management accounting end of week questions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:22 PM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
the planning process includes:
* setting objectives
* identifying means of achieving the objectives
* making decisions
* all of the above
* setting objectives
* identifying means of achieving the objectives
* making decisions
* all of the above
d
2
New cards
management accounting
* provides a framework to evaluate information in light of an organization's goals.
* provides relevant information to managers.
* provides relevant information to meet specific needs of persons inside the organization
* all of the above
* provides a framework to evaluate information in light of an organization's goals.
* provides relevant information to managers.
* provides relevant information to meet specific needs of persons inside the organization
* all of the above
d
3
New cards
which of the following characteristics does not pertain to management accounting ?
* provides information and estimates about future activity
* generates specific-purpose financial statements and reports
* provides financial and operating data multidisciplinary in scope
* has externally imposed standards
* provides information and estimates about future activity
* generates specific-purpose financial statements and reports
* provides financial and operating data multidisciplinary in scope
* has externally imposed standards
d
4
New cards
the setting of objectives and the identification of methods to achieve those objectives is called
* planning.
* controlling.
* performance evaluation.
* decision making.
* planning.
* controlling.
* performance evaluation.
* decision making.
a
5
New cards
___ is devoted to providing information for external users.
* Management accounting
* Financial accounting
* Internal accounting
* Cost accounting
* Management accounting
* Financial accounting
* Internal accounting
* Cost accounting
b
6
New cards
the monitoring of a plans implementation is called:
* planning
* controlling
* decision making
* budgeting
\
* planning
* controlling
* decision making
* budgeting
\
b
7
New cards
which of the following costing activities is associated with the financial accounting system ?
* determining the cost of a department
* determining the cost of goods sold for financial statements
* preparing budgets
* determining the cost of a customer
* determining the cost of a department
* determining the cost of goods sold for financial statements
* preparing budgets
* determining the cost of a customer
b
8
New cards
management accounting a finical accounting differ in that management accounting information is prepared …
* following prescribed rules
* using whatever methods the company finds beneficial
* for shareholders
* to summarise the whole company with little detail
* following prescribed rules
* using whatever methods the company finds beneficial
* for shareholders
* to summarise the whole company with little detail
b
9
New cards
Management accounting is concerned with which kind of decision?
* product costing and pricing
* continuous operational improvement
* financial control
* all of the above
* product costing and pricing
* continuous operational improvement
* financial control
* all of the above
d
10
New cards
Cost accounting
* is concerned with assigning costs to various cost objects.
* attempts to satisfy the costing objectives of both financial accounting and management accounting.
* provides cost information that supports planning, controlling, and decision making.
* All of the above descriptions are true.
* is concerned with assigning costs to various cost objects.
* attempts to satisfy the costing objectives of both financial accounting and management accounting.
* provides cost information that supports planning, controlling, and decision making.
* All of the above descriptions are true.
d
11
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly distinguishes between financial and management accounting?
* Management accounting reports on the whole organization.
* Financial accounting is oriented toward the future.
* Financial accounting is primarily concerned with providing information for internal users.
* Management accounting is oriented more toward the planning and control aspects of management.
* Management accounting reports on the whole organization.
* Financial accounting is oriented toward the future.
* Financial accounting is primarily concerned with providing information for internal users.
* Management accounting is oriented more toward the planning and control aspects of management.
d
12
New cards
setting the selling price of a company product is an examples of
* planning
* control
* decision making
* all of the above
* planning
* control
* decision making
* all of the above
c
13
New cards
which of the following is an example of a variable cost?
* insurance on the production equipment
* direct materials
* the production supervisors salary
* deprecation of the factory building
* insurance on the production equipment
* direct materials
* the production supervisors salary
* deprecation of the factory building
b
14
New cards
Mulholland Company manufactures various wooden furniture products. If the cost object is a product, a chair, what costs would be considered direct?
* manufacturing supervisor's salary
* depreciation on the factory building
* salary of the worker that glues the legs to the seat of the chair
* insurance on the factory
* manufacturing supervisor's salary
* depreciation on the factory building
* salary of the worker that glues the legs to the seat of the chair
* insurance on the factory
c
15
New cards
what is not allowed under the IAS 2
* AVCO
* LIFO
* FIFO
* WAC
* AVCO
* LIFO
* FIFO
* WAC
b
16
New cards
which of the following costs is an indirect product cost?
* property taxes on plant facilities
* wages of assembly workers
* materials used
* presidents salary
* property taxes on plant facilities
* wages of assembly workers
* materials used
* presidents salary
a
17
New cards
which of the following costs is a variable cost?
* supervisors salaries
* research and development
* materials used in production
* rent
* supervisors salaries
* research and development
* materials used in production
* rent
c
18
New cards
which item is not an example of a sunk cost?
* materials needed for production
* purchase cost of machinery
* depreciation
* all are sunk cost
* materials needed for production
* purchase cost of machinery
* depreciation
* all are sunk cost
a
19
New cards
mixed costs
* are step cost
* in total remain constant within relevant range
* have a fixed and variable component
