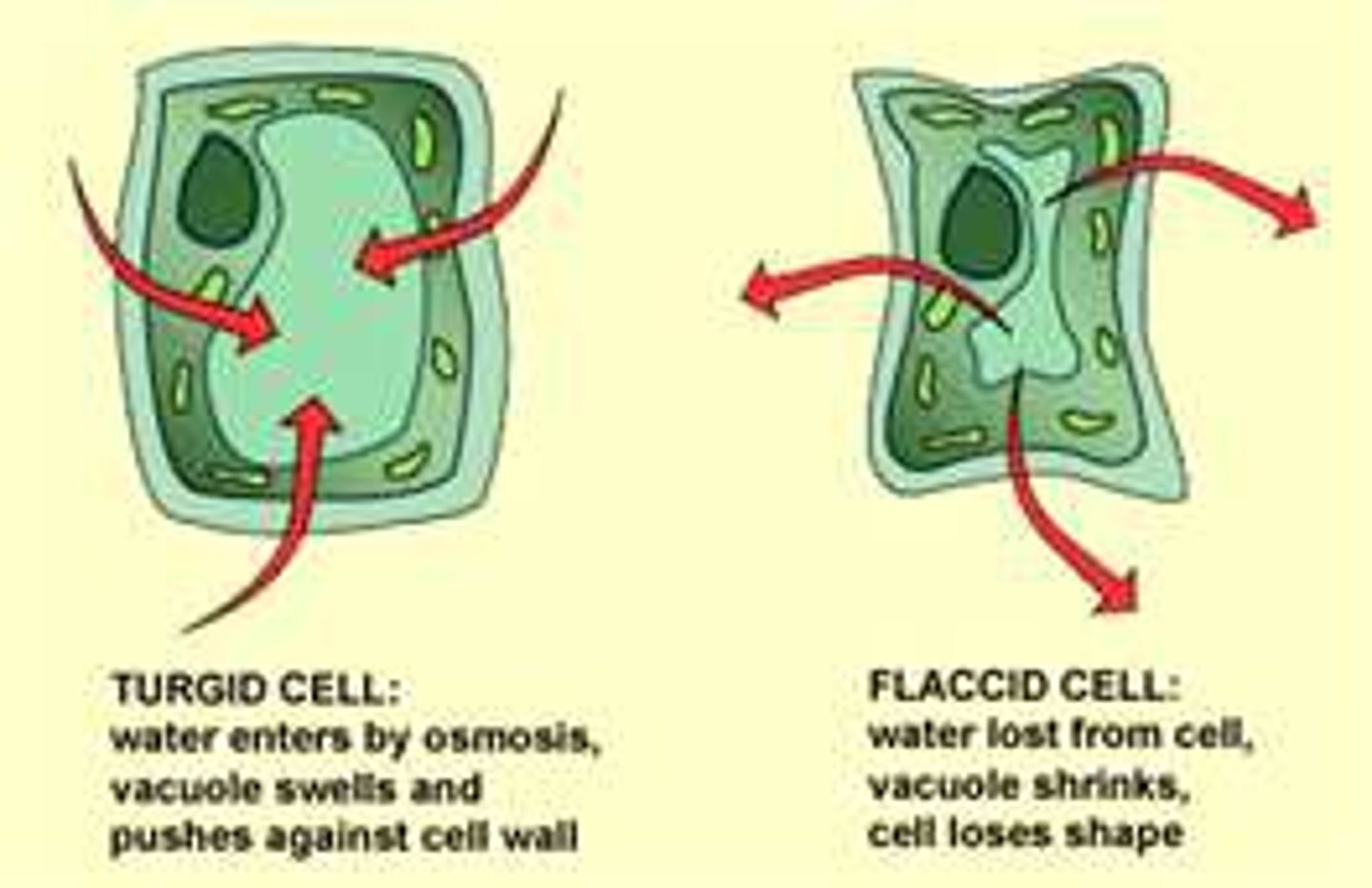
plasmolysis
the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. This occurs in a hypertonic solution.
