EKG Rhythms
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
normal sinus rhythm
P wave: normal
PR interval: 0.12-0.20s
QRS: <0.12
Rate: 60-100
Regularity: Regular
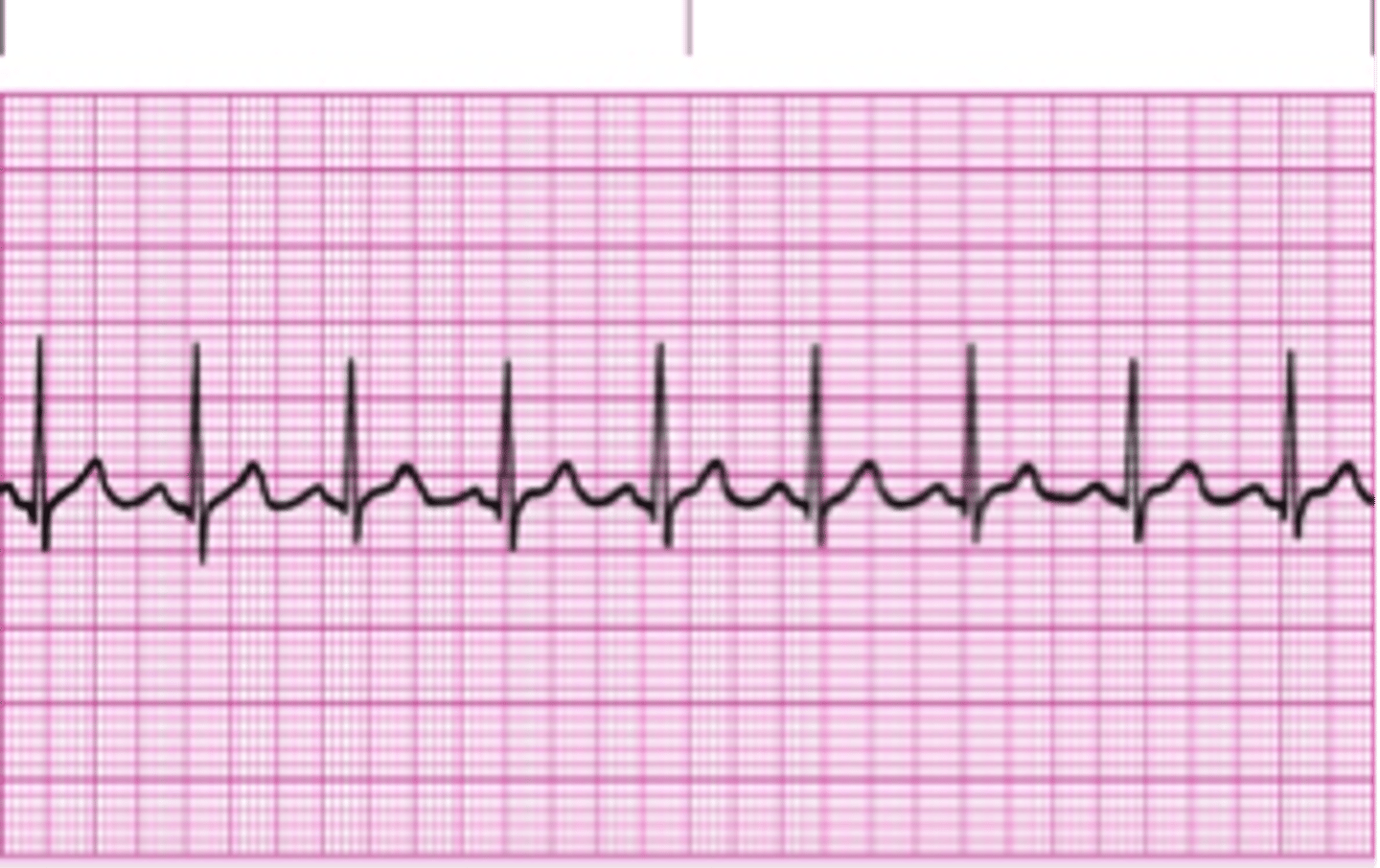
dysrhythmias
electricity not conducting properly
sinus bradycardia
p wave: normal
PR interval: 0.12-0.20
QRS: <0.12
Rate: <60
Regularity: Regular
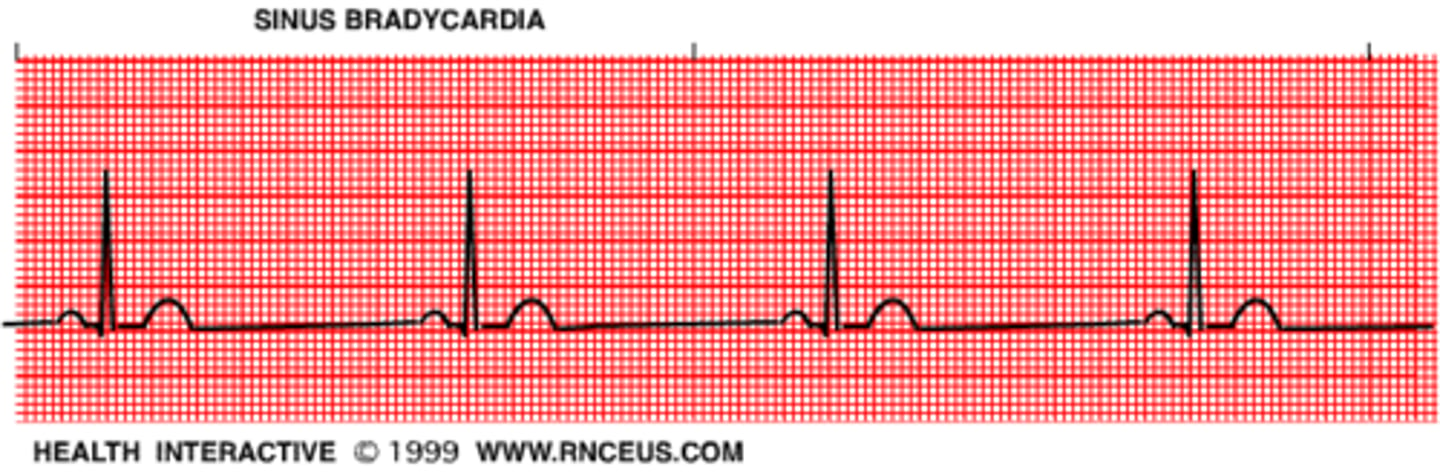
sinus bradycardia causes
Sleep
Inactivity
Very athletic (low resting HR)
Drugs
MI (muscle damage => impulses slowed down, pumping slowed down)
sinus bradycardia interventions
fix the cause
atropine (Symptomatic)
sinus tachycardia
P-wave: normal
PR interval: 0.12-0.20
QRS: <0.12
Rate: >100
Regular
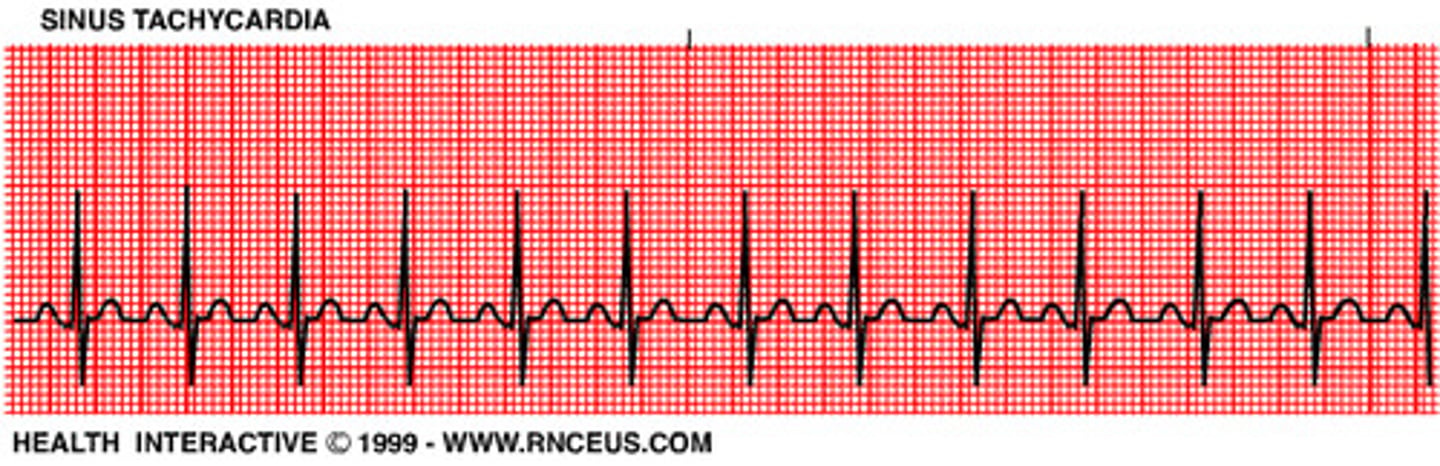
sinus tachycardia causes
Caffeine
Exercise
Fever
Anxiety
Drugs
Pain
Hypotension
Volume depletion (HR increase to perfuse, increase CO)
sinus tachycardia interventions
tx the cause
