Cells
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are the 3 main steps of cellular respiration and their locations
Glycolysis - cytoplasm
Krebs cycle - mitochondrial matrix
Oxidative phosphorylation - inner mitochondiral membrane
What are the main inputs and outputs of glycolysis
Glucose is broken down to 2x pyruvate molecules, and also produces 2 net ATP molecules, also an NADH+ is deprotonated to NAD
What are the main steps, inputs and outputs of the Krebs cycle
Starts with Acetyl-CoA adding its two carbons to oxaloacetate to form a 6C molecule
6C molecules gets oxidised to reduce 2x NAD+ molecules to 2x NADH and 2x CO2 to turn it into a 4C
4C phosphorylates ADP to ATP
4C gets oxidised to reduce an FAD and an NAD+ molecule to FADH2 and NADH, forming oxaloacetate
IN: Acteyl CoA, oxaloacetate, 3x NAD+, FAD, ADP
OUT: Oxaloacetate, 3x NADH, FADH2, 2x CO2, ATP
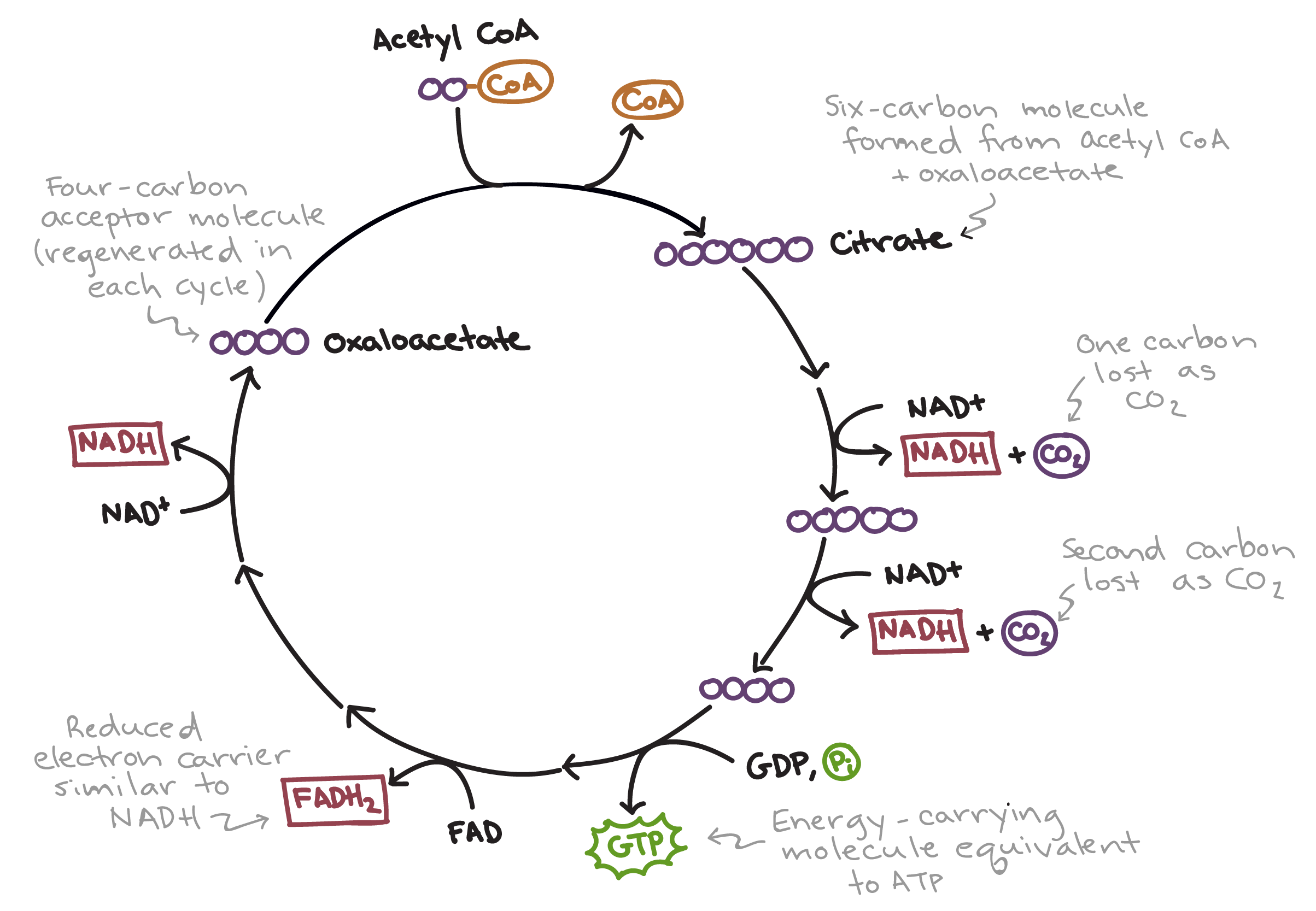
What is the main reacting group of acetyl-CoA
Reactive thiol groupKet
Key stages in stem cell → specialised cell cycle
Maintenance
Self renewal
Commitment
Expansion
Cell division + differentiation
Specialisation
Further cell division + differentiation
3 main morphological characteristics to consider when classifying epithelia
Number of cell layers - Simple/stratified/pseudostratified (looks like stratified, but is actually only one cell thick)
Shape of cells - Squamous/cuboidal/columnar (in stratified, shape is based on topmost layer)
Special features - Cilia, keratin, microvilli, etc.
