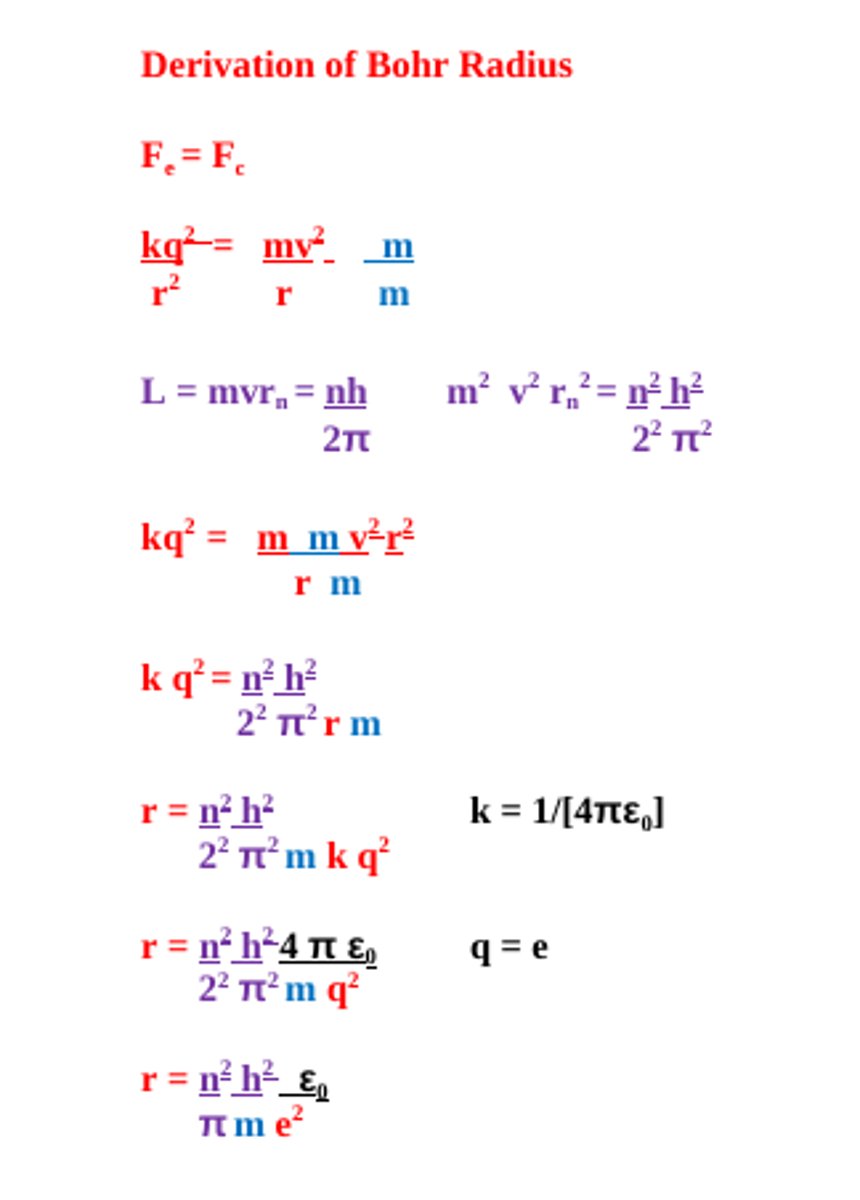Quantum and Atoms Study Guide
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Aristotle
Force is required to keep an object moving. Matter is continuous and infinitely divisible
Fire/Wind/Water/Earth/Aether(made by the gods).
Newton
Challenged Aristotle's views. 1st law if in motion will stay in motion if no retarding force and an object at rest wants to stay
at rest if the forces are balanced. 2nd law F=ma (unbalanced forces a is inversely proportional to m and directly proportional to F). 3rd law action-reaction involves two objects interacting with each other.
Galileo
Challenged philosophical views and showed all objects fall at the same rate (neglecting friction).
