Brain Functions, Nervous Tissue & Neurotransmission, Labeling the brain
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Cerebellum
Helps to regulate autonomic functions, relay sensory information, coordinate movement, and maintain balance.
Midbrain
Helps regulate movement and process auditory and visual information
Thalamus
a structure that relays sensory information for all senses, except smell, and relays it to the cerebral cortex.
Cerebrum
Made of 4 lobes; responsible for learning, thinking, memory, personality and movement
What are the 5 parts of a neuron
dendrites, cell body, axon, myelin sheath, axon terminal
What does a dendrite do?
detects and receives information from other neurons
What does the axon do?
transmits neural information from the dendrites to the axon terminal
What is the myelin sheath for?
it insulates and protects the axon while preventing interference from other neurons; speeds up the rate of signal transmission
What do axon terminals do?
store and secrete neurotransmitters (chemical messages)
Sensory neurons
transmit messages FROM the sense receptors TO the Central Nervous system through the Somatic Nervous System
Motor neurons
transmit commands FROM the Central Nervous system To skeletal muscles through the Somatic Nervous system
Interneurons
make the connection between sensory and motor neurons. Only found in the Central Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System divisions
Autonomic Nervous System (involuntary) and Somatic Nervous System (Voluntary)
Somatic Nervous System
Sensory neurons and Motor neurons
Corpus Callosum
nerve fibers linking the left and right hemispheres of the brain
Frontal Lobe
for sophisticated mental abilities such as reasoning, planning, problem-solving, decision making and symbolic thinking. It also regulates emotions and expression of personality and self-awareness.
Paretial Lobe
receives and processes sensory information including touch, pressure and pain
Occipital Lobe
process and enables vision
Temporal Lobe
auditory perception (hearing)
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
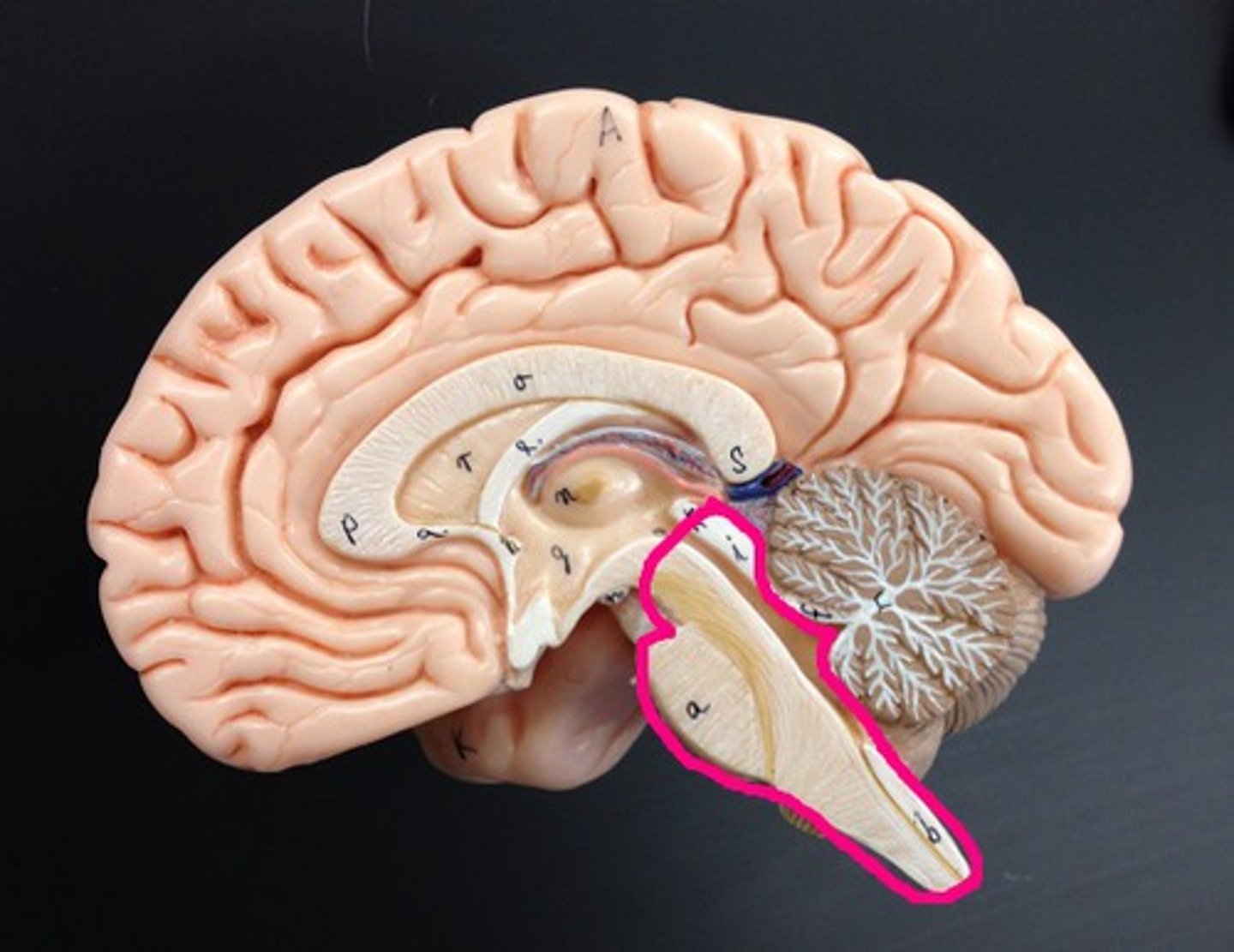
Structures of the brainstem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
gray matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies and dendrites
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
dendrite, cell body, axon
3 Main Parts of Neuron: (3)
dendrite
extensions that receive message and carry impulses toward cell body
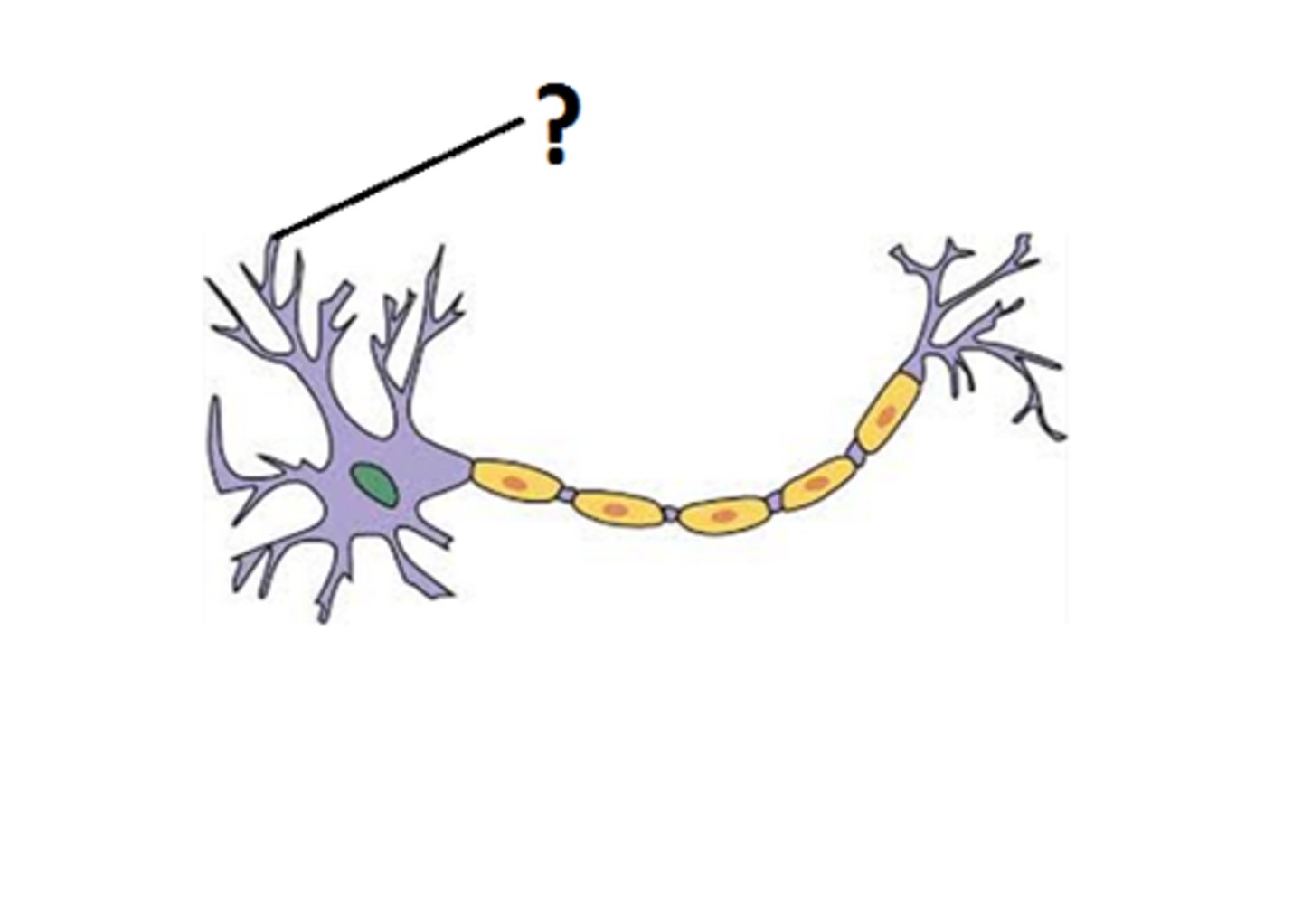
toward
Dendrite carries impulse _______ cell body.