Major functions of epithelia tissue
Absorption
Secretion
Protection
Sensory perception
What is laminin
A molecule containing a cell binding and collagen binding region. Helps epithelial cells stick to collagen in basement membrane
What is the extra cellular matrix?
A mandatory part of any multicellular organism, keep cells together as well as many other functions.
the interstitial matrix between basement membrane and other cells is filled with fibrous protein (e.g. collaged) and polysaccharide gels
What holds the basal layer of the epidermis in place
Basal lamina (basement membrane)
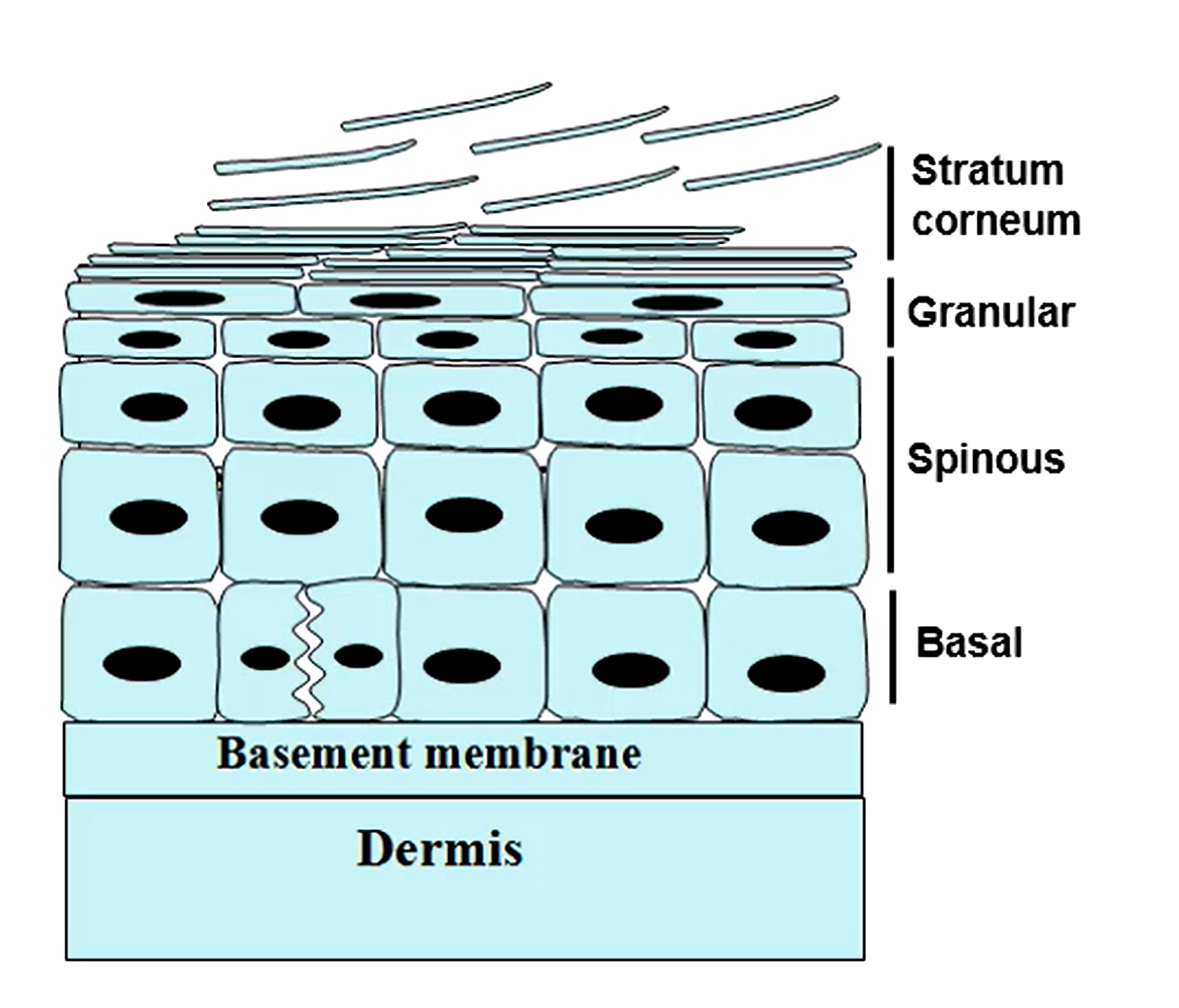
What part of the epidermis regularly sheds
Stratum corneum

