Executive Leadership Final
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Authentic Leadership
focuses on whether leadership is genuine and is about the authenticity of leaders and their leadership
Authentic Leadership- Intrapersonal Perspective
Focuses on the leader and leader knowledge, self-regulation, and self-concept. Emphasizes the life experiences of the leader
Authentic Leadership- Interpersonal Process
Relational, created by leaders and followers together. Results from not only the leader alone, but also the responses from the followers.
Authentic Leadership- Developmental Perspective
Views that authentic leadership can be nurtured, not a fixed trait. Develops over life and is triggered by critical life events.
Components of Authentic Leadership (Practical Approach)
- Self-awareness
- Internalized moral perspective
- Balanced processing
- Relational transparency
Self-awareness in Authentic Leadership
Refers to the personal insights of the leader. It is not an end in itself but a process in which individuals understand themselves, including their strengths and weaknesses, and the impact they have on others.
Internalized moral perspective in Authentic Leadership
Refers to a self-regulatory process whereby individuals use their internal moral standards and values to guide their behavior rather than allow outside pressures to control them
Balanced Processing in Authentic Leadership
Refers to an individual's ability to analyze information objectively and explore other people's opinions before making a decision. It also means avoiding favoritism about certain issues and remaining unbiased.
Relational Transparency in Authentic Leadership
Refers to being open and honest in presenting one's true self to others. Occurs when individuals share their core feelings, motives, and inclinations with others in an appropriate manner.
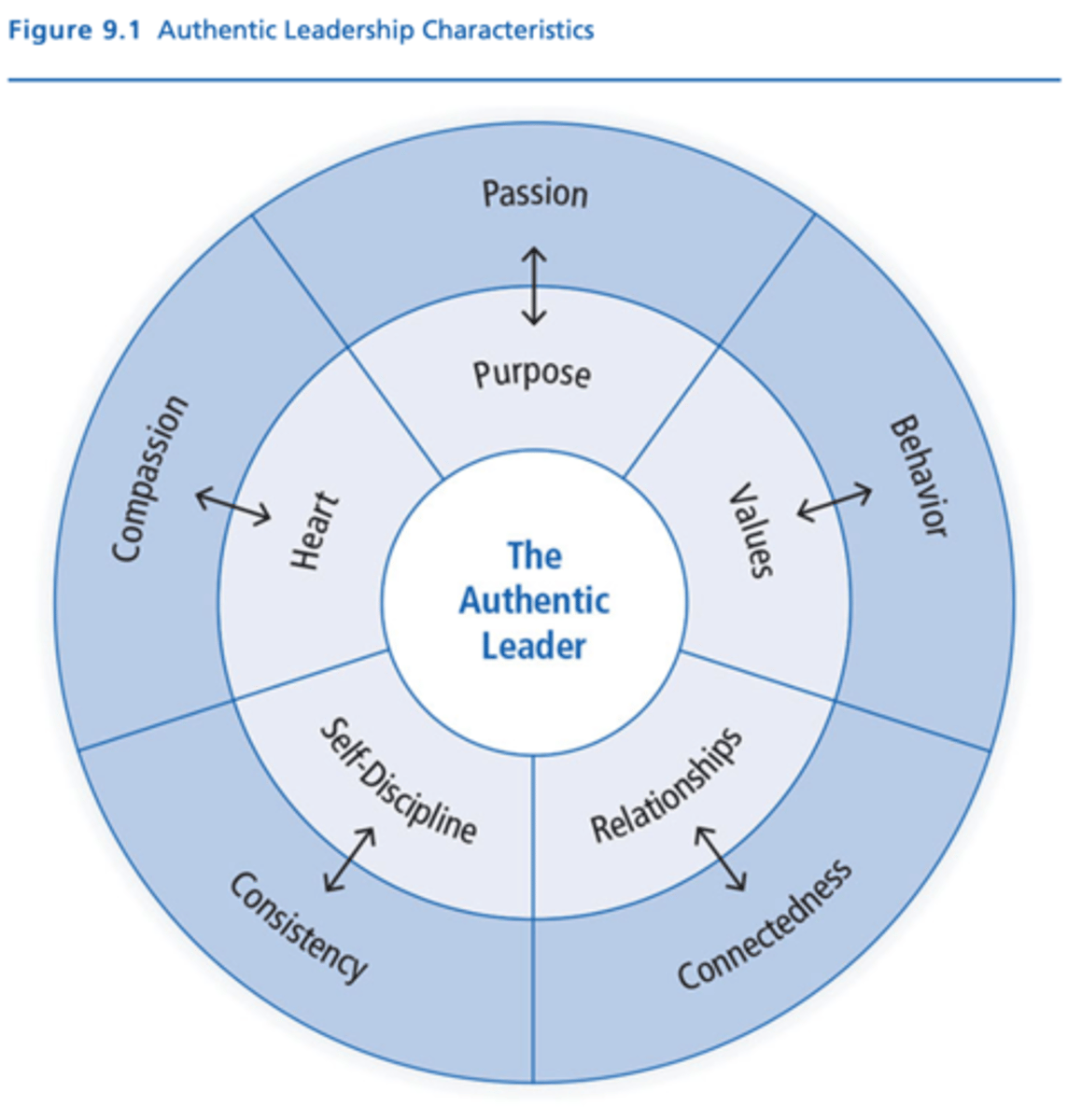
Dimensions of Authentic Leadership (Practical Approach)
Characteristic --> Dimension
- Purpose --> Passion
- Values --> Behavior
- Relationships --> Connectedness
- Self Discipline --> Consistency
- Heart --> Compassion
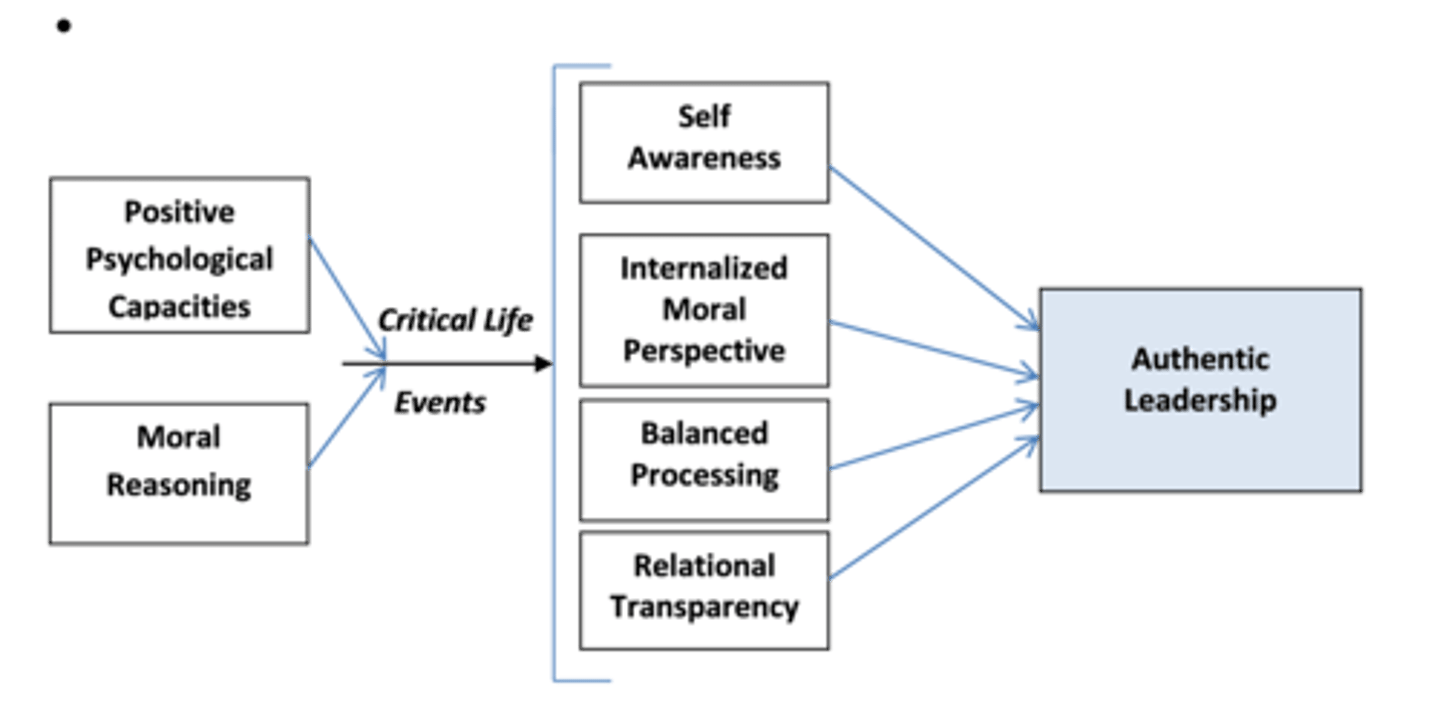
Authentic Leadership in the Theoretical Approach
a pattern of leader behavior that draws upon and promotes both positive psychological capacities and a positive ethical climate, to foster greater self-awareness, an internalized moral perspective, balanced processing of information, and relational transparency on the part of leaders working with followers, fostering positive self-development
Factors the Influence Authentic Leadership
- Positive psychological capacities
- Moral reasoning
- Critical life events
- Capacity for confidence, hope, optimism, and resilience determines hows individuals perceive the critical life events
Greenleaf's Approach to Servant Leadership
Servant leadership begins with the natural feeling that one wants to serve, to serve first. Then conscious choice brings one to aspire to lead. The difference manifests itself in the care taken by the servant- first to make sure that other people's highest priority needs are being served
What sets apart servant leadership from other leadership approaches?
