(2.1) morphology
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 2 - Bacteria
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what are the misconceptions of bacteria?
bacteria were only found on or in things that had gotten contaminated somehow
TRUTH- bacteria is everywhere, even in clean houses and outside, found on skin and digestive system
bacteria are always bad
TRUTH- bacteria on skin, digestive system, foods, nitrogen cycle and ecosystems are good
HOWEVER bacteria can still be pathogens
antibiotics
important for destroying bacterial infections but some broad spectrum antibiotics can harm some of the “good” bacteria as well
do antibiotics work for viruses?
no bcz viruses are pathogens that are not made of cells at all
but there are vaccines which can prevent many types of both bacterial and viral infections
shapes of bacteria
coccus (cocci)= sphere-shaped
bacillus (bacilli)= rod-shaped
spirillum (spirilla)= spiral shaped
autotroph vs heterooph in bacteria
heterotroph= consume or feed on some organic matter
autotroph= they can make their own food (plants aren’t the only autotrophs)
bacterium
prokaryotic cell which are generally much smaller than eukaryotic cells
no nucleus
no membrane-bound organelles
DO have ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall
DO have bacterial DNA
can also have flagellum to help with movement
can have capsule→ gives them extra protection or attachment abilities
can have pilli→ help w/ attaching to surfaces, including each other
bacterial DNA
double stranded
arranged in a circular shape
some bacteria have plasmids (it’s like extra DNA)
what are abilities that bacteria have that are diff from human body cells?
bacteria undergo binary fission (not mitosis, cytokinesis)
binary fission
type of fast asexual reproduction when the bacteria can easily divide to make a copy of themselves
are daughter cells identical to parent cells in binary fission?
yes! unless there is a mutation
conjugation
process where bacteria can share plasmids with each other
the pili can be used to share this genetic information with each other
bacterial transformation
process where bacteria take in DNA from their environment
bacterial transformation in a lab
scientists use stimuli like heat shock to induce bacteria in a lab setting to pick up genetic material
endospore
produced by bacteria, allow bacteria to be survivors in all kinds of hostile environments (lack of nutrients, freezing temp, dorught)
extremophiles
some archaea and bacteria can be extremophiles, can live in extreme environments where there may be excessive heat, chemicals that our cells would find toxic, or radiation
magnetotactic bacteria
they tracj the earth’s magnetic field to find the perfect spot in their watery homes
how do magnetotactic bacteria build their mini-compasses?
the bacteria take in iron from their surroundings and transport it to special compartments called magnetosomes
inside each compartment grows a small, near-perfect crystal of magnetite (type of iron oxide)
microbes chain up the crystals, combining them into one long, strong magnet and that’s what acts as a compass needle, detecting the earth’s field and rotating accordingly
magnetite
has north and south poles and is the most strongly magnetic natural mineral we know of
why do bacteria use magnetism?
use it to stay in their comfort zone
if there isn’t enough oxygen at the bottom of the ocean, they follow the magnetic field towards the surface where is more and if there’s too much oxygen then they just move in opposite direction
nanomagnets from bacteria
they are small and bind readily to other substances and can be easily retrieved from a mix of other particles
this can make them useful for medical technology (might show up in our pills one day)
might treat infected blood by delovering drugs to targeted parts of the body, speeding up treatment and reducing side-effects
making nanomagnets in the lab results in many shapes and sizes but magnetotactic bacteria craft their nanomagnets to precisely the same specs, every time
if u know which bacteria can make which shape of crystals then that can help you make nanomagnets in whatever shape you want
morphology of bacterial cells
bacteria can take many different shapes (or morphologies)
bacteria can also assume multicellular organizations
size of bacteria can vary greatly
there are exceptions to the general size of bacterial cells
what do bacteria look like?
spherical (singlular→ coccus, plural→ cocci)
rod-shaped (s. bacillus, pl. bacilli)
comma-shaped (s. vibrio, pl. vibrios)
spiral-shaped (s.spirillum, pl. spirilla)
pleiomorphic (varied shapes)
example of spherical shaped bacteria
staphylococcus aureus
streptococcus pyogenes
example of rod shaped bacteria
escherichia coli
bacillus anthracis
example of comma shaped bacteria
vibrio cholerae
example of spiral shaped bacteria
treponema pallidum
example of various shaped bacteria
pleiomorphic
what type of structures or “multicellular organizations” can bacteria form?
hyphae (branchinf filaments of cells)
mycelia (tufts of hyphae)
trichomes (smooth, unbranched chains of cells)
size of bacteria
usually smaller than eukaryal cells (bacteria are often 0.5- 5 µm in length)
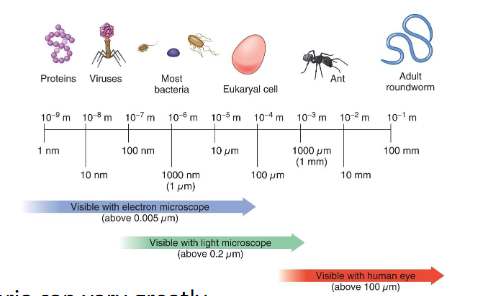
size of small eukaryal cells
usually > 5 µm in diameter
exceptions to the general size of bacterial cells
thiomargarita namibiensis: up to 700 µm in diameter
epulopiscium fishelsoni: 200 to 700 µm x 80 µm!
some mycoplasma cells are only 0.2 µm in diameter
what happens when u go from smallest end of scale to largest for bacteria size?
smallest is 0.2 to largest 750 µm
that’s a 3,750-fold difference
comparing average length of baby equivalent to 3.4 CN towers
this is the variation when it comes to bacteria in terms of cell size

2.1 checkpoint