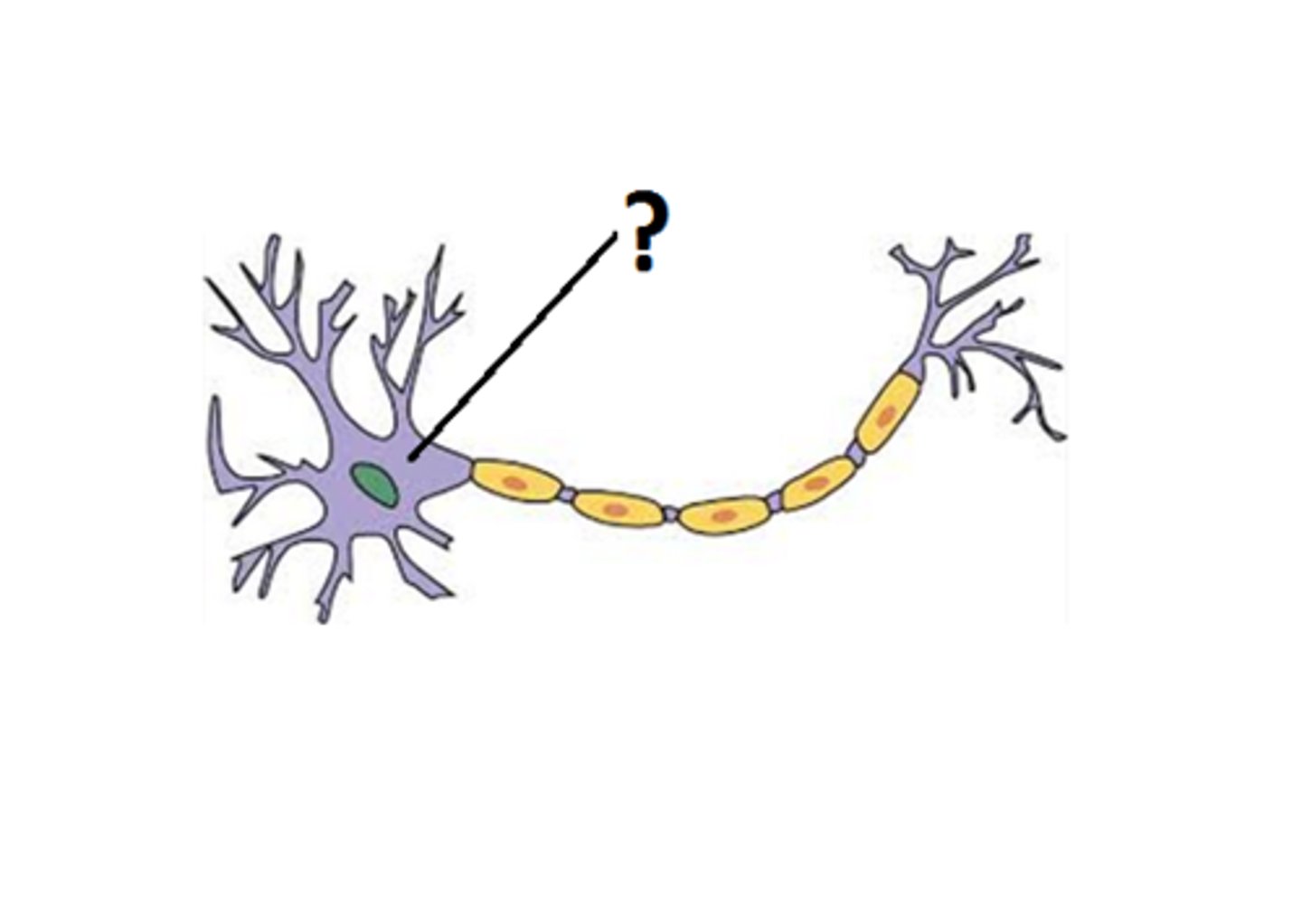
cell body
contains the nucleus of the neuron
axon
extension that carries impulse away from cell body
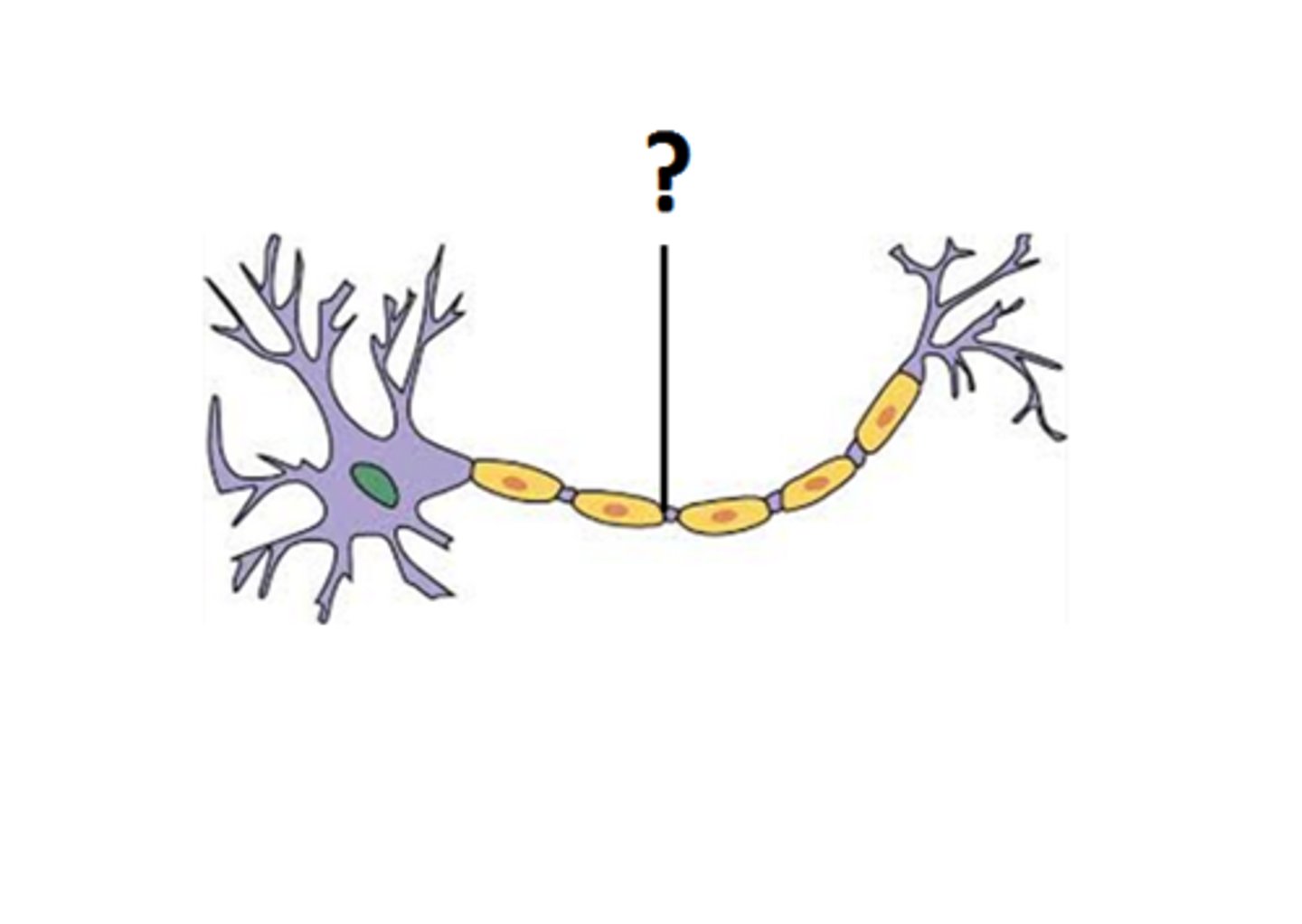
away
Axon carries impulse _____ from cell body.
myelin
sheath that surrounds axon; speeds up rate of impulse
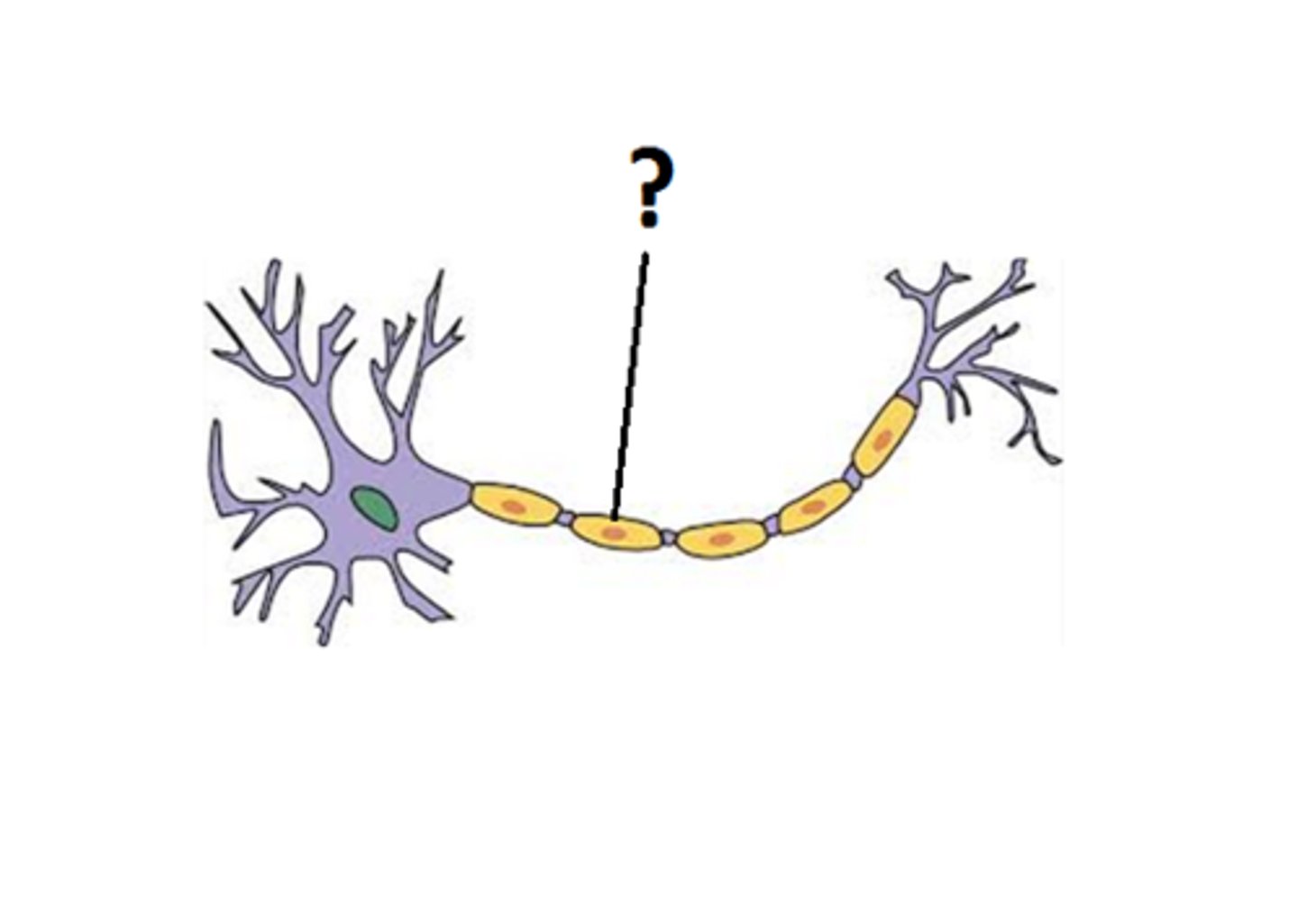
node of Ranvier
space between Schwann cells
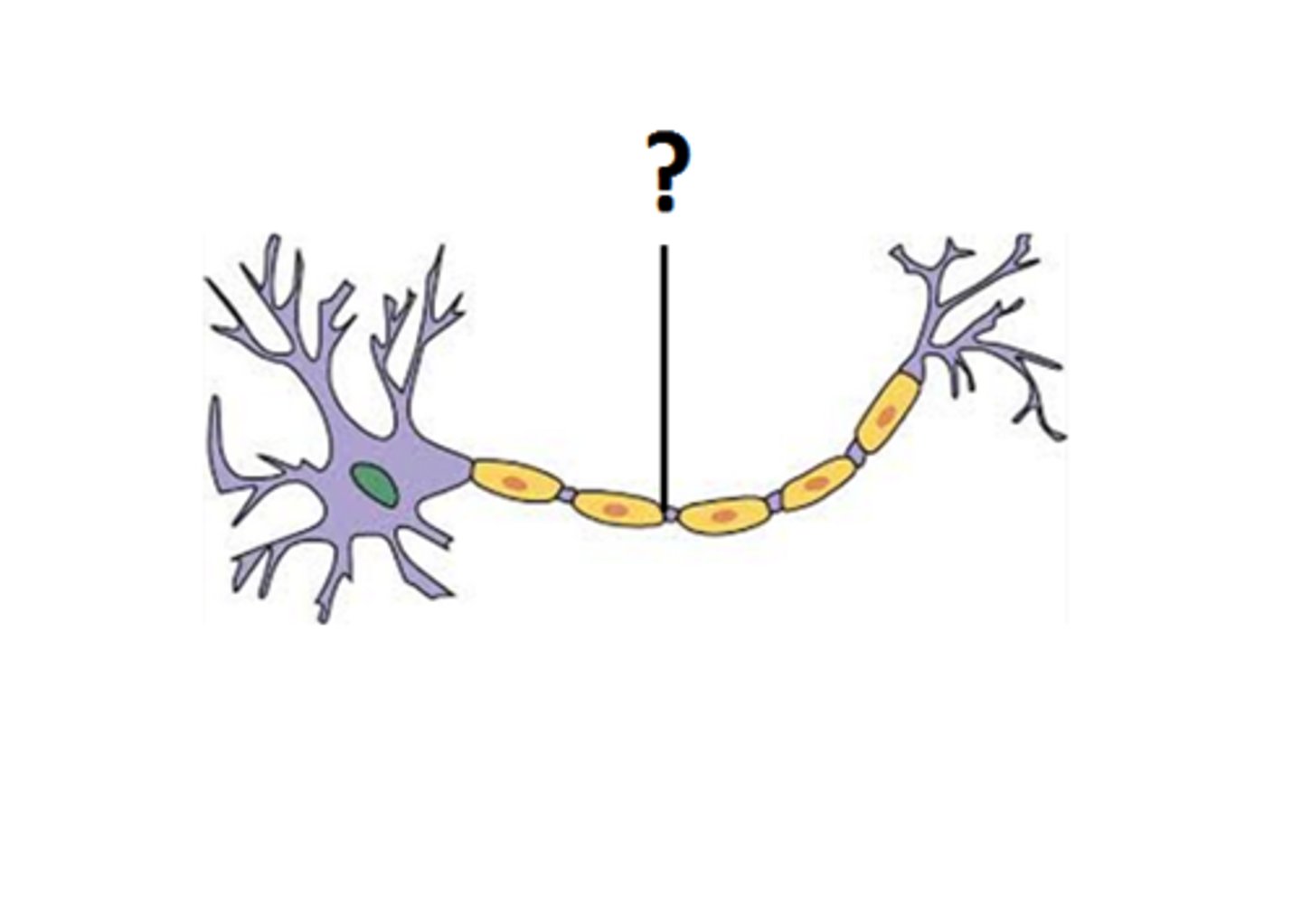
axon terminal
end of axon at synapse
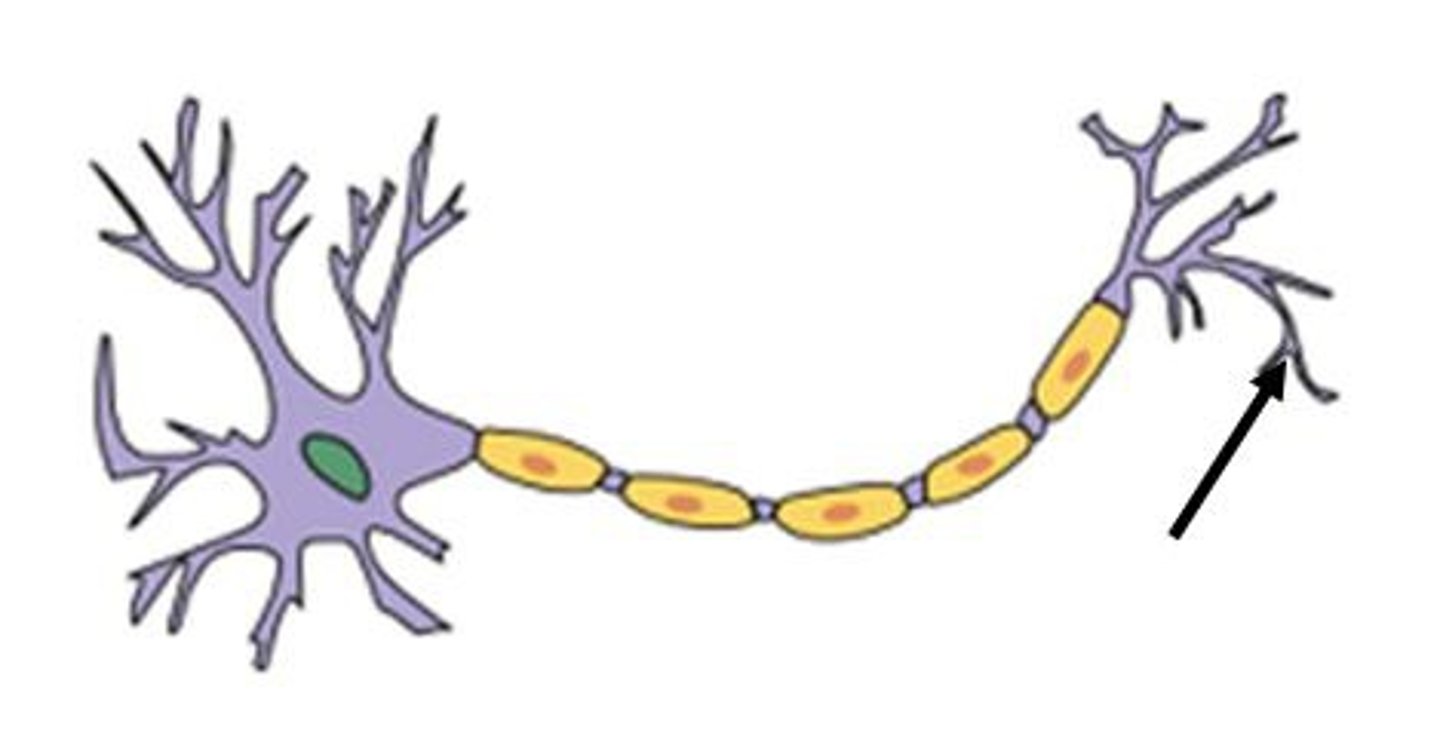
synapse
small gap between neurons
Neuron
a specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses; a nerve cell.
