Sympathetic transmission and Adrenergic Receptor (Drugs)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Beleh Slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe the Adrenergic System
Neurotransmitter
Difference in chemical structure
Receptor Subtypes
Termination
Metabolism
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine from adrenaline medulla
CH3 in Epi and H in NE
Alpha receptor: alpha 1 and 2 ; Beta receptor: beta 1,2,3
Reuptake back into the nerve terminal —> different from ACh
Metabolism by Monoamine oxidase (MAO) and cathechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
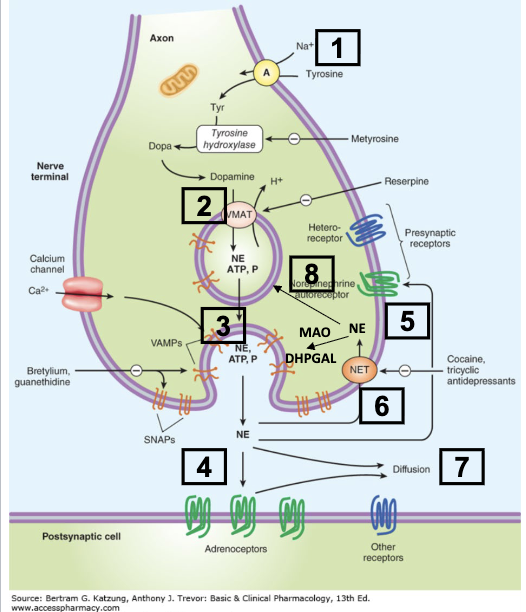
Describe the steps of adrenergic transmission:
uptake of tyrosine—> precursor for catecholamines in nerve terminals
biosynthesis of NE:
L-Tyrosine—(tyrosine hydroxylase)—> DOPA ——(DOPA carboxylase)→ Dopamine—(Dopamine B-hydroxylase)—> NE
Dopamine to NE happens within the storage vesicle
Release of NE from vesicles via exocytosis, which is caused by Ca2+ influx after depolarization of neuron
NE action at post synaptic adrenergic receptors or at presynaptic adrenergic autoreceptors (alpha 2)
Internal: NE reuptake into presynaptic neuron via Norepinephrine Transporter —> metabolized via mitochondrial MAO
External: NE diffuse out to general circulation and metabolized by COMT
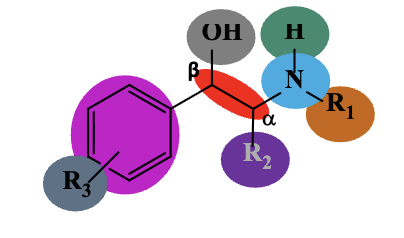
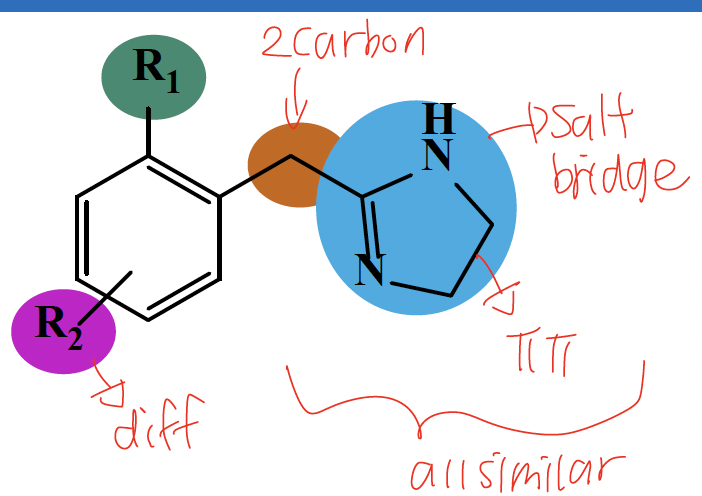
SAR for adrenergic agent (NE, E, Dopamine)
Basic Amine required for binding
R1 on nitrogen: larger alkyl group increase specificity to beta receptor and smaller groups increase specificity for alpha receptor
Bulky: iPr>Me>H
Small: H>Me>iPr
H: must be a hydrogen; tertirary amine shows decreased activity due to steric hinderance.
