Unit 5: The Brain & Neurotransmitters
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psych Module 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
biological psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological(genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes.
What other names are some biological psychologists referred to as?
behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
levels of analysis
the differing complementary views, from biological to psychological to social-cultural, for analyzing any given phenomenon
neuroplasticity
the brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
lesion
tissue destruction; brain lesions may occur naturally(from disease or trauma), during surgery, or experimentally(using electrodes to destroy brain cells)
EEG(electroencephalogram)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain’s surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
MEG(magnetoencephalography)
a brain-imaging technique that measures magnetic field from the brains natural electrical activity
CT(computed tomography)
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain structure
PET(position emission tomography)
a technique for detecting brain activity that displays where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
MRI(magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer generated images of soft tissue(brain anatomy)
fMRI(functional MRI)
a technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fMRIs show function as well as structure
fNIRS(functional near-infrared spectroscopy)
shines infrared light on blood molecules to identify brain activity
hindbrain
consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions, such as breathing, sleeping, and wakefulness, as well as coordination and balance
midbrain
found stop the brain stem; connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movement, and transmits auditory and visual information
forebrain
brainstem
the central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brain stem is responsible for automatic survival functions
thalamus
the forebrain’s sensory control center, located on top of the brain stem, it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
limbic system
neural system located mostly in the forebrain—below the cerebral hemispheres—that includes the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland; associated with emotions and drives
amygdala
two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
hypothalamus
lies below(hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities(eating, drinking, body temp), helps govern the endocrine system, and is linked to emotion and reward
hippocampus
a neural center in the limbic system that helps process explicit (conscious) memories—of facts and events—for storage
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the forebrain’s cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center
frontal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead. They enable linguistic processing
parietal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; it receives sensory input for touch and body position
occipital lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; it includes areas that receive information from the visual fields
temporal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; it includes the auditory areas that receive information primarily from the opposite ear. Also enable language processing
motor cortex
a cerebral cortex area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
somatosensory cortex
a cerebral cortex area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensation
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions, but rather are rather involved in higher mental function such a as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
neuron
nerve cells. Transport messages/signals between different parts of the body(mainly brain and other parts)
agonist
enhances the effect of a neurotransmitter. agonists mimics the neurotransmitter by occupying the receptors and activate them. The neurotransmitters are then trapped in the synaptic gap
antagonist
prevents the effects of neurotransmitter. Drugs that occupy receptors but do not activate the neurons and increases reuptake from presynaptic neuron
dopamine
helps control voluntary movement and affects sleep, mood, attention, learning, and the ability to recognize opportunities for rewarding experiences.
Excess: Schizophrenia
Deficit: Parkinson’s disease
serotonin
involved in the regulation of sleep, mood, attention, and learning. Also affects hunger and aggression.
Deficit: Depression
GABA
plays a key function in the brain by inhibiting many neurons from firing. Serves as the brain’s brake pedal, helping to regulate neuron firing and control the precision of the signal being carried from one neuron to the next.
acetylcholine(ACH)
involved in voluntary movement and muscle contraction, learning, memory, and sleep
deficit: Dementia and Alzheimers
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal(“fight or flight” response)
Glutamate
has a key role in exciting many neurons to fire and is especially involved in learning and memory
Endorphins
the body’s natural opiates—substances that reduce or eliminate pain
Neuropeptide(Substance P)
Transmitting pain signals between the brain and body
Drugs
External chemicals that have an impact on the function of neurotransmitters
stimulants
speed up neural activity and arouse body function
What are some common stimulants?
caffeine
nicotine
amphetamines
methamphetamine
cocaine
ecstasy/MDMA(methylenedioxymethamphetamine)
Depressants and Opioids
Depresses neural activity and slows down body function. Opioids are a kind of depressant that act as painkillers.
What are some common depressants and opioids?
alcohol
barbiturate(tranquilizers
opiates/narcotics
rohypnol (date rape drug)
hallucinogens
drugs that distort perceptions/evoke sensory images(hallucinations)
What are some common hallucinogens???
LSD
Ecstasy
THC(marijuana)
tolerance
requiring larger and larger doses of a drug to feel the same effect
addiction
disease involving physical and/or psychological dependence
withdrawl
symptoms associated with stopping use
neurotransmitters
internal chemicals that allow neurons to communicate throughout the body
glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low we feel hunger.
set point
the point at which the “weight thermostat” may be set. When the body falls below this weight, increased hunger and lower metabolic rate may combine to restore lost weight
basal metabolic rate
the body’s resting rate of energy output
obesity
defined as a BMI(body mass index) of 30 or higher, which is calculated from our weight-to-height ratio.(overweight is BMI of 25-30)
Phrenology
made by Franz Gall (German physician) in the early 1800’s. Said brain size correlates with higher mental ability. Bumps on the skull could reveal mental abilities and character traits.