Action Potential (AP)
electrical current in the neuron

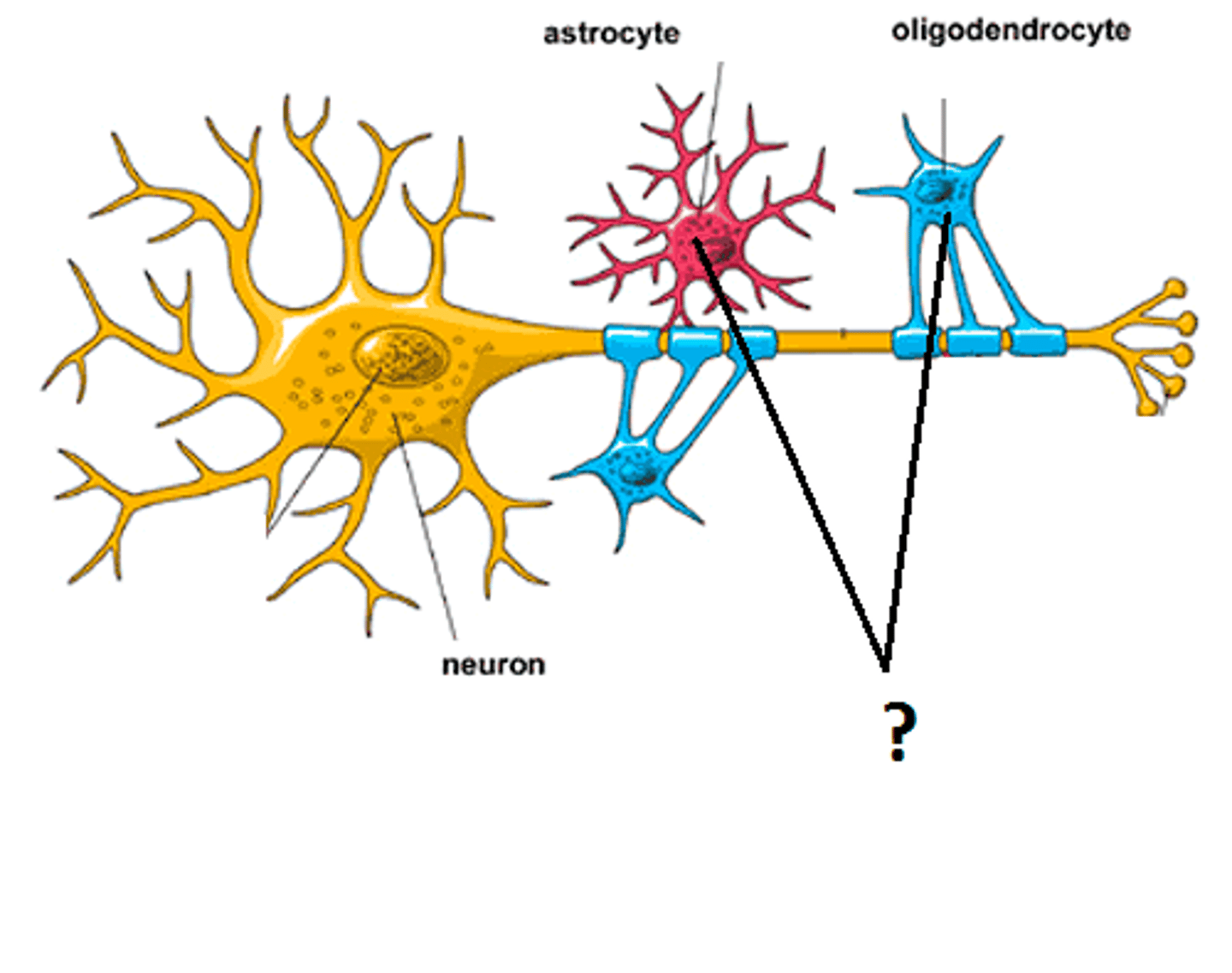
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
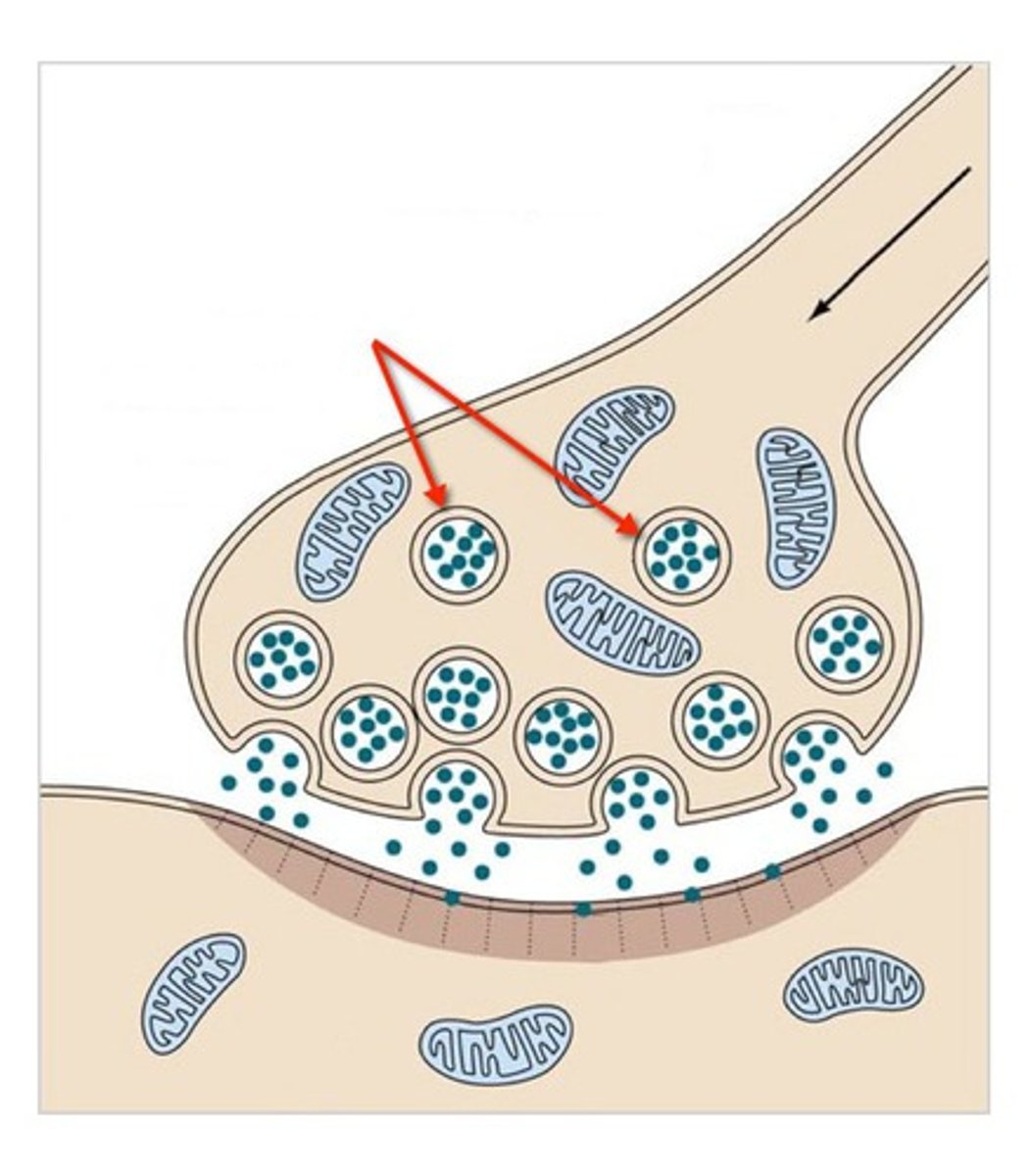
Vesicles
membranous sacs that house neurotransmitters; fuse with membrane of axon terminal to dump NT's into space