What part of the epidermis prevents water loss, and microbial invasion, and how
Stratum corneum are flat, anucelar keratinocytes embedded in a lipid matrix. These cells help prevent permeability of the skin
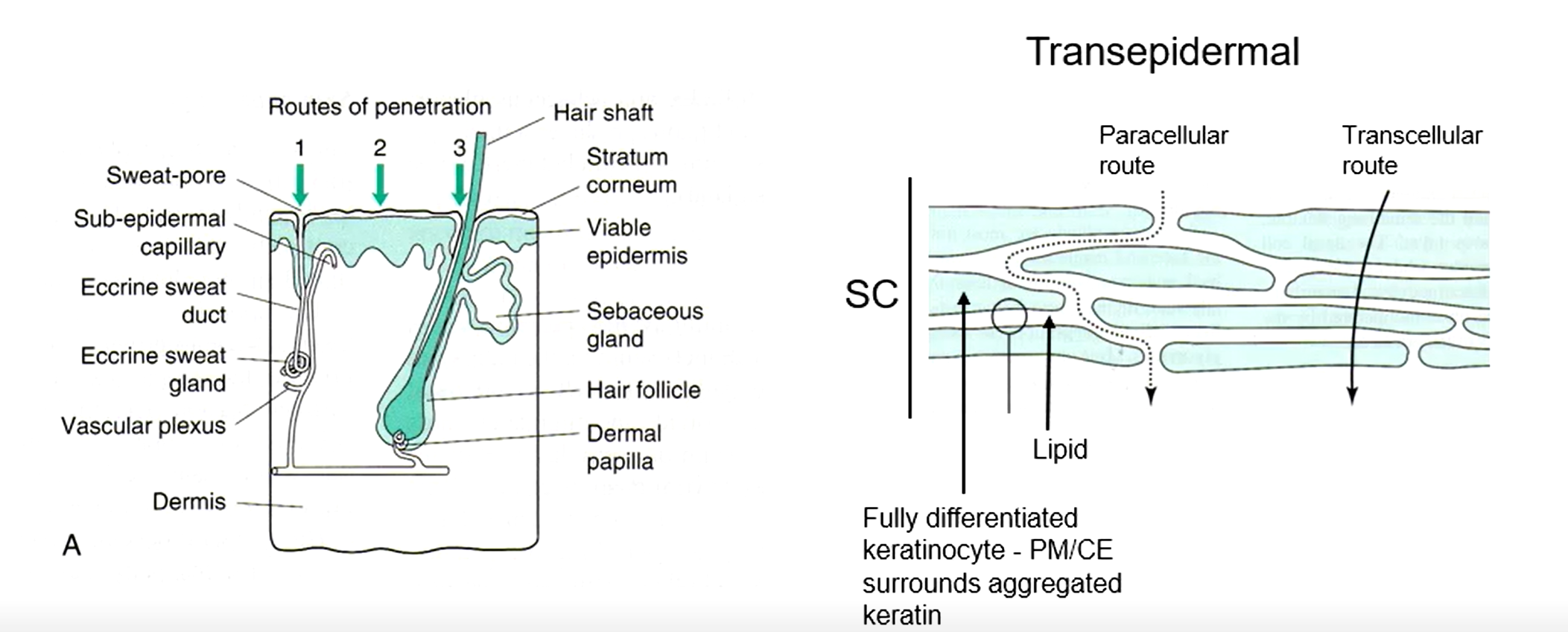
What are the 3 ways drugs can pass through the stratum corneum
Via sweat pores
Directly through the cells
Via hair follicles
3 components of cytoskeleton
Intermediate filaments
Microfilaments
Microtubules
3 functions of cytoskeleton
Maintaining tissue integrity (i.e. resisting stresses)
Cell migration (microfilaments)
Cell division (microtubules)
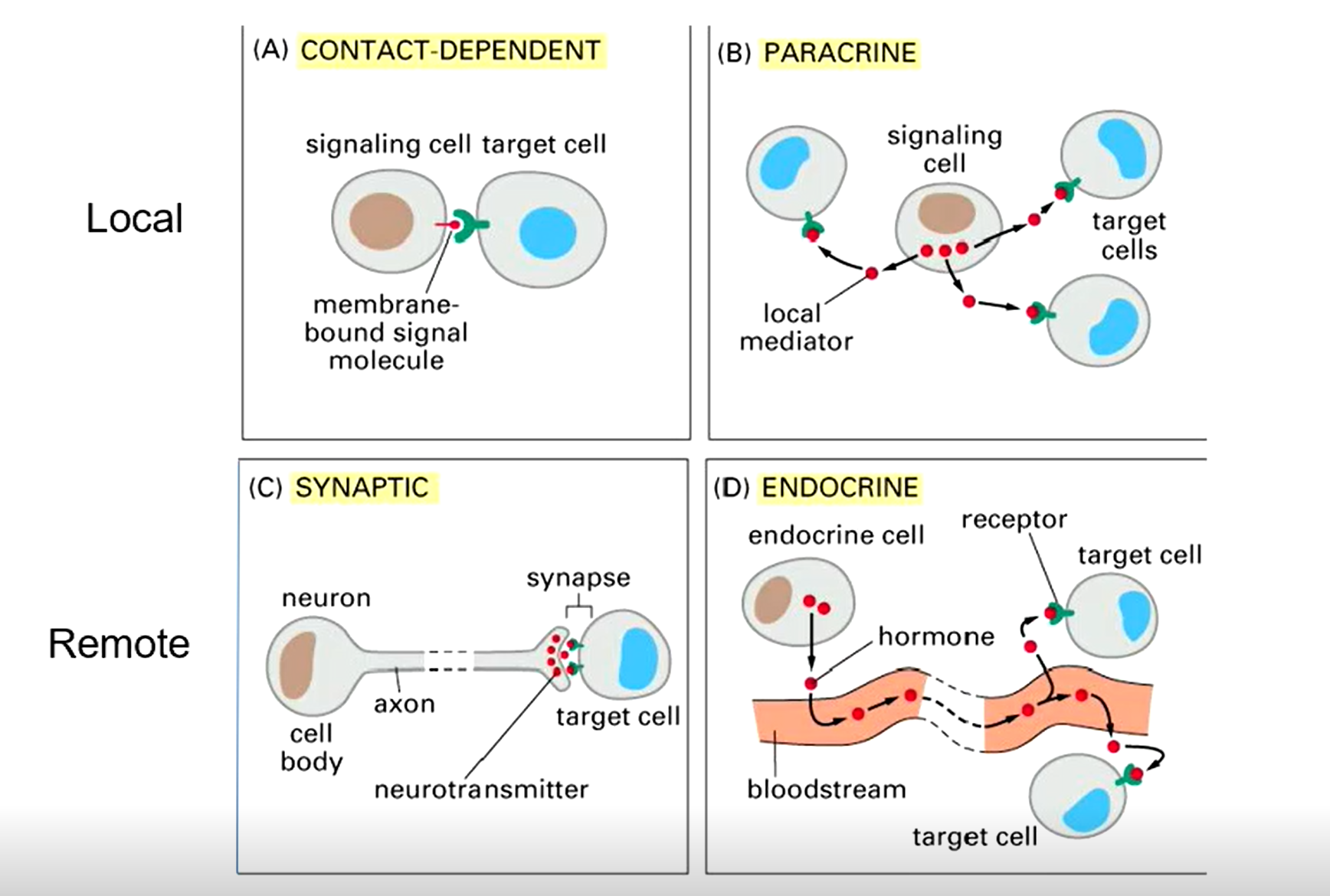
4 types of cell signalling
Local
Contact-dependent signalling
Paracrine signalling
a signalling cell sends out signalling molecules to local nearby cells usually in the same tissue (basically close-range hormones)
Remote
Endocrine signalling
Synaptic signalling
4 Steps of cAMP/PKA cell signalling pathway
Signalling molecule (e.g. adrenaline) binds to G-protein-coupled receptor
α subunit of G-protein detaches, and attaches to Adenylyl cyclase enzyme, activating it
Activated adenylyl cyclase catalyses conversion of ATP to cAMP
cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which goes off and phosphorylates other proteins
What is the function of a CREB protein?
CREB proteins (CRE-Binding protein) binds to CRE, which causes regulation of gene expression