L.9 Nuclear Structure
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Name 8 structures of the nucleus
Nucleolus
Nuclear pores
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear laminal matrix
Chromatin diffuse
Chromatin condensed
Nuclear bodies
Kargo/nucleo-plasm
Nucleus bonded by?
Membrane complex (nuclear envelope)
Components of nuclear envelope
Inner and outer membranes
Perinuclear space (between)
Outer membrane shares a common boarder with ?
ER (associated ribosomes)
Perinuclear space
Inner membrane integrated with
Nuclear lamina and matrix
What is the nuclear lamina/matrix
Coats inside, adds structural integrity
Nucleolus function (secondary)
houses 46 chromosomes
How many Gb of info in nucleolus? Gigacodons?
33 Gb
10 gigacodons
Describe interphase nucleus
Highly condensed heterchromatin connected with Amina and inner membrane
non-coding/normal state
What is heterochormatin
Very dense DNA
What is non-condensed DNA-protein complex called
Euchromatin
Describe euchromatin
non-condensed protein-DNA
Fills most of nucleus
Contain actively transcribed DNA
Cell type specific
Individual chromosomes form ____, which can be seen by ____.
chromosomal territories
FISH (fluorescence)
Structure of nucleolus
largest structure in nucleus
1-6/cell
Granular component, fibrilar centre, dense fibrilar component
Functions of parts of nucleolus
granular component →rRNA transcription
Dense fibrillar component → rRNA processing (create RNA)
Major function of nucleolus
rRNA transcription and pre-ribosome processing and assembly
Structure of nucleus determined by
Proteins of nuclear lamina and nuclear matrix
Describe nuclear lamina and matrix
Intra-nuclear cytoskeleton structure network
What does the nuclear lamina/matrix enable?
Chromosome territories
What are nuclear bodies? What do they do?
memernbaens structres in nuclei of eukaryotes
Dynamic structures that grow/shrink in response to metabolic needs
4 types of nuclear bodies
Cajal bodies
Nuclear speckles
Paraspeckles
PML bodies
Describe cajal bodies
1-10/ nucleus
Manufacture some specialized RNA molecules
Describe nuclear speckles
Enriched in pre- mRNA splicing factors
Describe paraspeckels
Alter in response To changes in cellular metabolic activity and stress
Rapid response
10-30/muscle
Describe PML bodies
unknown function
Composition varies
Implanted in cell processes (telomere lengthening/ DNA damage response)
When do you see more PML bodies
Cancer
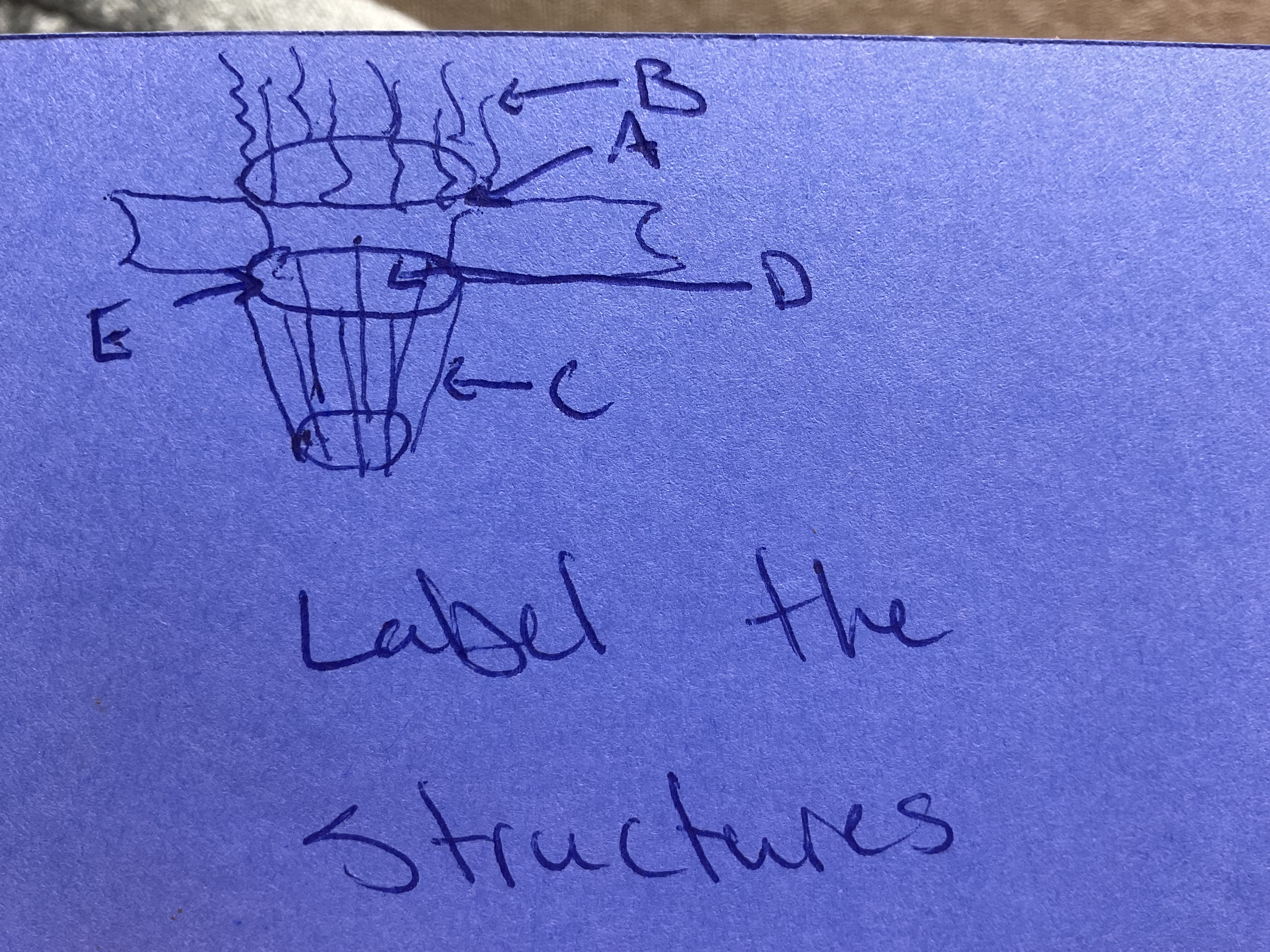
Label the structures
A- cytoplasmic ring
B- cytoplasmic filaments
C- nuclear basket
D- nuclear pore
E- nuclear ring
Type of symmetry of nuclear pores
Eightfold rotational
What is the nuclear pore complex
npc is largest protein complex in cell
Easily recognized by 2M*