* on a per unit basis, are constant as activity increase and decreases
* are step cost
* in total remain constant within relevant range
* have a fixed and variable component
* on a per unit basis, are constant as activity increase and decreases
c
20
New cards
If total warehousing cost for the year amounts to £350 000, and 40 per cent of the warehousing activity is associated with finished goods and 60 per cent with direct materials, how much of the cost would be charged as a product cost?
* 70,000
* 140,000
* 210,000
* 350,000
* 70,000
* 140,000
* 210,000
* 350,000
c
21
New cards
which of the following is an example of a fixed cost?
* power cost in the machine department
* wood in the manufacture of furniture
* labour cost paid on a piece basis
* lease payments on machinery
* power cost in the machine department
* wood in the manufacture of furniture
* labour cost paid on a piece basis
* lease payments on machinery
d
22
New cards
which of the following is a product cost
* advertising expenditures
* insurance on the office buildings
* depreciation of the salesmens car
* depreciation of the production facilities
* advertising expenditures
* insurance on the office buildings
* depreciation of the salesmens car
* depreciation of the production facilities
d
23
New cards
___ refers to the assignment of indirect cots to cost objects
* allocation
* direct tracing
* physical observation
* cost management
* allocation
* direct tracing
* physical observation
* cost management
a
24
New cards
the calculation of units costs is important for
* inventory valuation
* income determination
* pricing
* all of the above
* inventory valuation
* income determination
* pricing
* all of the above
d
25
New cards
which of the following accurately describes advantage and disadvantages of employing a system of allocation that uses a plant - wide rate?
* the plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but it is also the most costly to implement.
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but most likely provides the least accurate product costs.
* The plant-wide rate may be straightforward, but it is not appropriate for small businesses that offer a single service or product.
* The plant-wide rate really offers no advantage whatsoever.
* the plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but it is also the most costly to implement.
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but most likely provides the least accurate product costs.
* The plant-wide rate may be straightforward, but it is not appropriate for small businesses that offer a single service or product.
* The plant-wide rate really offers no advantage whatsoever.
b
26
New cards
support departments
* are responsible for manufacturing the products sold to customers
* work directly on the products of the firm
* provide services directly to customers
* provide essential services to the producing departments
* are responsible for manufacturing the products sold to customers
* work directly on the products of the firm
* provide services directly to customers
* provide essential services to the producing departments
d
27
New cards
traditional - based product costing uses which of the following procedures?
* overhead costs are traced to departments, the costs are traced to products
* overhead cots are traced to activities, then costs are traced to produced
* overhead costs are traced to departments, the costs are traced to products
* overhead cots are traced to activities, then costs are traced to produced
28
New cards
which of the following is NOT a support department?
* food services
* bottling
* health services
* security
* food services
* bottling
* health services
* security
b
29
New cards
examples of support departments include all of the following except
* maintenance
* personnel
* machining
* data processing
* maintenance
* personnel
* machining
* data processing
c
30
New cards
support department costs are accounted for in which one of the following ways?
* They are allocated directly to units of product.
* They are allocated to producing departments and then allocated to units of product.
* They are allocated to units of product and then allocated to the producing departments.
* They are expensed as incurred
* They are allocated directly to units of product.
* They are allocated to producing departments and then allocated to units of product.
* They are allocated to units of product and then allocated to the producing departments.
* They are expensed as incurred
b
31
New cards
which of the following is a key consideration inn selecting allocation base?
* the allocation base should have an indirect association with the cost objective
* the allocation base should be difficult to measure
* there should be logical association between the allocations base and the incidence of costs
* the allocation base should be out of the control of management
* the allocation base should have an indirect association with the cost objective
* the allocation base should be difficult to measure
* there should be logical association between the allocations base and the incidence of costs
* the allocation base should be out of the control of management
c
32
New cards
examples of producing departments include all od the following except
* mixing
* molding
* packaging
* accounting
* mixing
* molding
* packaging
* accounting
d
33
New cards
___ is (are) a method of allocating service department costs that give(s) partial recognition to interdepartmental services by using a methodology that allocates service department costs sequentially both to the remaining service departments and the producing departments.
* the direct method
* the step method
* the linear algebra method
* the direct and step methods
* the direct method
* the step method
* the linear algebra method
* the direct and step methods
b
34
New cards
an example of a production or unit level driver is
* pounds of direct materials
* number of set up
* number of batches
* number of product lines
* pounds of direct materials
* number of set up
* number of batches
* number of product lines
d
35
New cards
a possible casual factor to use when allocation cafeteria costs would be
* number of square feet
* number of direct labour hours
* number of employees
* appraised value of square footage
* number of square feet
* number of direct labour hours
* number of employees
* appraised value of square footage
c
36
New cards
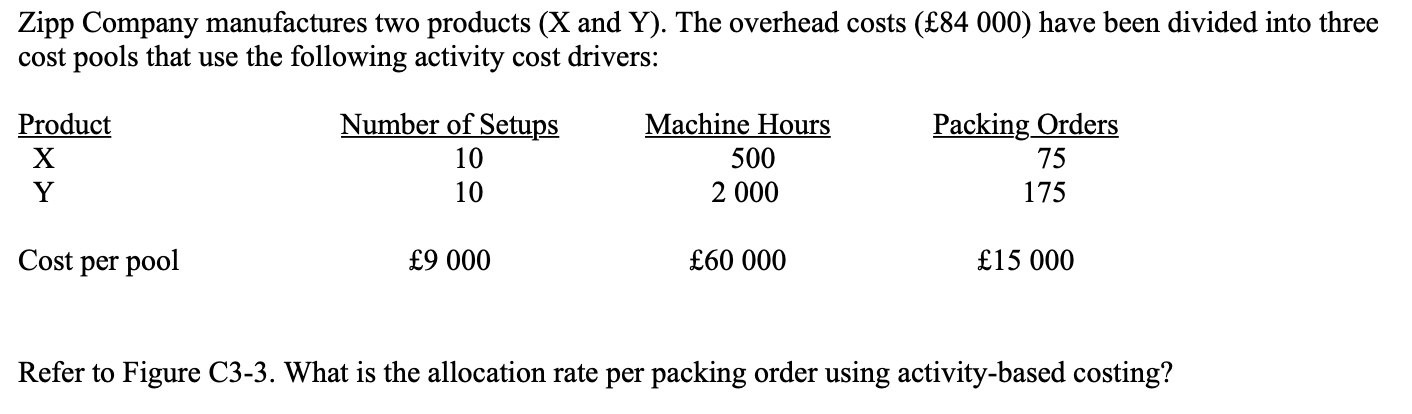
* 15000
* 60
* 7500
* 200
* 60
* 7500
* 200
b
37
New cards
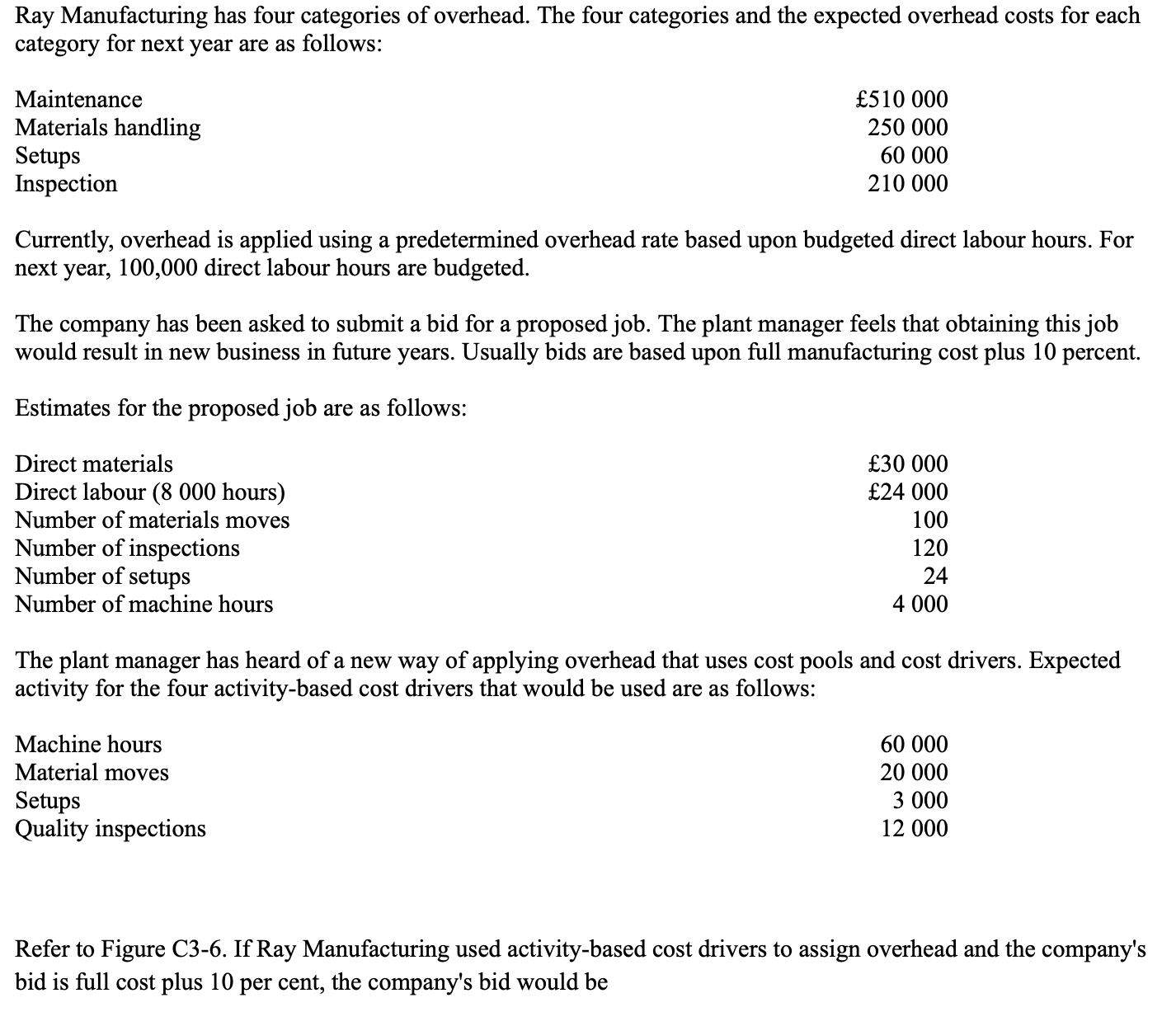
* 108,804
* 105,413
* 103,235
* 101,013
* 105,413
* 103,235
* 101,013
d