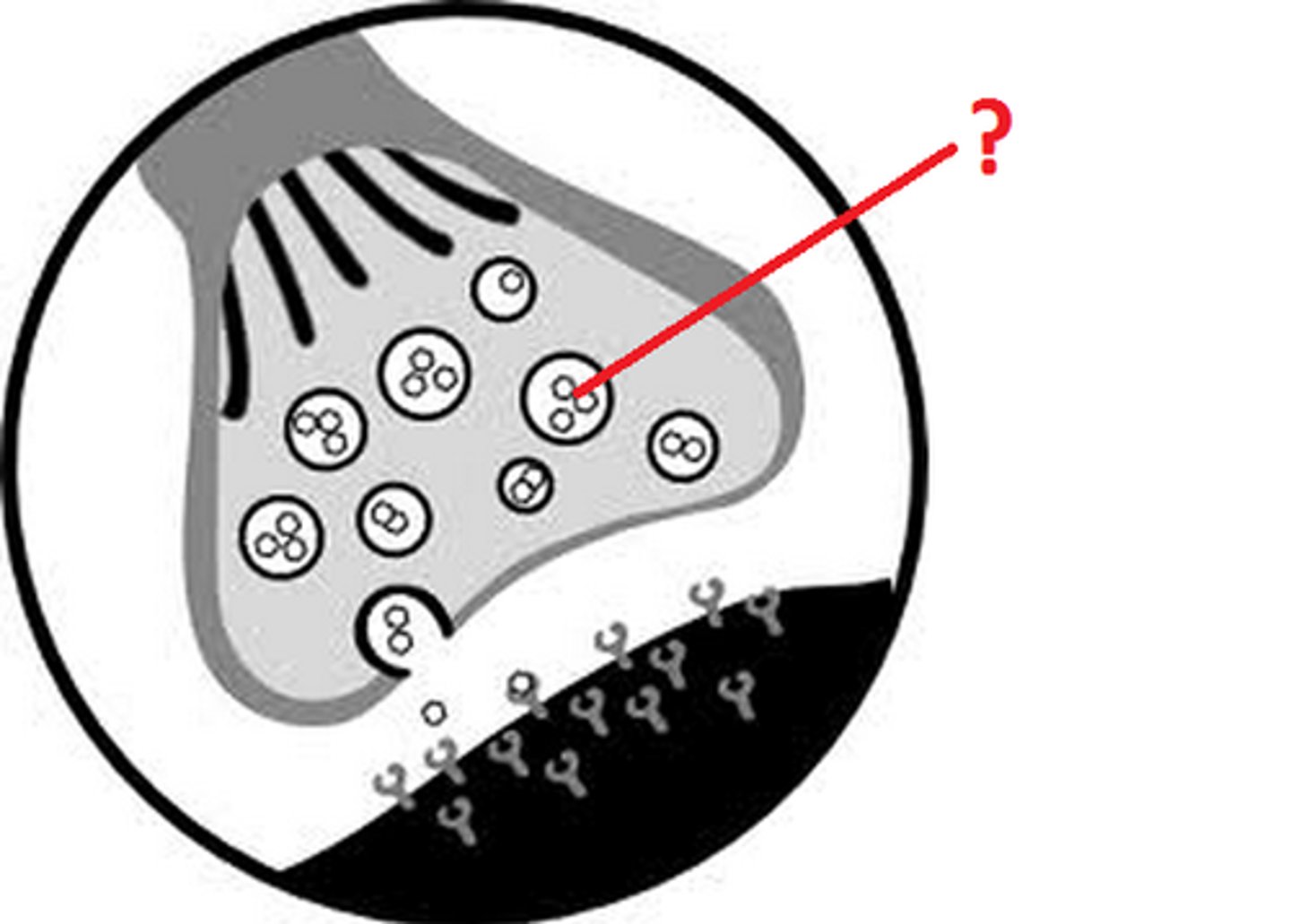
Neurotransmission
the process of transferring information from one neuron to another at a synapse
parietal lobe
Identify D
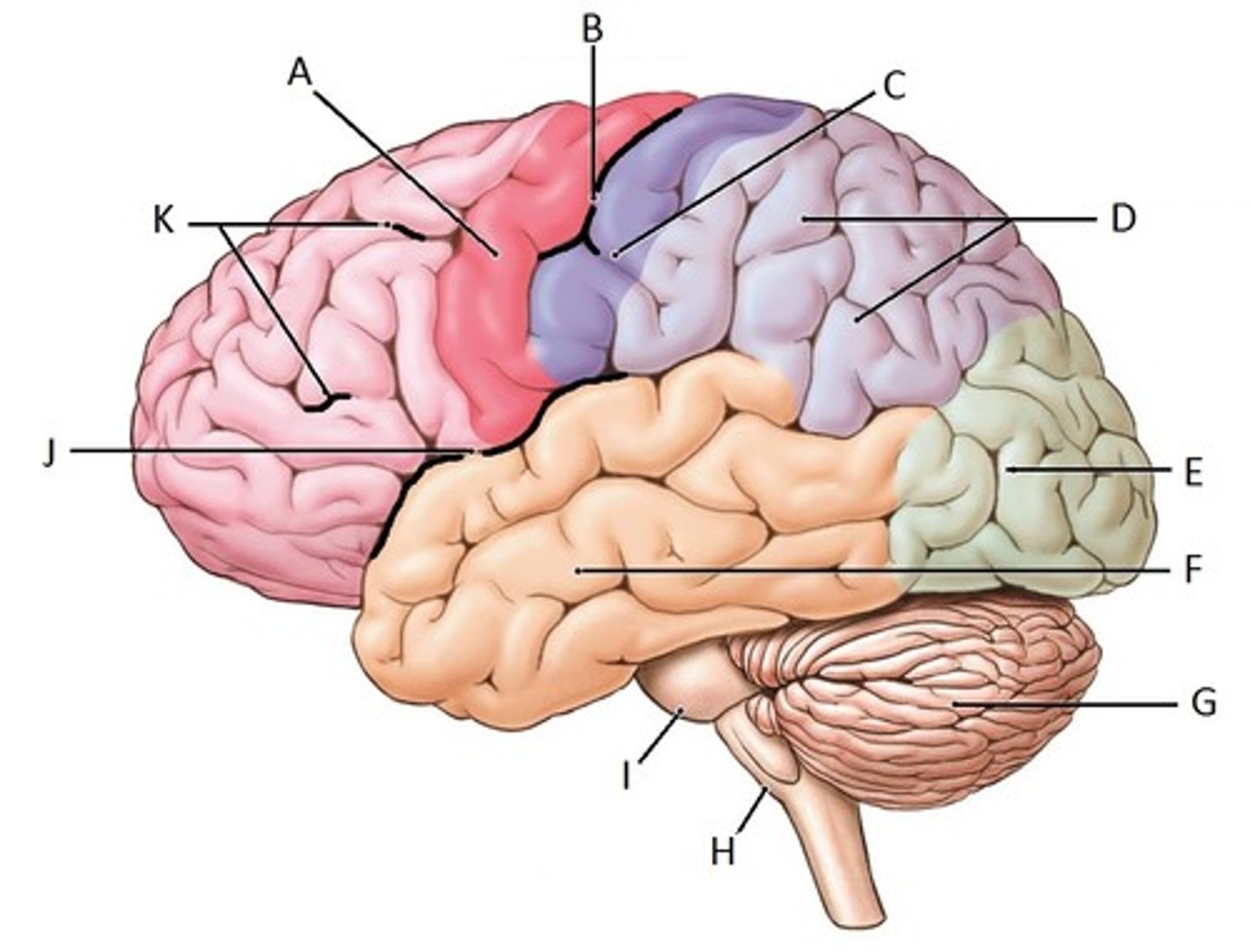
occipital lobe
Identify E
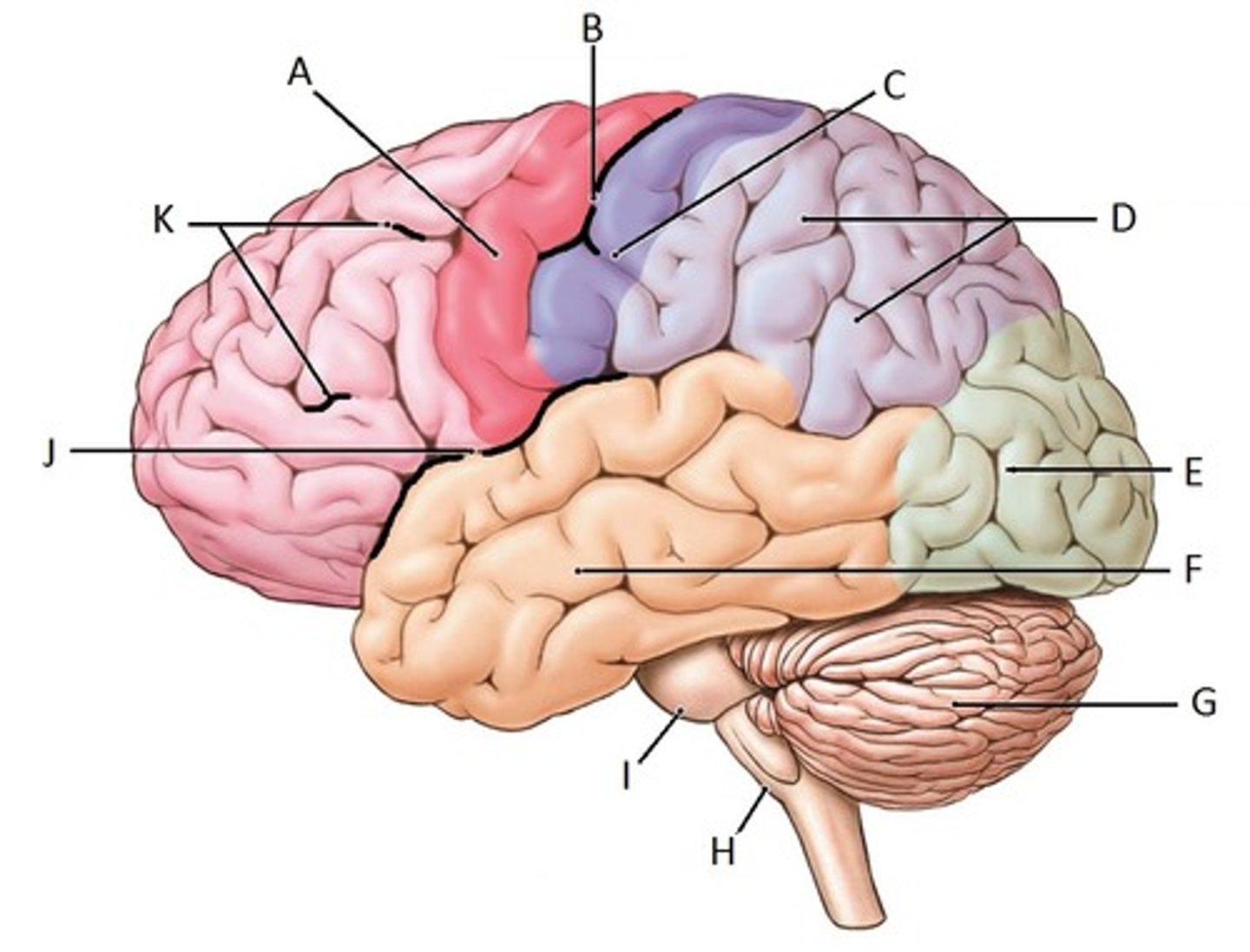