R2 on alpha carbon: small (H or Me) is required. A methyl substitution—> slow down MAO metabolism
beta carbon: hydroxyl is required for maximal binding: R>S
R3 on Benzene: 3,4 di-OH> 3-OH> 4-OH
a benzene right shows best activity
A two-atom side chain is required between the terminal amine and the aromatic ring
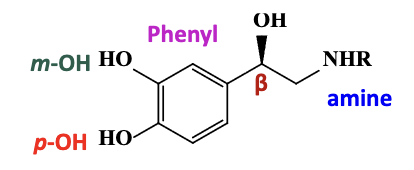
NE binding interactions with a1 adrenergic receptor
the basic amine or positively charged amine (NHR) forms a salt bridge
the phenyl ring forms pi-pi interactions
the para-catechol forms a hydrogen bond
the meta-catechol does not participate
the beta hydroxyl forms a hydrogen bond
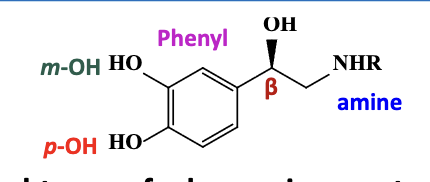
NE binding interactions with alpha 2 & beta adrenergic receptor : different from a1
the basic amine or positively charged amine (NHR) forms a salt bridge
the phenyl ring forms pi-pi interactions
the meta & para-catechol forms a hydrogen bond
the beta hydroxyl forms a hydrogen bond
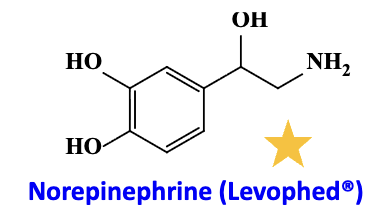
Norepinephrine
agonist (admin route)
agonist: alpha 1 receptor (vasoconstriction), beta 1 receptor (positive inotropic effect)
admin route: IV infusion to counteract acute hypotensive state: make low BP to high BP after heart transplant, shock or cardiac arrest
Short acting but can terminate effect quickly.
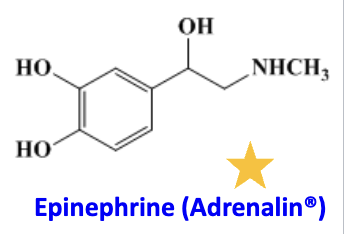
Epinephrine
agoinst
admin
agoinst: alpha 1 receptor, beta 1 receptor (positive inotropic effect), beta 2 receptor (bronchodilation)
anaphylaxis (epipen and nasal spray), temporary relief in asthma (inhaler), and as adjunct with local anesthetic (injection)—> how vasoconstriction makes it local
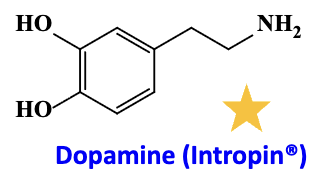
Dopamine
its selectivity on receptor is
Low
Intermediate
High
usage:
Suprising fact:
Dose dependent
Low dose: dopaminergic receptor (vasodilation)
Intermediate dose: elective at the B1 receptor (tachycardia)
High dose: activate alpha receptor (vasoconstriction)
Shock and to increase renal perfusion & Heart failure
in epithelial cells: Has specific actions in kidney at low doses: Vasodilatation; ↑ Glomerular filtration rate, ↑ Na excretion, ↑urine
What are the alpha 1 adrenergic agonist?