Its focus on serving these multiple stakeholders
Problem to Servant Leadership
Servant Leadership is a paradox. It seems contradictory and challenges traditional beliefs about leadership, but offers a unique perspective
Characteristics of Servant Leadership
1. listening
2. empathy
3. healing
4. awareness
5. persuasion
6. conceptualization
7. foresight
8. stewardship
9. commitment to the growth of people
10. building community
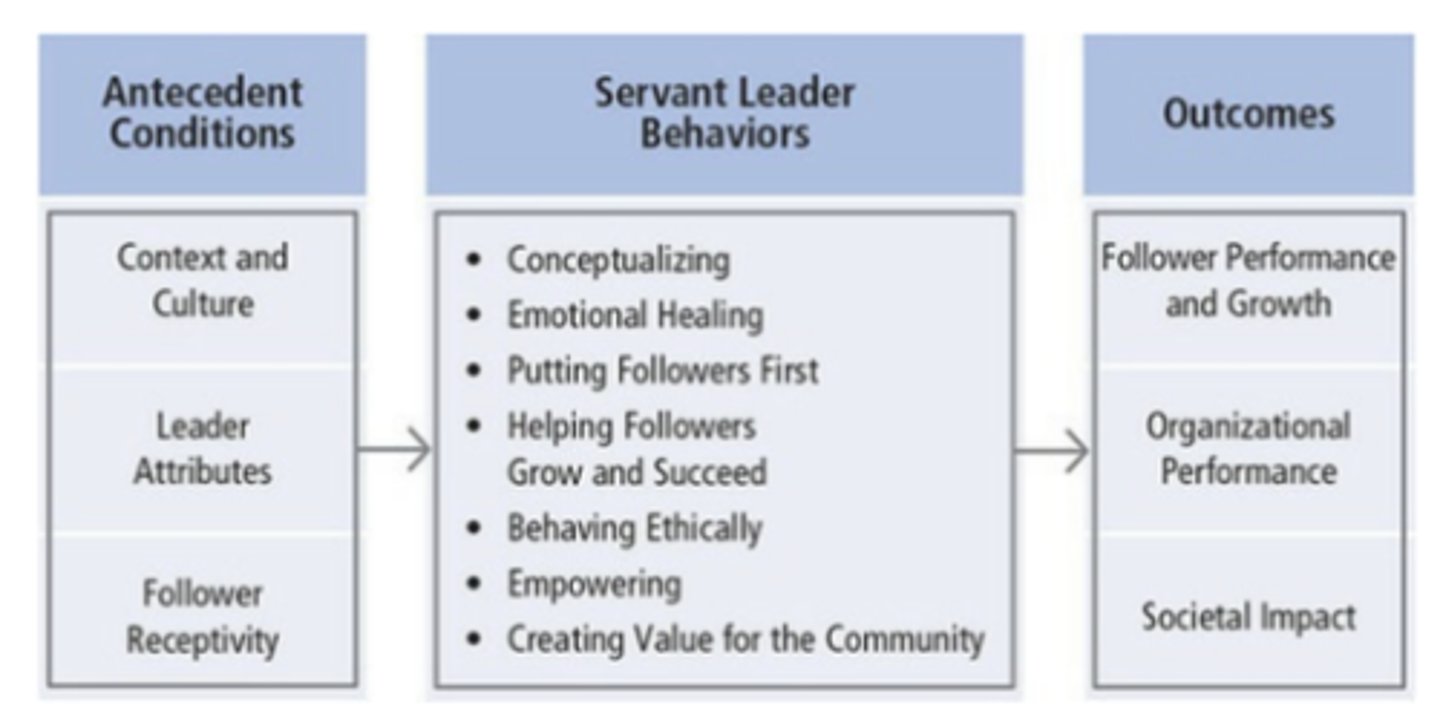
Antecedent Conditions of Servant Leadership
1. context and culture
2. leader attributes
3. follower receptivity
Context & Culture in Servant Leadership
A particular culture and the context of the organization (like industry or credo) influences the way servant leadershio is able to be achieved
Leader Attributes in Servant Leadership
The qualities and disposition of a leader influence the servant leadership process
Follower Receptivity in Servant Leadership
Influences the personal and organizational job performance outcomes of servant leadership. Servant leadership benefits followers with a higher level of self-interest but can negatively affect those who don't want it and may make them feel micromanaged.
Behaviors of Servant Leaders
- Conceptualizing (Understanding of Organization)
- Emotional Healing (Sensitive to the well-being of others)
- Putting Followers First (DEFINING CHARACTERISTIC)
- Helping followers grow and succeed
- Behaving ethically
- Empowering
- Creating Value for the Community
Outcomes of Servant Leadership
- follower performance and growth
- organizational performance
- societal impact
What differentiates adaptive leadership from authentic leadership and the trait approach?
Stresses the behaviors of the leader in relation to the work of followers in the situations in which they find themselves
Adaptive Leadership according to Heifetz
Adaptive leadership is the practice of mobilizing people to tackle tough challenges and thrive. Also helping others explore and change their values
Activities Adaptive Leaders do for others
- mobilize
- motivate
- organize
- orient
- focus
Biases of Adaptive Leadership
- System Bias
- Biological Bias
- Service Orientation Bias
- Psychotheapeutic Bias
System Bias in Adaptive Leadership
Assumes that many problems people face are embedded in complicated interactive systems
Biological Bias in Adaptive Leadership
Recognizes that people develop and evolve as a result of having to adapt to internal and external environments
Service Orientation Bias in Adaptive Leadership
Leaders should use their expertise or bias to serve others by diagnosing their problems and helping them find solutions
Psychotherapeutic Bias in Adaptive Leadership
Understands that people need a supportive environment and adapt more successfully when they face difficult problems directly, learn to distinguish between fantasy and reality, resolve internal conflicts, and learn new attitudes and behaviors
Situational Challenges of Adaptive Leadership
- technical
- technical and adaptive
- adaptive

Technical Challenges of Adaptive Leadership
Problems in the workplace, community, or self that are clearly defined, with known solutions that can be implemented through existing organizational procedures.
Adaptive Challenges of Adaptive Leadership
Problems that are not clear-cut or easy to identify. Cannot be solved normally by the organization or by the leader's expertise and requires leaders to others to define challenges and implement solutions. Often resisted because it requires changes in people's beliefs, priorities, roles, and values.
Technical & Adaptive Challenges of Adaptive Leadership
Challenges are clearly defined but do not have distinct straightforward solutions within the existing organizational system. The responsibility of tackling this type of challenge is shared between the leader and the people.
Leader Behaviors in the Process of Adaptive Leadership
- Get on the Balcony
- Identify the Adaptive Challenge
- Regulate Distress
- Maintain Disciplined Attention
- Give the Work Back to the People
- Protect Leadership Voices from Below
Adaptive Work in Adaptive Leadership
The process toward which adaptive leaders direct their work. It is the focus and intended goal of adaptive leadership. Adaptive work develops from the communication processes that occur between the leader and followers but is primarily the work of followers.
Holding Environment of Adaptive Leadership
Place where adaptive work can be conducted and people can feel safe as they confront possible changes in their roles, priorities, and values. Encourages interaction between leaders and followers.