38
New cards
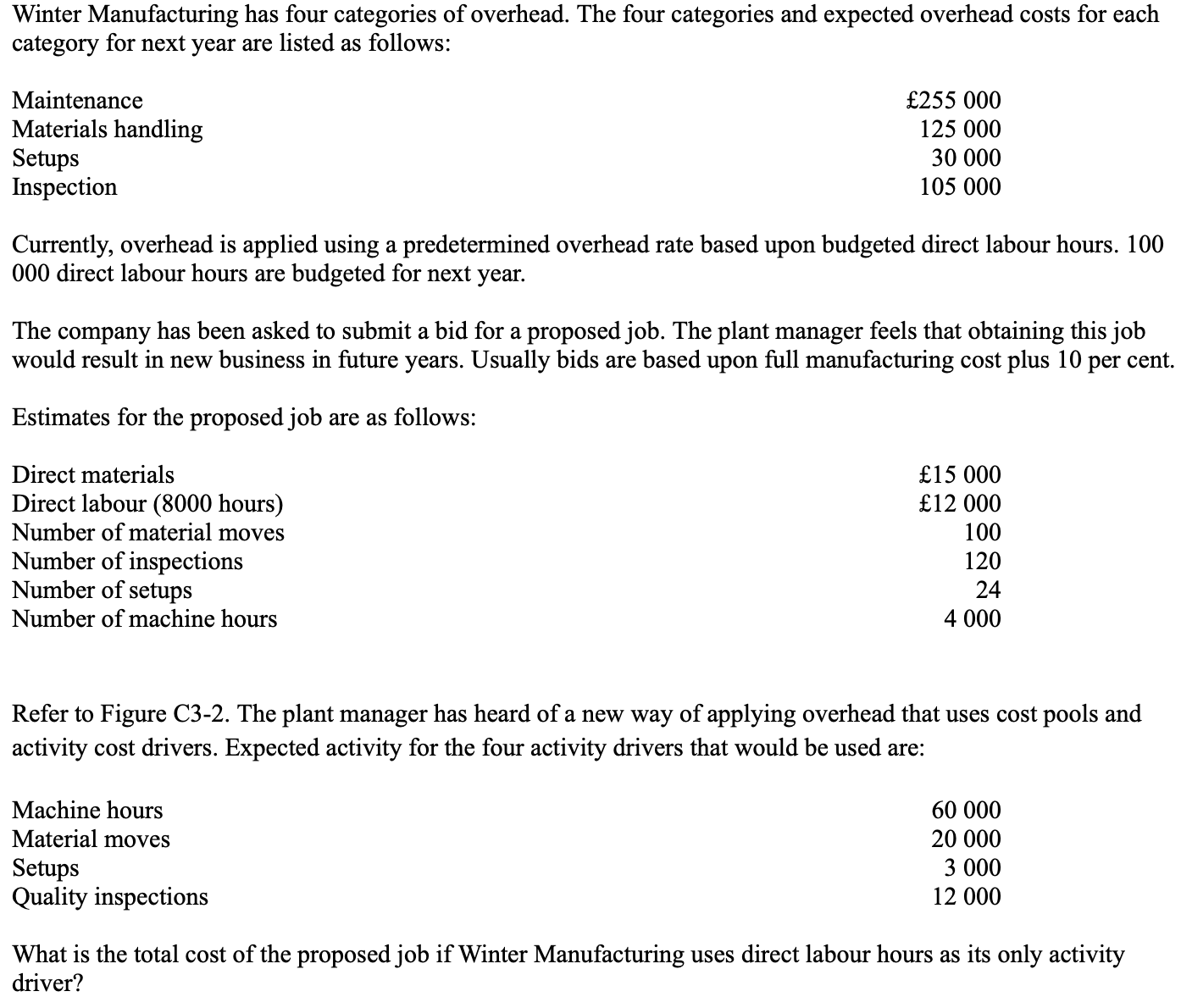
* 72000
* 68200
* 56200
* 53200
* 68200
* 56200
* 53200
b

39
New cards

* 9230
* 8180
* 2250
* 1680
* 8180
* 2250
* 1680
b

40
New cards
Which of the following accurately describes advantages and disadvantages of employing a system of allocation that uses a plant-wide rate?
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but it is also the most costly to implement
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but most likely provides the least accurate product costs.
* The plant-wide rate may be straightforward, but it is not appropriate for small businesses that offer a single service or product.
* The plant-wide rate really offers no advantage whatsoever.
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but it is also the most costly to implement
* The plant-wide rate approach is the simplest to apply, but most likely provides the least accurate product costs.
* The plant-wide rate may be straightforward, but it is not appropriate for small businesses that offer a single service or product.
* The plant-wide rate really offers no advantage whatsoever.
b
41
New cards
support departments
* are responsible for manufacturing the products sold to customers
* work directly on the products of the firm
* provide services directly to customers
* provide essential services to the producing departments
* are responsible for manufacturing the products sold to customers
* work directly on the products of the firm
* provide services directly to customers
* provide essential services to the producing departments
d
42
New cards
An activity-based costing system uses which of the following procedures?
* Overhead costs are traced to departments, then costs are traced to products.
* Overhead costs are traced to activities, then costs are traced to products.
* Overhead costs are traced directly to products.
* All overhead costs are expensed as incurred.