heart blocks
Conduction is excessively delayed or stopped at AV node or bundle of His
first degree heart block
P-wave:
Normal
PR Interval: >.20 (prolonged)
QRS: <0.12
Rate: 60-100
Regularity: Regular
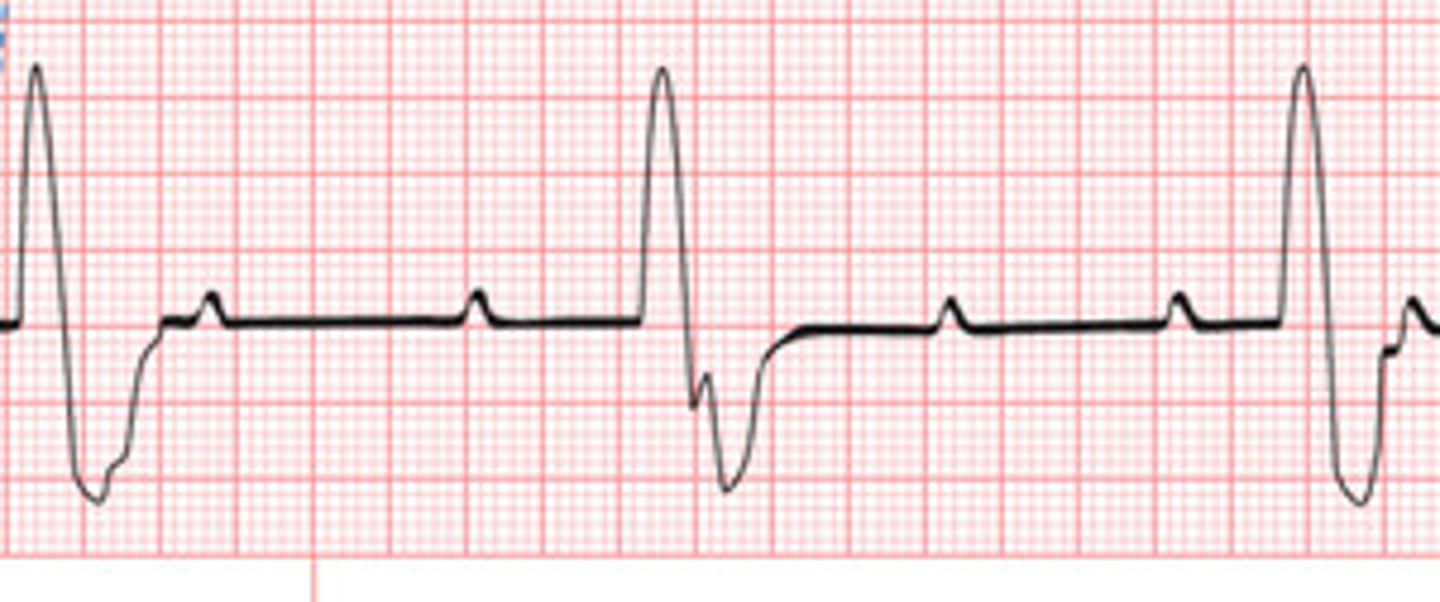
first degree heart block causes
often an incidental finding
peds - infection
myocarditis
congenital heart disease
first degree heart block interventions
fix the cause
treatment is generally not required
if extreme - pacing
second degree heart block type 1
P-wave: Not a P for every QRS
PR Interval: longer, longer, longer....drop
QRS: <0.12
Rate: 60-100
Regularity: Regular
dropped beat, P wave but no QRS complex, electricity does not reach ventures from Atria
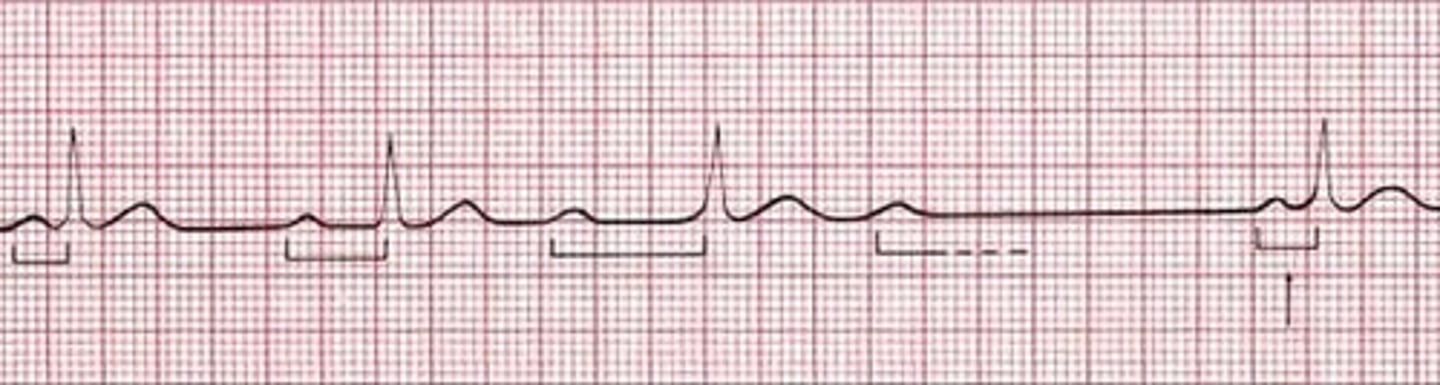
second degree heart block type 1 causes
Ischemia
Myocarditis
Status post-cardiac surgery
second degree heart block type 1 interventions
fix the cause