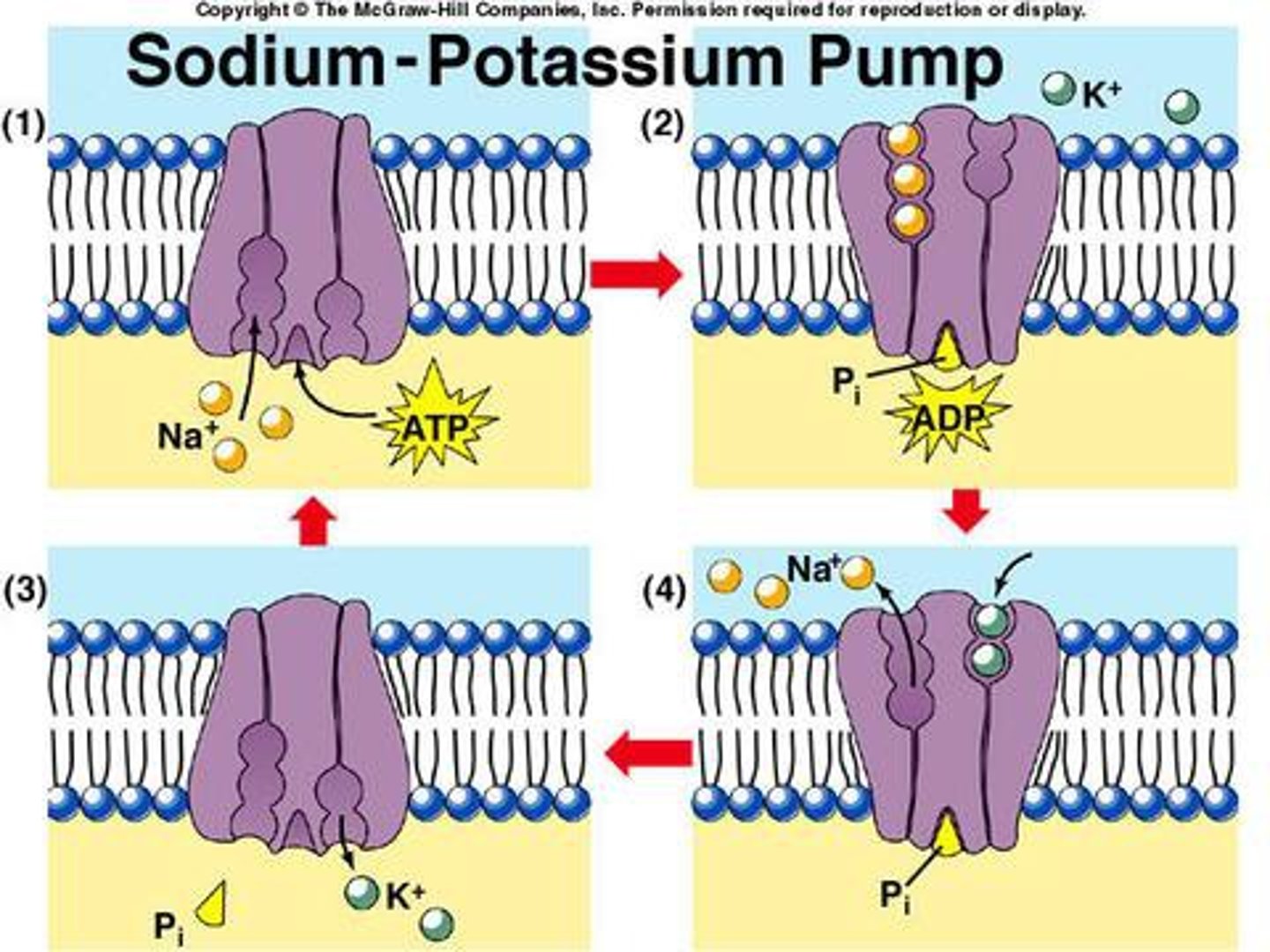
sodium-potassium pump
a type of active transport in which ATP energy molecules provide the energy for movement of sodium and potassium ions across the membrane from low to high concentration through a protein channel