Leucippus
Small indivisible elements not infinitely divisible. He claimed to be the first to pronounce this theory.
Democritus
Named atoms, "atomos" greek meaning indivisible.
Huygens
light consist of waves, small wavelets produce new wave-fronts
Hauy
1st Crystallographer - cleaved calcite and saw it cleaved in a regular geometric pattern along the atoms plane.
Bragg-Bragg
Studied x-ray diffraction and developed a formula for determining wavelengths of diffraction.
Mendeleev
Developed the first periodic table organized in columns and rows by properties, in order by atomic mass.
Moseley
Developed the modern periodic table organized in columns and rows by properties, in order by atomic number.
Proust
Law of definite proportions (compound elements are in the same proportions by mass).
Gay-Lussac
Law of gas volumes based on his formula PV =nRT is P1T1 =P2T2
Roentegen
Accidentally discovered x-Rays.
Geiger
Geiger-Marsden experiment, which proved the existence of the atomic nucleus. Geiger-Nuttal Law, which deals with radioactive decay. Geiger co-invented a measurement device for radioactivity - the Geiger counter.
Muller
Co-inventor of the Geiger-Muller tube or Geiger counter.
Curie-Curie
Discovered polonium, radium, and radiation. Found that radiation came from the decay of the nucleus of the element.
Compoton effect
Light scatters when it encounters matter and wavelength and frequency changes. Compton effect - helps demonstrate the particle concept of electromagnetic radiation.
JJ Thomson
Used cathode ray tube to obtain the charge to mass ratio of the "corpuscle"
Perrin
Showed that Cathode rays were made of corpuscles with negative electric charge. Determine Avogadro's number using Brownian motion which was later verified using other ways.
Stoney
Coined the word electron to replace "corpuscle"
Becquerel
The SI unit for radiation is the Becquerel. He discovered natural radioactivity (X-rays).
Hertz
SI unit of frequency is the Hz, He helped establish the photovoltaic effect when he noticed that a charged object loses its charge when illuminated by ultraviolet light. He studied numerous electromagnetic waves. He measured that radio waves traveled at the speed of light.
Fraunhofer
Studied absorption spectra with spectroscopes. Fraunhaufer lines are the absorption lines of the sun proving
Balmer
Formula for calculation of the wavelengths of light for the visible H spectrum.
Paschen
Formula for calculation of the wavelengths of light for the infrared H spectrum.
Lyman
Formula for calculation of the wavelengths of light for the ultraviolet H spectrum.
Rydberg
Formula for calculation of the wavelengths of light for Hydrogen's entire spectrum.
Win
There is an inverse relationship between wavelength of the peak of emission of a black body and temperature.
Planck
Energy of the atom is quantized. Planck's Postulate - E = nhv. He was the founder of quantum theory.
Einstein (photelectric)
Pioneered intelligent study of the Photoelectric Effect. Light is composed of photons. Electrons emitted from objects after absorbing light aren't constant, because light doesn't come out at a constant rate Metals when subjected to electromagnetic waves with enough threshold frequency release electrons.
Who named the following?
a) Atomos -
b) Corpuscles -
c) Electrons -
Democritus
J.J. Thompson
G.J. Stoney
What are these constants •
a) Avogadro's number -
b) Faraday's constant -
6.02 X 10^33 molecules / mol
96485 C / mol
Absorption pectra
When the atom absorbs energy and the electron transitions to a higher energy or quantum state in the atom
Emissions spectra
When the electron transitions down to a lower energy level or the ground state and releases energy, if in the visible spectrum, a photon of light is emitted.
Define the following:
a) α - Alpha particle
b) β - Beta particle
c) γ - Gamma particle
a) ( Ealpha < Ebeta < Egamma ) He - 4 with no electrons
b) High energy electron, Negative charge, negligible mass relative to atomic mass units
c) High energy particle with no charge and no mass released usually during an annihilation
Half-life
Time it takes a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half their original numbers. Unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay.
Dalton's Theory
Compounds react to form new compounds in whole number ratios - Law of definite combinations.