asymptomatic: no treatment required
symptomatic: pacing
second degree heart block type 2
P-wave: Not a P for every QRS (happens at random times)
PR Interval: 0.12-0.20
QRS: <0.12
Rate: >100
Regularity: Regular
int. dropped beats, P wave then no QRS, atria is contracting but not the ventricles
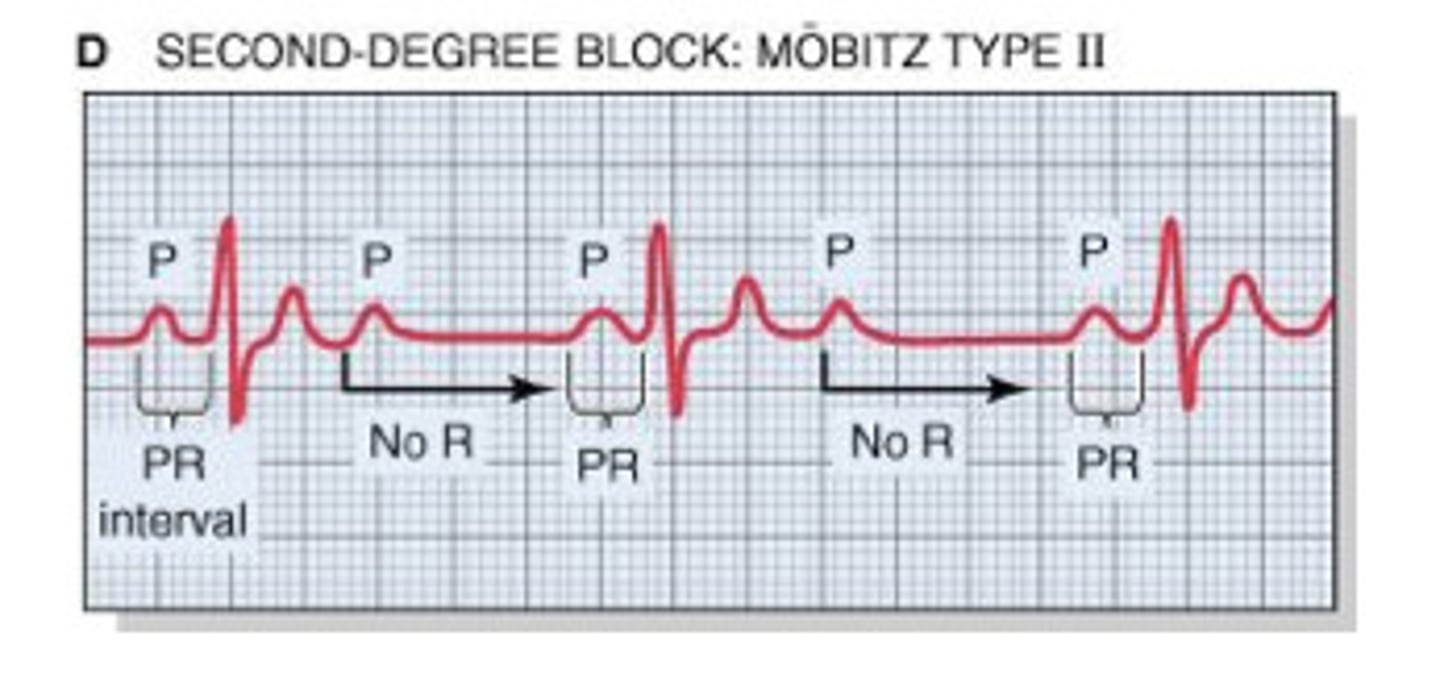
second degree heart block type 2 causes
MI, ischemia
second degree heart block type 2 interventions
fix the cause
pacing
third degree heart block
P-wave: Normal
PR Interval: Variable
QRS: <0.12
Rate: <60
Regularity: Irregular
complete dissociation between Atria + ventricles, not sufficient enough CO to support VS
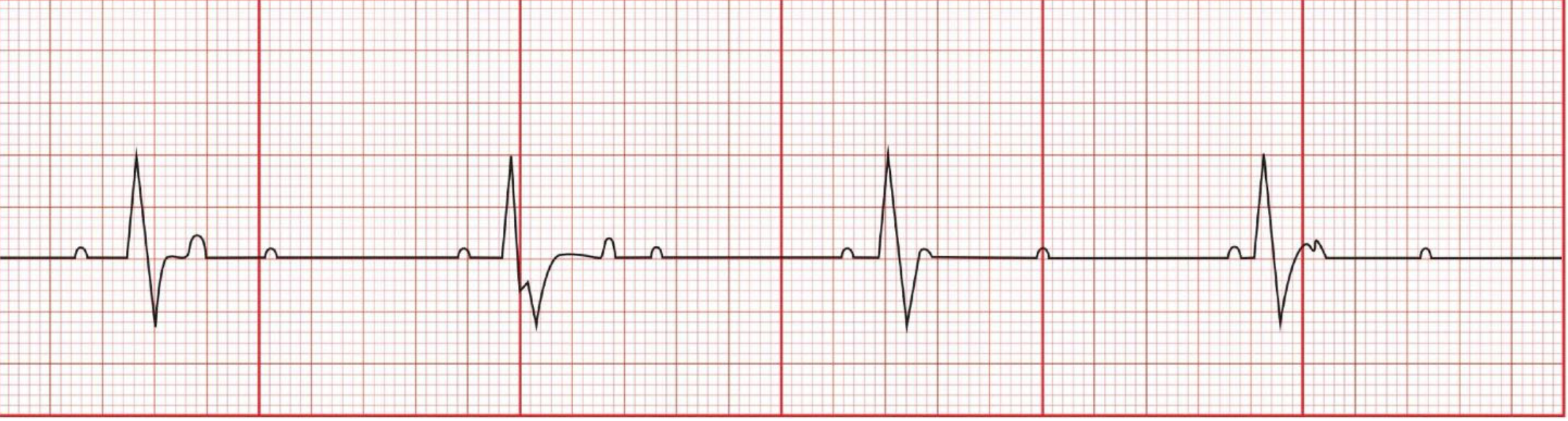
third degree heart block causes
damage to the heart
MI
heart valve disease
rheumatic fever (heart valves damaged by rheumatic fever)
sarcoidosis (inflammation in myocardium)
third degree heart block interventions
fix the cause
pacing (may need permanent), will be symptomatic
if R is far from P
then you have FIRST DEGREE
longer longer drop
Then you have a Wenkebach (2nd degree type 1)
if some P's dont go through
then you have a Mobitz II (2nd degree type 2)
if Ps and Qs disagree
then you have a third degree
pacemaker types
transcutaneous: through skin, pads. usually in ER situation
transvenous: veins (come back from OR), if they are cardiac risk. can easily be paced from machine
permanent: implanted into their body
pt education about permanent pacemaker
-keep pacemaker ID card in wallet
-you can take a bath and showers
-don't apply pressure over the generator, dont wear tight clothing
-operating household appliances are safe
-notify airport security of pacemaker
-for temporary pacemakers: ensure lead wires dont get wet
-contraindx for MRI (MRIS use magnets, do CT scan instead)
atrial flutter
P-wave: saw tooth (lots of pwaves!)