temporal lobe
Identify F
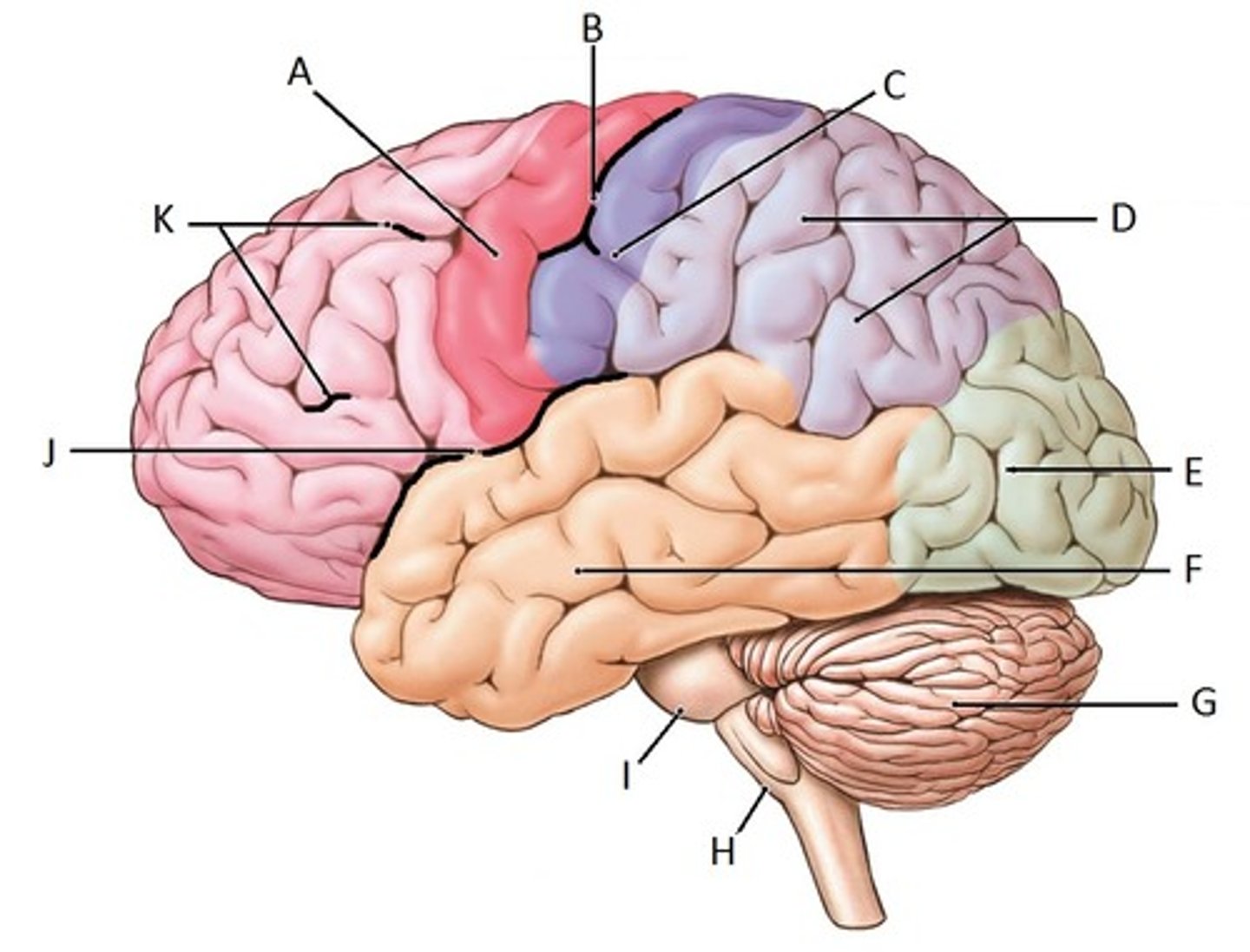
cerebellum
Identify G
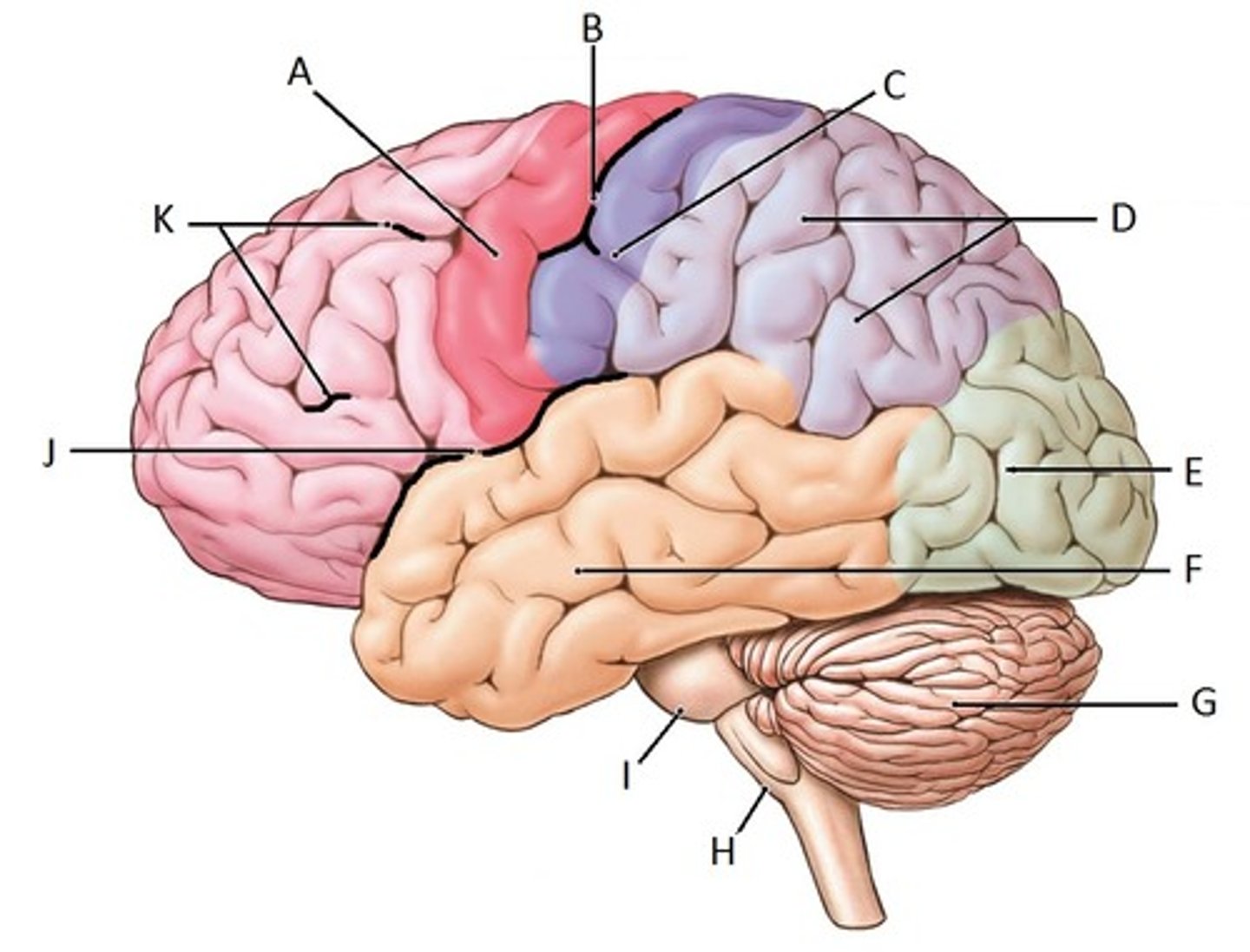
frontal lobe
Identify K
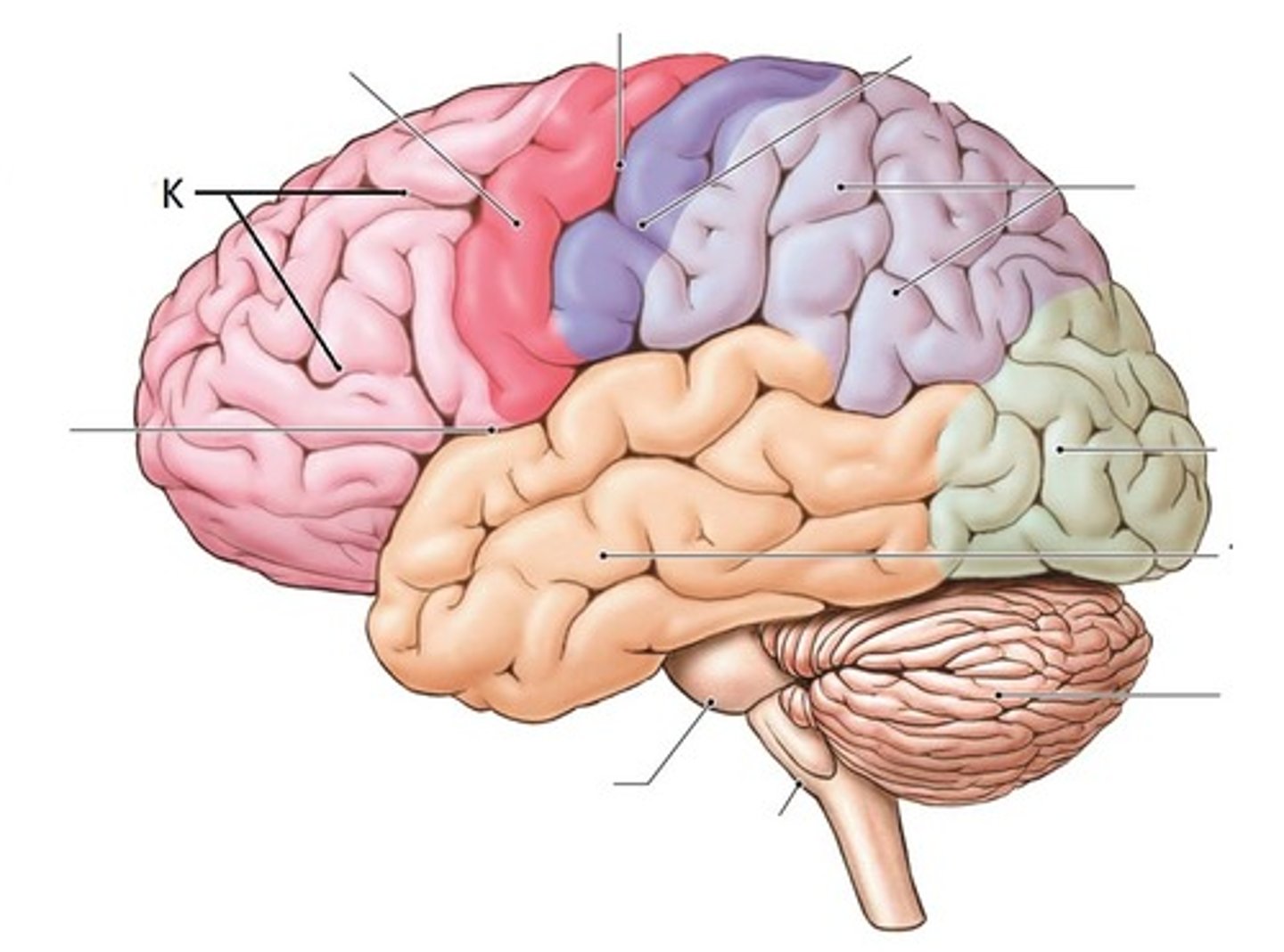
cerebrum
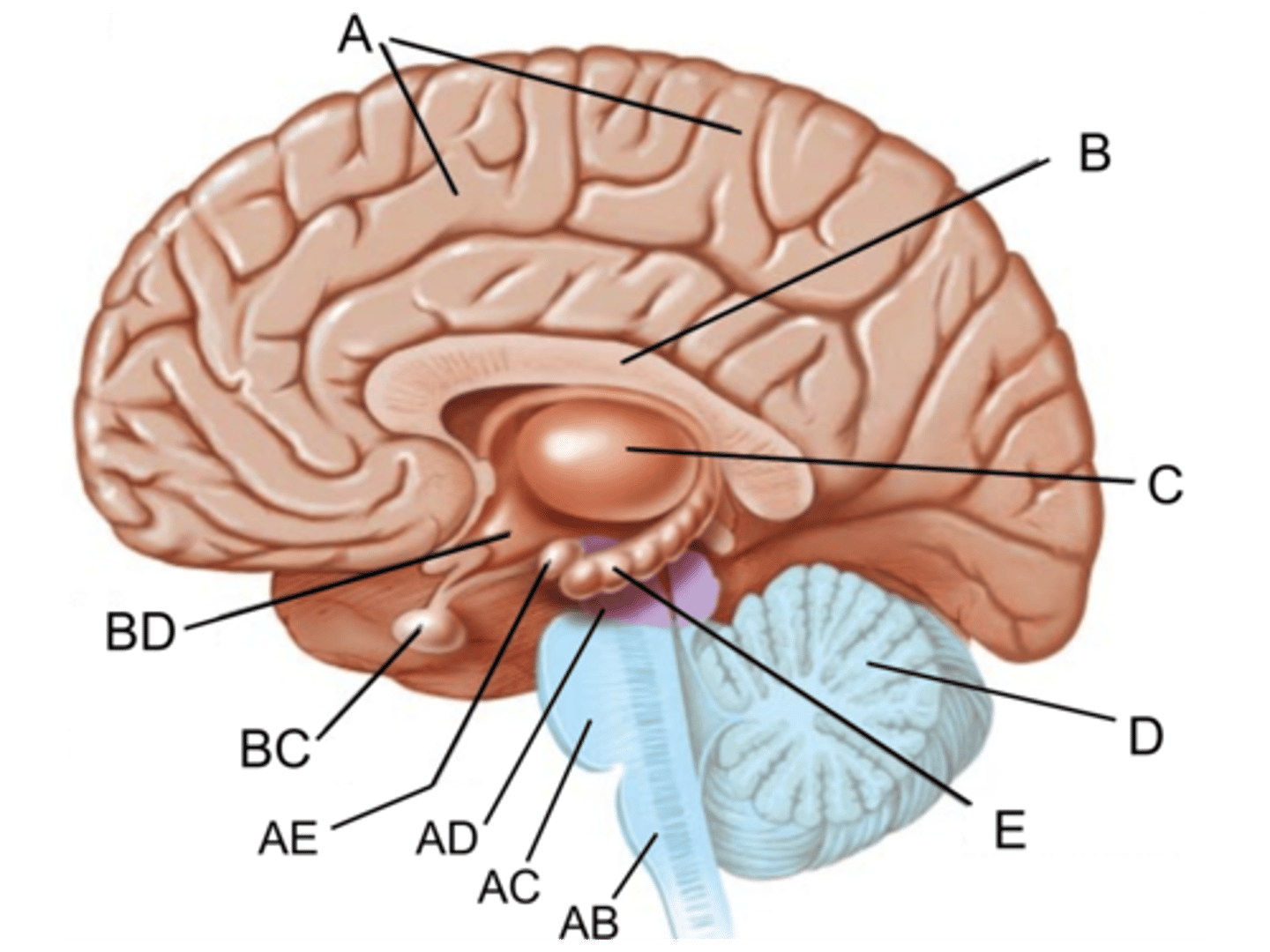
Identify A