* Overhead costs are traced to departments, then costs are traced to products.
* Overhead costs are traced to activities, then costs are traced to products.
* Overhead costs are traced directly to products.
* All overhead costs are expensed as incurred.
b
43
New cards

* 17480
* 16583
* 13110
* 12765
\
* 16583
* 13110
* 12765
\
b

44
New cards
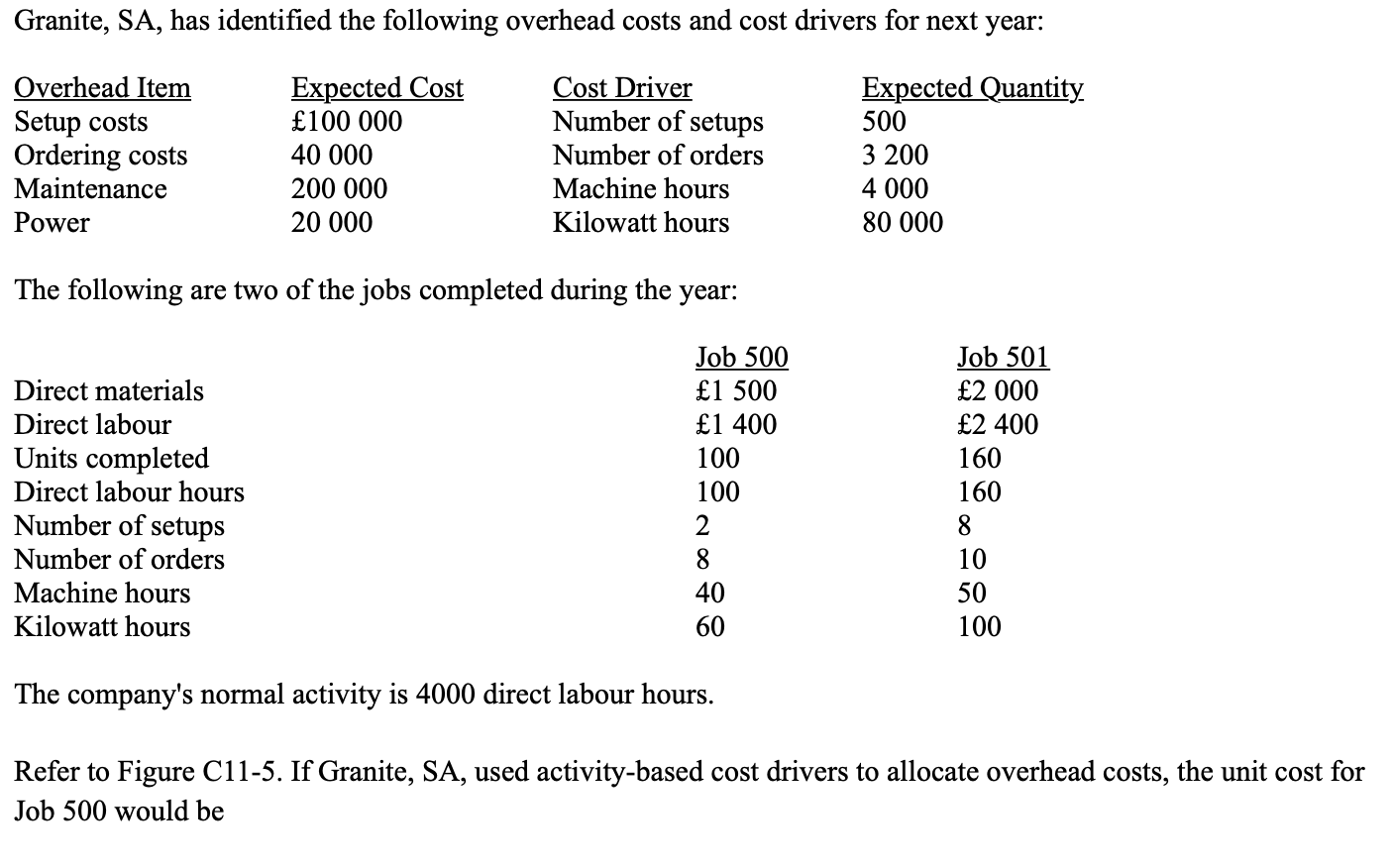
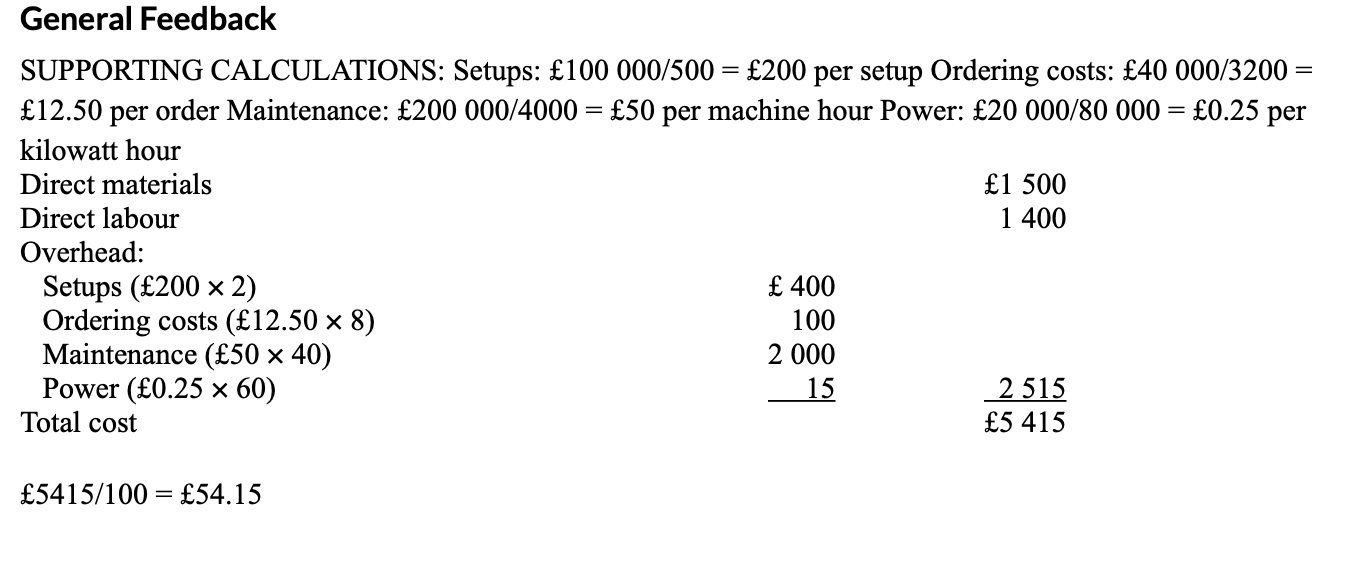
* 53.13
* 54.15
* 56.67
* 57.15
* 54.15
* 56.67
* 57.15
b
45
New cards
Which of the following is a reason to accumulate and separately assign costs by departments?
* The company wants to reduce the complexity of its cost accounting system.
* The company is comprised of multiple departments, each of which exhibit unique cost behaviour patterns.
* The company wishes to implement an activity based costing system.
* The company has a large amount of capital invested in human resource training.
* The company wants to reduce the complexity of its cost accounting system.
* The company is comprised of multiple departments, each of which exhibit unique cost behaviour patterns.
* The company wishes to implement an activity based costing system.
* The company has a large amount of capital invested in human resource training.
b
46
New cards
Assuming sales prices and cost behaviour remain unchanged, when absorption costing is used, overproducing creates which of the following situations?
* a buildup of inventory levels
* higher net income
* less fixed costs on the income statement
* all of the above
* a buildup of inventory levels
* higher net income
* less fixed costs on the income statement
* all of the above
d
47
New cards
In a cost-volume-profit graph, the slope of the total revenue line represents
* the selling price per unit
* the contribution margin per unit.
* the variable cost per unit.
* total contribution margin.
* the selling price per unit
* the contribution margin per unit.
* the variable cost per unit.
* total contribution margin.
a
48
New cards