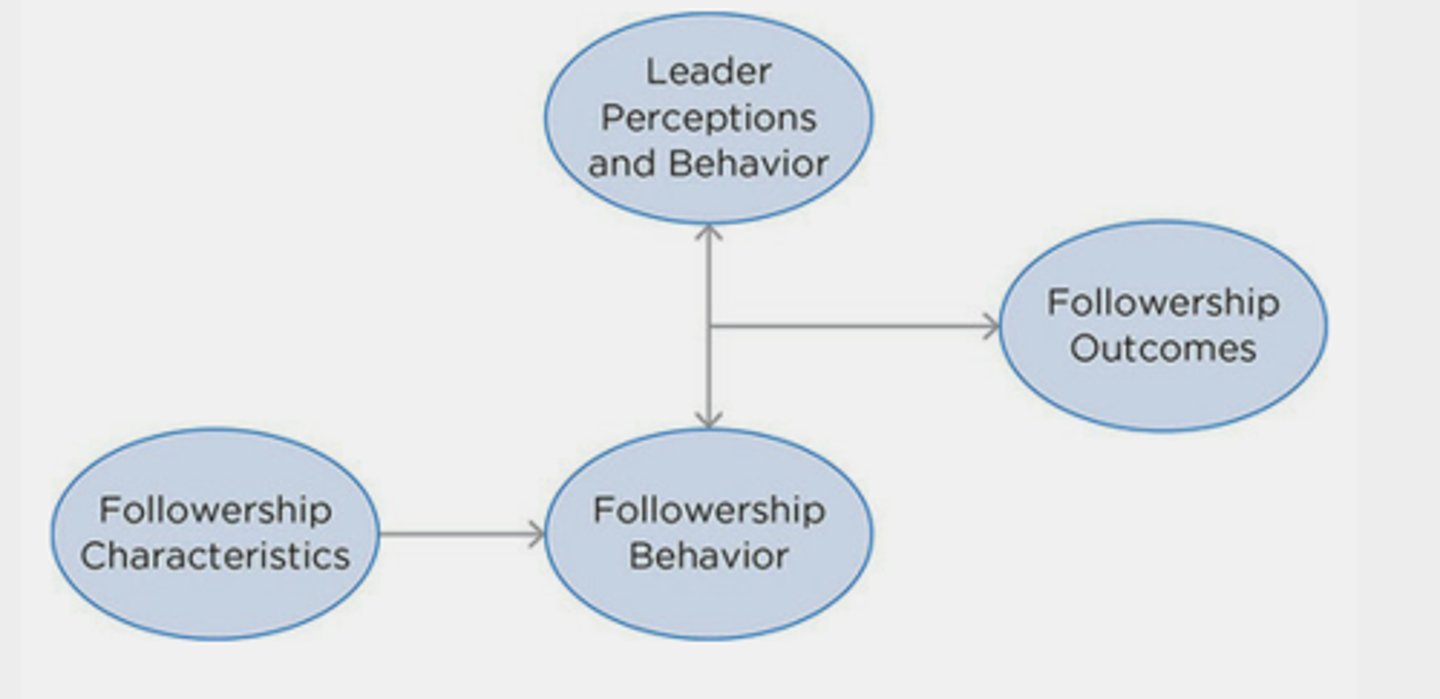
Followership
A process whereby an individual or individuals accept the influence of others to accomplish a common goal.
Ethical Dimension of Followership
Followership carries a responsibility to consider the morality of one's actions and the rightness or wrongness of the outcomes of what one does as a follower. The character and behavior of followers has an impact on leaders and on organizational outcomes.
Categories of Followership
- Role-based
- Relational-Based
Role-based Perspective of Followership
Focus is on the typical roles followers enact while occupying a formal or informal position within a hierarchical system.
Followers' behaviors affect the leader and organizational outcomes.
Relational-based Perspective of Followership
Based on social constructivism: People create meaning about their reality as they interact with each other.
Followership is co-created by the leader and follower in a given situation through communication.
Leadership occurs as people exert influence on each other and respond to those influence attempts.
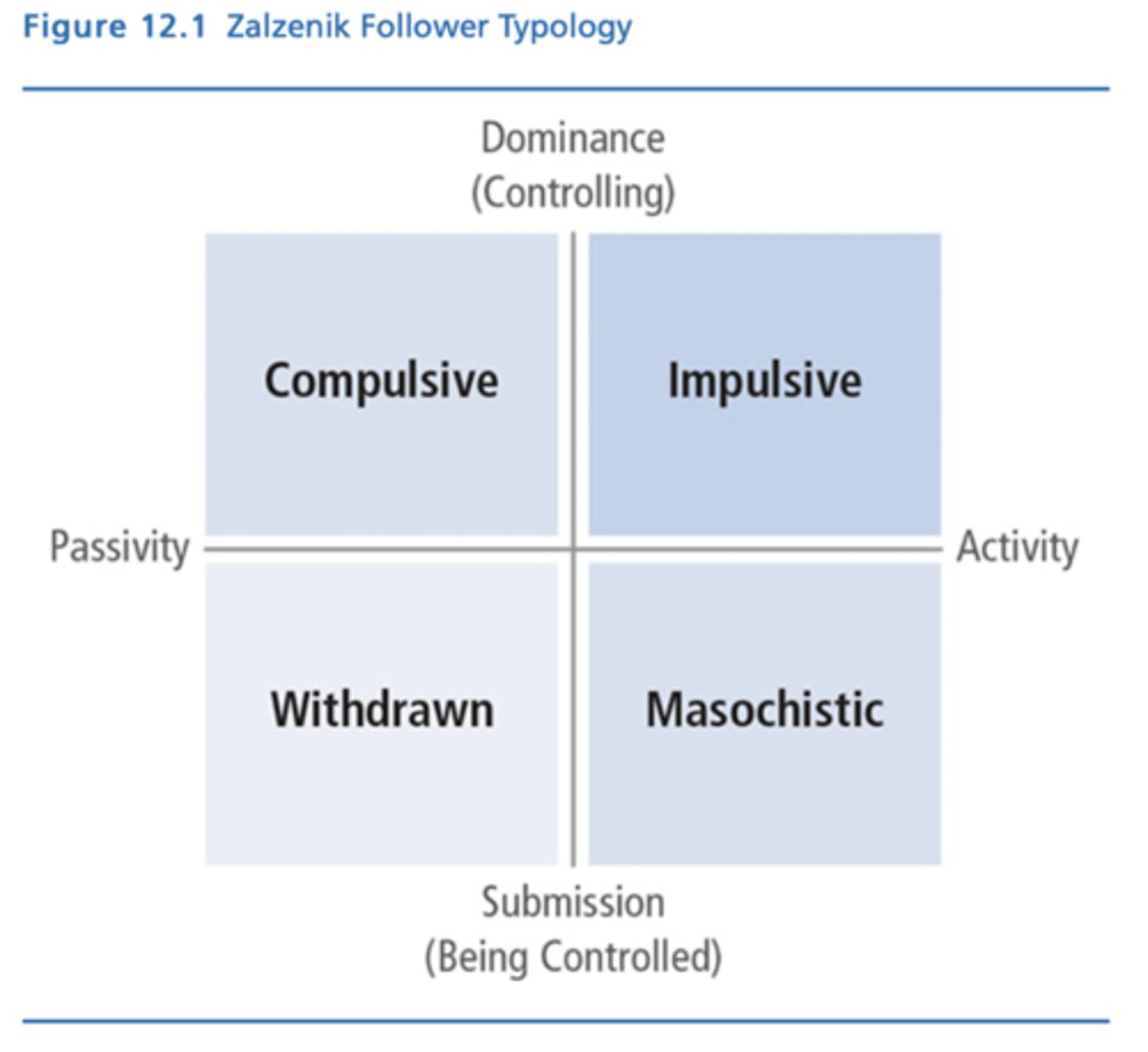
Zaleznik Typology of Followership
Displays followers' behaviors along two axes: dominance-submission and activity-passivity
Kelley Typology of Followership
The most recognized followership typology. Believes followers are enormously valuable to organizations and that the power of followers often goes unrecognized.