PR Interval: none
QRS <0.12
Atrial Rate: 250-400
Ventricular Rate: varies
Regular or IRregular
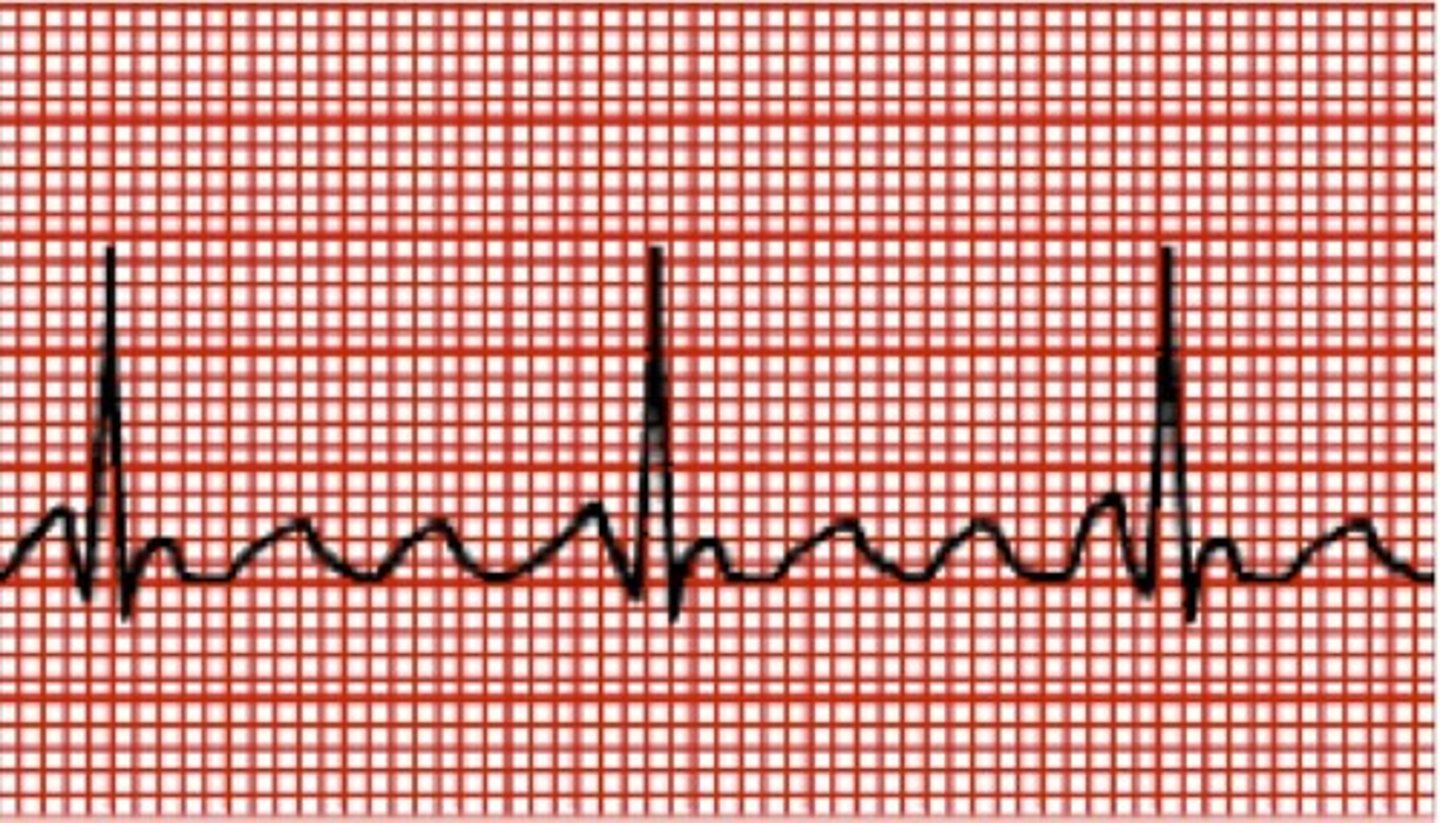
a flutter causes
Heart disease
MI
CHF
Pericarditis
a flutter interventions
-fix the cause
-cardioversion
-antiarrhythmics: amiodarone
-beta blockers: metoprolol (slow HR)
-CCB: diltiazem (regulate rhythm)
a fib
P wave: wavy
PR interval: none
QRS 0.12
Atrial Rave >400
Ventricular rate: irregular
atria deterioriate and quiver, not sending blood forward
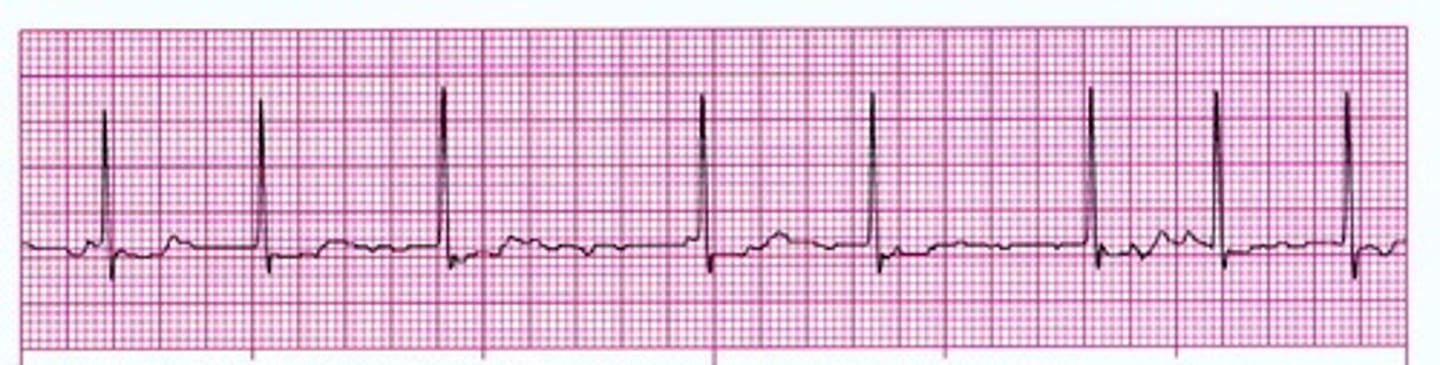
a fib causes
Heart disease
Pulmonary disease (increases pressure that our RV has to pump)
Stress
Alcohol
Caffeine
a fib interventions
