inorganic chemistry
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the flame test for group 2 ions?
Dip a nichrome wire loop in concentrated HCl
Dip loop into unknown compound
Hold the loop in the clear blue part of a Bunsen burner flame and observe colour change in the blame
Calcium turns brick red, strontium turns red, barium turns pale green
What is the other test for group 2 ions with NaOH?
Add dilute NaOH dropwise to a test tube containing the metal ion solution
Observe the precipitate formed if there is one
Add more NaOH until it is in excess and record any changes you see
Mg forms a slight white precipitate and in excess a white precipitate
Ca and Sr forms a slight white precipitate both times
Ba has no change for both
What is the test for ammonium ions?
Add some dilute sodium hydroxide solution to the substance
Gently heat the mixture
Test if there is any ammonia gas given off by holding damp litmus paper above the solution
If ammonium ions are present the litmus paper turns blue
How do you test for sulfate ions?
Add a little dilute HCl
Add barium chloride solution
A white precipitate of barium sulfate forms
How do you test for hydroxide ions?
Hydroxide ions make solutions alkaline so you can use a pH indicator to test it
For example if you dip a piece of red litmus paper into the solution it will turn blue
How do you test for carbonate ions?
Add dilute hydrochloric acid
If it contains carbonate ions it will fizz as CO2 is formed
You can then test for carbon dioxide by bubbling the gas through limewater
The limewater should go cloudy
What is the trend in atomic radius down group 2?
The atomic radius gets larger because extra electron shells are added as you go down the group.
What is the trend in first ionisation energy down group 2?
First ionisation energy decreases down the group
This is because each element down group 2 has an extra electron shell compared to the one above.
This means shielding increases and the distance between the outer electrons and the nucleus increases so there is less attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus
This makes it easier to lose outer electrons
What is the trend in reactivity down group 2?
Reactivity increases down the group as it gets easier to lose electrons further down the group.
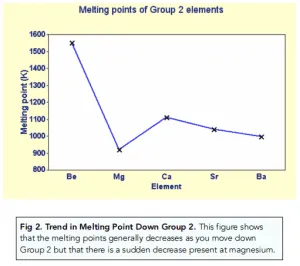
What is the trend in melting point down group 2?
Melting point generally decreases as metal ions get bigger down the group with the number of delocalised electrons staying the same and the charge
The larger the ionic radius, the further away the delocalised electrons are from the positive nuclei
So it takes less energy to break the bonds
However, there is an increase at Mg as the crystal structure changes
What is the trend in reducing power down group 7?
How easy it is for a halide ion to lose an electron depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons.
As you go down the group, the attraction gets weaker because ions get bigger, so electrons are further away from the positive nucleus
There is also increased shielding
Therefore reducing power increases down the group
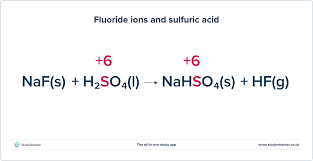
How does NaF or NaCl react with sulfuric acid?
NaCl/ NaF reacts for form either HCl or HF
You will see misty fumes as the gas comes into contact with moisture in the air.
HF and HCl aren’t strong enough reducing agents to reduce sulfuric acid so the reaction stops
This is an acid base reaction, not a redox reaction
How does NaBr react with sufuric acid?
1st reaction: NaBr + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HBr
This gives misty fumes of hydrogen bromide gas. But the HBr is stronger reducing agent than HCl and reacts with the H2SO4 in a redox reaction
2nd reaction: 2HBr + H2SO4 O2 and orange fumes of Br2
How does NaI react with sulfuric acid?
1st reaction: NaI + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HI
HI then reduces H2SO4
2nd reaction: 2HI + H2SO4 → I2 + SO2 + 2H2O
But HI keeps going and reduces the SO2 to H2S
3rd reaction: 6HI + SO2 → H2S + 3I + 2H2O
The reaction produces fumes of H2S and solid iodine
What is the test for halides?
Add dilute nitric acid to remove ions which might interfere with the test.
