Lecture 4 - Pericardium/Epicardium
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Hemorrhage
What condition can occur due to stretching, tearing, lacerating, and crushing of blood vessels and can be small or large? Piercing wounds, fractured bones, shear forces, and tears from loss of structural integrity like due to hemangiosarcomas can all cause this.
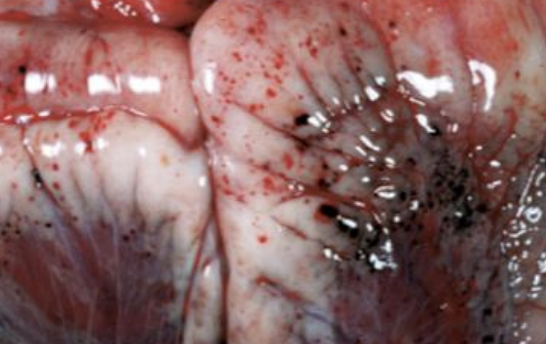
Hemangiosarcoma
Which tumor can cause hemorrhage of the heart?
Petechia
What is the term for a small hemorrhage of 1-2 mm?
Ecchymoses
What is the term for a small hemorrhage of 2-10 mm?
Hydropericardium
What is the term for general edema in the heart, due to CHF, ascites syndrome in poultry, renal failure, or hypoproteinemia?
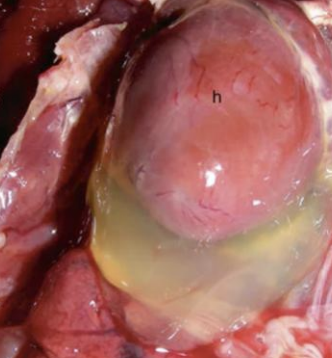
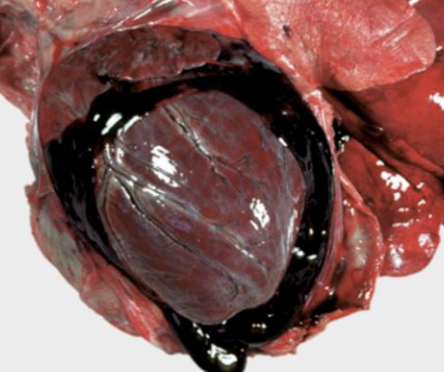
Hemopericardium
What is the term for blood loss from the heart such as due to a cardiac tamponade, which compresses the atria, blunt force trauma, atrial rupture, aorta rupture, or injections?
PPDH
What is the abbreviated term also known as peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernias, in which there is incomplete development of the diaphragm, such as in Persian cats, leading to defective separation of the liver and septum transversum, allowing the peritoneal and pericardial cavities to communicate?
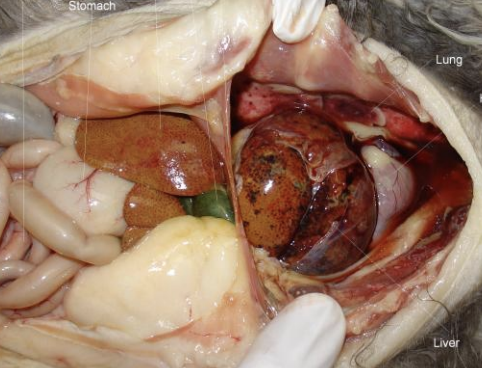
Persian
What breed of cats is especially prone to PPDHs?
Serous atrophy
What is another term for a gelatinous malformation, formed due to a negative energy balance?
Fibrinous
What type of infection response is due to hematogenous infection in the CBPP, streptococcus, pasteurella, salmonella, and other causes, and is also known for its bread and butter appearance? Yellow sheets/strands of fibrin will be seen on the pericardial surface, and adhesions will occur if it is chronic. Death or recovery can occur.
