Translocation in plants
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What does translocation mean ?
Is the movement of sugars and other assimilates from where they’re synthesised
( source ) to where they are used ( sink )
where does translocation occur ?
Translocation occur in the phloem
Facts about phloem
Two way transport
many mitochondria
Living cells
Sieve tube plates , between the phloem cells
what are the function of a sieve tube ?
It allows sugars and water to transport through the plant in both directions.
what does the term assimilates means ?
Substances that become part of the plant.
Where does glucose synthesised + where is it used ?
Glucose is synthesised in the photosynthesising cells ( palisade mesophyll ) and used by respiring cells or stored as starch in cells.
what is a source ?
A source is any part of the plant loads sucrose into the sieve tube.
The roots, where energy stored as starch ( glucose ) is converted to sucrose for later usage.
what is a sink ?
Anywhere that removes sucrose from the phloem sieve tubes.
extra info
the suicose could be converted to starch for storage in roots, where sucrose is being used in the cells, it can diffuses out of the sieve tube via plasmodesmata.
Movement of sucrose
how does the sucrose move along the phloem ?
By mass flow
what causes the mass flow ?
The flow is caused by a differences in hydrostatic pressure between the two ends of the tube which produces a pressure gradient .
Info ~ movement of water + sucrose
water enter the tube at the source , increasing the pressure and it leaves at the sink , reducing the pressure. Solution of sucrose + assimilates flow from source to sink/
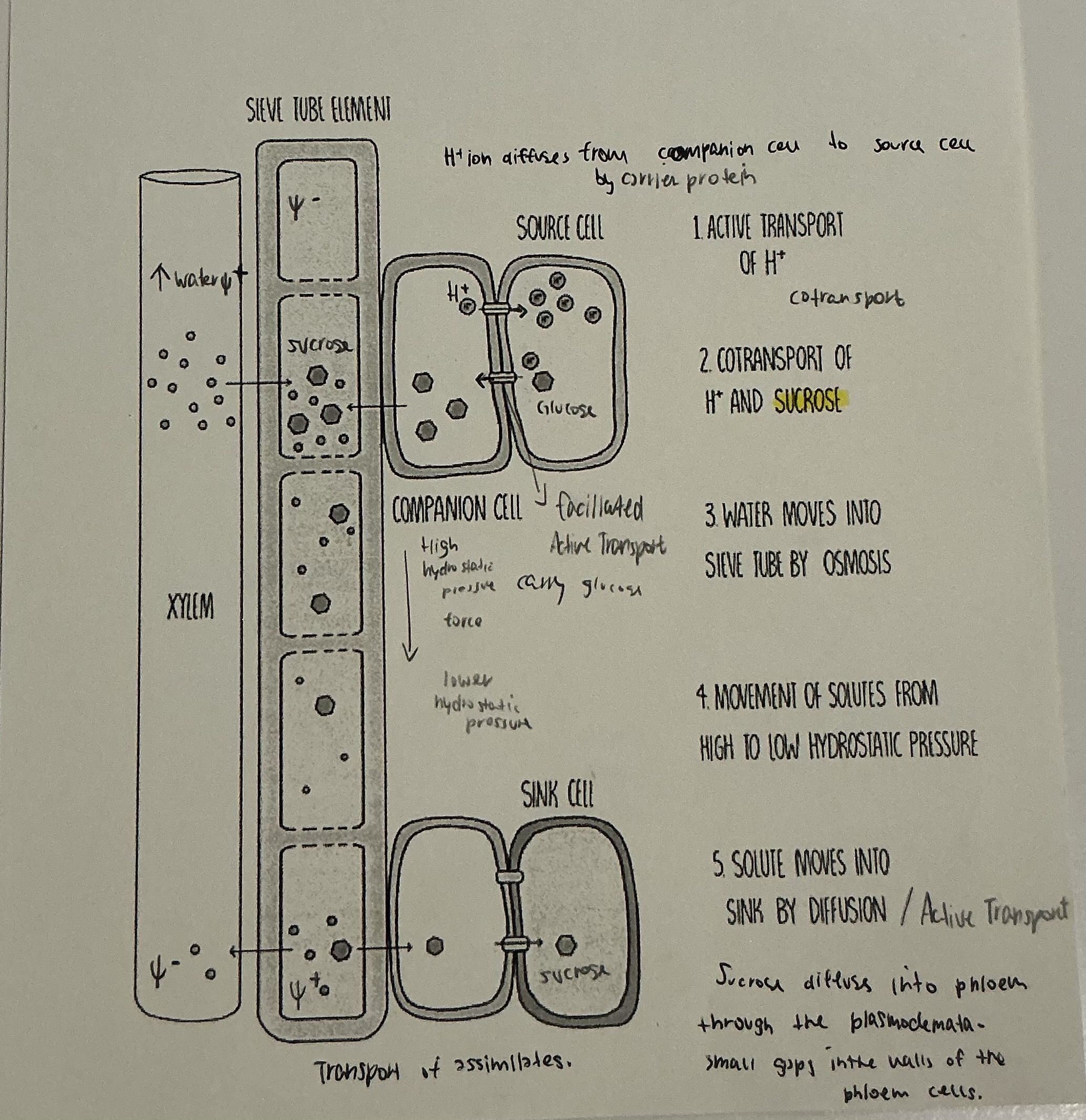
The process of movement of sucrose part 1 ( Active loading )
Sucrose loading into sieve tubes is an active process
Companion cells uses ATP to actively transport H +ions out of the cel, this creates a high H + con.c outside and a low H + con.c inside → con.c gradient
H + ions diffuse back in cotransporter proteins, it allows H+ ions in only is sucrose molecules move in with them. → Cotransport.
Sucrose is moved against its con.c gradient into the companion cell. Sucrose then diffuses through plasmodesmata into the sieve tube.
The process of movement of sucrose part 2
Sucrose transport in phloem occurs by mass flow. Sap can flow both ways in the plant.
Movement is driven by hydrostatic pressure gradient between source and sink.
The process of movement of sucrose part 3
Source : Sucrose is actively loaded into sieve tubes, water enters by osmosis, increasing hydrostatic pressure.
Sink : sucrose is removed from the phloem, sap flows from source ( high pressure ) to sink ( low pressure )
The process of movement of sucrose part 4 ( the source )
Sucrose enters sieve tube → water potential become negative. Water move in by osmosis from surroundings tissues, → increases hydrostatics pressure inside the sieve tube at the source.
The process of movement of sucrose part 5 ( the sink )
Sink = any part of plant that removes sucrose from the phloem.
Sucrose leaves sieve tube by diffusion via plasmodesmata and active transport.
Removal is
sucrose make water potential in sieve tube higher.
Water leaves by osmosis into surroundings cells. This lowers hydrostatic pressure in the phloem at the sink.