what is the next income for Eastwood using the absorption costing method
* £452 000
* £480 000
* £1 200 000
* £600 000
* £452 000
* £480 000
* £1 200 000
* £600 000
a
49
New cards
The method of accounting for inventory that assigns all manufacturing costs to inventory is sometimes referred to as:
* absorption costing.
* FIFO.
* the weighted average cost method.
* conversion costing.
* absorption costing.
* FIFO.
* the weighted average cost method.
* conversion costing.
a
50
New cards
Inventory values calculated using variable costing as opposed to absorption costing will generally be
* equal
* less
* greater
* twice as much
* equal
* less
* greater
* twice as much
b
51
New cards

During the period, the company produced and sold 1000 units.
What is the inventory cost per unit using variable costing?
* 52
* 62
* 42
* 70
What is the inventory cost per unit using variable costing?
* 52
* 62
* 42
* 70
c
52
New cards
Total contribution margin is calculated by subtracting
* cost of goods sold from total revenues.
* fixed costs from total revenues.
* total manufacturing costs from total revenues.
* total variable costs from total revenues.
* cost of goods sold from total revenues.
* fixed costs from total revenues.
* total manufacturing costs from total revenues.
* total variable costs from total revenues.
d
53
New cards
Assuming all other things are the same, variable cost per unit must have ____ if there was an increase in the break-even point.
* remained the same
* increased first, then decreased
* increased
* depends on the circumstances
* remained the same
* increased first, then decreased
* increased
* depends on the circumstances
c
54
New cards

\
What is the contribution margin per unit?
* £7.20
* £1.20
* £4.80
* £120 000
What is the contribution margin per unit?
* £7.20
* £1.20
* £4.80
* £120 000
c
55
New cards

Refer to Figure C8-3. What selling price per unit is needed to obtain a before-tax profit of £270 000 at a volume of 4000 units?
£150.00
£330.00
£225.00
£105.00
£150.00
£330.00
£225.00
£105.00
b

56
New cards

margin of safety:
* 2000 units.
* 3000 units.
* 5000 units.
* 7000 units.
* 2000 units.
* 3000 units.
* 5000 units.
* 7000 units.
b

57
New cards
All of the following costs are included in inventory under absorption costing EXCEPT
* direct materials.
* direct labour.
* fixed selling expenses.
* fixed factory overhead.
* direct materials.
* direct labour.
* fixed selling expenses.
* fixed factory overhead.
c
58
New cards

During the period, the company produced and sold 1000 units.
What is the inventory cost per unit using absorption costing?
£104
£70
£84
£32
What is the inventory cost per unit using absorption costing?
£104
£70
£84
£32
b
59
New cards
a budget is
* a planning tool
* a control tool
* a means of communicating goals to the firms divisions
* all of these
* a planning tool
* a control tool
* a means of communicating goals to the firms divisions
* all of these
db
60
New cards
Which of the following appears in the cash budget?
* interest payments
* purchase of equipment on credit
* depreciation
* all of these
* interest payments
* purchase of equipment on credit
* depreciation
* all of these
b
61
New cards