corpus callosum
Identify B
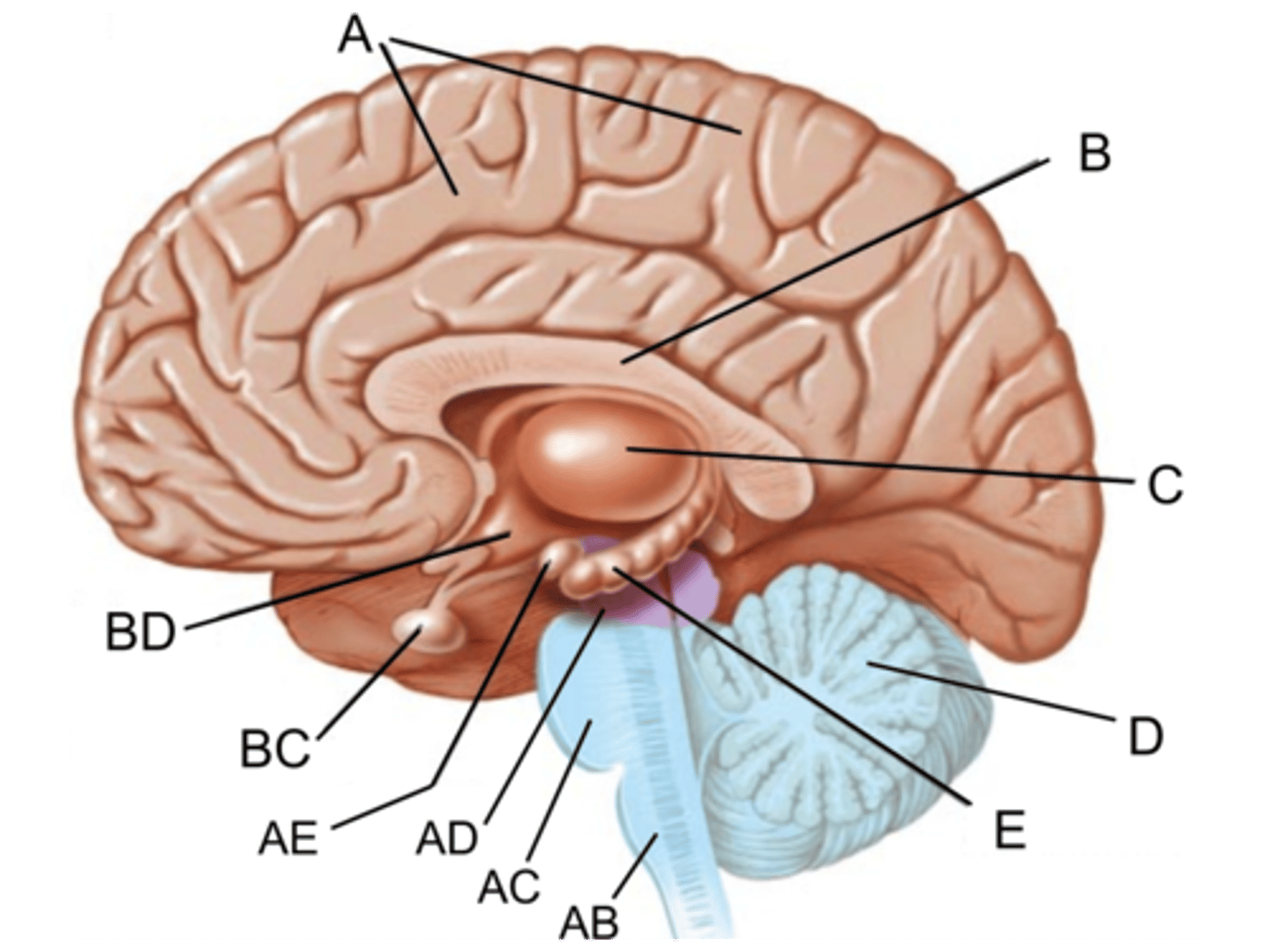
thalamus
Identify C
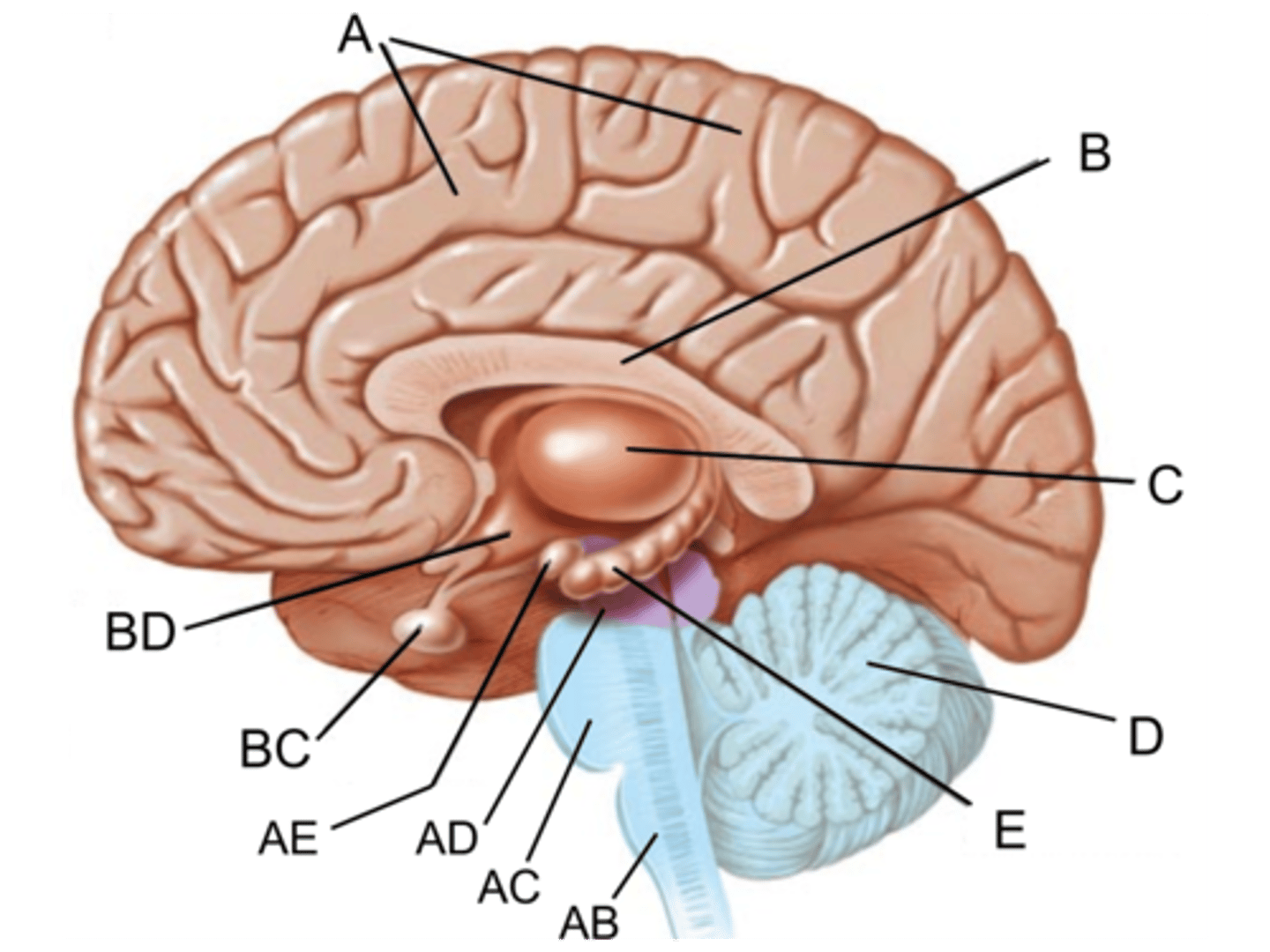
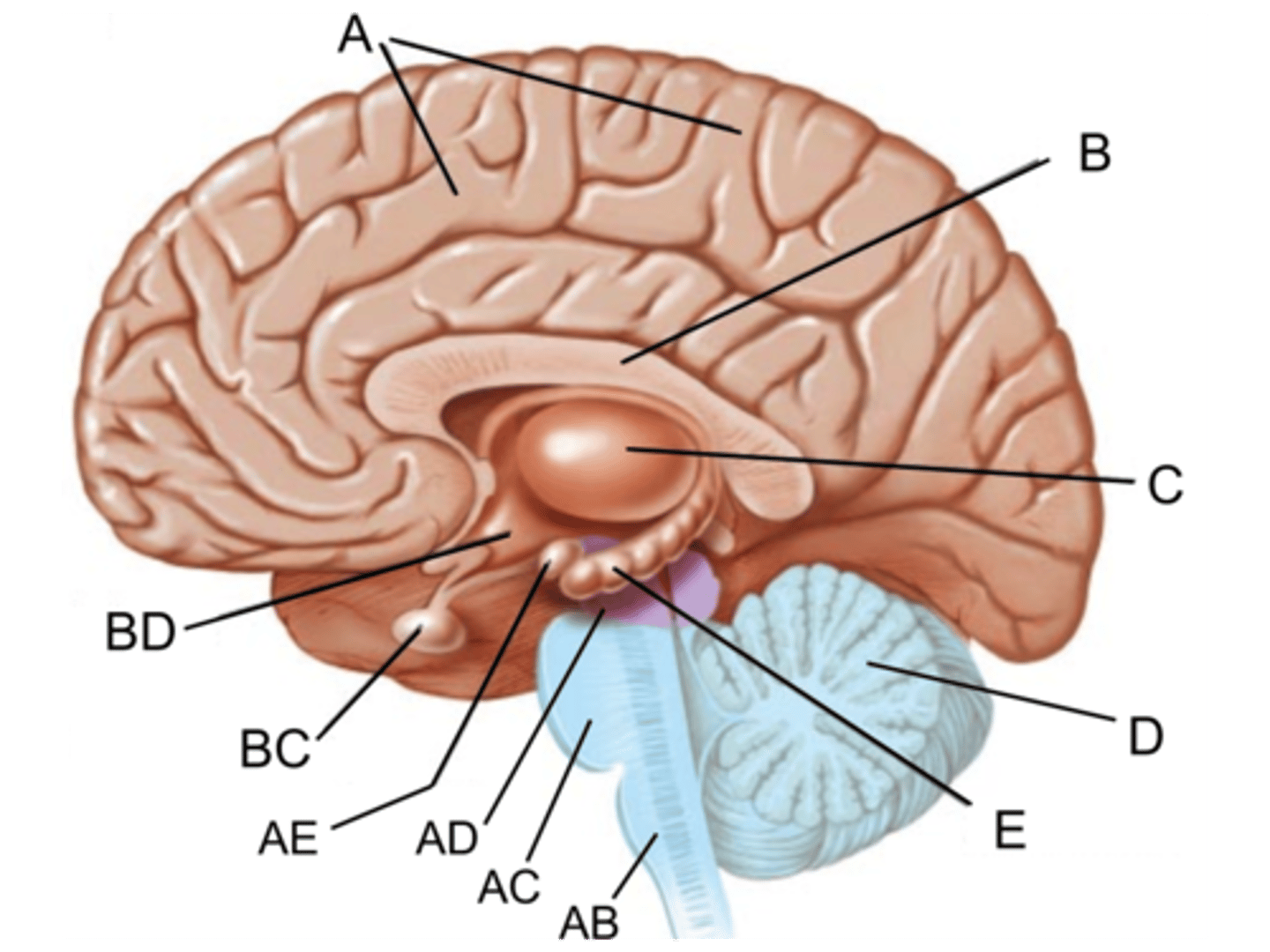
Medulla oblongata
Identify AB
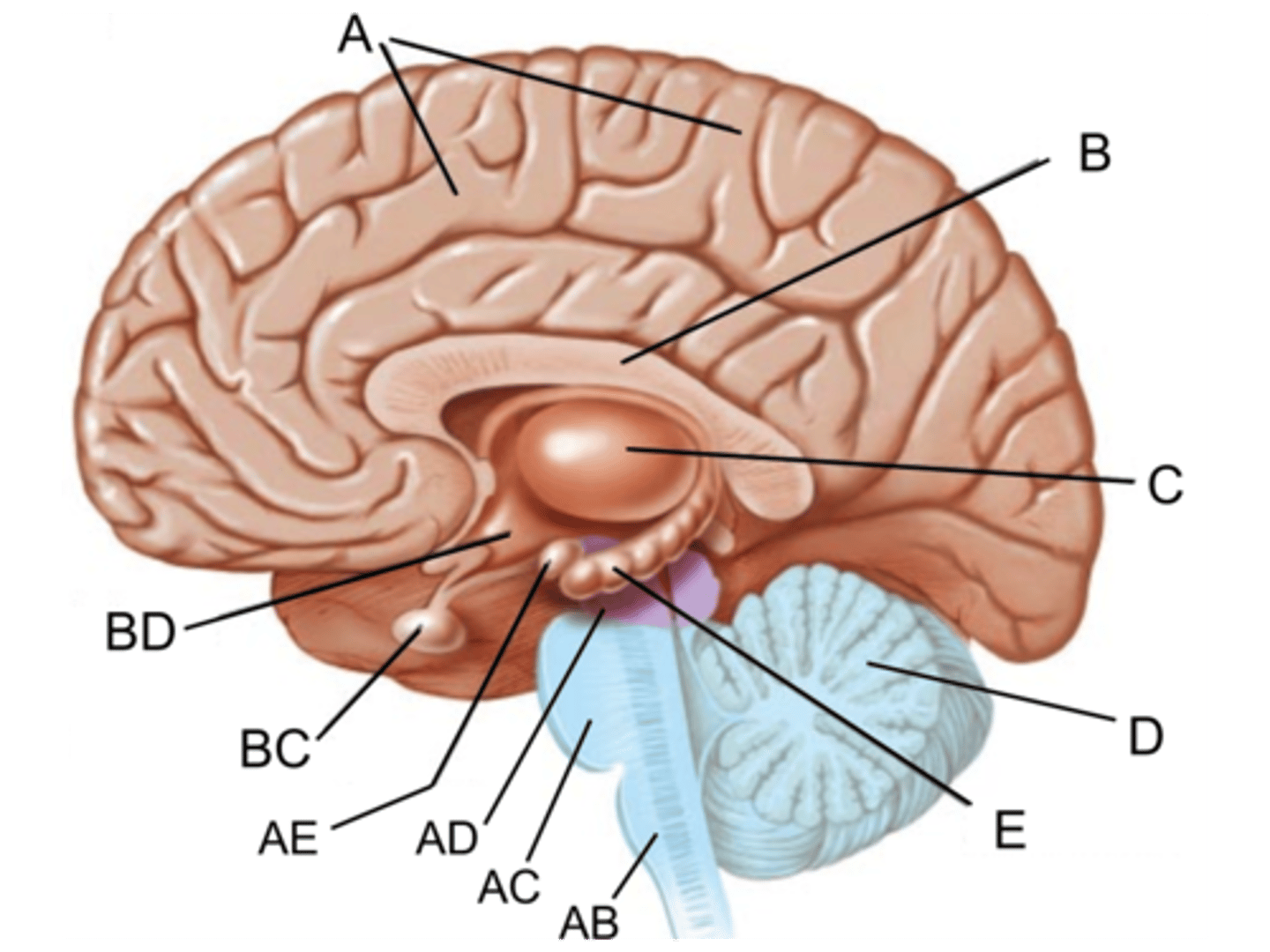
Pons
Identify AC
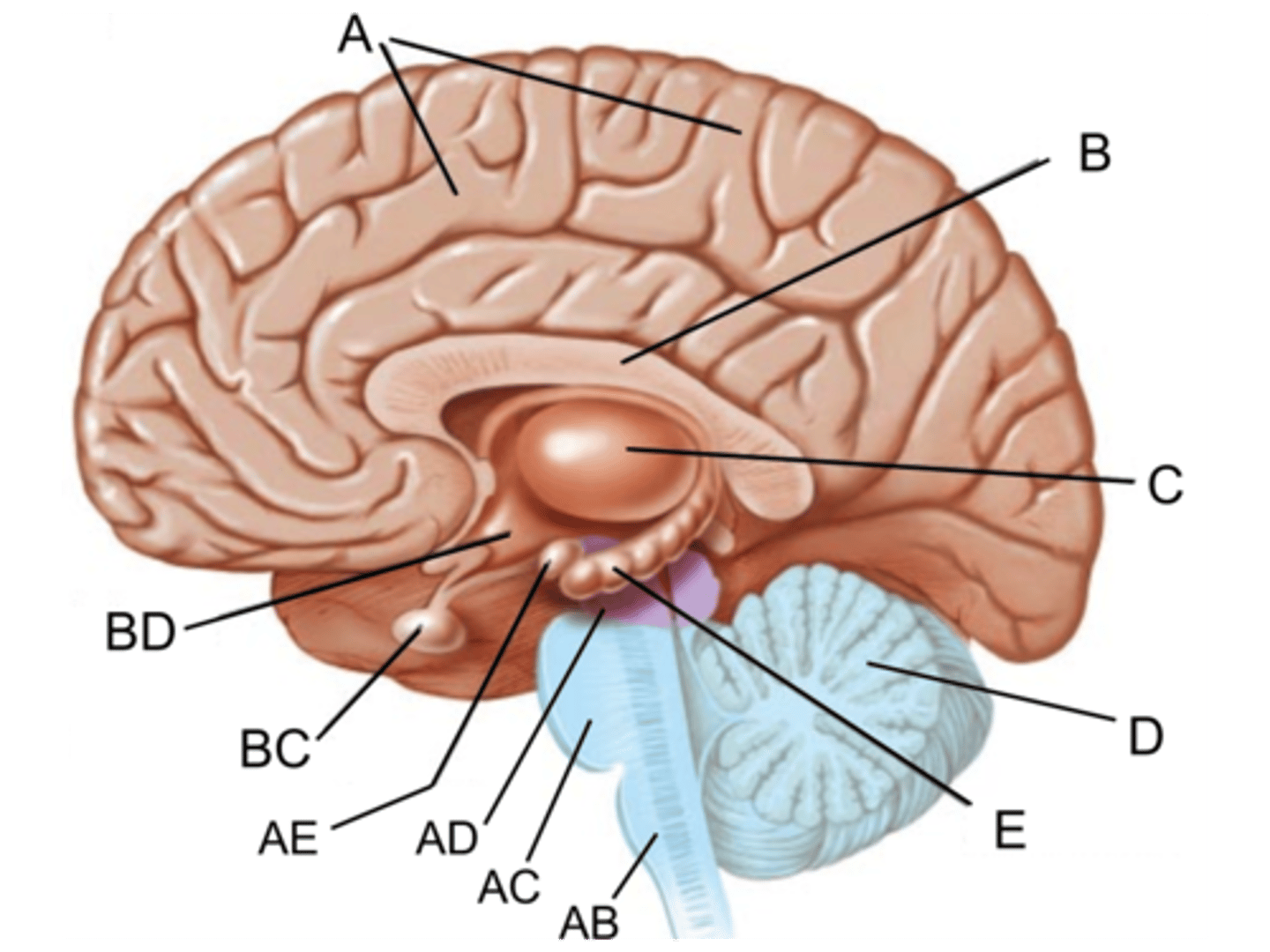