De Broglie hypothesis
Any moving particle or object had an associated wave, created wave mechanics, and united the physics of light and matter. λ = h/p
Heisenberg
When there are 2 variables in a quantum equation, they both cannot exist with arbitrary precision.
Schrodinger
Mathematically showed how electrons behave as a wave.
Pauli
No two electrons can occupy the same quantum state in an orbital. One must have a clockwise and counterclockwise spin at the same time.
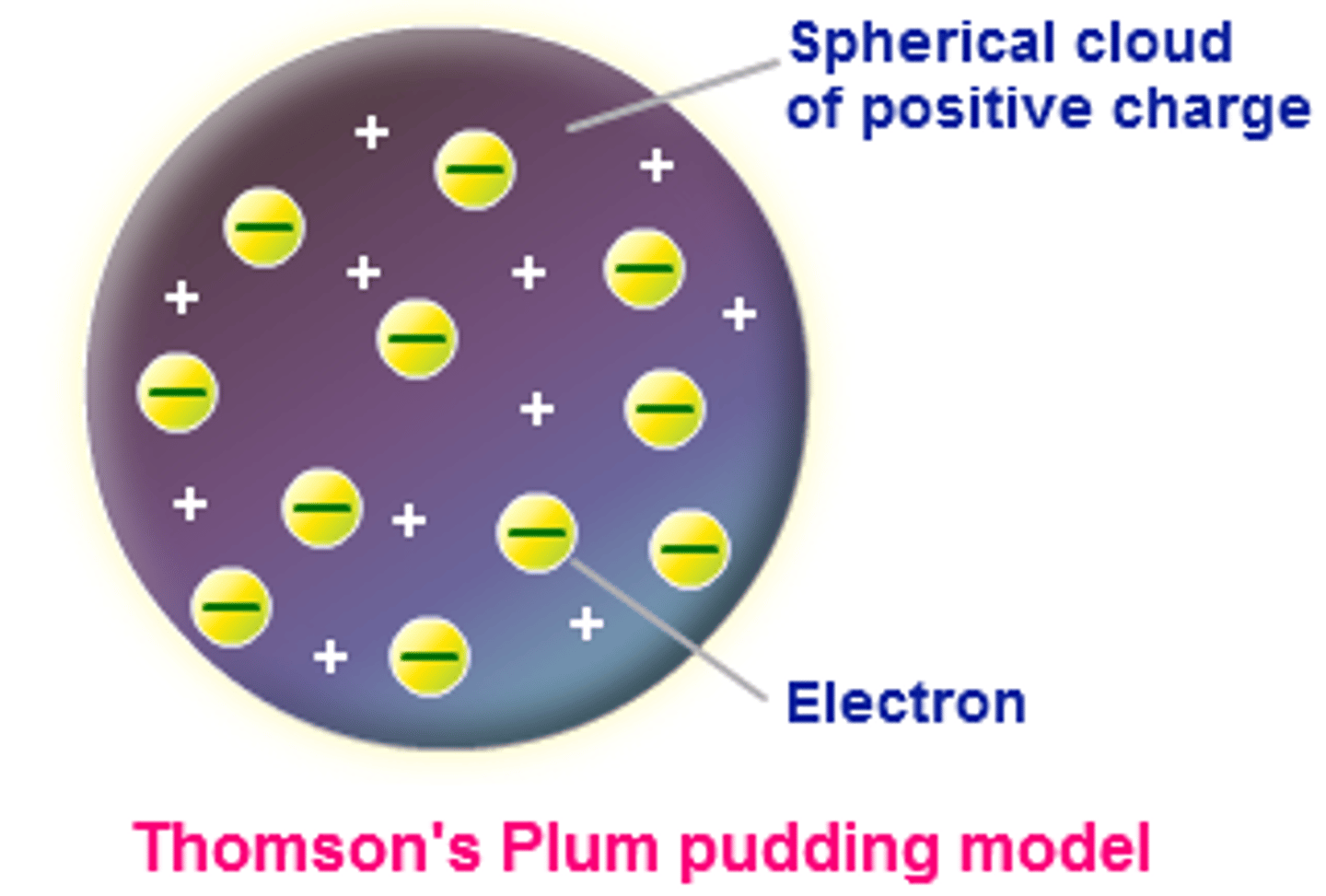
Thompson model of the atom
electrons scattered throughout the atom
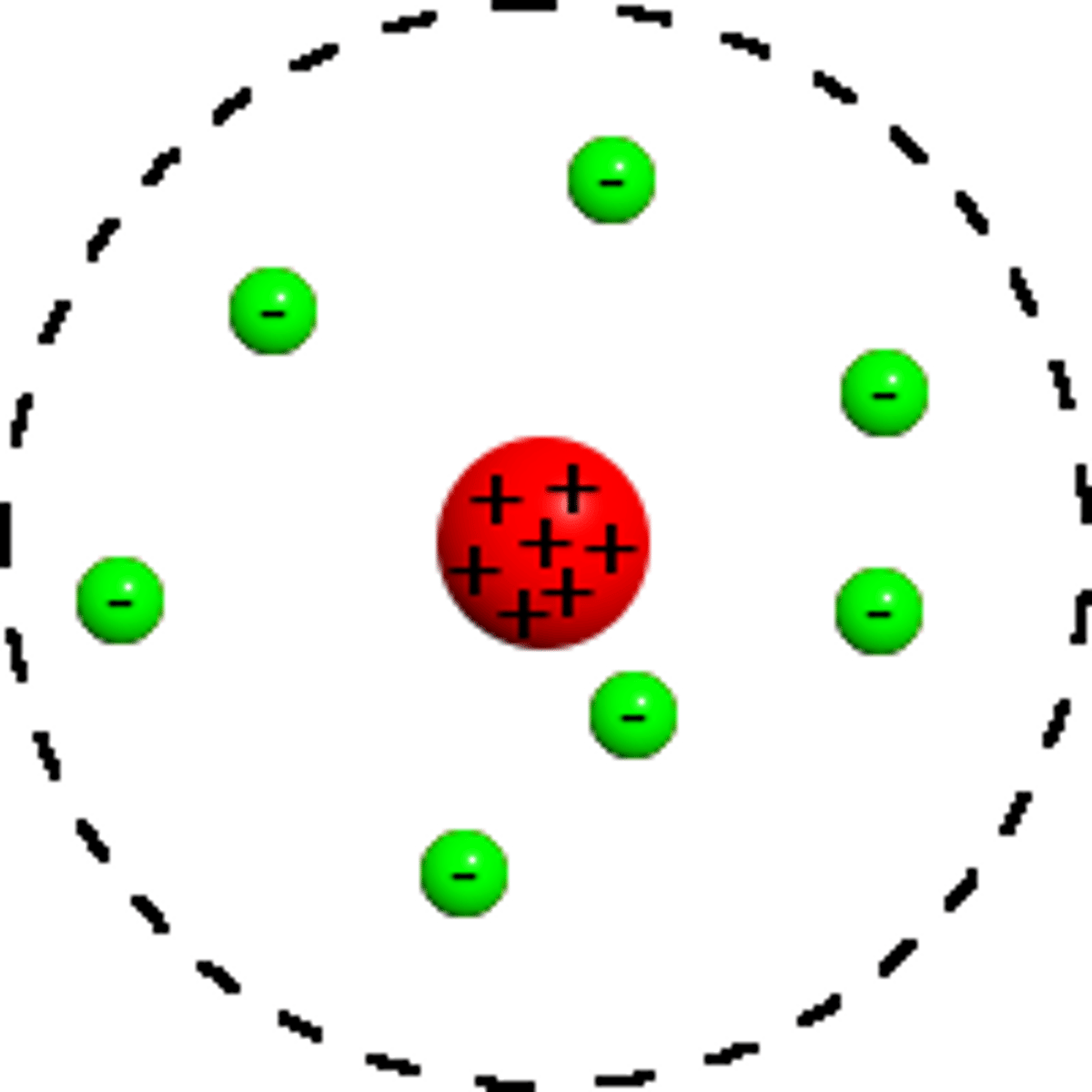
Rutherford model of the atom
Electrons in orbit around a nucleus - planetary model.