Refer to Figure C15-3. How many pounds of material would Sommers need to purchase?
216 000
225 000
207 000
201 000
216 000
225 000
207 000
201 000
c
62
New cards
Canceco Company produces and sells pillows. It expects to sell 10 000 pillows in the year 2008 and had 1000 pillows in finished goods inventory at the end of 2011. Canceco would like to complete operations in the year 2008 with at least 1250 completed pillows in inventory. There is no ending work-in-process inventory. The pillows sell for £5 each.
\n Refer to Figure C15-5. What would be the total sales for the year 2008?
£50 000
£55 000
£56 250
£51 250
\
\n Refer to Figure C15-5. What would be the total sales for the year 2008?
£50 000
£55 000
£56 250
£51 250
\
a
63
New cards

how many units of products X and Y should dot company produce?
Product X Product Y
* 16 000 -0-
* 8 000 4 000
* 7 000 -0-
* 3 000 8 000
Product X Product Y
* 16 000 -0-
* 8 000 4 000
* 7 000 -0-
* 3 000 8 000
d
64
New cards

If Caddo can produce only one of the products in the next period, which product should be produced?
* Alpha should be produced because it requires less machine hours.
* Beta should be produced because it generates more revenue.
* Beta should be produced because it generates more contribution margin per unit.
* none of these.
* Alpha should be produced because it requires less machine hours.
* Beta should be produced because it generates more revenue.
* Beta should be produced because it generates more contribution margin per unit.
* none of these.
d
65
New cards

What is the actual cost per sticker? (Round to three decimal places.)
£0.468
£0.478
£0.486
£0.487
£0.468
£0.478
£0.486
£0.487
c
66
New cards
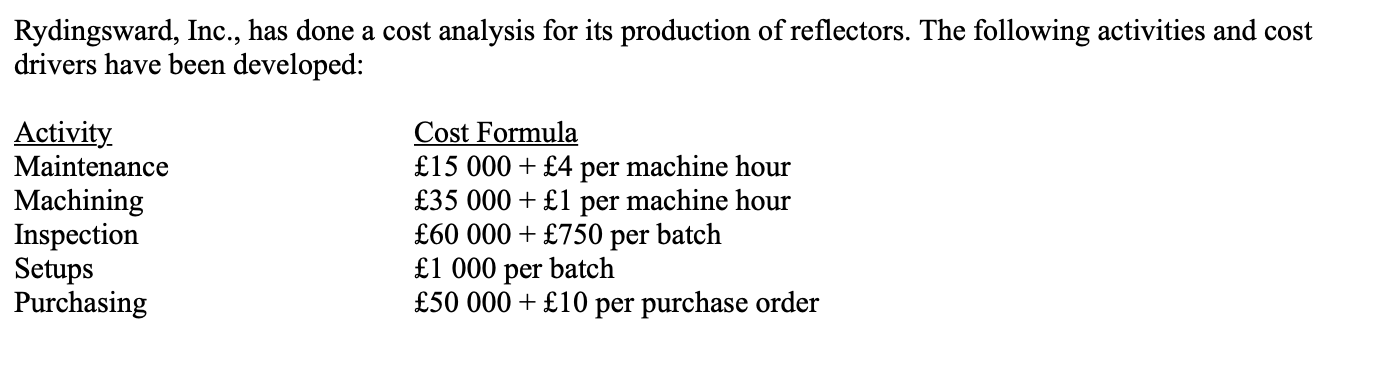
What is the budgeted purchasing cost if there was production of 50 000 reflectors that will require 8000 machine hours, 25 batches and 15 000 purchase orders?
* £150,000
* £200,000
* £100,000
* none of these
* £150,000
* £200,000
* £100,000
* none of these
b
67
New cards
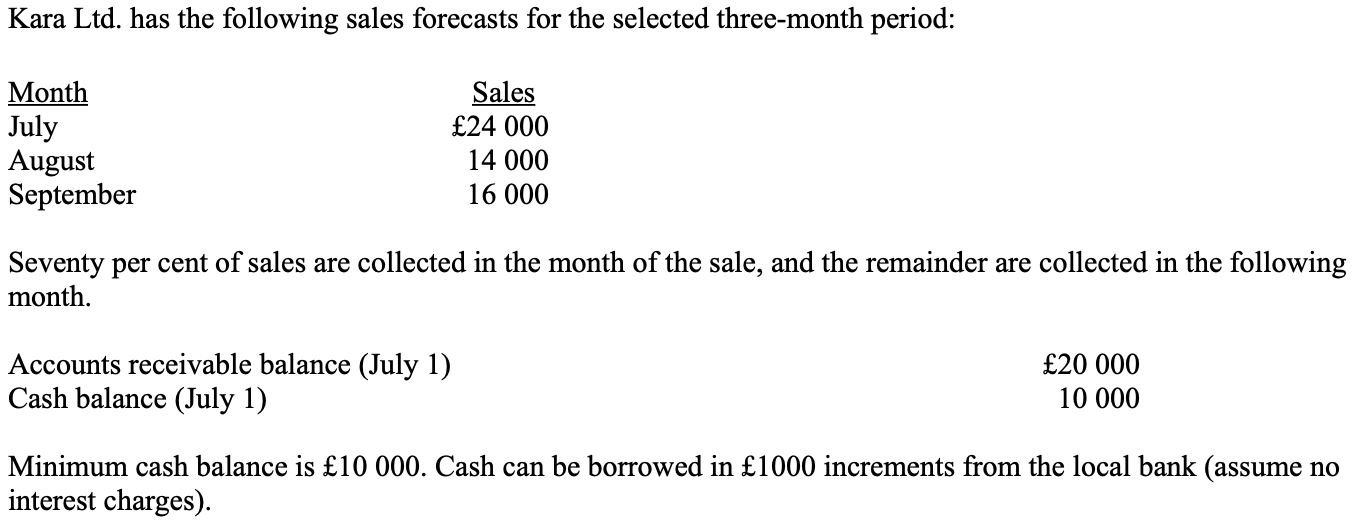
How much cash would be collected in September from sales?
£15 400
£17 000
£16 000
£20 000
£15 400
£17 000
£16 000
£20 000
a
68
New cards
Gerald Company manufactures books. Manufacturing a book takes 10 units of A1 and 1 unit of A2. Scheduled production of books for the next two months is 1000 and 1200 units, respectively. Beginning inventory is 4000 units of A1 and 30 units of A2. The ending inventory of A1 is planned to decrease 500 units in each of the next two months, and the A2 inventory is expected to increase 5 units in each of the next two months.
How many units of A1 does expect to use in production during the second month?
* 12 000 units
* 12 500 units
* 10 000 units
* 10 750 units
How many units of A1 does expect to use in production during the second month?
* 12 000 units
* 12 500 units
* 10 000 units
* 10 750 units
a
69
New cards
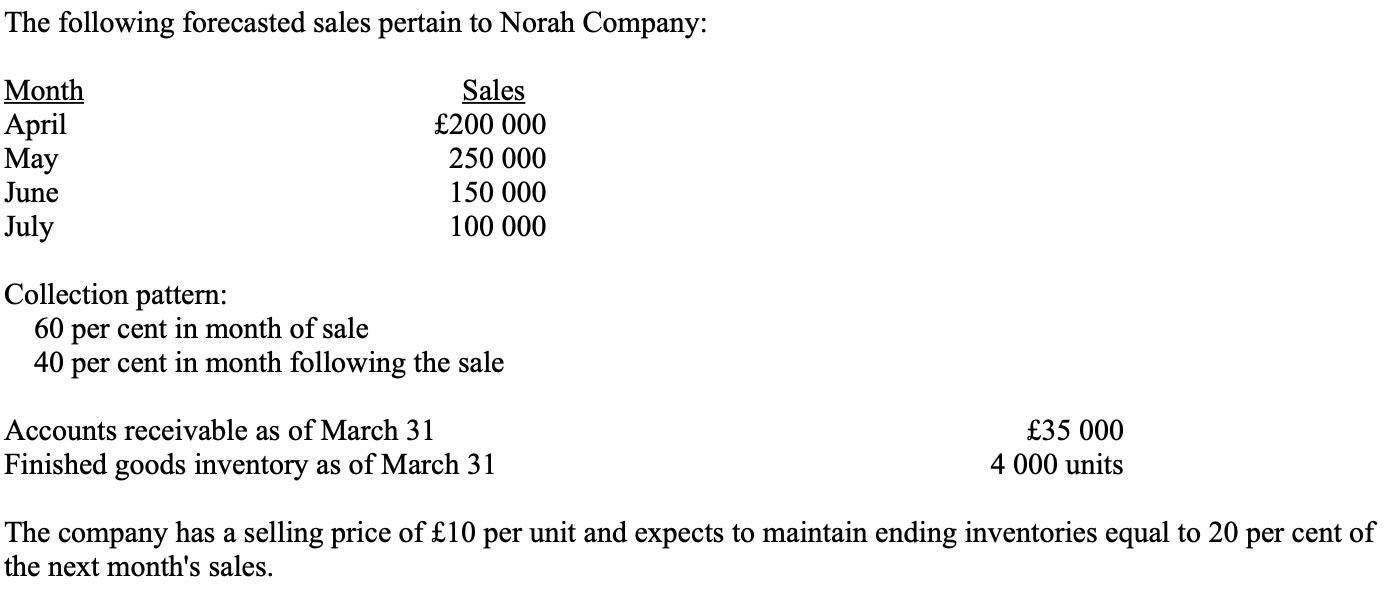
How many units are expected to be produced in April?
* 21 000 units
* 19 000 units
* 25 000 units
* 20 000 units
* 21 000 units
* 19 000 units
* 25 000 units
* 20 000 units
a
70
New cards
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information:
Direct labour: 1.25 hours × £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12 000 units. Shannon actually made 10 000 units using 13 000 hours.
Shannon's standard hours allowed for production was
* 12 500.
* 15 000
* 16 250.
* 13 000.
Direct labour: 1.25 hours × £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12 000 units. Shannon actually made 10 000 units using 13 000 hours.
Shannon's standard hours allowed for production was
* 12 500.
* 15 000
* 16 250.
* 13 000.
a
71
New cards
During April, 80 000 units of product were produced. The standard quantity of material allowed per unit was two pounds at a standard cost of £5 per pound. If there was a favourable materials usage variance of £40 000 for April, the actual quantity of materials used must have been
* 168 000 pounds.
* 152 000 pounds.
* 84 000 pounds.
* 76 000 pounds.
* 168 000 pounds.
* 152 000 pounds.
* 84 000 pounds.
* 76 000 pounds.
b
72
New cards