main action & usage
Phenylephrine and Midodrine (prodrug)
peripheral vasoconstriction
midorine —> orthostatic hypotension (BP downs on standing)
active drug after releasing the amine (H2N-C=O)
phenylephrine—> nasal decongestant but ineffective; Pupillary dilation and glaucoma
act similarly to NE and Epi

SAR of alpha 1 adrenergic agonist that is imidazolines
imidazoline in place of the basic amine
single carbon link between aromatic and imidazoline
Ortho substituent R1 must be lipophilic and an aromatic ring is required
Bulky lipophilic meta and/or para substituents (R2) improve alpha 1 selectivity and form hydrophobic interaction
What are alpha 1 adrenergic agonists that are imidazolines?
main action
peripheral vasoconstriction
Xylometazoline: nasal decongestants
Tetrahydrozoline: eye drops and nasal spray
SAR of alpha 2 adrenergic agonist imidazolines
imidazoline in place of the basic amine forms salt bridge
single carbon link between aromatic and imidazoline
Ortho substituent R1 must be lipophilic and an aromatic ring is required—> at least one or 2 ortho Cl, Br, or methyl group is essential to create a twist in the molecule then bind
the two rings forms pi-pi interaction
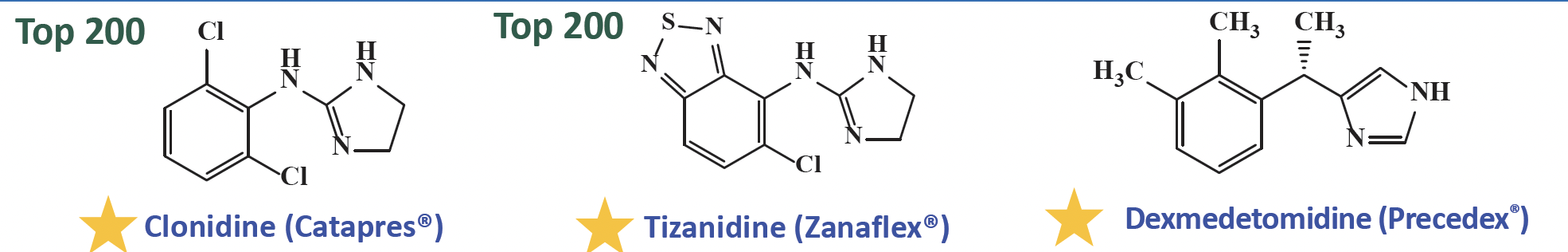
What is alpha 2 adrenergic agonists that are imidazoline
usage
adverse
Clonidine (Beer’s List)
treat hypertension
ER table—> ADHD
epidural solution—> post operative or cancer related pain = sedation effect
Tizanidine
muscle spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury
DDI: CYP 1A2 inhibitor
Dexmedetomidine
adjunct to general anesthesia and for sedation in intubated patients in ICU unites
reduce agitation in biplor disorder and schizophrenia
Adverse Effect
drowsiness, confusion, fatigue
do not use with other CNS depressants
