COMP 002 LEC 1 & 2: Computer Programming Concepts, Algorithm
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Computer
Electronic device that accepts data, processes, produces results, displays, and stores for future usage
Input in Hardware
Keyboard, Mouse, Other I/P devices
Process in Hardware
CPU, RAM, Memory
Output in Hardware
Monitor, Printer, Speaker, Other O/P devices
System Software
Programs to control and manage operation of a computer hardware
Operating System
Runs and manages the computer. (Microsoft Windows, Linux)
Utility Programs
Utilizes, nanages, and protects the computer. (Antivirus, File Compression)
Device Drivers
Helps the hardware components. (Monitor Driver, Printer Driver)
Application Software
Used to perform various applications
Examples of Application Software
• Word Processor (MS Word)
• Spreadsheet (MS Excel)
• Database Software (Oracle, MS Access)
Program
A set of instructions that drives computers to do tasks
Syntax
How we write the program correctly
Semantics
Rules in writing a program
Software instructions
Programmed in a computer language, translated into machine language, and executed by computer
Program and Programming
• Program is done for human needs and wants
• Processing is controlled by detailed step by step instructions
• Consist of statements written in a specific programming language
• When writing a program, we are solving a problem
• Computer only understands 0 and 1. Hence, the need to compile the program to transform it into 0 and 1.
Program Development Procedure (Program Life Cycle) – Unending
Program/Problem Definition
Program Design
Program Coding
Program Testing
Program Documentation
Program Maintenance
1: Program/Problem Definition
Specify program objectives and identify users
Specify the output requirements
Specify the input requirements (comes from the problem from your analysis)
Specify processing requirements (comes from analysis)
Study feasibility of implementing program (We did the solution, can we implement it?)
Document the analysis
2: Designing the Program
Determine the program logic through top-down approach and modularization, using hierarchy charts.
Design details using pseudo-code and /or flowcharts.
Test design with a structural walkthrough. Structural walkthrough consists of reviewing the process with other programmers and system analyst and scrutinize (“walkthrough”) the programmer’s work.
3: Program Coding
Translates the logic of the program based on the pseudo-code (algorithm) or flowcharts into a high level programming language using the syntax and semantics of the specific language.
Determine the appropriate programming language to use.
Code the program in the specific programming language decided on.
4: Program Testing
Desk checking
Debugging (detecting, locating and removing errors in the computer program.)
Running real data
Syntax Error
typographical error or incorrect format of the statement used (Ex: Semicolon, etc.)
Logic Errors
caused by incorrect use of control structures (Ex: Wrong analysis, etc.)
System Errors
predefined error codes and error messages that software programmers can use with their software to tell you (the software user) that the program is experiencing a particular problem.
5: Program Documentation
Program consists of the written descriptions of what the program is all about and how to use it
User Documentation - Manual that is prepared to help the user use the programs.
Operator Documentation- Manual that gives the computer operator information on what to do when the program flashes an error message.
Program Documentation - Consists of the testing of the whole programs. This documentation helps train the new programmers to maintain existing system. Maintenance here means keeping the programs in working conditions, error free and up to date.
6: Program Maintenance
• provide education and support to end users
• correct any unanticipated errors that emerge
• identify user-requested modification(enhancements), once errors or enhancement are identified, the program development life cycle begins again at step 1
Algorithm
• Step step by step procedure to solve a given problem.
• Precise, systematic method for producing a specified result.
• Set of steps used to complete a specific task.
5 Properties of an Algorithm:
1. Input specified
2. Output specified
3. Definiteness
4. Effectiveness
5. Finiteness
2 Types of an Algorithm:
1. Flowchart
2. Pseudocode
Flowcharting
• Visual representation of the sequence of the steps and decisions needed to perform a process.
• Diagram that represents an algorithm or process.