Add a few drops of silver nitrate solution
A precipitate is formed (of the silver halide)- Chloride is white, bromide is cream, iodide is yellow
You can also test your results by adding ammonia solution. Each silver halide has different solubility in ammonia
Chlorides dissolve in dilute ammonia
Bromide dissolves in conc. ammonia
Iodide is insoluble in conc. ammonia
What are the colours of the first 4 halogens?
Fluorine- pale yellow
Chlorine- green
Bromine- red-brown
Iodine- grey
What is the trend in boiling point?
Boiling points increase down the group
This is due to increasing strength of van der Waals forces
What is the trend in electronegativity?
Electronegativity decreases down the group.
Larger atoms attract electrons less than smaller ones. This is because their outer electrons are further from the nucleus and are more shielded
What is formed when chlorine reacts with KBr?
An orange solution is formed as bromine is displaced by chlorine
What is formed when chlorine/bromine reacts with KI?
A brown solution is formed since iodine is displaced by chlorine/bromine.
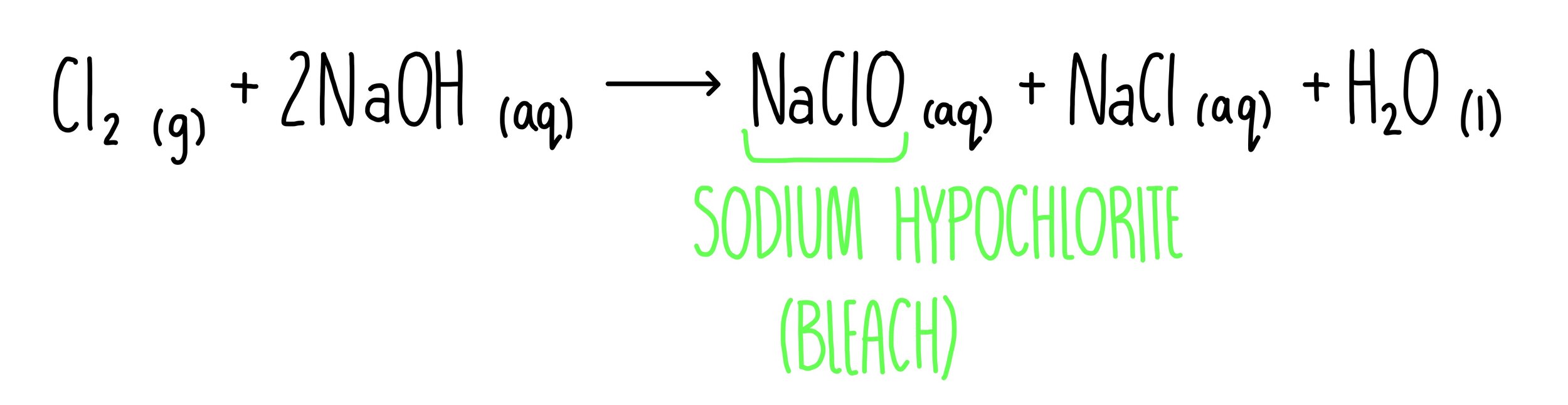
How do you make bleach?
Mix chlorine gas with cold, dilute sodium hydroxide solution at room temperature
This makes sodium chlorate solution which is the main component in bleach
In this reaction Cl is oxidised and reduced. This is called disproportionation.
How does chlorine react with water?
Cl undergoes disproportionation and you end up with a mix of chloride ions and chlorate ions
In sunlight chlorine can also decompose water to form chloride ions and oxygen
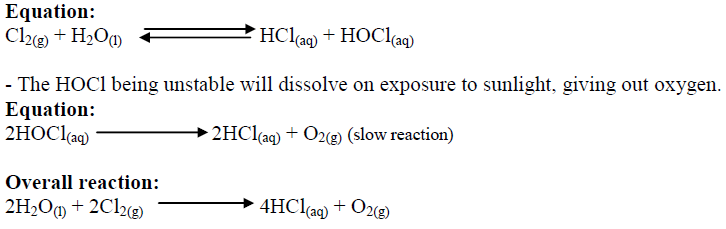
How is chlorine used in water treatment?
Since chlorate ions kill bacteria, adding chlorine to water makes it safe to drink or swim in.
When treating drinking water, chlorine kills disease causing microorganisms and prevents growth of algae
What are risks of using chlorine to treat water?