Entry/exit of nucleus
Average of ____ NPC in envelope
2000
What is classical nuclear import/export
Through NPC, cargo with classical NLS/NES drives active transport
Importing cargo through NPC requires ____ which occurs via ____. Export requires ___, via _____
classical NLS
Importing-proportional*/importin B heterodomer
NES
Exporting
Active transport through NPC driven by ____
Gradient of RanGTP and RanGDP (across nucleus)
Classic NLS is ___
Stretch of basic residues
What can pass freely through NPC/across envelope?
metabolites
Small ions/molecules
What requires active transport through NPC?
large macromolecules
Protein
M/tRNA
Ribosomes subunits
Viruses
What is an NLS
Nuclear localization sequences
Nuclear pore import step 1
Proteins show NLS and recognized by cytoplasmic receptor molecule (importin), forms complex
Step 2 nuclear pore import
Binding/ regcognition → docking with fibres (form cytoplasmic ring)
Step 3 nuclear nuclear pore import
Docking recruits accessory proteins (GTPases and NTF2) to promote interaction, hydrolyze
Step 4 nuclear pore import
hydrolysis of RanGTP → RanGDP
Allow for movement through pore
Release cargo
Steps of nuclear pore export
Cargo has nuclear export signal (NES) recognized by exportin
Complex associates with basket
Docking recruits energy creating Ran-GTPase (hydrolysis) for energy
Export into cytoplasm form RanGTP/RanGTP energy
Roughly how many proteins in NPC
~30
Pro and con of NPC complexity
higher specificity
Higher chance of error
Dysfunction if NPC associated with ____. Examples
many diseases
ALS, FTD, Alzheimer’s triple A syndrome, many cancers
Which nuclear structres play roles in breakdown/reassembly in mitosis?
Envelope and lamina
What triggers prophase?
End of GZ*, activate cyclin-dependant kinases
Example of cyclin-dependant kinases
CDK1
What promotes lamina tearing/NE fragmentation
Microtubule stretching
What happens what nuclear membrane breaks down
NE- associate proteins translocation to kinetic horse, distribute with ER fragments, dissolve in cytoplasm
NE reassembly When/how
anaphase
SUN 1, LAP 2 around condensed chromatin
Nuclear laminsjoin at periphery in telophase
NE breakdown because of ___, what has what function?
lamin kinase
Phospholylates lamin A,B and C →depolymerization lamin matrix
What happens to lamin A, B, and C after phosphorylation
B- associate with membrane vesicles
A,C- dispersed
When decomdonsation of chromosomes in daughter cells being (telophase) what occurs coincidentally
phosphates removed from laminate protein by activated lamin phosphatase
polymerization of lamina
Membrane bound lamin B= nuclatiensile
What is nucleation site? Why?
membrane bound lamin B
Already there, didn’t disappear
Alternative route out of nucleus
Via ER