Phineas Gage
had a tamping iron go through his skull, survived and
medulla
part of the hindbrain that controls life-maintaining processes such as breathing and heartbeat. also triggers vomiting and sneezing
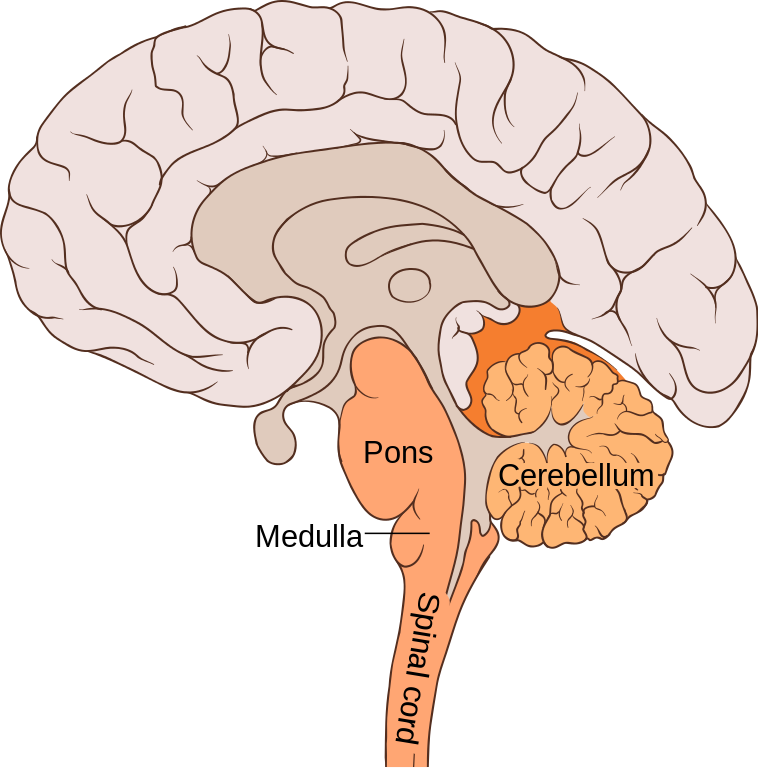
pons
part of the hindbrain that connects the spinal cord to the brain and is involved in autonomic processing such as the sleep-wake cycle
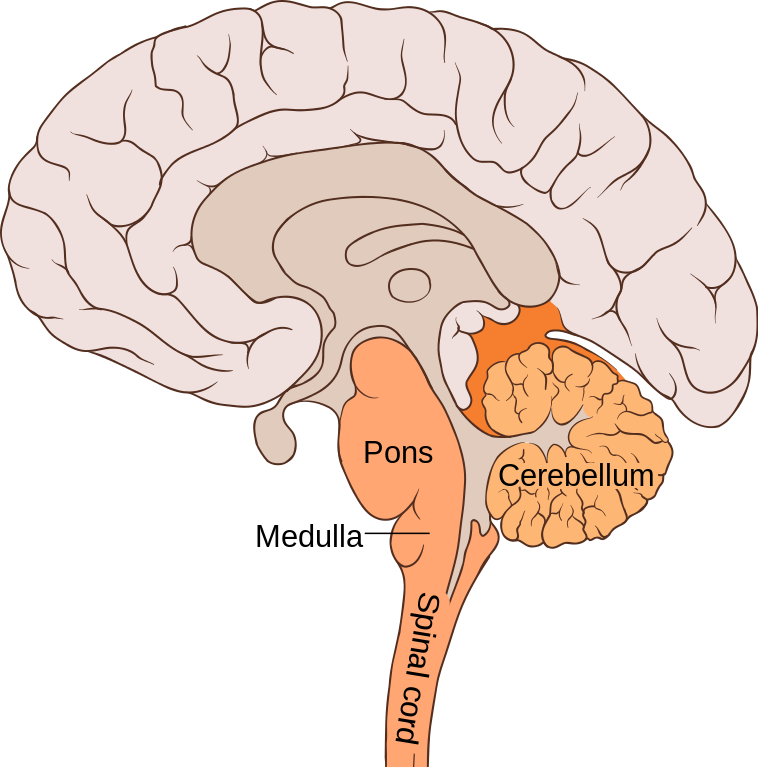
cerebellum
