Sensation
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What is the difference between sensation and perception?
Sensation are the beginning stages, perception is the latter interpretation stages
What do our senses do in order to produce sensation?
Gather information about the outside world
Out senses translate …. into something the brain can use
Physical energy
What are the 4 stages of sensation?
Accessory structures modify physical stimulus
Transduction: Physical energy in picked up by receptors and converted in neural energy
Sensory nerves send transduced neural energy to the brain (Thalamus- relay station, then to different parts of the cortex)
Sensation is produced once message reaches the brain
What is neural noise?
Random excitation or inhibition of neurons that either increase or decrease the sensed intensity of a physical stimulus
Repeated presentations of the same physical level of intensity….
Do not always produce the same internal sensation
If physical signal is doubled….
It does not always produce a doubling of sensation
What is the term for the physical intensity at which a person can detect the stimulus 50% of the time?
Absolute threshold
What are the 3 implications of neural noise?
Repeated presentation of the same physical level of intensity do not always produce the same internal sensation
If a physical signal is doubled, that does not always produce a doubling of sensation
Absolute threshold
What is a the difference threshold?
The smallest amount of change in the intensity of a stimulus before a change is detected
What is the Weber fraction?
Different threshold increases in proportion to the standard
What is the ‘standard’ in Weber fraction
The stimulus with original intensity
What is Weber’s law?
Change in intensity of stimulus/ intensity of standard= C(onstant)
What is hearing measured in?
Soundwaves
What part of a wave gives the wave it’s pitch?
Frequency
What is frequency measured in?
Hertz (HZ)
What pitch would come from a frequent wave?
High pitch
What pitch would come from an infrequent wave?
Low pitch
From and to what HZ can humans hear?
20 → 20,000
What part of the sound wave produces volume?
The amplitude
What is volume measured in?
Decibels (dB)
What is timbre?
The complexity/ nature of the sound
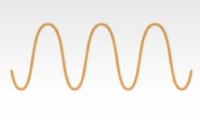
Does this wave show a loud or soft sound?
Loud
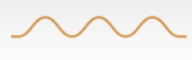
Does this wave show a loud or soft sound?
Soft
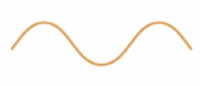
Does this wave show a low or high pitch?
Low
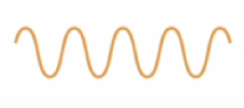
Does this wave show a low or high pitch?
High
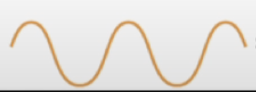
Does this wave show a simple or complex timbre?
Simple
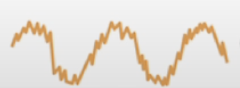
Does this wave show a simple or complex timbre?
Complex
What is the eardrum also known as?
Tympanic membrane
What happens in the ear in response to soundwaves?
Eardrum starts to vibrate then the hammer, anvil and stirrup
Stirrup vibrating causes the oval window to vibrate → creates waves within the fluid filled cochlea
Fluid causes the basilar membrane to vibrate
Basilar membrane vibration stimulates nerve cells
= Hearing
What is the collective term for the middle ear bones?
Ossicles
What does place theory argue?
Different parts of the basilar membrane vibrate more depending on the pitch
What parts do high frequencies stimulate?
The base
What part do low frequencies stimulate?
The apex
What has research on hearing pitch done?
Artificially stimulated particular areas of the membrane (cochlear implants), producing sensations of different hearing pitches
Why is it harder for elderly to hear?
Speech is made up on high and low frequencies, they find it harder to hear high ones so it doesn’t really make sense when it’s just low ones
What part of the ear is damaged in elderly people?
The base of the basilar membrane
What is an issue with place theory?
Below 1000Hz, no specific place on the membrane vibrates more than any other, however we can still distinguish between tones below that
What is the alternative theory to place theory?
Frequency (temporal) theory
What does frequency theory argue?
The basilar membrane is like a guitar string, vibrates faster when frequency is high
What is the difference between place theory and frequency theory?
