chem (h) - module 1, lesson 2
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
scientific notation, base and derived units, and unit conversions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
define matter.
anything that has volume and mass; is tangible
define volume.
the space something takes up
define mass.
how much matter is present in something
what is a quantitative observation?
a property that is tied to numbers (ex. temperature or distance)
what is a qualitative observation?
an observable property NOT tied to numbers (ex. color or texture)
write out 3,000 in scientific notation.
3 × 10³
why do we use scientific notation?
to make numbers more compact & adjust their scale
write 2,500,000 in scientific notation.
2.5 × 10^6
write out 0.089 in scientific notation.
8.9 × 10^-2
take 4.3 × 10^-6 out of scientific notation
0.0000043
take 7.70 × 10^5 out of scientific notation.
7,700,000
what is a unit?
a unit is a label that represents an exact quantity.
what 2 pieces of information do units give about a measurement?
the dimension—or what type of measurement—and the scale—the approximate size of the measurement.
what is a unit system?
a unit system is a group of units that are related to each other/defined relative to each other.
give examples of unit systems.
the metric system, imperial/standard system, and the international system (SI)

fill in the white blank according to the information given.
speed
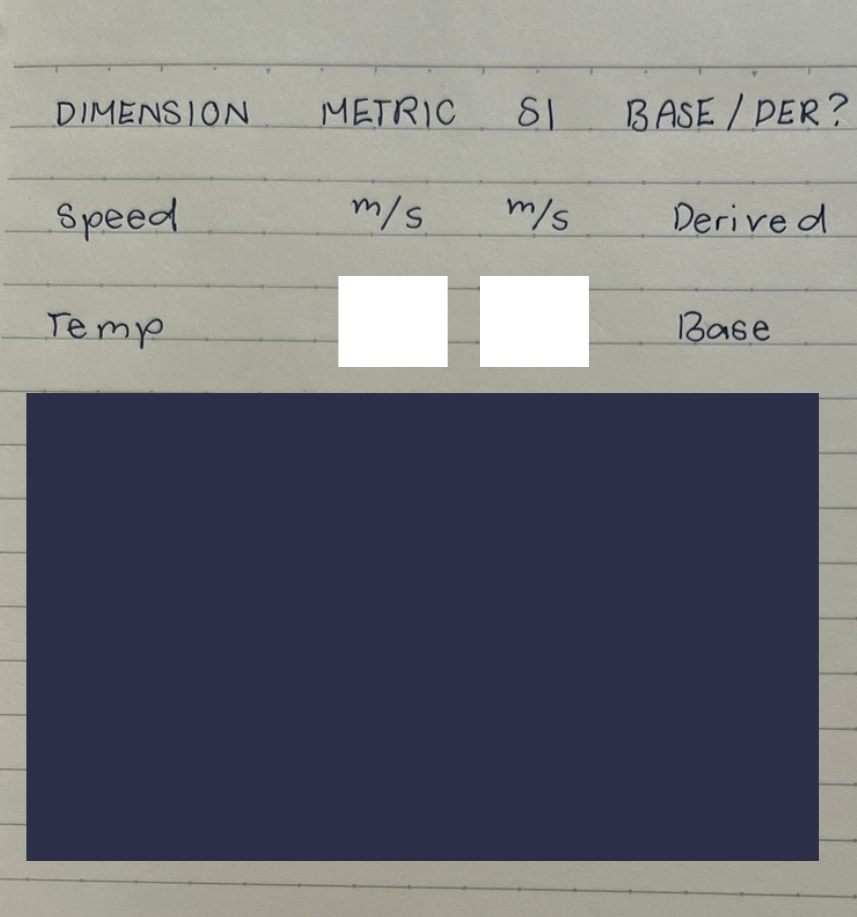
fill in the white blanks according to the information given.
°C, K

fill in the white blanks according to the information given.
kg, base unit

fill in the white blanks according to the information given.
volume, L

fill in the white blanks according to the information given.
m, base

fill in the white blanks according to the information given.
s, s
what is the difference between base units and derived units?
base units are directly measured, while derived units are calculated instead of directly measured.
list the SI prefixes in order from greatest to least (each being 3 decimal places apart).
M k __ m µ n

fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
^6

fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
kilo (k)

fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
__/no prefix

fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
^-3

fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
micro (µ) ^-6
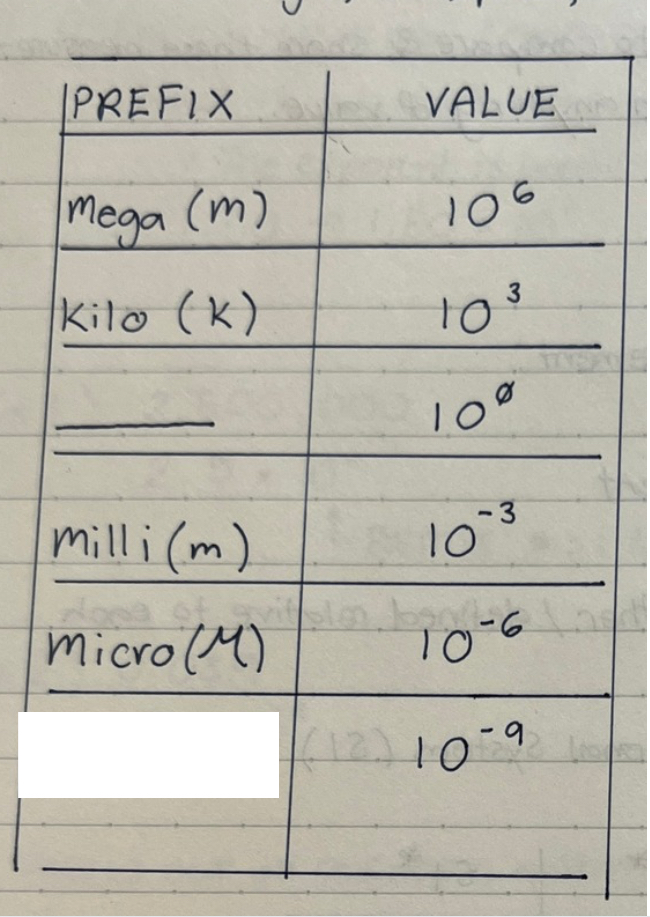
fill out the white blank(s) on the chart
nano (n)