midbrain
Identify AD
pituitary gland
Identify BC
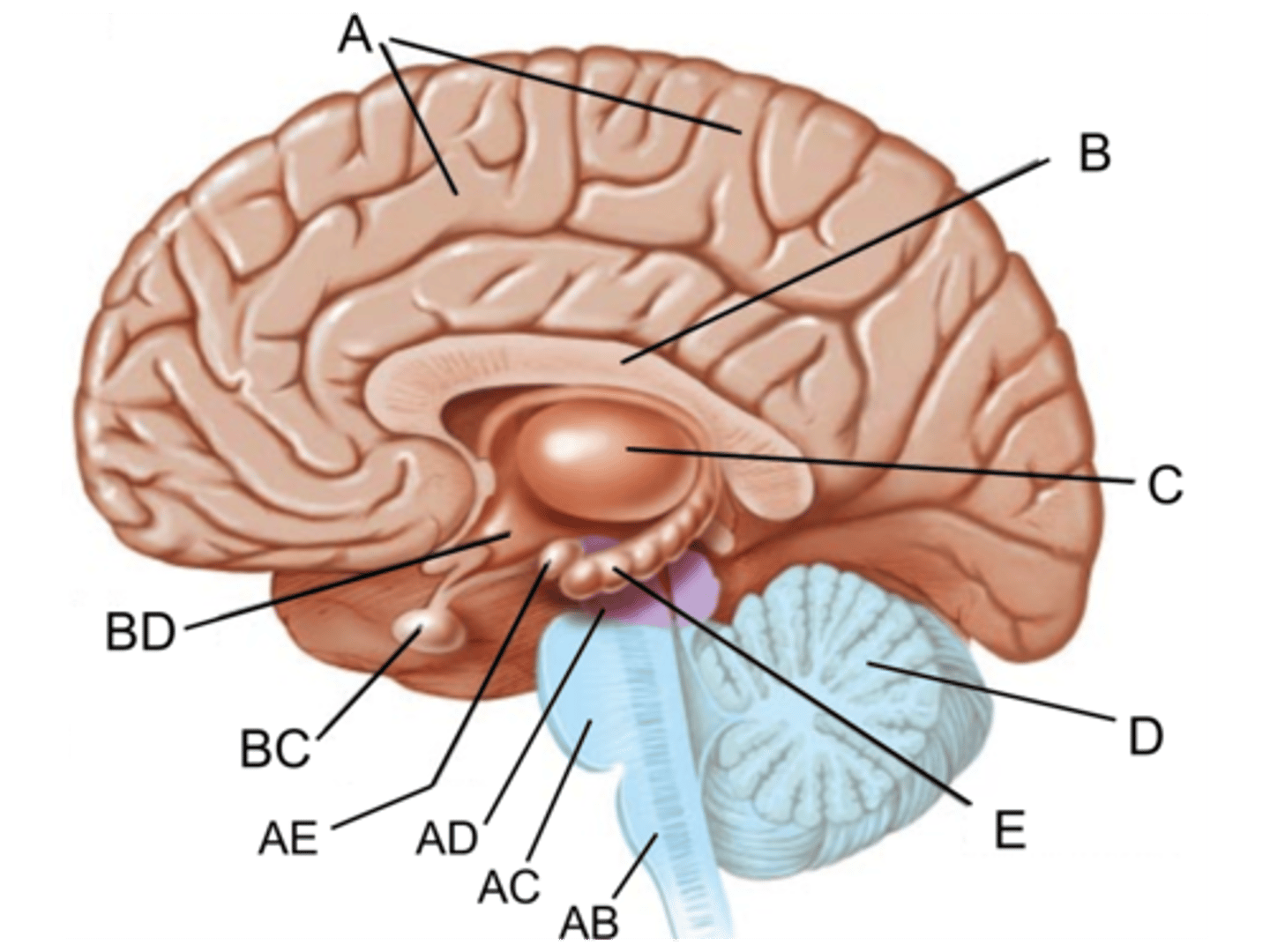
hypothalamus
Identify BD
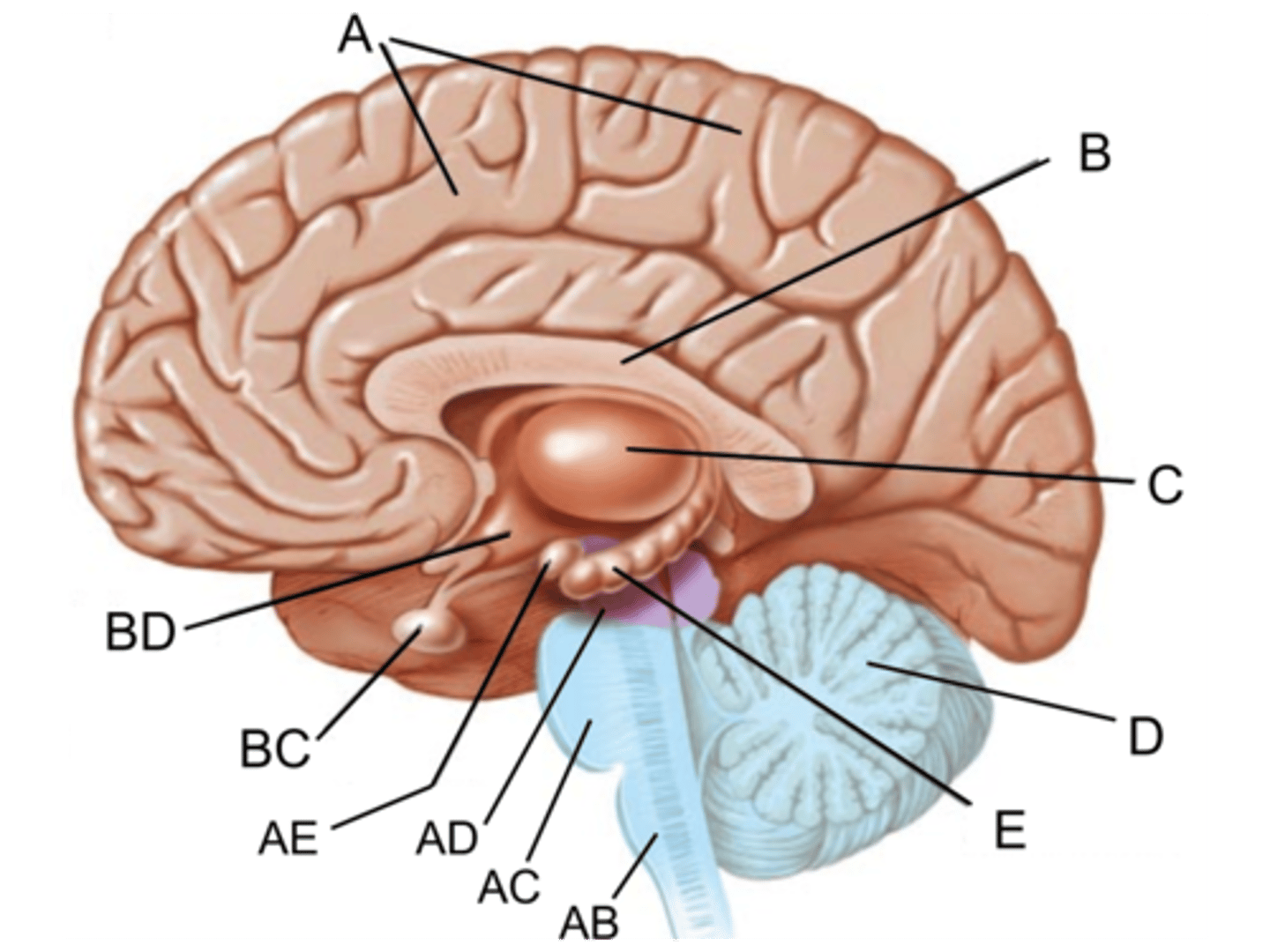
sulcus (sulci)
Identify the structure at the green pointer
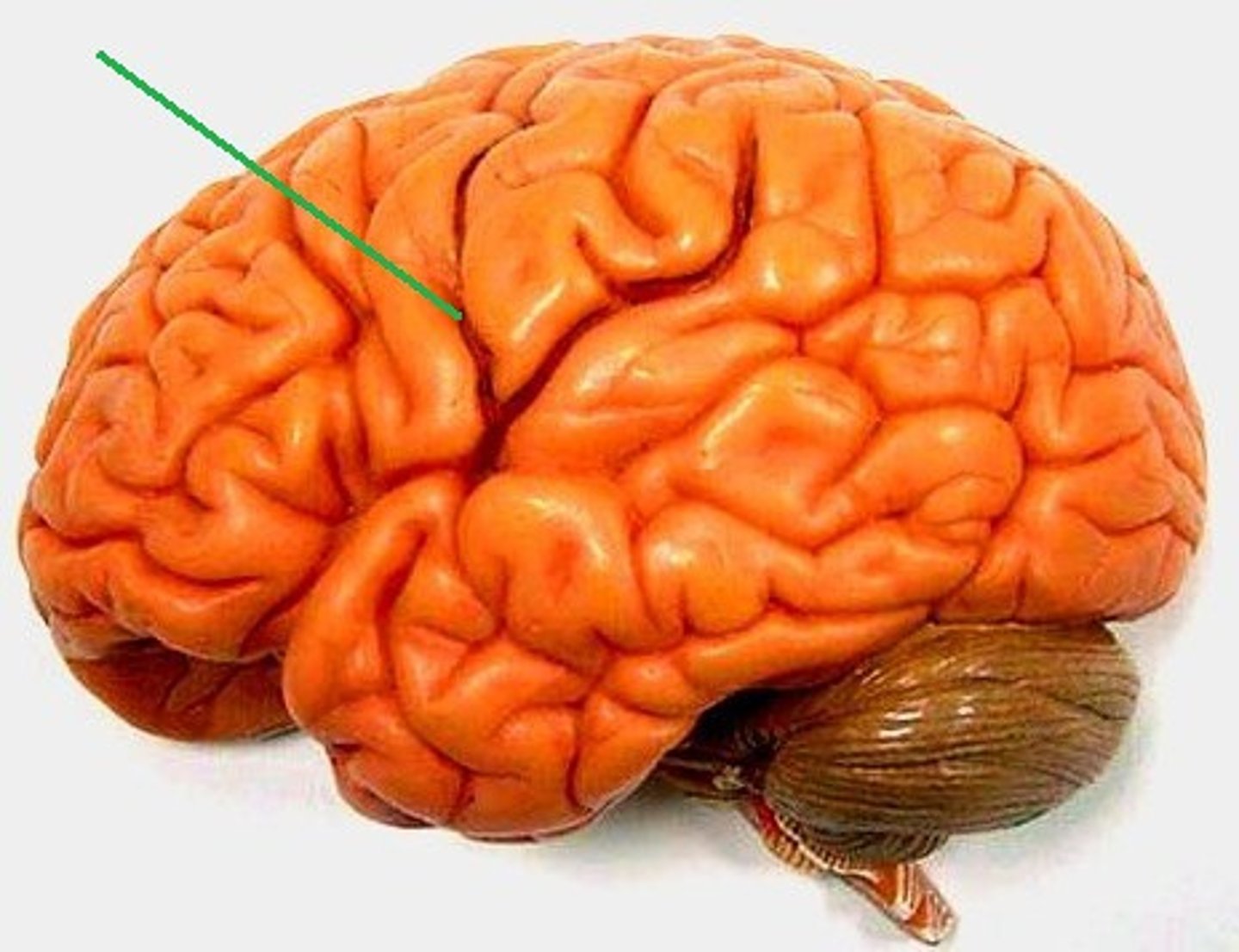
Gyri (gyrus)