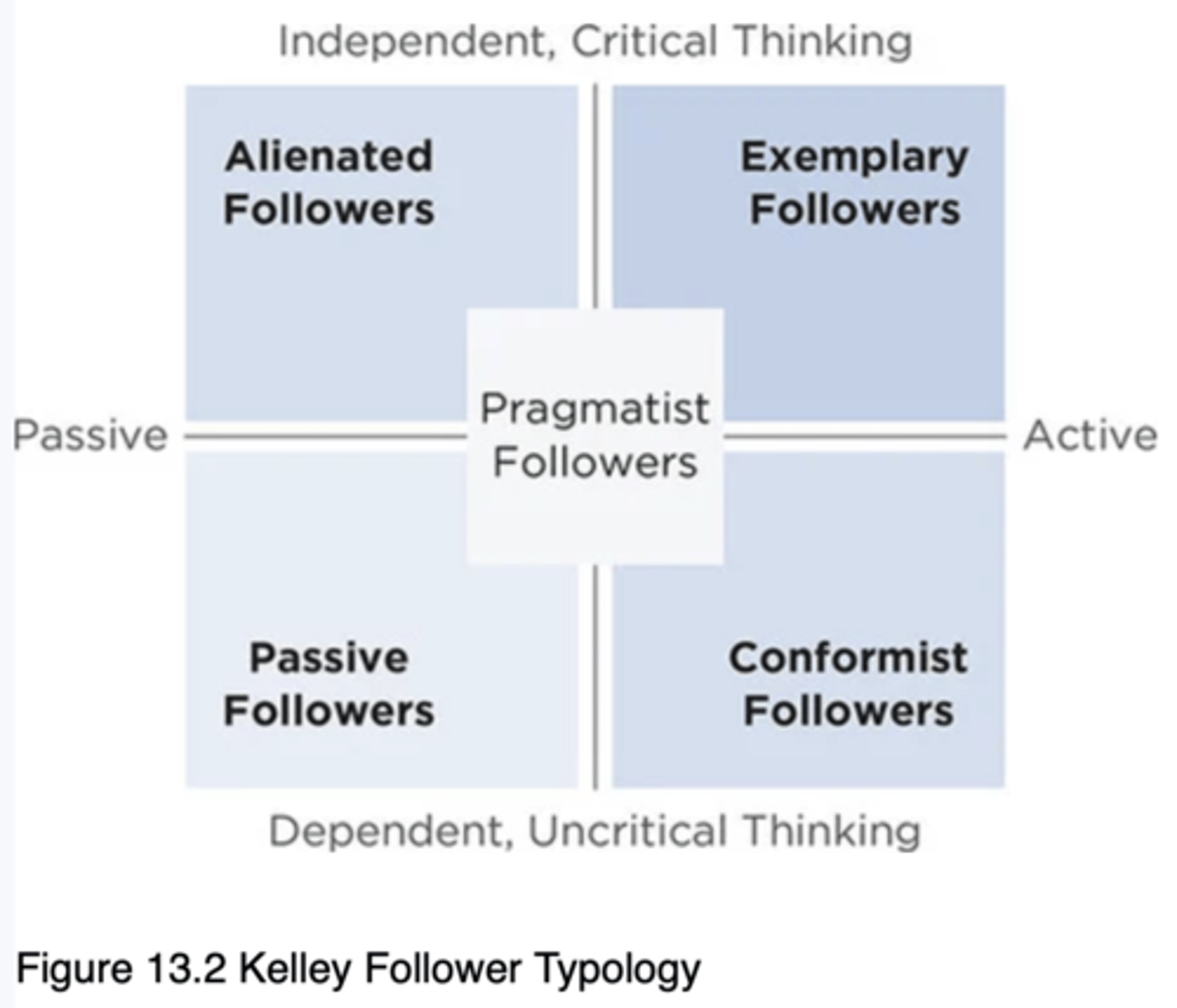
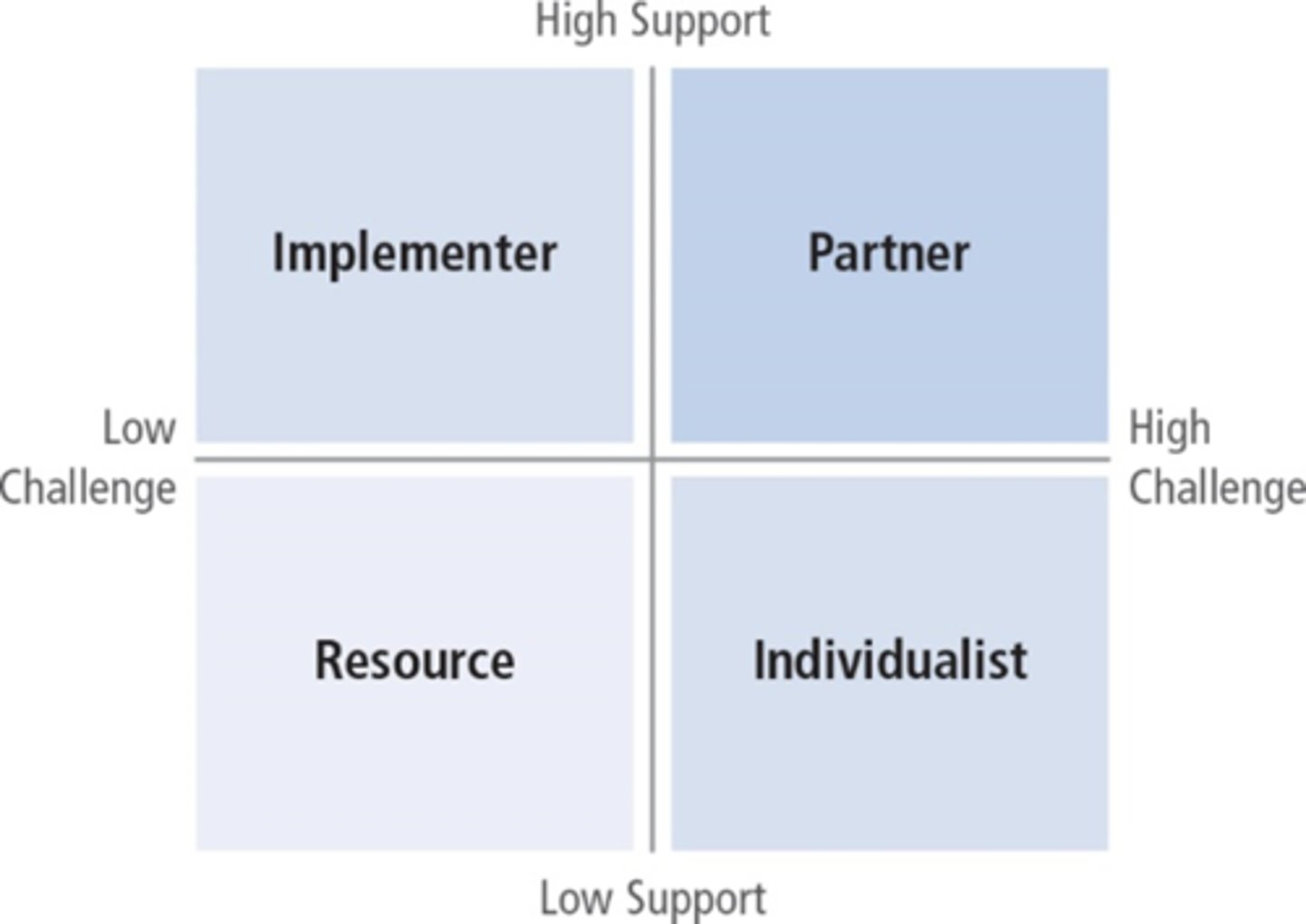
Chaleff Typology of Followership
Followers serve a common purpose along with leaders and that both leaders and followers work to achieve common outcomes. Followers need to take a more proactive role
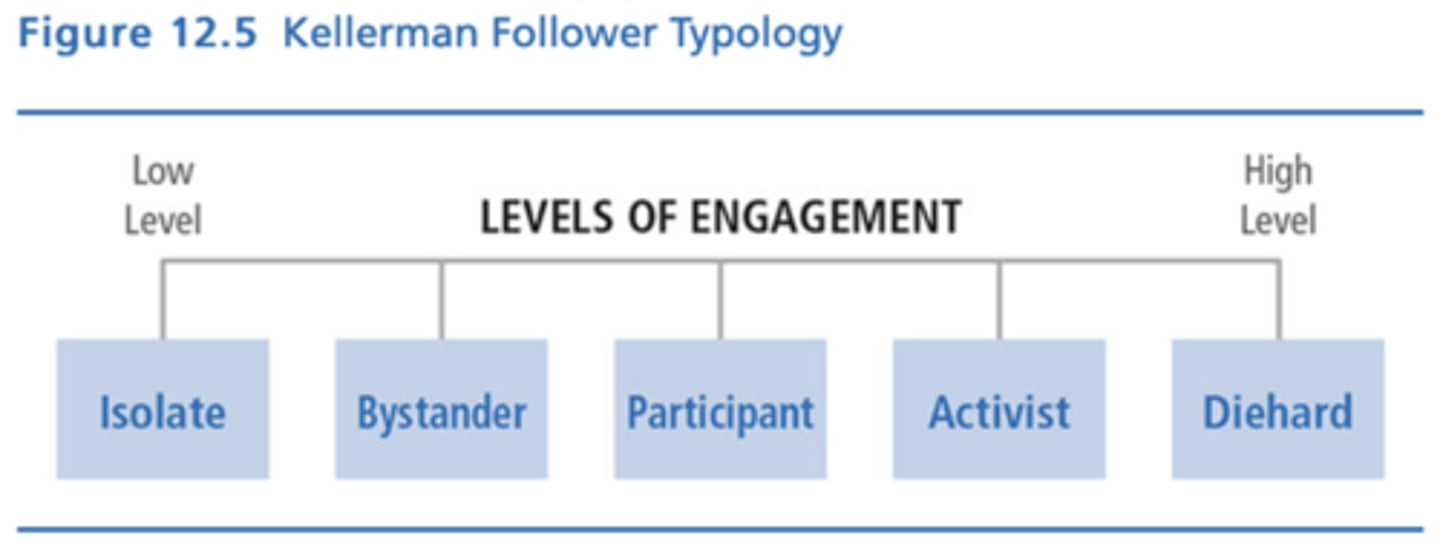
Kellerman Typology of Followership
The importance of leaders tends to be overestimated because they generally have more power, authority, and influence, while the importance of followers is underestimated.