avoid sudden withdrawal of these agenst due to the risk of developing CNS adverse effects plus a rapid rise in catocholamines levels and in blood pressure
What is alpha 2 adrenergic agonists that are phenylethanolamines
mechanism
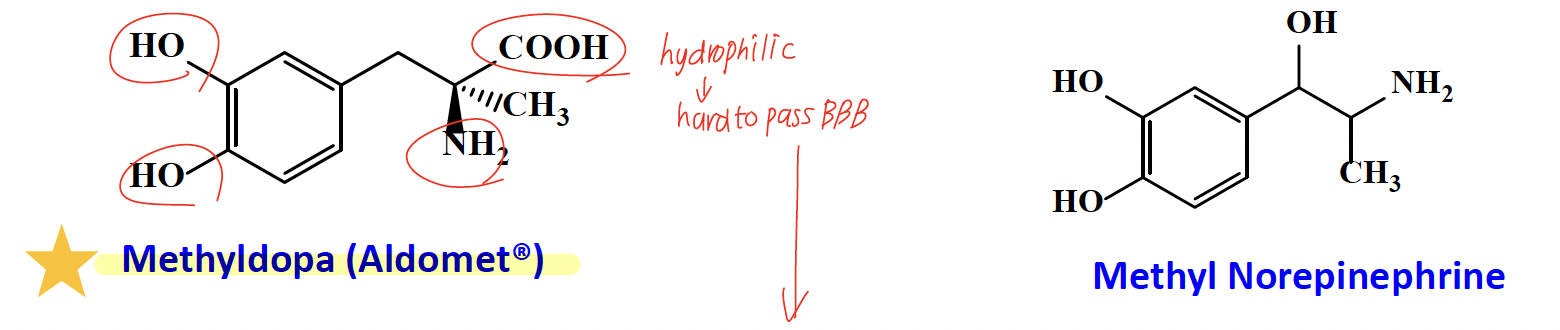
α-Methyldopa (binds similary to E, NE)
It is transported to the CNS via an aromatic amino acid transport system due to hydrophilic group (-COOH)
Methyldopa →decarboxylated and hydroxylated to alpha methyl NE= fake NE in the brain → turns down sympathetic tone → lowers BP (pregnancy-safe)
fake NE —> Metabolized mainly by COMT (minimal MAO metabolism).
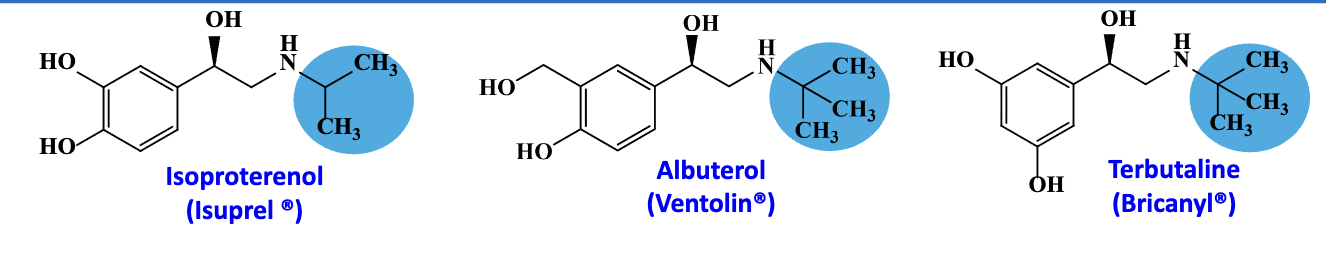
SAR of beta adrenergic agonist- phenylethanolamines
bulky groups (-CH3) on amine —> specific to beta receptors
higher branched & bulk —> better beta 2 specificity
Non-cathecol hydroxl group on the aromatic chain in albuterol and terbutaline improve beta 2 specificity
**specificity is relative term
what is beta 1 adrenergic agonist that is phenylethanolamine?
what is beta 2 adrenergic agonist that is phenylethanolamine?
what is beta nonselective adrenergic agonist that is phenylethanolamine?
dobutamine, albuterol, isoproterenol,
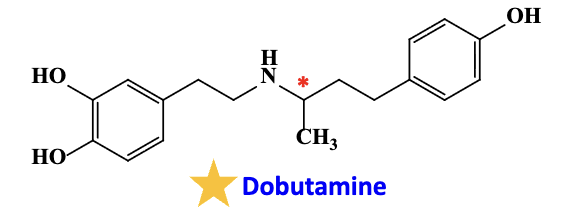
Dobutamine
acts on specifically to
used
specific to heart due to
beta 1 receptor
in critical care by IV infusion as it suffers from first pass effect due to the formation of the 3 methoxy metabolites via enzyme COMT
racemic mixture: the s isomer is beta 1 and alpha 1 agonist, while the r isomer is alpha 1 antagonist and beta 1 agonist —> net: beta 1 agoinst
Isoproterenol
Receptor
Used for
nonselective beta agonist
bronchospasm during anesthesia, as adjucnct therapy in cardiac arrest, heart block, and hypotension due to shock.