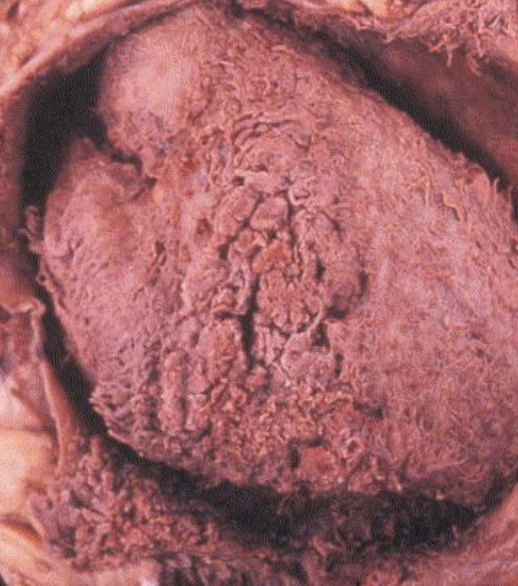

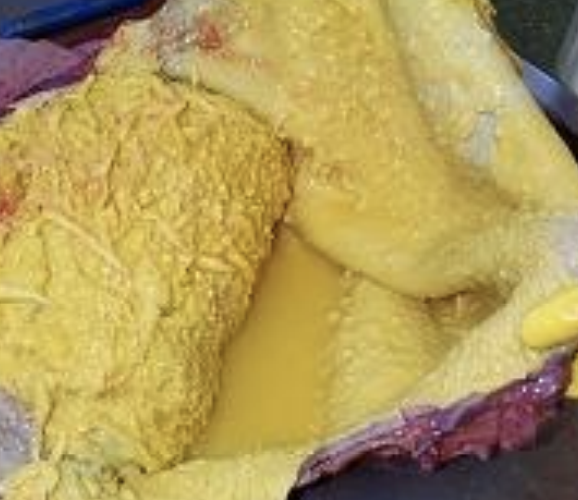
Suppurative
What type of infection response is due to hardware disease, in which there is a distended pericardial sac with yellow-white pus, a thick fibrous pericardium, and a fetid odor? Death or chronic heart failure can occur.

Granulomatous
What type of infection response is due to formation of granulomas usually from TB, higher-level bacteria, or fungi?
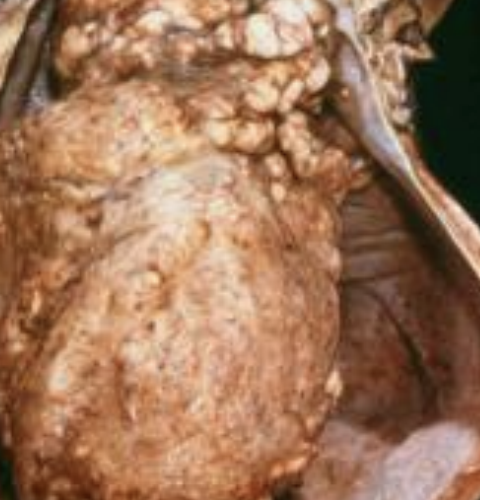
Primary
Which type of cardiomyopathy is due to idiopathic causes, and can be hypertrophic, dilatative/congestive, or restrictive? It leads to arrhythmogenic right ventricular CMP, thickening of walls, can lead to saddle thrombi after formation of emboli in the left atrium in cats, leads to formation of moderator bands in the left side of the heart in cats (false tendons), and leads to pulmonary congestion, edema, ascites, hydrothorax, hepatic congestion, thromboemboli, and poikilothermy.
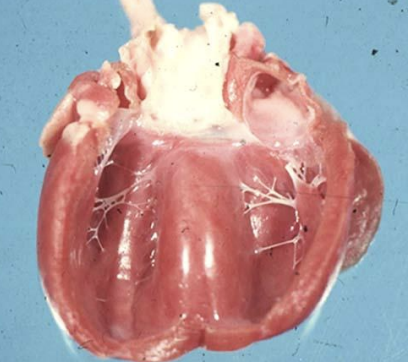
False tendons
What is the term for the formation of moderator bands on the left side of the heart during primary cardiomyopathy in cats?
Secondary
Which type of cardiomyopathy is due to a specific disease, such as heritable causes, nutrition deficiency, toxicity, physical injury, shock, endocrine disorder, infection, neoplasias, and systemic hypertension?