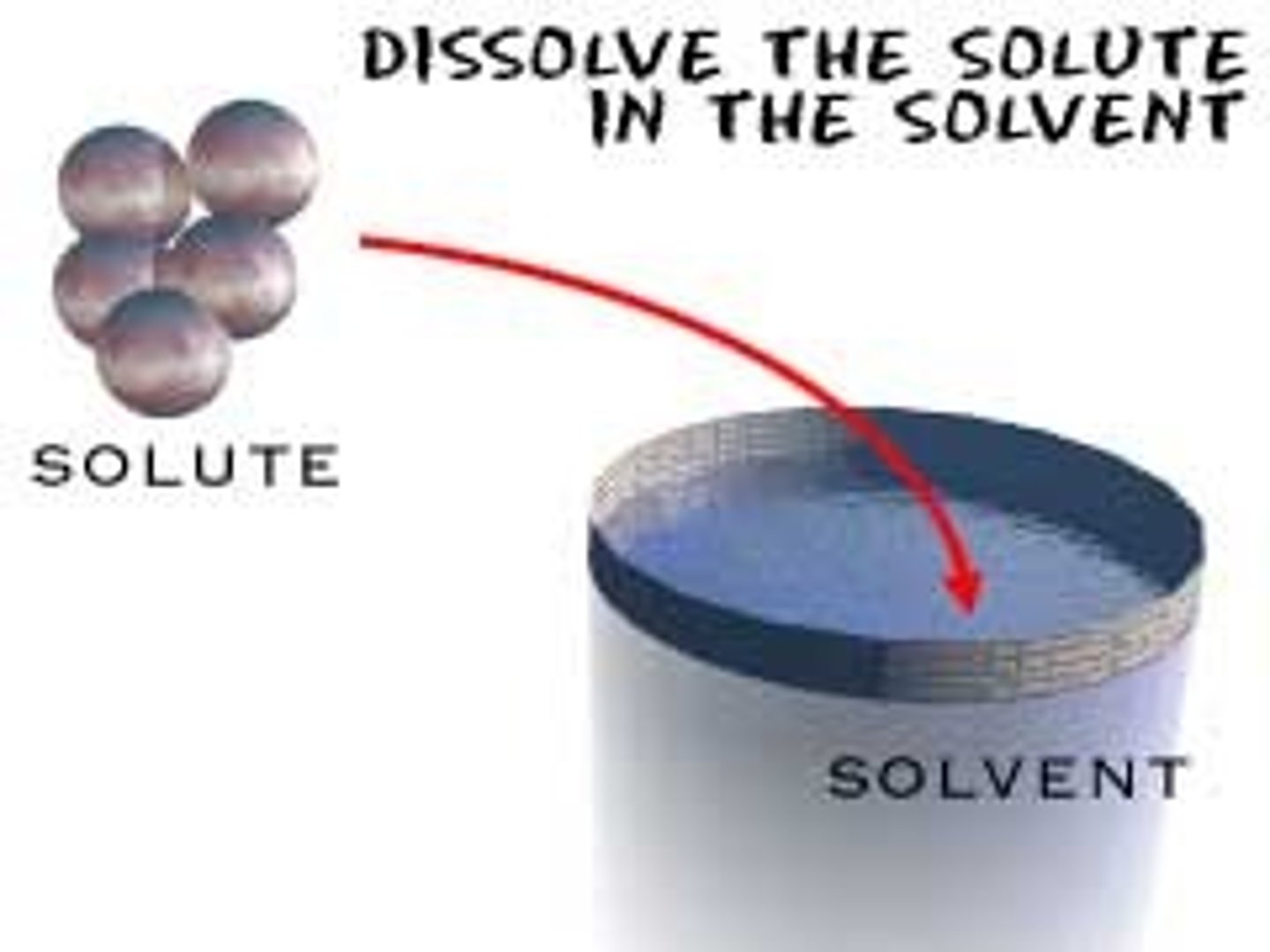
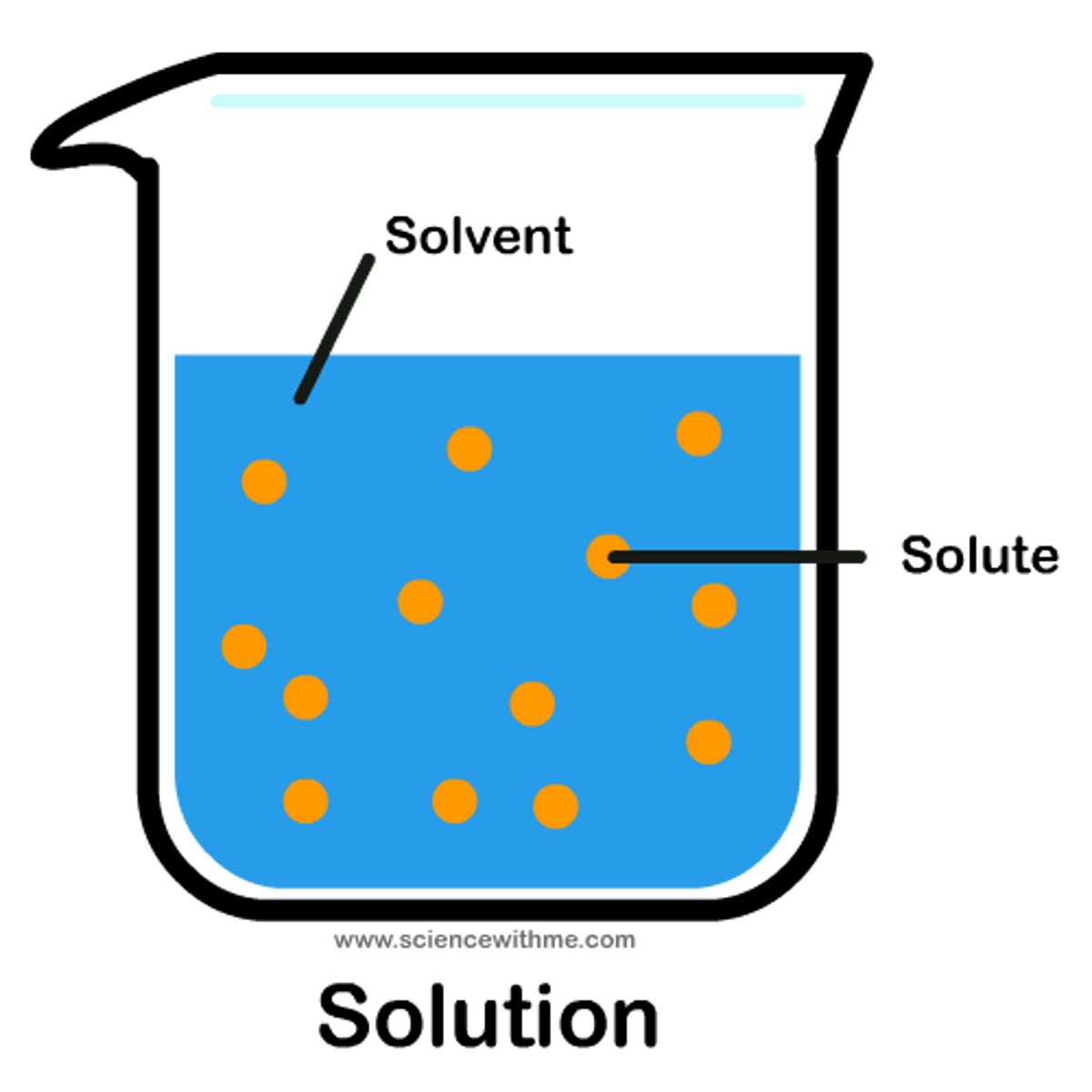
solute
substance that is dissolved into a solvent; examples are glucose (simple sugar) and sodium chloride (salt)
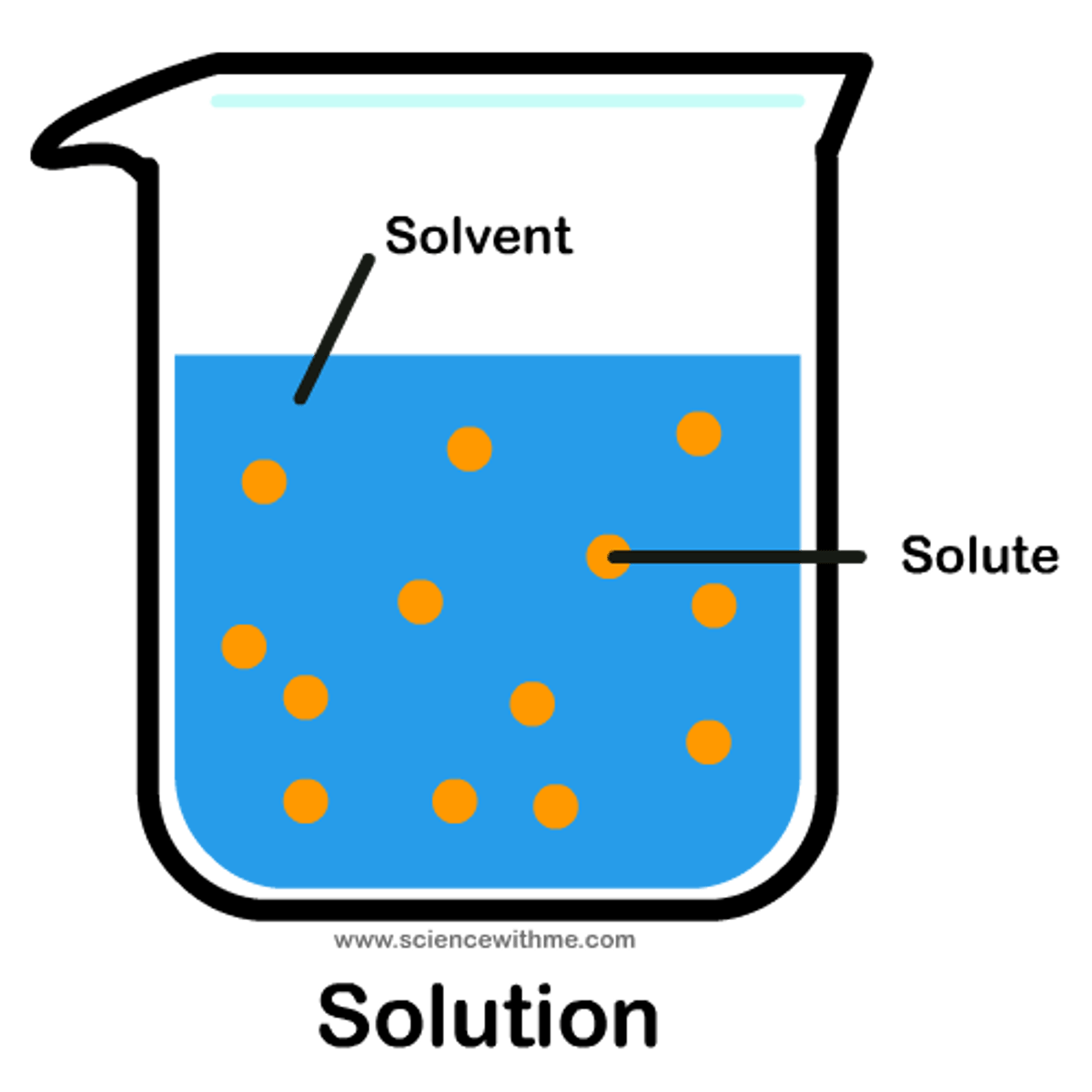
solvent