Albuterol
receptor
used for
administration route
short acting beta 2 adrenergic agonist
used in acute treatment in asthma, prophylaxis, especially induced asthma
used orally, via inhaler or nebulizer
inhaler fast onset but better specificity to bronchi but relative short duration of action
what is long acting beta 2 adrenergic agonist?
used for
What is its nature?
How?
BBW
salmeterol
used in combination with inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) in asthma and COPD
lipophilic nature
when the receptor is activated by albuterol at first, its long chain anchors onto another pocket within the receptor via a hydrogen bond, pi-pi, hydrophobic bond.
use of this without concomitant use of ICS increase the risk of asthma-related death

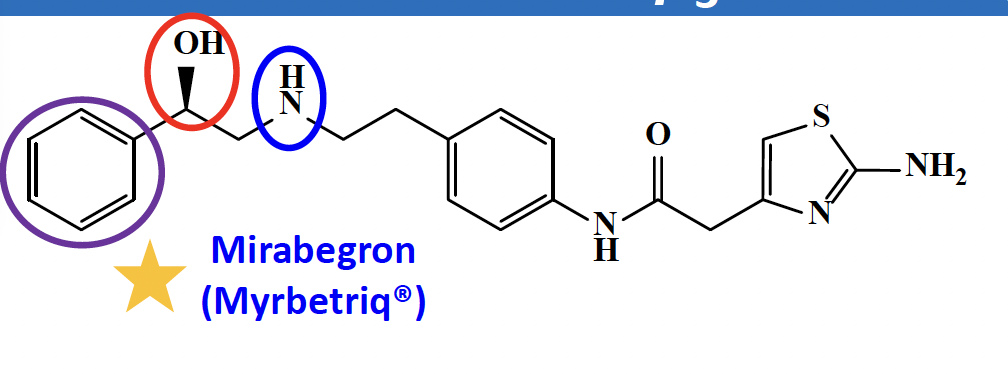
What is selective beta 3 adrenergic agonist?
Mirabegron:
overactive bladder
on the kid’s list
bind in a perpendicular: salt bridge between the amine, aromatic ring—> pipi bond, beta hydroxyl group and amine form additional hydrogen
What is mixed acting antagonist?
what are their direct and indirect effects & administration?
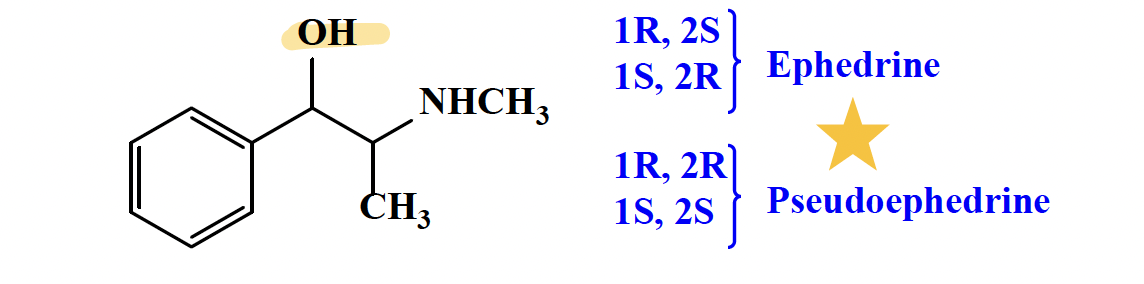
Ephedrine/Pseudoephedrine
both direct and indirect effects
direct: agonist effect at alpha and beta; binding similar to norepinephrine and epinephrine
indirect: increase the release of norepinephrine from nerve terminals
Ephedrine: CNS stimulant —> IV infusion to counteract hypotension or hypothermia associated with the use of anesthesia.