Bohr model of the atom
Electrons are at specific quantifiable energy levels in orbit around the nucleus. The Bohr model is difficult to model in three dimensions. Usually looks like a target with rings where electrons can be placed based on the energy sublevel.
Quantum Model of the Atom
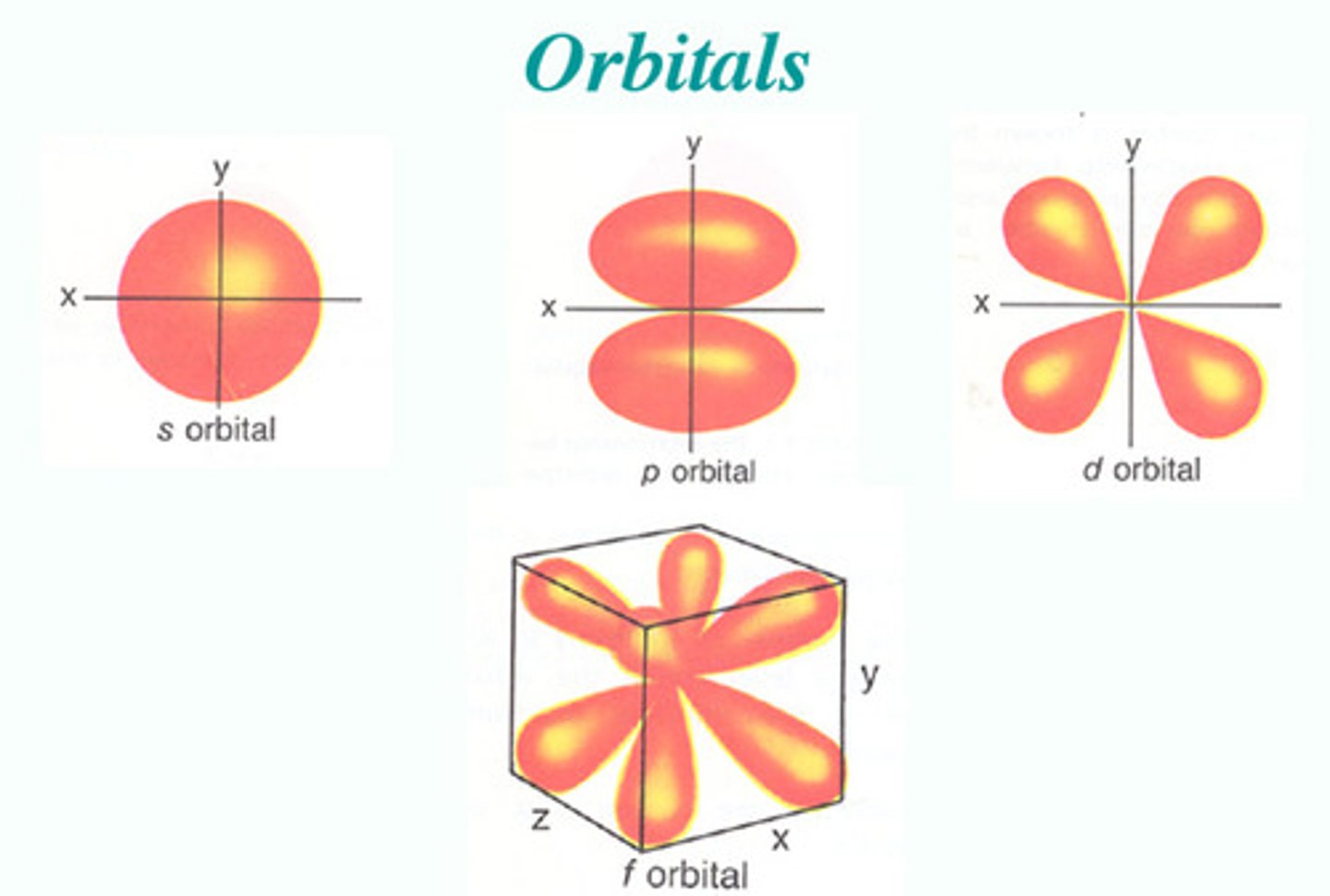
Electrons are at a specific quantifiable energy level but exist as wave functions. Electrons position can be calculated in a specific orbital area within a 95% probability, s orbitals are spherical, p orbitals are dumbbell shaped, d and f orbitals are much more complex.
