Dynamic Earth - Lecture 17: Earth's Magnetic Field
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Lodestone compass
discovered in China ~1000 AD
Refers to a mineral that is a natural magnet (ex. magnetite)
used for geomancy long before it was used for navigation
William Gilbert
Personal physician to Queen Elizabeth I
Published De Magnete in 1600, a 6-volume treatise documenting his experiments with magnetism
Proposed that Earth behaves like a giant bar magnet with the magnetic axis approximately North-South
Who confirmed the idea of an internally generated field?
C.F. Gauss
Magnetic dipole
a bar magnet generates a magnetic dipole
produced by a pair of magnetic poles of equal strength, but opposite sign, a small distance apart

How many dimensions in Earth’s magnetic field?
3-dimensional
Three possible measurements of Earth’s magnetic field
Inclination = angle measured from horizontal (angle at which it points into Earth) - also called “dip angle”
Declination = angle measured from geographic north
Intensity = magnetic field strength
How is the field generated?
CANNOT actually be generated by a permanent bar magnet at its center because high temps destroy magnetism
When ferromagnetic materials exceed a certain temperature (known as their Curie temperature) they lose their permanent magnetism
Maxwell’s equations showed that… (2)
A changing magnetic field creates an electric field
A changing electric field creates a magnetic field
What generates a dipole magnetic field?
A current loop
an electrical current flowing in a loop
Dynamo
A machine for converting mechanical energy to electrical current flow (and magnetic field)
dynamo action in earth’s core generates geomagnetic field
requires movement of electrically conductive liquid Fe in the core
What causes the motion of liquid Fe in the outer core?
Thermal convection in the outer core
compositional convection in the outer core
Thermal convection in the outer core
Caused by heat released from the inner core to the outer core
Some heat is released due to freezing of the inner core
Some radioactive heating may also contribute
Compositional convection in the outer core
Inner core is made of solid Fe and is growing due to freezing of the liquid outer core (as Earth cools over time)
Pure Fe is freezing out and grows the inner core while the lighter elements remain in the outer core
Due to their low density, light elements rise in the outer core creating convection cells
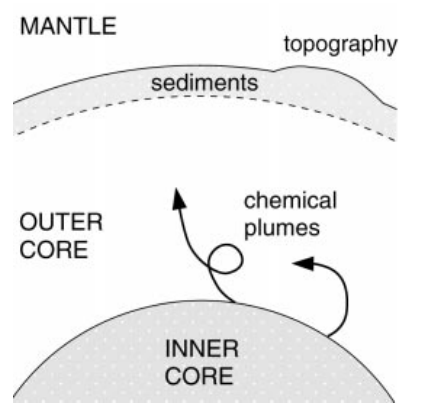
What is the dominant cause of convection today?
compositional convection
Is the geomagnetic field dynamic or static?
Dynamic - unlike bar magnet
What is the source of the field in the Earth’s outer core?
Motion of molten metal generates field in a process called geodynamo
3 parts of Earth’s total magnetic field
Main (internally generated) Magnetic Field - 99.2%
External Magnetic Field - 0.6%
Induced Magnetic Field - 0.2%
Solar wind
Charged particles ejected from the sun
Magnetosphere
A zone where charged particles are affected by Earth’s magnetic field
Magnetotail
Portion of magnetosphere that is pushed away from the sun by the solar wind