Orient's materials usage variance would be
£22 000 unfavourable.
£12 000 favourable.
£10 000 unfavourable.
£4000 unfavourable.
£22 000 unfavourable.
£12 000 favourable.
£10 000 unfavourable.
£4000 unfavourable.
d
73
New cards
A 5 per cent wage increase for all factory employees would affect which of the following variances?
* materials price variance
* labour rate variance
* labour efficiency variance
* variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
* materials price variance
* labour rate variance
* labour efficiency variance
* variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance
b
74
New cards
An unfavourable materials price variance may be caused by
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
d
75
New cards
Labour efficiency variances may be caused by
* the use of highly skilled workers.
* frequent machinery breakdowns.
* the use of marginally skilled workers.
* all of these.
* the use of highly skilled workers.
* frequent machinery breakdowns.
* the use of marginally skilled workers.
* all of these.
d
76
New cards
During May, 6000 pounds of raw materials were purchased at a cost of £2.60 per pound. If there was a favourable materials price variance of £900 for December, the standard cost per pound must be
* £2.75.
* £2.60.
* £2.45.
* none of these.
* £2.75.
* £2.60.
* £2.45.
* none of these.
a
77
New cards
An unfavourable materials price variance with a favourable materials usage variance would most likely be the result of
* machines breaking down.
* problems with labour efficiency.
* purchase of high quality materials.
* problems with labour rates.
* machines breaking down.
* problems with labour efficiency.
* purchase of high quality materials.
* problems with labour rates.
c
78
New cards

Tuvok's materials usage variance is
* £1000 unfavourable.
* £1100 unfavourable.
* £2000 unfavourable.
* cannot be determined from the information given.
* £1000 unfavourable.
* £1100 unfavourable.
* £2000 unfavourable.
* cannot be determined from the information given.
a
79
New cards