• Used to describe processing procedures based on detailed analysis

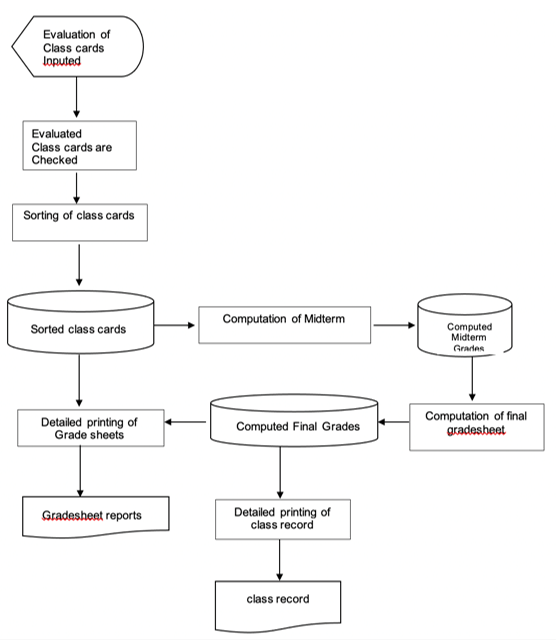
System Flowchart (process chart)
Indicates a flowchart for a targeted system as a whole.
Program Flowchart
Describes processing procedures based on detailed analysis.
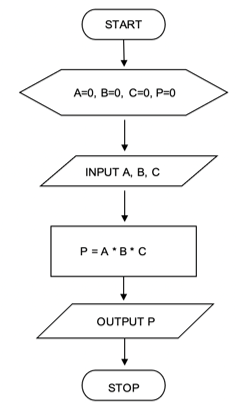
Sequential Structure
Steps are performed in a strictly sequential manner, each step being executed exactly once. This is the simplest method of control. It is easy to develop and understand.
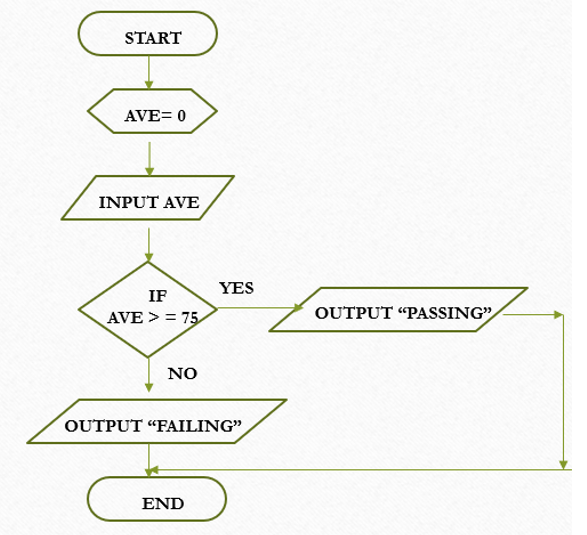
Selection Structure
One of several alternative actions is selected and executed. It involves the use of decision based on the given condition. It use decision block or the diamond-shaped block. Alternative action will be represented by a processing block.
Repetition Structure
One or more steps is performed repeatedly.
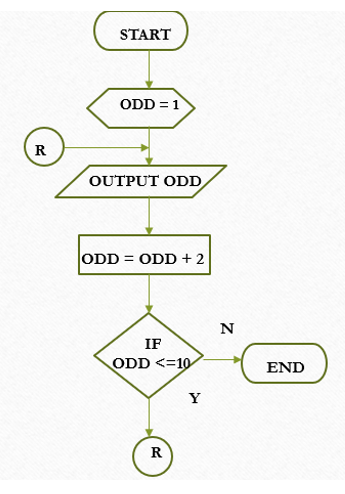
Pseudocode
• Mixture of language and symbols, terms and other feature commonly used one or more high-level languages. High-level languages are programs used by the computer.
• Is a simpler version of a programming code in plain English before it is implemented in a specific programming language
• A compact and informal high-level description of a program.
2 Types of Software
System Software
Application Software
3 Types of Control Structure Flowchart
Sequential Structure
Selection Structure
Repetition Structure