Chlorine gas is harmful if breathed in
Liquid chlorine on eyes or skin causes severe chemical burns
Accidents involving chlorine could be really serious
Chlorine can react with organic compounds in water to form chlorinated hydrocarbons like chloromethane which are carcinogenic.
However this risk is small compared to risks of untreated water
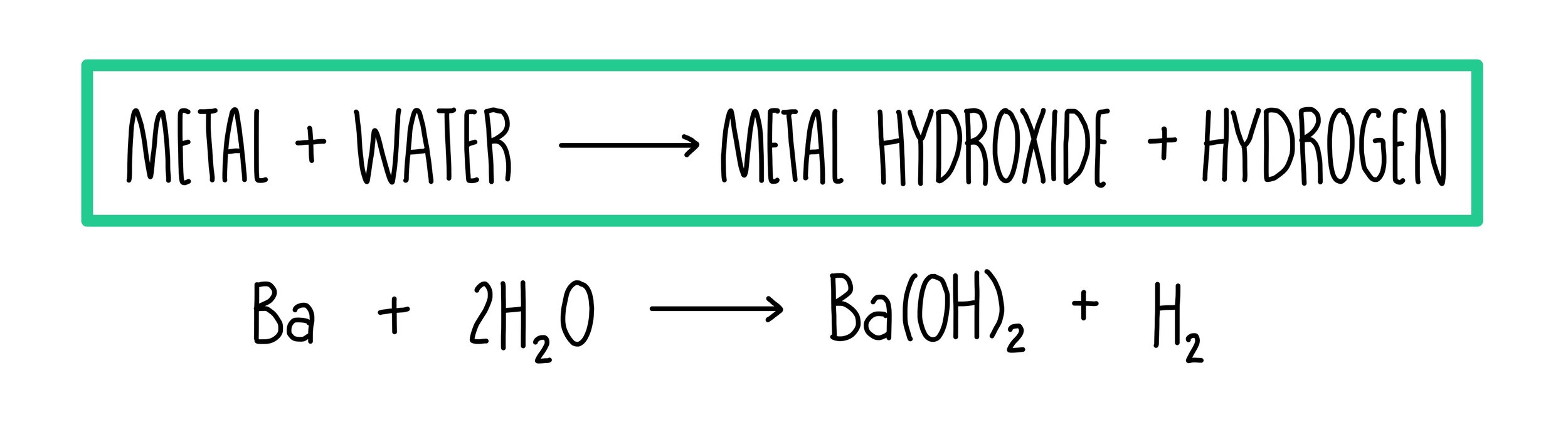
How do group 2 compounds react with water?
When group 2 elements react with water, they are oxidised from a state of 0 to +2, forming 2+ ions
Group 2 metals react with water to give a metal hydroxide and hydrogen
The elements react more readily down the group as ionisation energies decrease
What is the trend in solubility down the group?
It depends on the anion in the compound
Compounds in group 2 that contain singly charged negative ions increase in solubility down the group
Compounds that contain doubly charged negative ions decrease in solubility down the group
What are barium meals?
Soft tissues don’t show up on X-rays. Barium sulfate is used in ‘barium meals’ to show the structure of organs in X-rays
The patient would swallow the barium meal, the barium sulfate coats the tissues
This helps diagnose problems with the oesophagus, stomach or intestines
What is a use of magnesium?
Mg is used as part of extracting titanium from its ore.
Titanium oxide is first concerted to titanium chloride by heating it with carbon in a stream of chlorine gas
The titanium chloride is then purifies by fractional distillation before being reduced by magnesium in a furnace
How is sulfur dioxide removed from flue gas?
Calcium oxide and calcium carbonate can both be used
A slurry is made by mixing the calcium oxide or calcium carbonate with water.
It is then sprayed onto the flue gases
The sulfur dioxide reacted with the alkaline slurry and produces a solid waste product, calcium sulfite
What are other uses of group 2 compounds?
Many of their common compounds are used for neutralising acids
Calcium hydroxide is used in agriculture to neutralise acidic soils
Magnesium hydroxide is used in some indigestion tablets as an antacid (a substance that neutralises excess stomach acid)