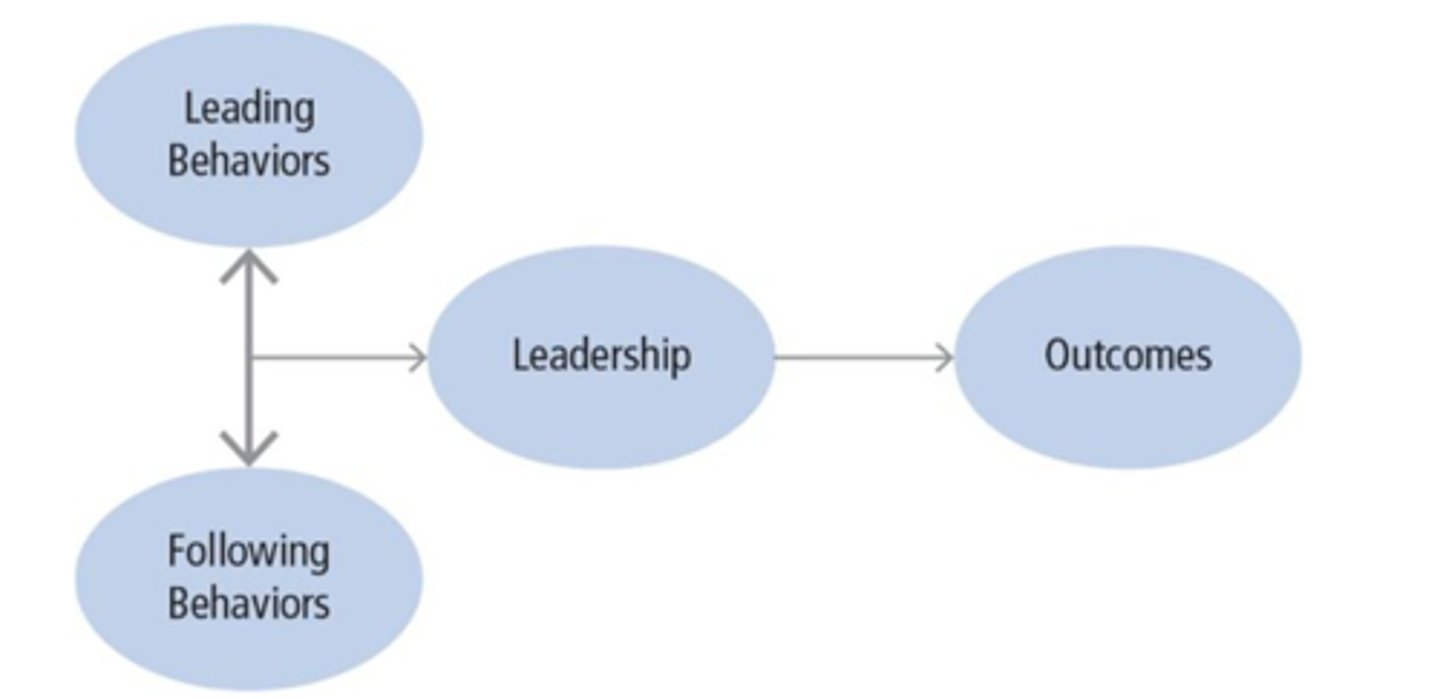
Leadership Co-Created Process Theoretical Approach to Followership
Conceptualizes followership as a give-and-take process where one individual's following behaviors interact with another individual's leading behaviors to create leadership and its resulting outcomes
Reversing the Lens Approach to Followership
Focuses on how followers affect leaders and organizational outcomes. Emphasizes that followers can be change agents
Ethics
- A derivative of the Greek word ethos, meaning customs, conduct, or character.
- Concerned with the values and morals an individual or society ascribes as desirable or appropriate.
- Provides a system of rules or principles as a guide in making decisions about what is right/wrong and good/bad in a specific situation
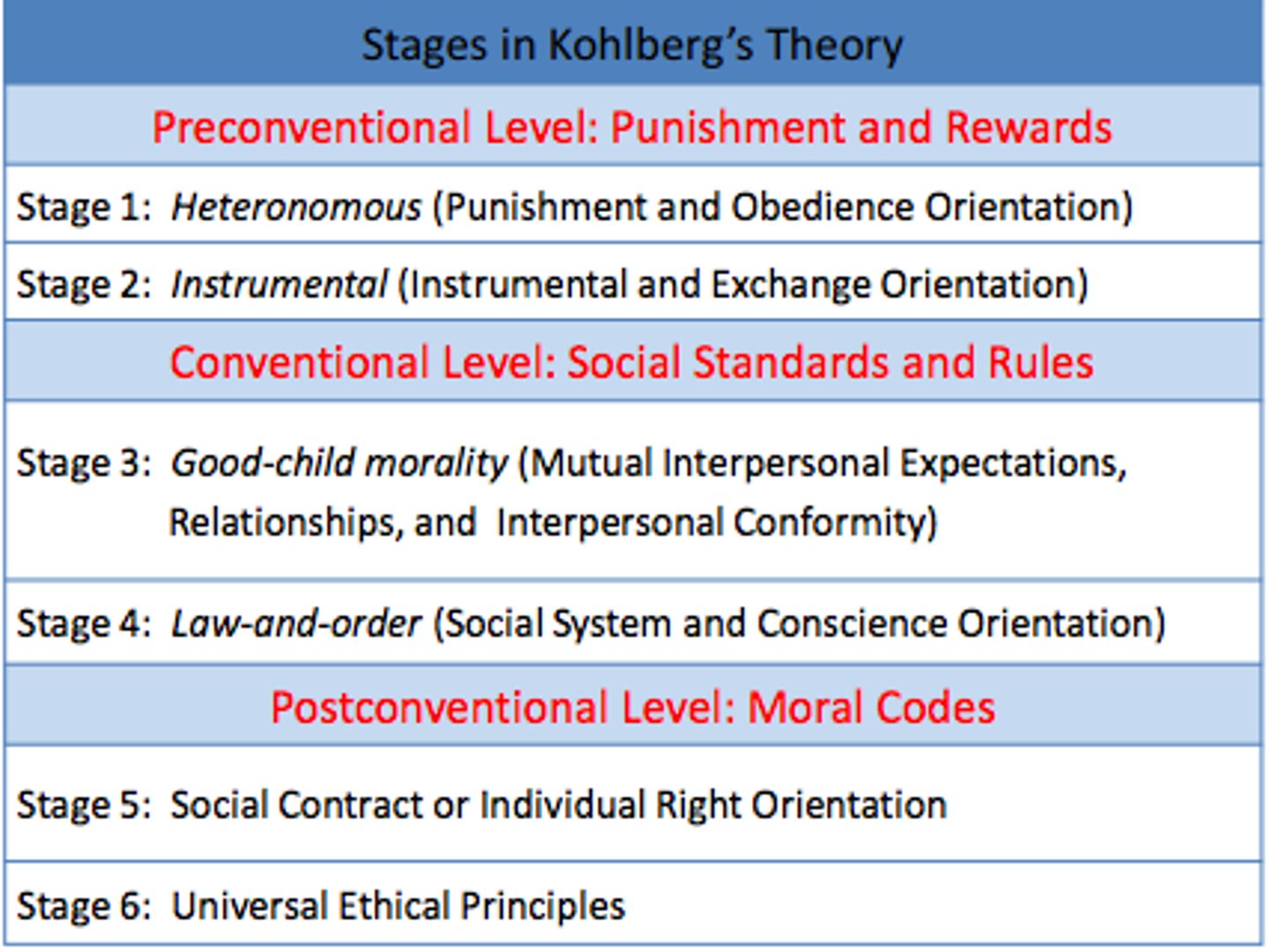
Kohlberg's Stages of Moral Development
preconventional, conventional, postconventional
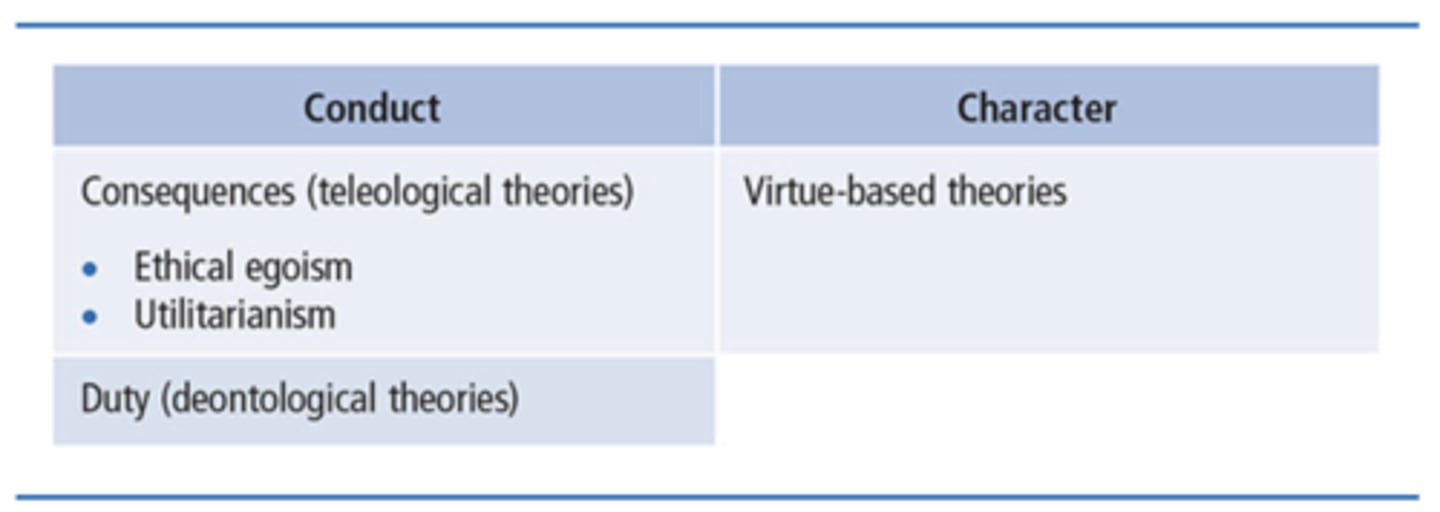
Domains of Ethical Theories
Conduct (Consequences of behaviors and Duty of behaviors) and Character
Approaches to Making Decisions regarding Ethical Conduct
- Ethical Egoism
- Utilitarianism
- Altruism

Ethical Egoism
A person should act so as to create the greatest good for themselves.