part of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills such as coordination, balance, and posture and nonverbal learning and memory. Is severely affected by alcohol
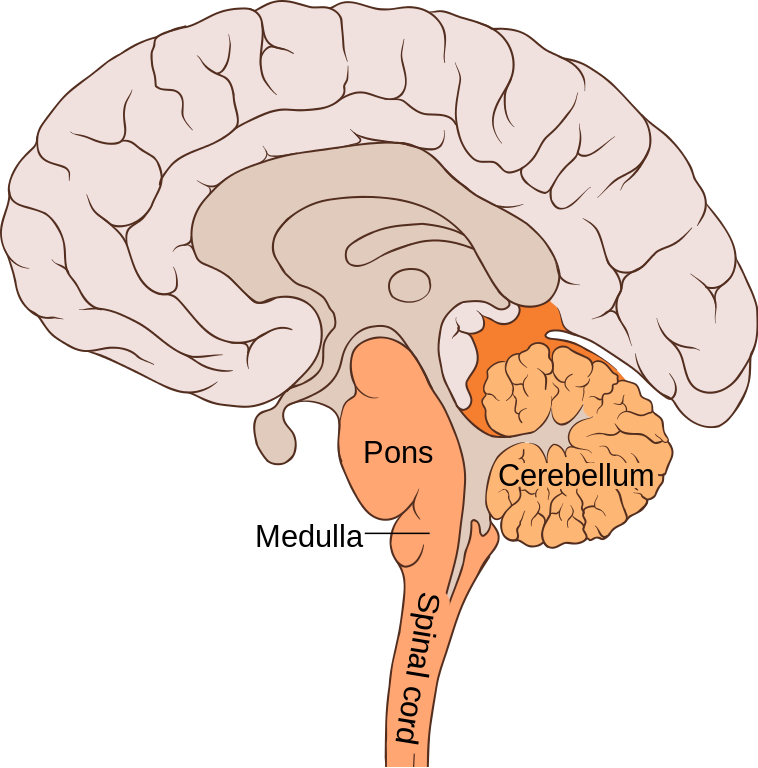
basal ganglia
Part of the brain at the bottom of the forebrain and top of the midbrain that initiates movements
reticular formation
part of the pons that controls arousal and consciousness
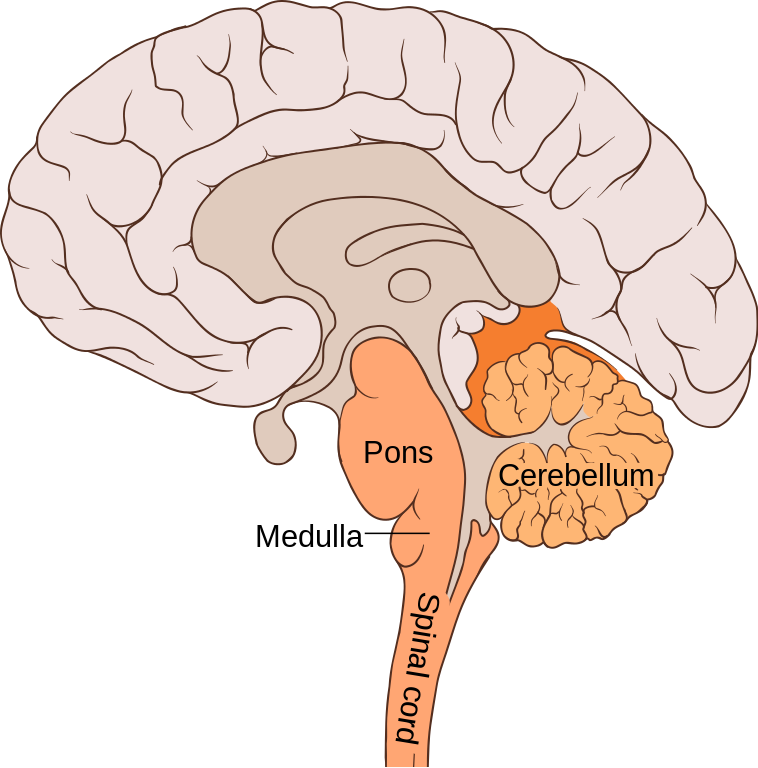
thalamus
part of the forebrain that acts as the