Identify the structure at the green pointer
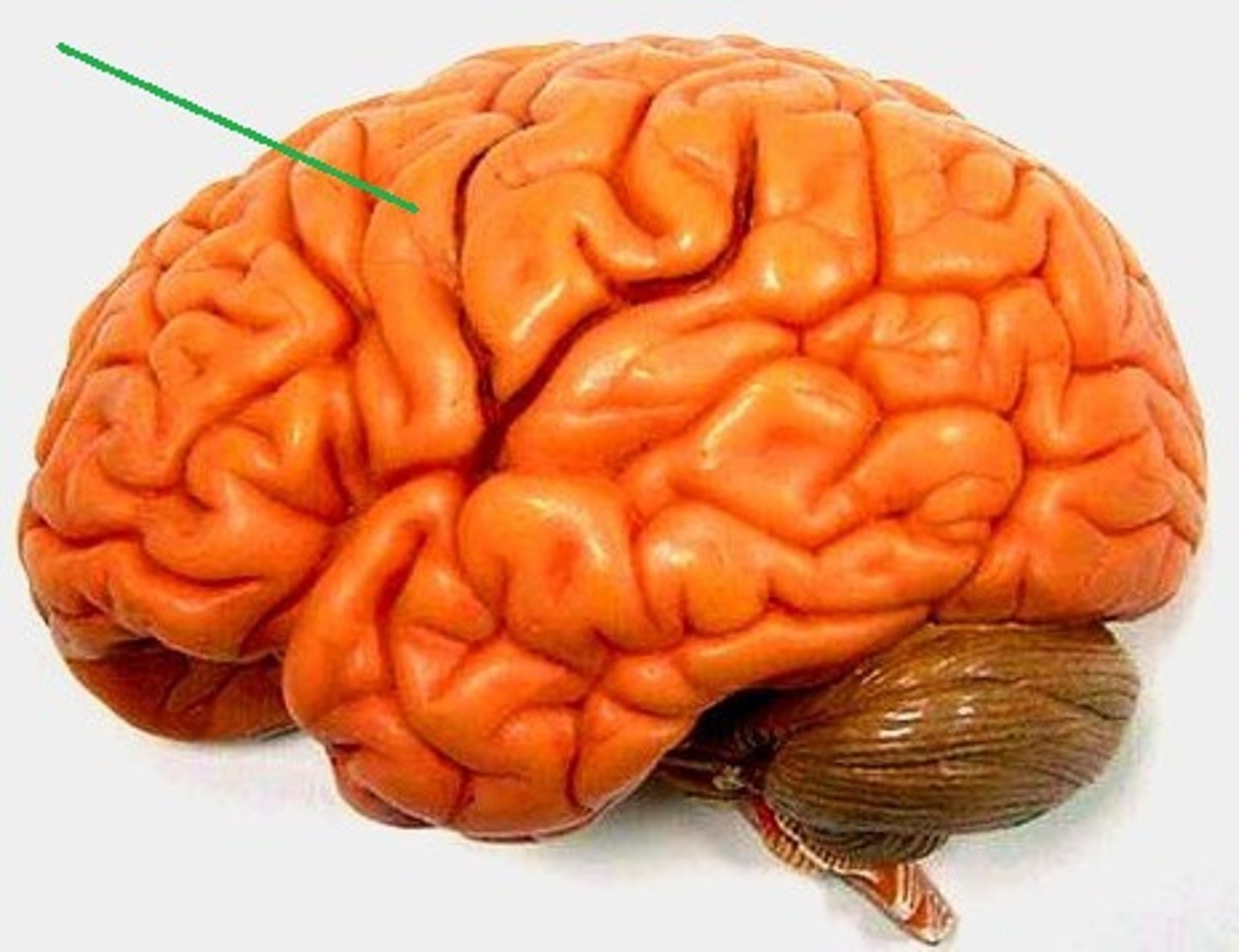
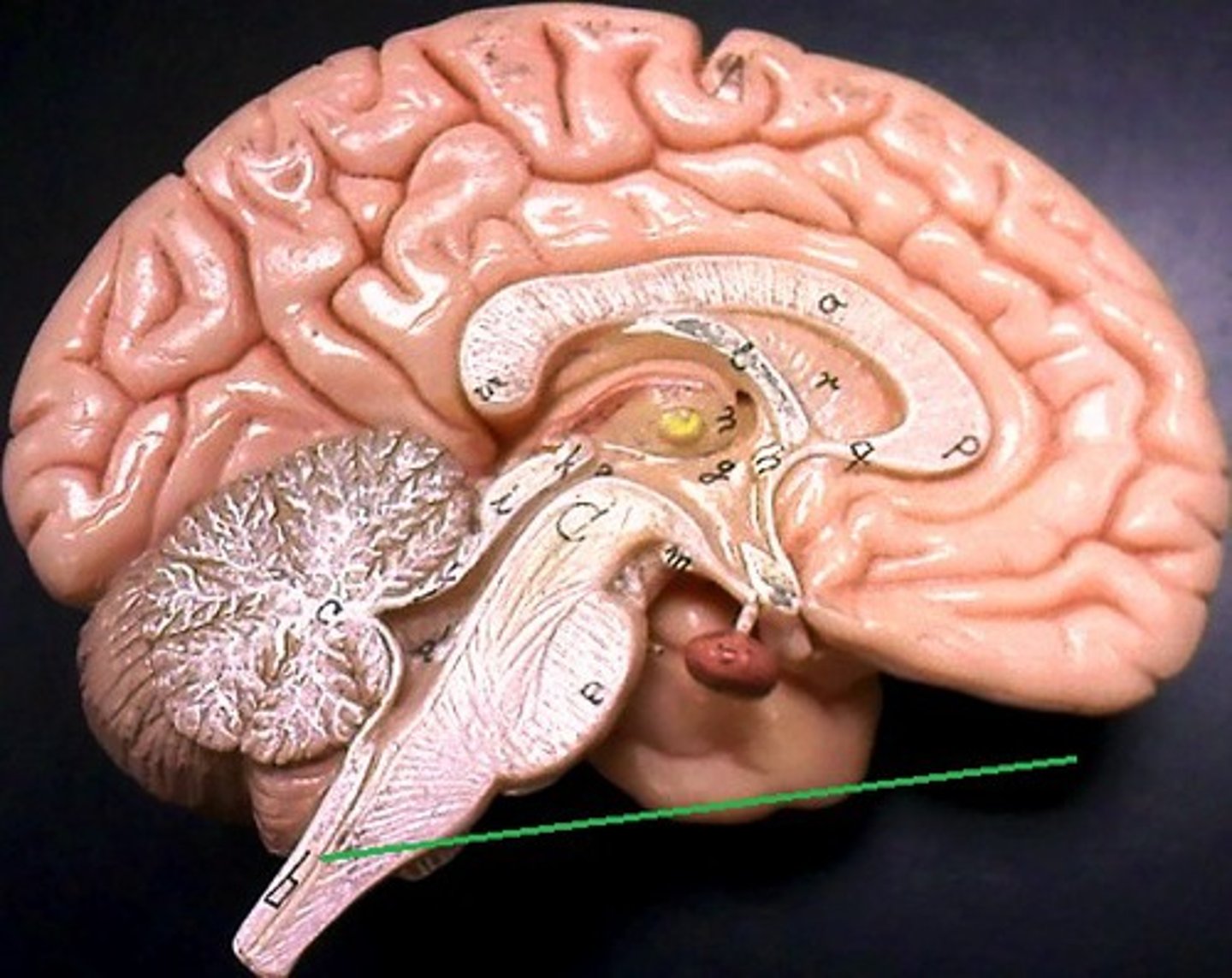
spinal cord
Identify the structure
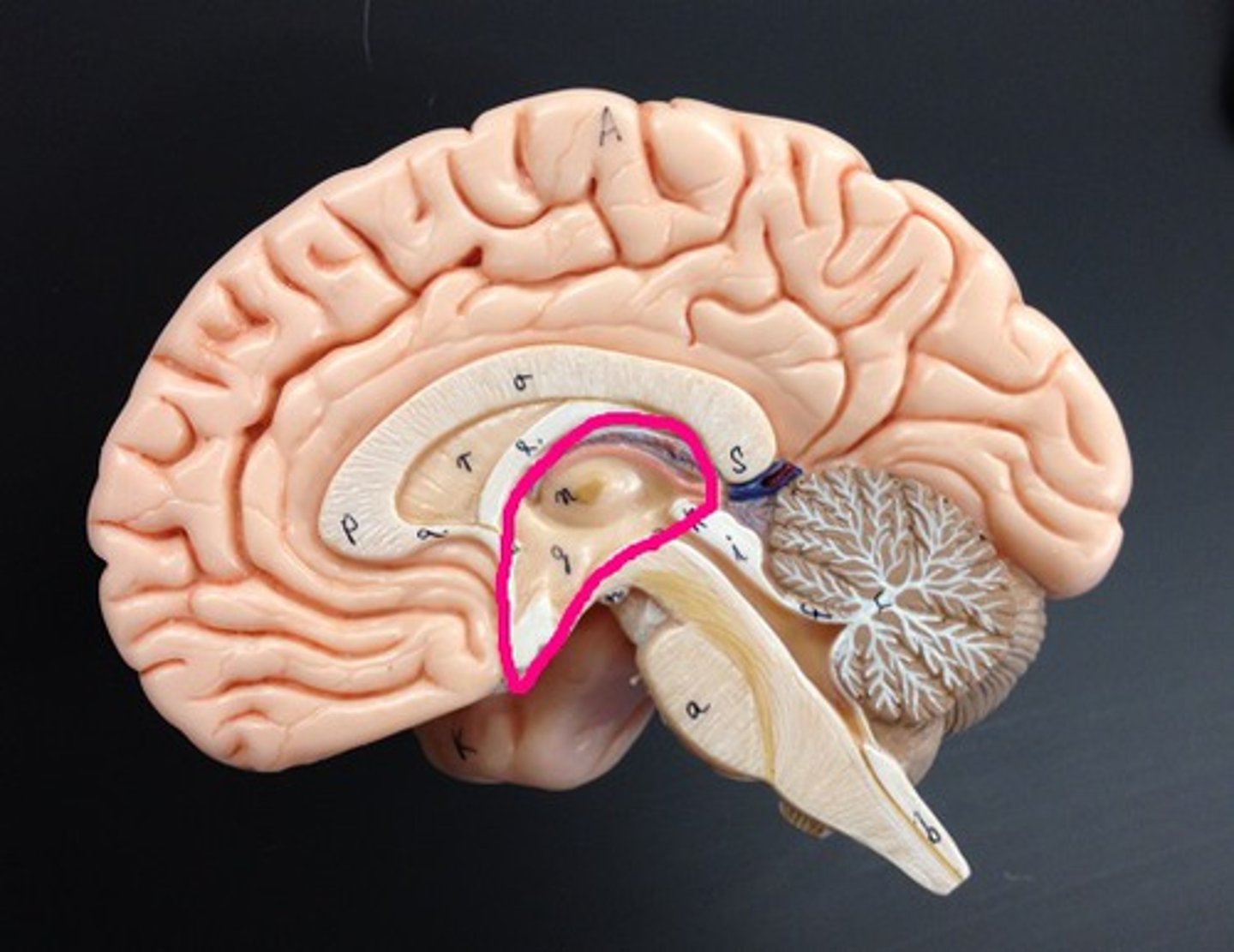
Diencephalon
Identify the red structure
brain stem
Identify the structure