Utilitarianism
We should behave so as to create the greatest good for the greatest number
Altruism
Actions are moral if their primary purpose is to promote the best interests of others
Duty Ethics
Whether a given action is ethical rests not only with its consequences (teleological), but also with whether the action itself is good. A leader's actions are moral if the leader has a moral right to do them, if the actions do not infringe on others' rights, and if the actions further the moral rights of others
Virtue-Based Ethics
About being and becoming a good, worthy human being. Although people can learn and develop good values, virtues are present in one's disposition. When practiced over time, good values become habitual, and part of the people themselves.
Centrality of Ethics
Ethics is central to leadership because of the nature of the process of influence, the need to engage followers in accomplishing mutual goals, and the impact leaders have on the organization's values.
Dark Side of Leadership
The destructive and toxic side of leadership in that a leader uses leadership for personal ends
Criticisms of Ethical Leadership
- Lacks a strong body of traditional research findings to substantiate the theoretical foundations
- Relies heavily on writings of just a few individuals that are primarily descriptive and anecdotal in nature, and are strongly influenced by personal opinion and a particular worldview
- Focused primarily on the Western world and AngloAmerican countries
- Generational differences in ethical perspectives
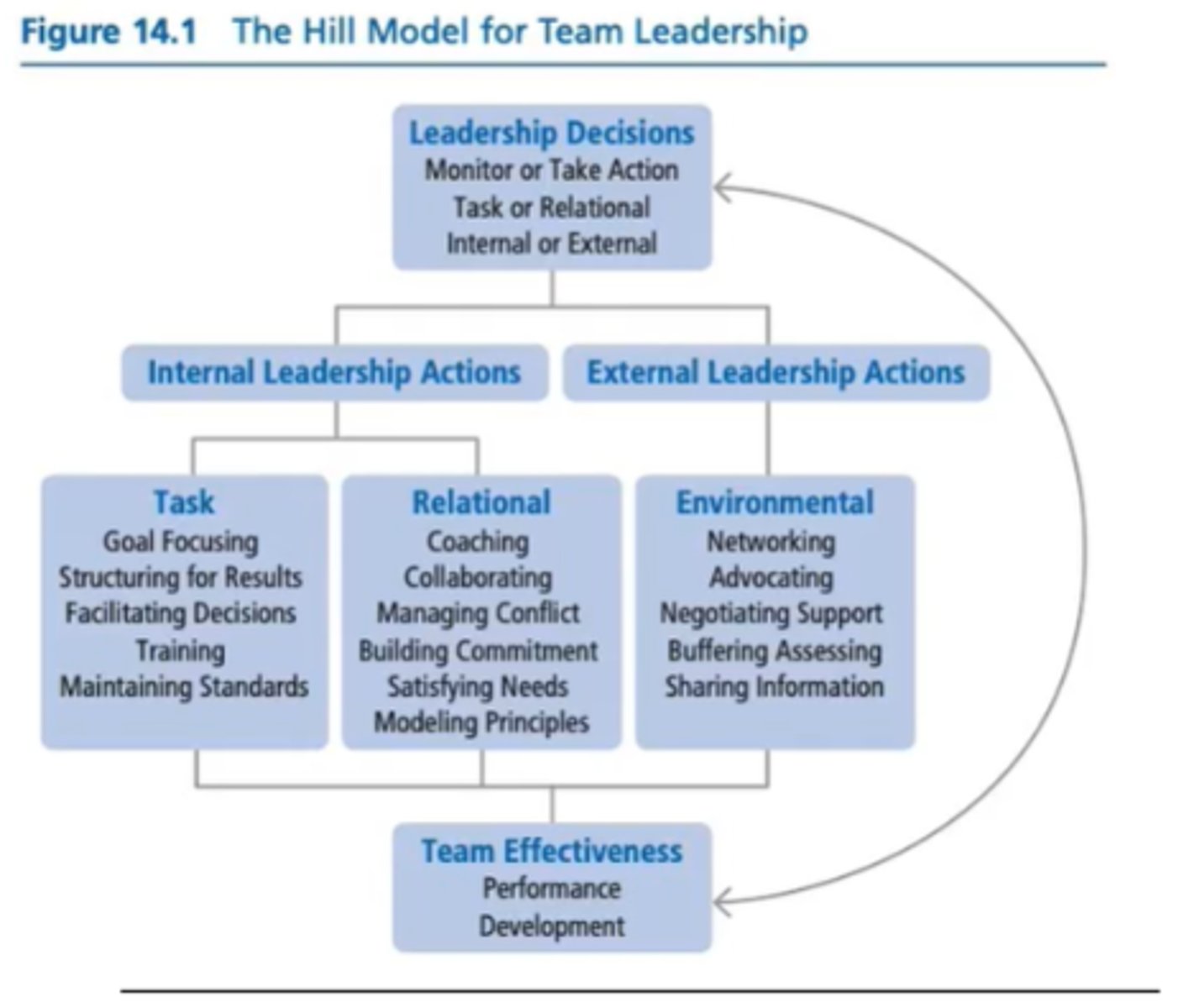
Team Effectiveness of the Hill Model
Team Effectiveness focuses on team excellence or the desired outcomes of teamwork.
- Performance (Task Accomplishment)
- Development (Team Maintenance)
Heterarchy
Fluid shifting of power within teams
Organization Culture MUST of Successful Teams
Organizational culture must support employee involvement
Process Oriented Team Leadership
Effective team leadership facilitates team success and helps teams to avoid team failure. Effective leadership processes are the most critical factor in team success
The Hill Model for Team Leadership
Provides leader or designated team member(s) with a framework to assemble a mental model to help diagnose team problems, and take appropriate action to correct team problems
Leadership Decisions
The major decisions the team's leadership needs to make when determining whether and how to intervene to improve team functioning.