Rydberg Equation
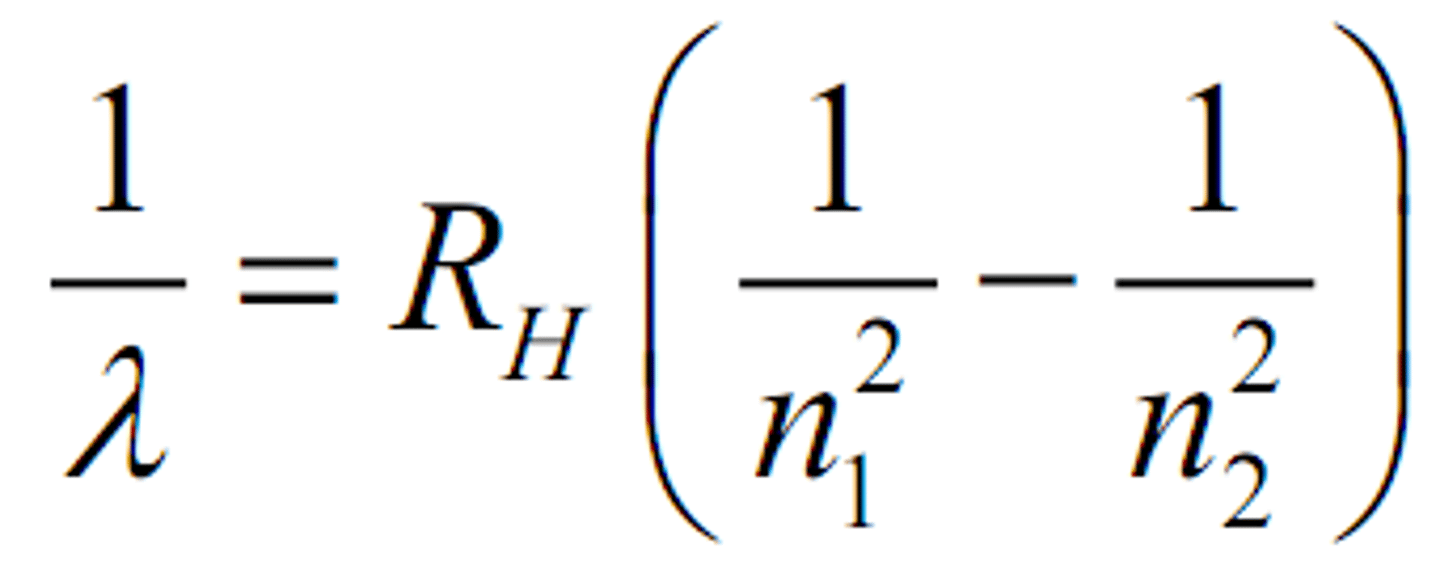
Moseley Equation and Law
f = 3/4 c R∞ ( Z - 1 )^2 Moseley's Law - conveyed relationship between frequency and x-rays of atoms
Einstein photoelectric equation
KE= hf-φ
Planck equation
E=hf
Balmer equation
λ = [ 364.5 nm ] [ n2 / (n2 - 2^2) ]
Bohr equation
hf or hΔf = E1 - E2
Wien's Displacement Equation
λ T = 2.9 X 10-3 m K
Derivation of Bohr Radius