Place theory puts importance on the place of the membrane that is being stimulated whereas frequency theory puts importance on the rate of stimulation
What is a problem for frequency theory?
Above 1000Hz, cells cannot fire any faster (refractory period) however, we can distinguish between above this frequency
What is frequency and volley theory?
There is alternation in the firing of hair cells to send a higher frequency of signal to the brain
What is a problem with frequency and volley theory?
Above 10,000 Hz would need very complex teamwork
Light is ….like
Wavelike
What is light measured in?
Nanometers
Light is part of what spectrum?
The electromagnetic specturm
What is in the electromagnetic spectrum?
X-rays
Ultraviolet
Infrared
Radar
FM radio
TV
AM radio
In between which two types of light is visible light?
Ultraviolet and infrared

The pupil is an opening in your…?
Iris
What is the first layer of the eye called?
The cornea
What is the proper name for the goo behind the cornea?
Aqueous humour
The is the name for the opaque tissue which controls the size of the pupil?
The iris
What does the lens do?
Changes shape to focus the object you’re looking at
What is the liquid called that fills the centre of the eyeball?
Vitreous humour
What is the term for the things that recieve light in the retina?
Photorecpetors
What do photoreceptors contain?
Photopigment
What happens when light is projected onto photoreceptors?
Photopigment breaks down
What does the breakdown of photopigment cause?
Transmission of information to the brain through the optic nerve
What is the term for the breakdown of photopigment?
Bleaching
What are the two types of photoreceptors?
Rods and cones
What type of light are rods responsible for?
Vision in dim light
What is the fovea?
The focal point of your visual field
What type of photopigment do rods contain?
Rhodopsin
Which type of photoreceptor gives colour information?
Cones
What type of light are rods responsible for?
Bright light
What is photopigment in cones called?
Iodopsin
How many types of cone are there?
3
Why are there 3 different types of cones?
Each are sensitive to different types of light (different wavelength)
What can be seen because of different types on cone?
Colour
Which theory was developed by Young & Helmholtz?
Trichromatic theory
What are the primary colours of light?
Red, blue, and green
What type of mixture is light?
Additive
What type of mixture is pigment?
Subtractive
Cones sensitive to short wavelengths produce sensation of:
Blue
Cones sensitive to medium wavelengths produce sensation of:
Green
Cones sensitive to long wavelengths produce sensation of:
Red
What is the support for trichromatic theory?
How many types of iodopsin do people with dichromatic colourblindness have?
2
How many types of iodopsin do people with monochromatic colourblindness have?
1
What is a problem with trichromatic theory?
Dichromats can see yellow → how can this happen if dichromats don’t have either green or red iodopsin?
How are visual receptors organised according to opponent process theory?
Blue/yellow
Red/green
Black/white
Where is information from roads and cones conveyed to?
Ganglion cells
What do ganglion cells do?
Send information up the optic nerve to the brain
What is the name of the place where the optic nerve leaves the eye?
Optic disk
What reroutes visual information to the thalamus and vidual coretx?
Optic chiasm
What are the 3 types of receptors involved in touch?
Temperature
Pressure
Pain
What temperature is physiological zero?
32 degrees Celsius
Which neurotransmitter allows nerves to communicate when in pain?
Substance P
How can you reduce pain?
Stimulate parts of brain with electrodes to reduce endorphins
What are released with the anticipation of pain?
Endorphins
Acupuncture may work by stimulating…
Endorphins
What is the olfactory sense?
Smell
What are pheremones?
Chemical secreted into the body which produce a physiological response
What are women asked to do more when ovulating?
Dance
What may pheromones cause menstrual cycles to do?
Sync up
Over time, the ability to detect odour drops by what %?
30%
What percentage of people who lose sense of smell also lose interest in sex?
8%
What part gives us our sense of smell?
Olfactory mucosa
What are the 4 main group taste buds can sense?
Bitter, salty, sour, sweet (possibly umami)