fix cause
cardioversion***
antiarrhythmic: amiodarone
BB - metoprolol
surgery: ablation
ablation
removal of tissue to destroy its function
SVT
P-Wave: hidden
PR interval: immeasurable
QRS: <0.12
Rate: 150-250
REgularity: LOCKED IN REGULARITY
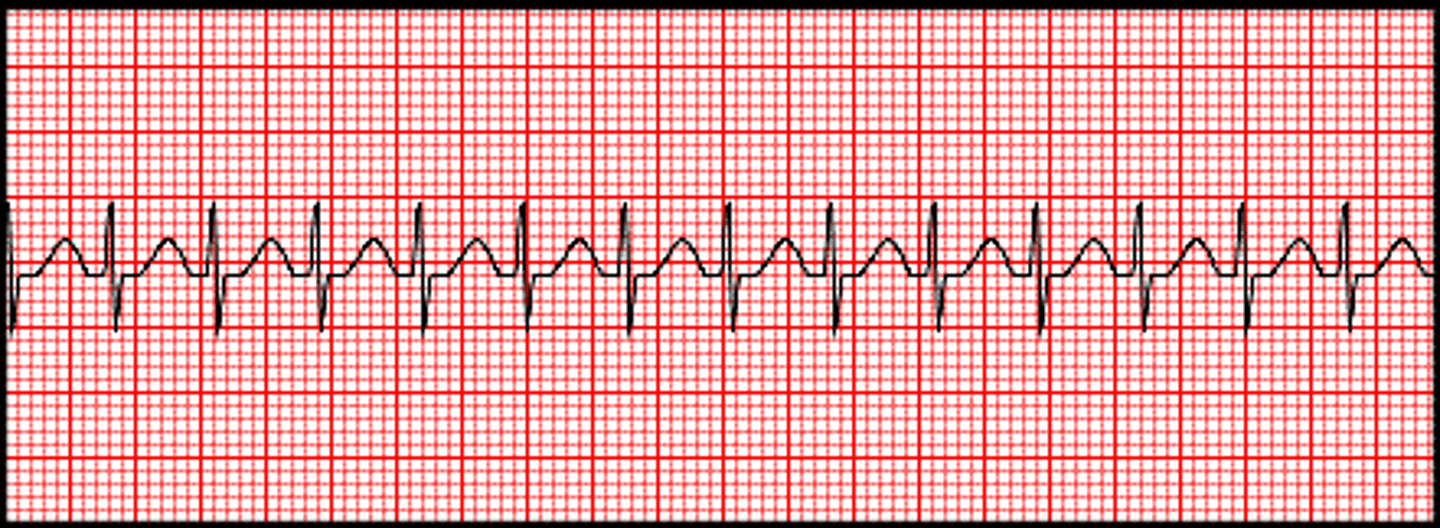
SVT causes
Caffeine
CHF
Fatigue
Hypoxia
Altered pacemaker in the heart (changes in SA node)
SVT interventions
fix causes
cardioversion
adenosine
vagal maneuver
to restart in SVT
adults: bear down, stimulates vagal nerve (CN X), can flip back into normal rhythm
infants: ice to face, blow on pinwheel (kids)
V tach
P-wave: none
PR Interval: none
QRS >0.11 wide and bizzare
Rate 150-250