1. monitor or take action
2. intervene to meet task or relational needs
3. intervene internally or externally
Monitor or Take Action
The first decision confronting the team's leadership is whether to keep observing the team or to take action to help the team
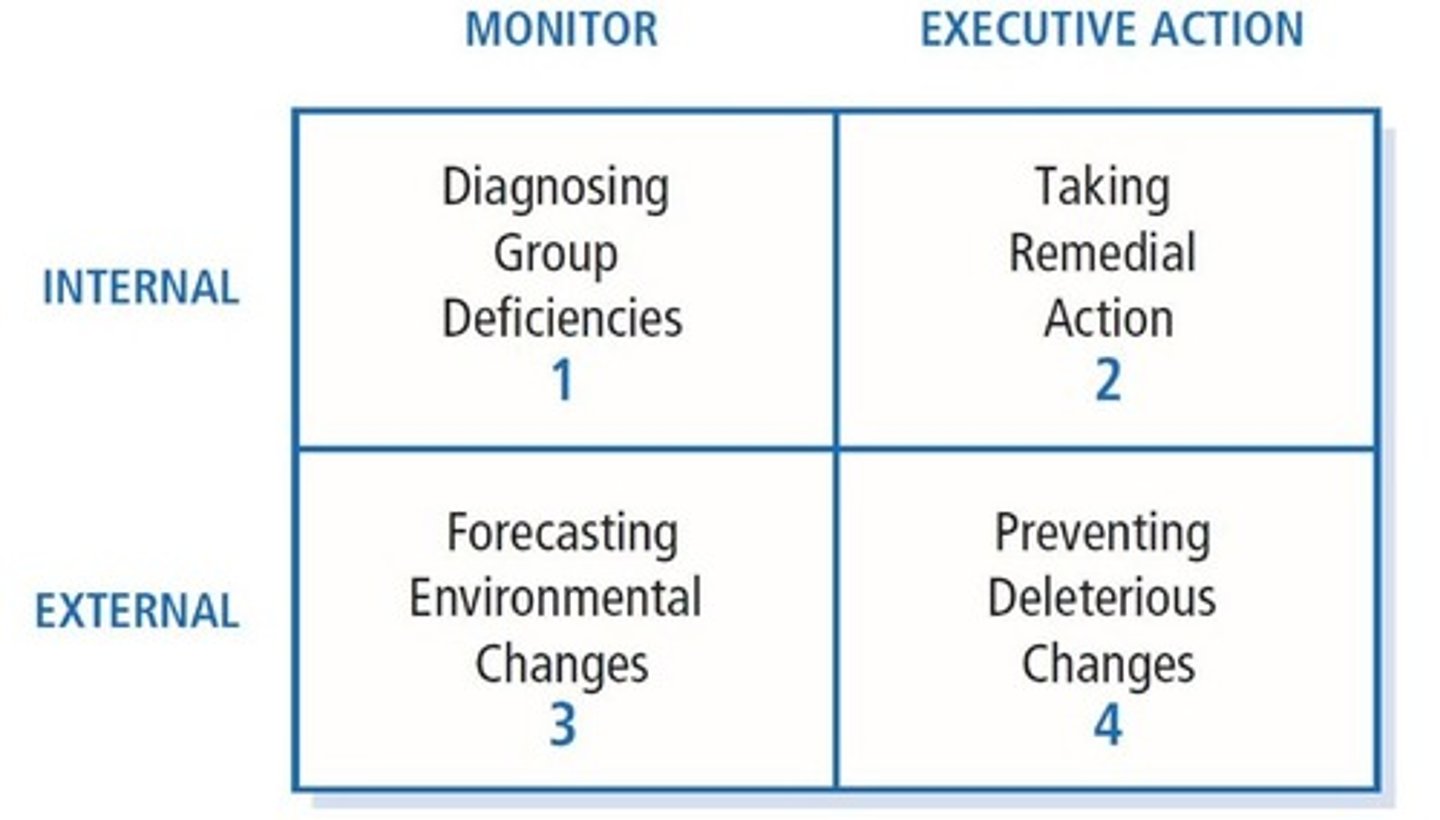
Intervene to Meet Task or Relational Needs
Task leadership functions include getting the job done, making decisions, solving problems, adapting to changes, making plans, and achieving goals. Maintenance functions include developing a positive climate, solving interpersonal problems, satisfying members' needs, and developing cohesion.
Intervene Internally or Externally
Asks if the leader need to intervene inside of the team, or is the problem external to the team? Effective team leaders analyze and balance the internal and external demands of the team and react appropriately
Gender Gap
Global phenomenon whereby women are disproportionately concentrated in lower level and lower authority leadership positions than men.
Evidence of the Leadership Labyrinth
Conveys the impression of a journey riddled with challenges all along the way— not just near the top—that can be and has been successfully navigated by women
Explanations of the Underrepresentation of Women in High-Level Leadership Positions
-differences in women's and men's investments in human capital.
- gender differences between women and men
- prejudice and discrimination against female leaders
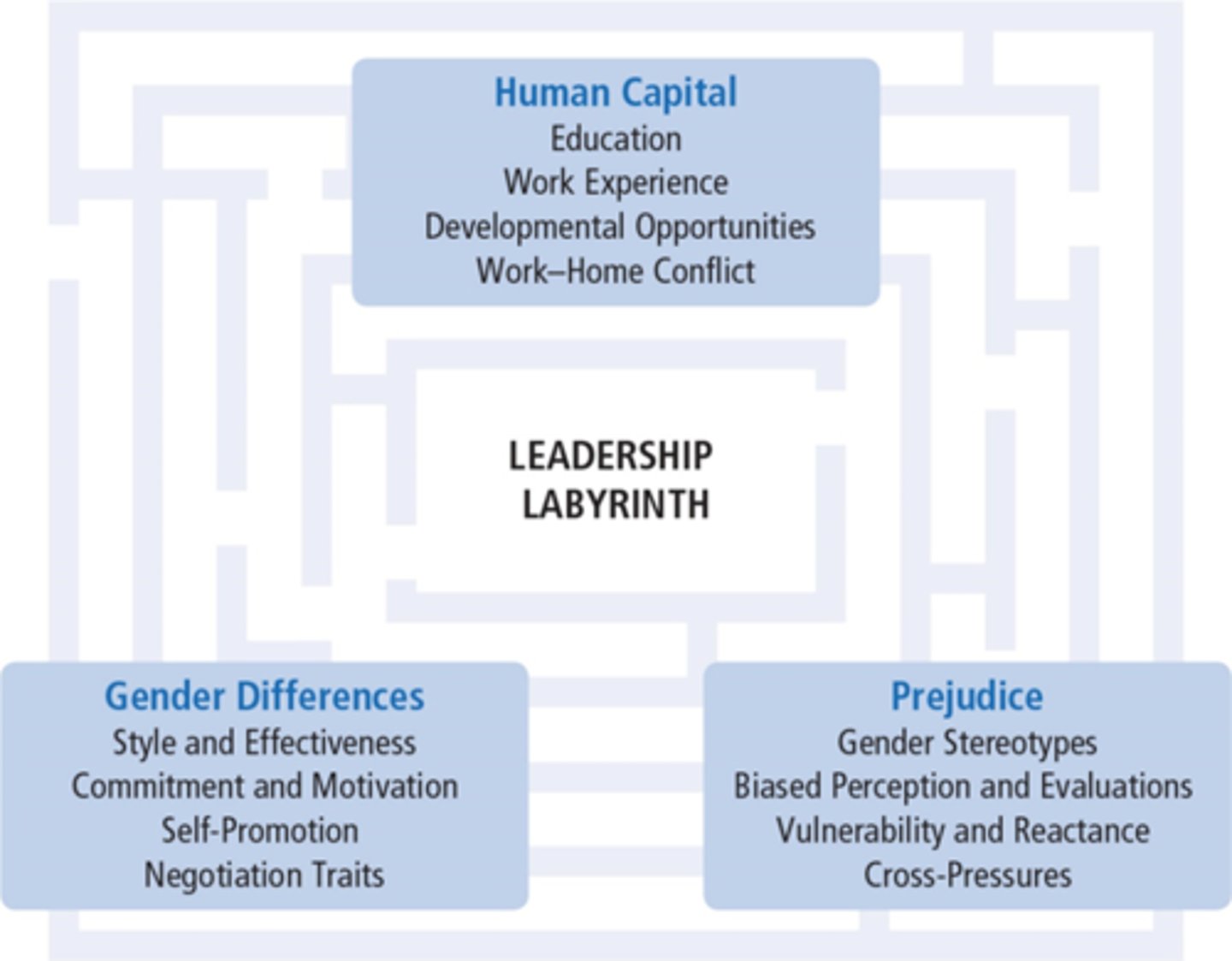
Prejudice Against Female Leaders
-Due to descriptive stereotypes people may evaluate a female leader poorly because she lacks agentic qualities
-Due to prescriptive stereotypes, people evaluate a female leader less favorably than a male leader if she possesses agentic leadership qualities: these qualities conflict with her gender role
Structural Role Redefinition
involves negotiating with both family and colleagues to renegotiate role expectations both at work and at home and helps women balance home and work life
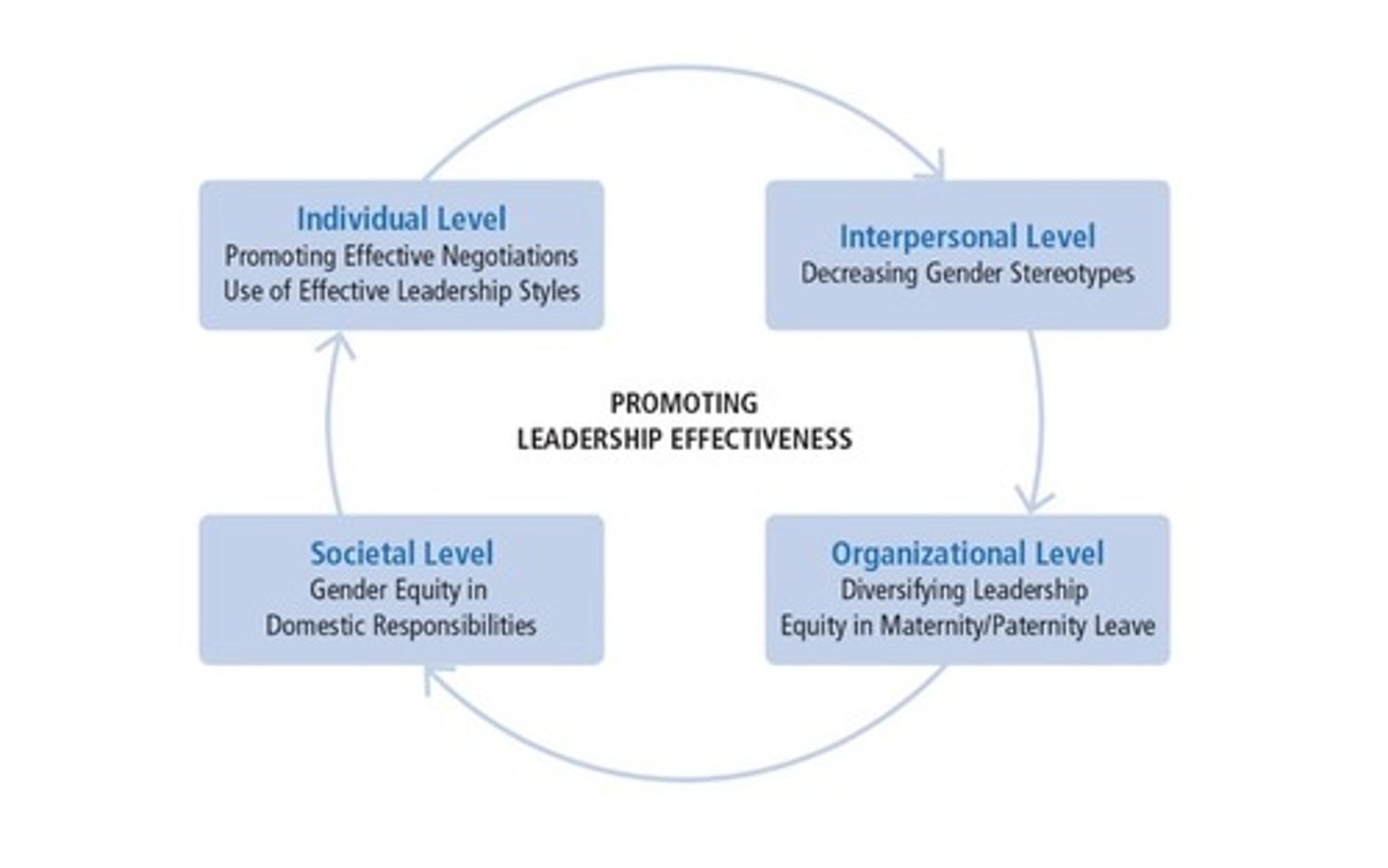
Navigating the Labyrinth
Levels to promoting leadership effectiveness:
- Individual Level
- Interpersonal Level
- Organization Level
- Societal Level
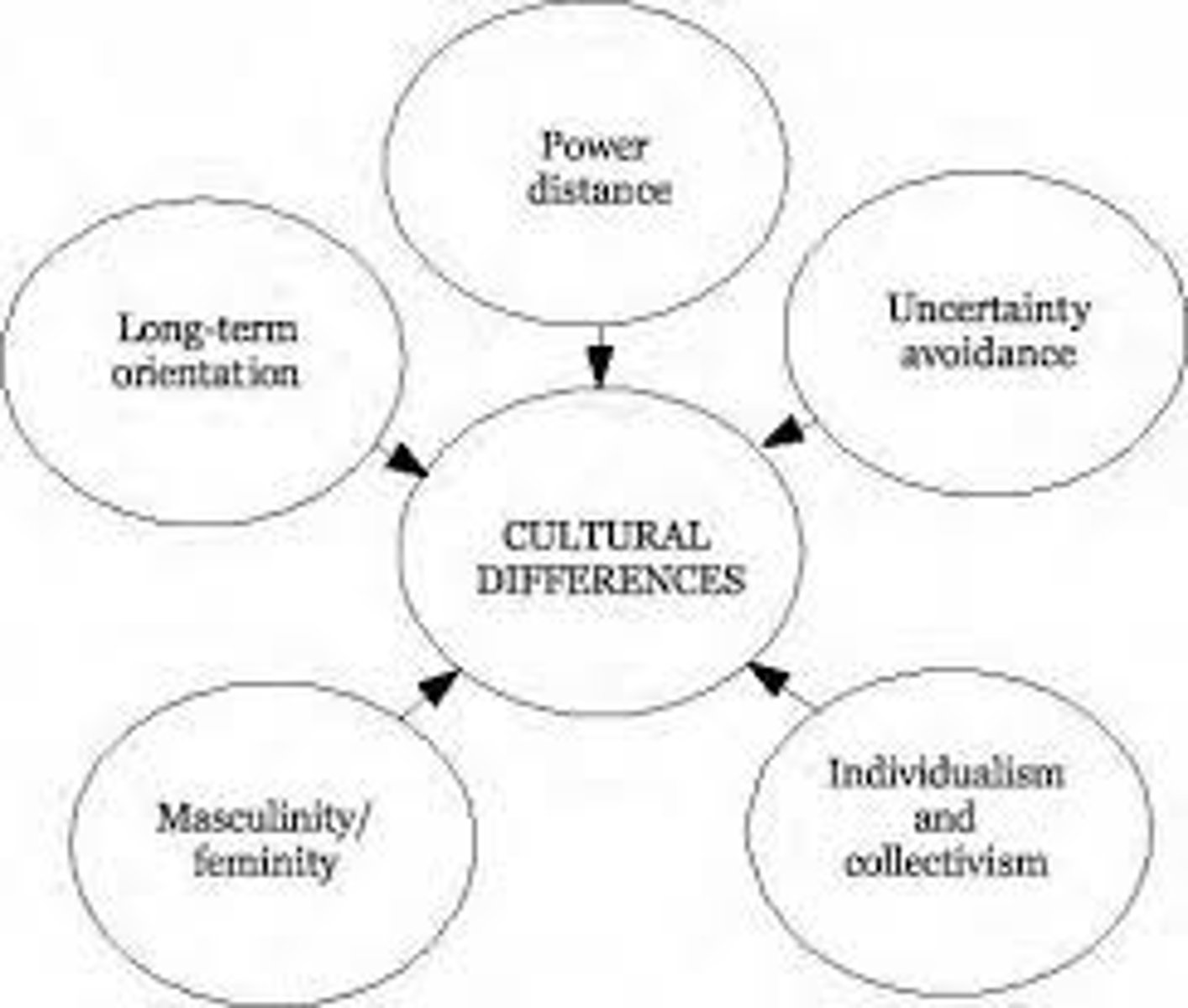
Hofstede's Cultural Differences
a. Power distance: is the extent to which people in a country accept that power is distributed unequally in society and organizations.
b. Individualism: is the degree I which societies believe that individuals should be self-sufficient
c. Masculinity and Femininity: capture the difference between highly assertive and highly nurturing cultures.