the liquid in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution; in living cells the solvent is water
solution
a mixture of a solute dissolved into a solvent
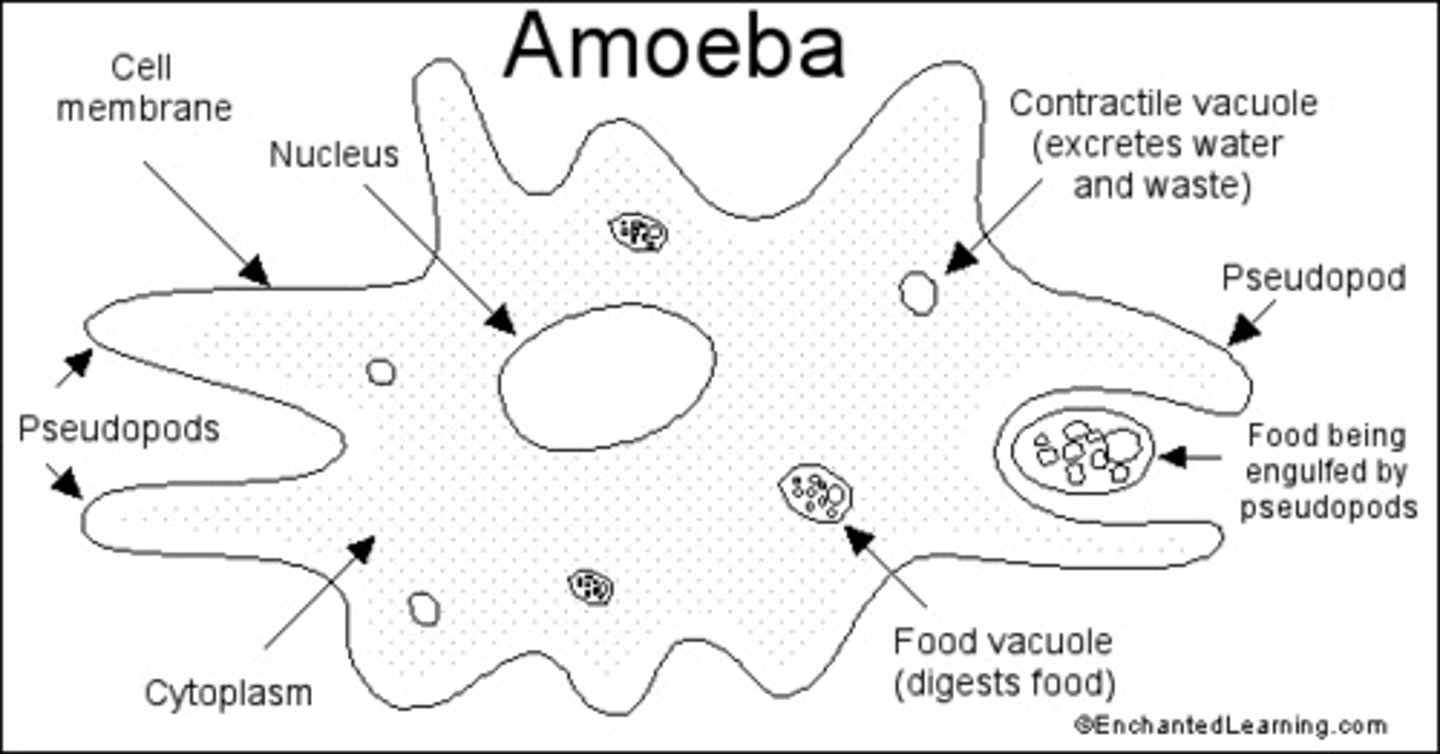
amoeba
a unicellular protist which uses phagocytosis (active transport) to bring in large amounts of food
White blood cells
human body cells which use phagocytosis (active transport) to defend the body from foreign invaders (bacteria) by "eating" them
facilitated diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentration across the cell membrane by going through a channel protein
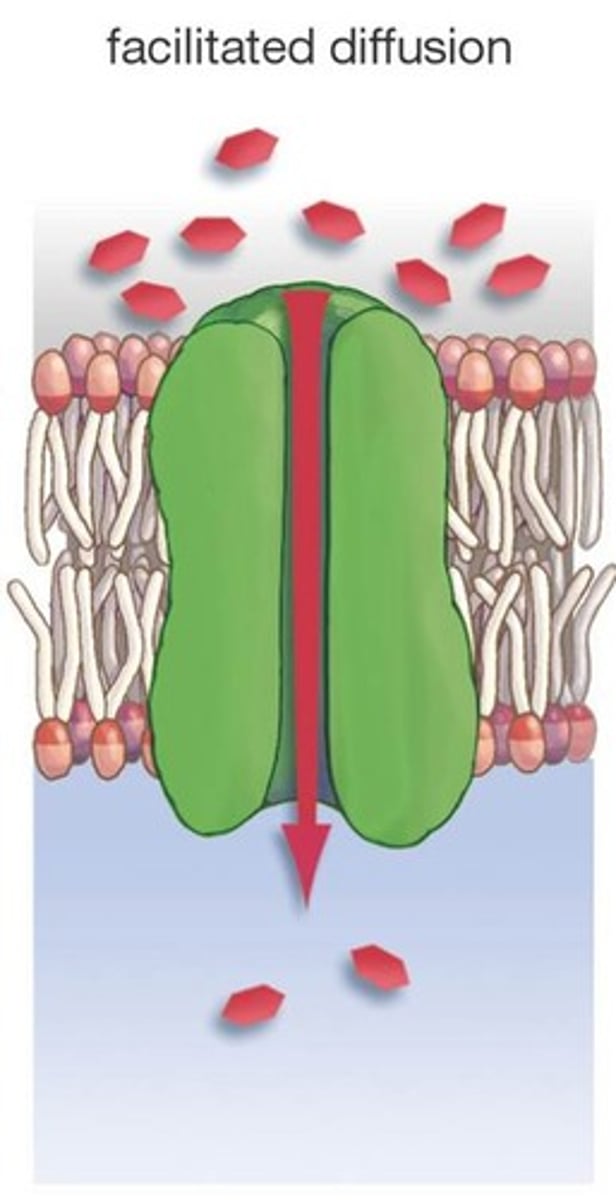
passive transport
the movement of molecules across the cell membrane from HIGH to LOW concentration without added energy