Rax's labour efficiency variance would be
* £4300 unfavourable.
* £4300 favourable.
* £1800 unfavourable.
* £1800 favourable.
* £4300 unfavourable.
* £4300 favourable.
* £1800 unfavourable.
* £1800 favourable.
c
80
New cards
During October, 16 000 direct labour hours were worked at a standard cost of £6 per hour. If the labour rate variance for October was £4000 unfavourable, the actual cost per labour hour must be
* £6.25.
* £6.00.
* £5.75.
* none of these.
* £6.25.
* £6.00.
* £5.75.
* none of these.
a
81
New cards
Shannon Ltd.'s standard cost card contained the following information: Direct labour: 1.25 hours × £8.00 per hour = £10.00
Shannon planned to make 12 000 units.
Shannon actually made 10 000 units using 13 000 hours.
Shannon's labour efficiency variance was
* £4625 unfavourable.
* £4000 unfavourable.
* £27 750 unfavourable.
* £24 000 unfavourable.
Shannon planned to make 12 000 units.
Shannon actually made 10 000 units using 13 000 hours.
Shannon's labour efficiency variance was
* £4625 unfavourable.
* £4000 unfavourable.
* £27 750 unfavourable.
* £24 000 unfavourable.
b
82
New cards
Labour rate variances can be the result of
* the use of an average wage rate.
* unexpected overtime.
* seniority mix changes.
* all of these.
* the use of an average wage rate.
* unexpected overtime.
* seniority mix changes.
* all of these.
d
83
New cards
An unfavourable materials usage variance may be caused by
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
a
84
New cards
The purchase of inferior direct materials at a lower price might affect which of the following variances?
* materials price variance
* materials usage variance
* labour efficiency variance
* all of these
* materials price variance
* materials usage variance
* labour efficiency variance
* all of these
d
85
New cards
A favourable materials price variance may be caused by
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
b
86
New cards
The sales price variance is created by a difference between
* actual and standard contribution margin.
* actual and expected sales price.
* expected and standard net income.
* actual and expected sales volume.
* actual and standard contribution margin.
* actual and expected sales price.
* expected and standard net income.
* actual and expected sales volume.
b
87
New cards
For better control of direct material prices, when should direct material price variance be recognized?
* when material is purchased
* when material is issued from the storeroom
* when material is put into production
* when production is completed
* when material is purchased
* when material is issued from the storeroom
* when material is put into production
* when production is completed
a
88
New cards
If variable overhead is applied based on direct labour hours and there is an unfavourable labour efficiency variance,
* the materials usage variance will be unfavourable.
* the labour rate variance will be favourable.
* the variable overhead efficiency variance will be unfavourable.
* the variable overhead spending variance will be unfavourable.
* the materials usage variance will be unfavourable.
* the labour rate variance will be favourable.
* the variable overhead efficiency variance will be unfavourable.
* the variable overhead spending variance will be unfavourable.
c
89
New cards
Noelle's variable overhead efficiency variance would be
* £7000 favourable.
* £8000 unfavourable.
* £15 000 favourable.
* £23 000 unfavourable.
* £7000 favourable.
* £8000 unfavourable.
* £15 000 favourable.
* £23 000 unfavourable.
c
90
New cards
The labour rate variance is calculated as
* (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) × Actual direct labour hours used.
* (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) × Standard direct labour hours that should have been used.
* (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) × Actual hourly wage rate.
* (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) × Standard hourly wage rate.
* (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) × Actual direct labour hours used.
* (Actual hourly wage rate - Standard hourly wage rate) × Standard direct labour hours that should have been used.
* (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) × Actual hourly wage rate.
* (Actual direct labour hours used - Standard direct labour hours that should have been used) × Standard hourly wage rate.
a
91
New cards

The fixed overhead spending variance would be
* £2500 unfavourable.
* £2500 favourable.
* £1000 unfavourable.
* £1000 favourable.
* £2500 unfavourable.
* £2500 favourable.
* £1000 unfavourable.
* £1000 favourable.
d
92
New cards
An unfavourable materials price variance may be caused by
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
* excessive rework.
* a special price offered by suppliers.
* use of experienced workers.
* none of these.
d
93
New cards
The volume variance is caused by:
* the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the budgeted activity used in computing the fixed overhead rate.
* the difference between total budgeted fixed overhead and total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
* the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
* the difference between the standard fixed overhead rate and the actual fixed overhead rate.
* the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the budgeted activity used in computing the fixed overhead rate.
* the difference between total budgeted fixed overhead and total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
* the difference between the activity allowed for the actual output and the total standard fixed overhead assigned to production.
* the difference between the standard fixed overhead rate and the actual fixed overhead rate.
a
94
New cards

Rax’s variable standard cost per unit would be
* 78
* 192
* 246
* 222
* 78
* 192
* 246
* 222
c
95
New cards
The standard fixed overhead rate is calculated as
* Actual fixed overhead/Actual activity.
* Budgeted fixed overhead/Budgeted activity.
* Budgeted fixed overhead/Actual activity.
* Budgeted overhead/Budgeted activity.
* Actual fixed overhead/Actual activity.
* Budgeted fixed overhead/Budgeted activity.
* Budgeted fixed overhead/Actual activity.
* Budgeted overhead/Budgeted activity.
b
96
New cards
If actual fixed overhead was £120 000 and there was a £2600 favourable spending variance and a £2000 unfavourable volume variance, budgeted fixed overhead must have been
* £124 600.
* £122 000.
* £120 000.
* £122 600.
* £124 600.
* £122 000.
* £120 000.
* £122 600.
d
97
New cards

Noelle's fixed overhead spending variance would be
* £10 000 unfavourable.
* £11 000 unfavourable.
* £21 000 favourable.
* £31 000 favourable.
* £10 000 unfavourable.
* £11 000 unfavourable.
* £21 000 favourable.
* £31 000 favourable.
a
98
New cards

Noelle's standard fixed overhead rate is
* £14.82.
* £14.48.
* £14.34.
* £14.00 \n
* £14.82.
* £14.48.
* £14.34.
* £14.00 \n
d
99
New cards

Noelle's variable overhead spending variance would be
* £7000 favourable.
* £8000 unfavourable.
* £15 000 favourable.
* £23 000 unfavourable.
* £7000 favourable.
* £8000 unfavourable.
* £15 000 favourable.
* £23 000 unfavourable.
b
100
New cards
The volume variance provides information to management about
* utilisation of plant facilities.
* cost control.
* performance for evaluation purposes.
* all of these.
* utilisation of plant facilities.
* cost control.
* performance for evaluation purposes.
* all of these.
a