Regular
ventricles are just contracting to get cardiac output out to body, can be with or without pulse
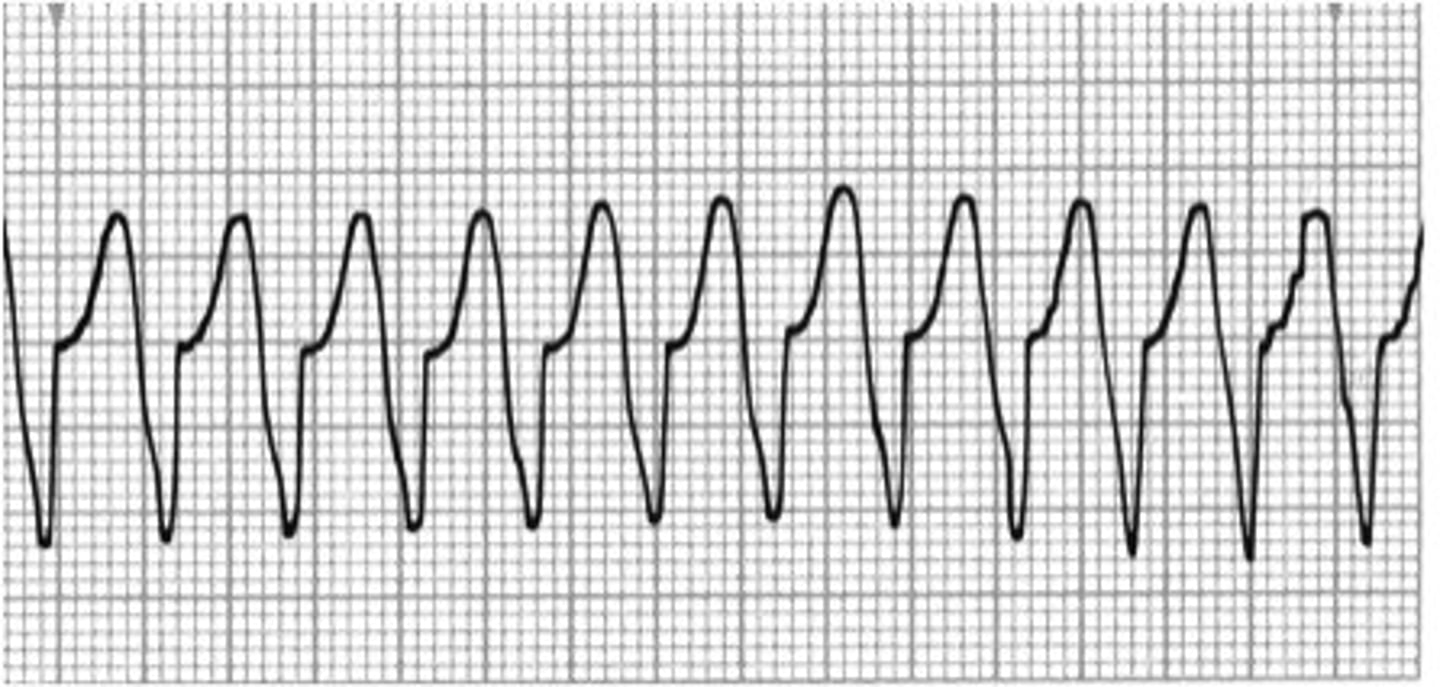
v tach causes
- MI
- ischemia
- digoxin toxicity
- hypoxia
- acidosis
- hypokalemia (or hyperkalemia)
- hypotension
v tach interventions
pulse: check pulse for 5-10 seconds
cardioversion
no pulse:
CPR
defibriliate
Epinephrine
v fib
p wave: none
pr interval: none
qrs: none
rate: none
regularity: irregular
ventricles are quivering, life threatening
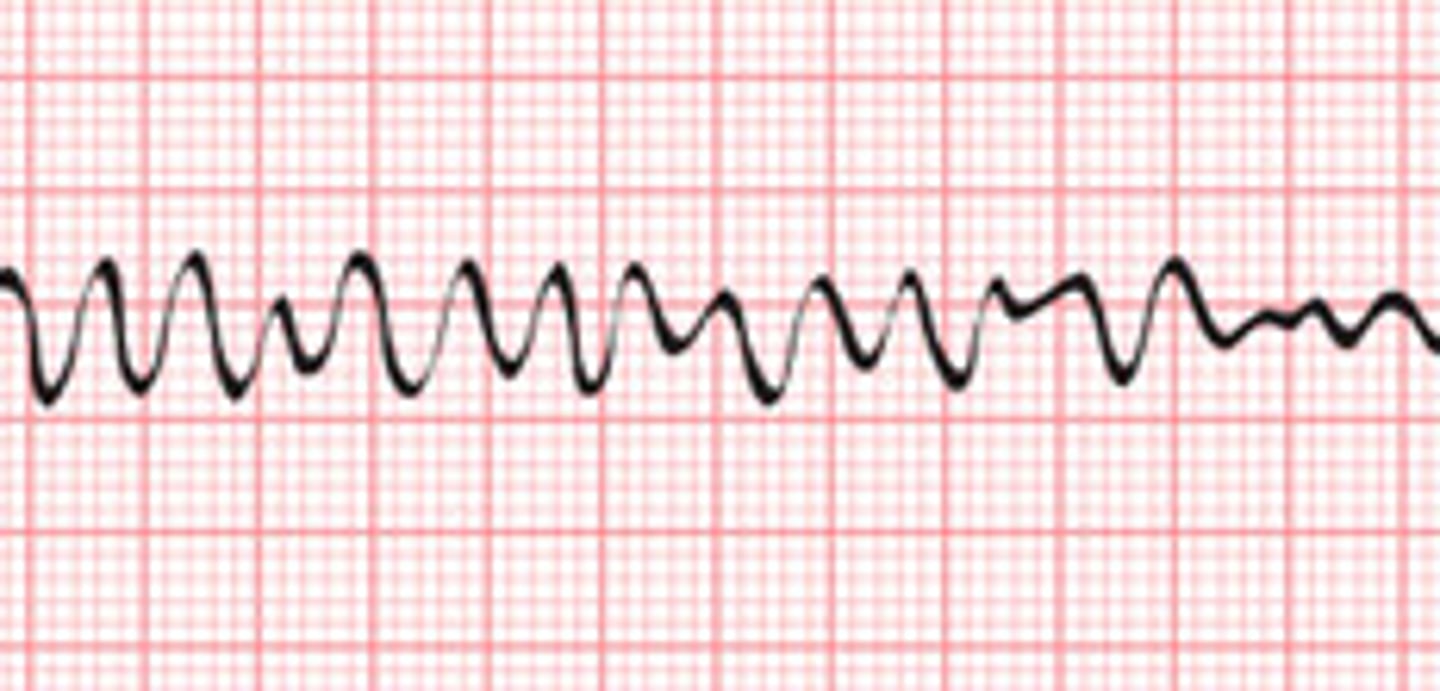
v fib causes
- MI
- Ischemia
- Hypoxia
- acidosis
- hypokalemia
- hypotension
- most common cause of sudden death
= digoxin toxicity