Pseudoephedrine: very little or less CNS stimulant —> nasal decongestant effect and in allergic rhinitis.
What are indirect adrenergic agonists and their structural characteristics?
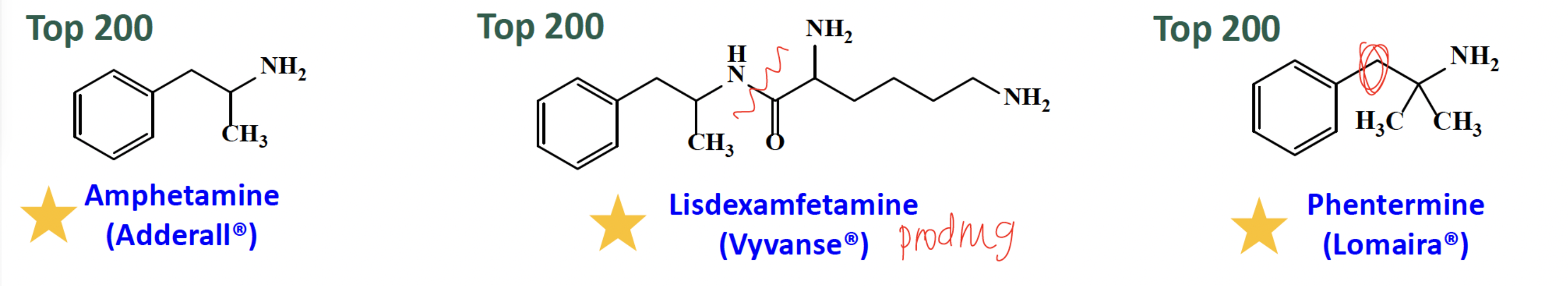
Amphetamine, Lisdexamfetamine, Phentermine
lack the catechol and beta hydroxyl groups, lowering their receptor binding affinity
Amphetamine: centrally to reverse NET and inhibit VMAT and may affect other neurotransmitters. It is used in ADHD and narcolepsy
Lisdexamfetamine= prodrug—> cleave (N-C=O)
Phentermine is used in obesity
How does indirect agonists work
increase level of NE and other monoamines
What are other indirect agonists
Other indirect agonists include MAO inhibitors and COMT inhibitors, NRI and SNRI (NRI = Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors), which are used in different CNS-related disorders such as ADHD, narcolepsy, Parkinson’s disease and major depressive disorders.
This is how amphetamine mainly affects NET
reverse NET by accumulating NE in cytosol by replacing it from the vesicle
This is an advantage of using non-catechol containing agents in adrenergic agonists.
What is resistance to COMT metabolism? Or improve selectivity
•These are the two factors that affect mean arterial pressure.
What are cardiac output and peripheral resistance?
•The difference between initial effect of administering epinephrine and norepinephrine on heart rate. Reason.
Drug | Initial HR effect | Why |
|---|---|---|
Epinephrine | ↑ HR | β1 ↑ HR + β2 vasodilation → no strong reflex |
Norepinephrine | ↓ HR | α1 ↑ BP → baroreceptor reflex bradycardia |
•This is the structural change to adrenergic agents more specific to β2-receptors.
What is substitution of a t-Bu group on the amine?
This is an additional substituent that leads to long-acting β2 agonists. Reason.
What is long chain on the amine? Additional binding (anchoring) —> 3 bindings
This is an advantage, beside providing a twist, that the chlorines provide in clonidine.
What is increased lipophilicity?
I am a prodrug of amphetamine primarily used to avoid dependence.
What is lisdexamfetamine?
The effect of adrenergic stimulation in uterine smooth muscles and receptor involved
What is contract and α1 and relaxation and β2?
The effect of adrenergic stimulation in eye radial and receptor involved.
What is contraction (causing pupil dilation and mydriasis) and α1