d. Uncertainty avoidance: people in a country are uncomfortable which unstructured, ambiguous, unpredictable situations.
e. Short term versus long-term orientation: addresses whether cultures are oriented to the present and seek immediate gratification or to the future and defer gratification.
Ethnocentrism
The tendency for individuals to place their own group at the center of their observations and believes that their group is better or more natural than other cultures. This is a universal tendency but is a major obstacle to effective leadership because it prevents people from understanding other cultures.
Hall's Primary Characteristic of Cultures
Individualistic (Individuals) or Collectivist (The group)
Egalitarian-hierarchical Organizational Culture
Degree to which cultures exhibit shared power versus hierarchical power
Person-Task Orientation Organizational Culture
Extent to which cultures emphasize human interaction versus focusing on tasks
GLOBE Research Program
Initiated in 1991--this program involved more than 160 investigators. Used quantitative methods to study the responses of 17,000 managers in more than 950 organizations, 62 different cultures
Nine Cultural Dimensions of GLOBE Model
- Assertiveness Orientation
- Future Orientation
- Gender Egalitarianism
- Humane Organization
- In-group Collectivism
- Institutional Collectivism
- Performance Orientation
- Power Distance
- Uncertainty Avoidance
Power Distance
Degree to which members of a group expect and agree that power should be shared unequally and which power bases (legitimate, expert, etc.) are preferred in a culture
Uncertainty Avoidance
Extent to which a society, organization, or group relies on established social norms, rituals, and procedures to avoid uncertainty
Charismatic / Value Based Leadership
reflects the ability to inspire, to motivate, and to expect high performance from others based on strongly held core values
Team-Oriented Leadership
emphasizes team building and a common purpose among team members
Participative Leadership
reflects the degree to which leaders involve others in making and implementing decisions
Cross Cultural Competencies
- Understand business, political, & cultural environments worldwide
- Learn the perspectives, tastes, trends, and technologies of many cultures
- Be able to work simultaneously with people from many cultures
- Be able to adapt to living and communicating in other cultures
- Learn to relate to people from other cultures from a position of equality rather than superiority