v fib interventions
fix the cause
CPR
defibrillate
epinephrine
cardioversion
synchronized shock - in time with client's own rhythm
NEED PULSE
lower energy
adults: 100-360 J
peds: 2J/kg
defibriliation
asynchronous - does not coordinate with the clients own rhythmn
higher energy
adults: 200-360J
peds: 2J/kg
asystole
p wave none
PR interval none
QRS none
rate none
regularity n/a
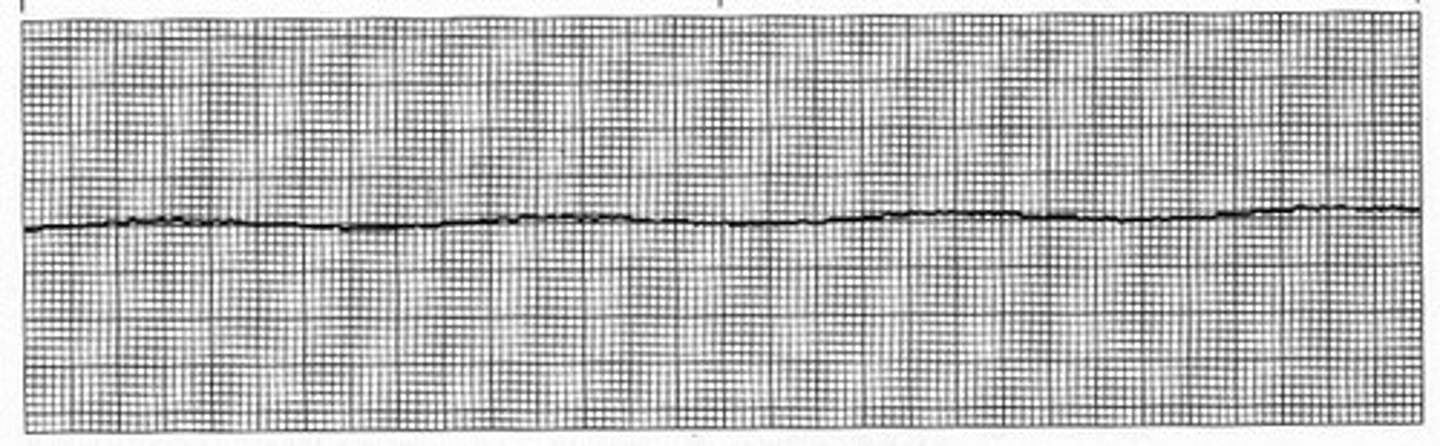
asystole causes
Follows VT/VF in cardiac arrest
Acidosis
Hypoxia
Hypokalemia
Hypothermia
Overdose
asystole interventions
fix the cause
CPR
epinephrine
epinephrine in an emergency situation
1mg every 3-5min there is no maximum dose in a code