Abdomen Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/181
Earn XP
Last updated 1:14 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
1
New cards
What is ultrasound?
Sound frequencies beyond the upper limits of human hearing (\>20kHz)
2
New cards
What is the range of audible frequency?
20 Hz - 20 kHz
3
New cards
Acoustic is the study of ?
generating and propagating sound waves
4
New cards
What is Diagnostic Medical Sonography?
An imaging technique used to visualize soft tissue structures of the body by recording the returning reflection of ultrasonic waves directed into the body
5
New cards
Echogenic
the ability of a structure to produce echoes
6
New cards
Anechoic
no echoes (sonolucent) -appears black on ultrasound
7
New cards
Hypoechoic
less reflective and low amount of echoes, appears as varying shades of gray
8
New cards
Hyperechoic
highly reflective and echo rich appears bright
9
New cards
Isoechoic
having similar echogenicity to a neighboring structure
10
New cards
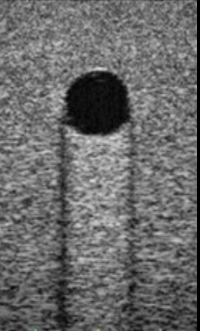
Identify the echogenicity
Anechoic
11
New cards
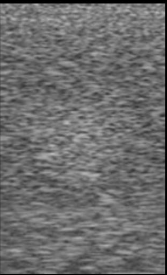
Identify the echogenicity
Isoechoic
12
New cards
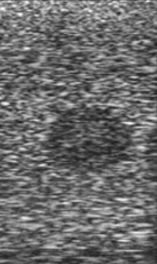
Identify the echogenicity
Hypoechoic
13
New cards
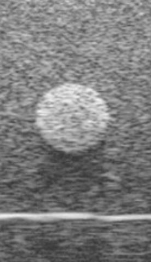
Identify the echogenicity
Hyperechoic
14
New cards
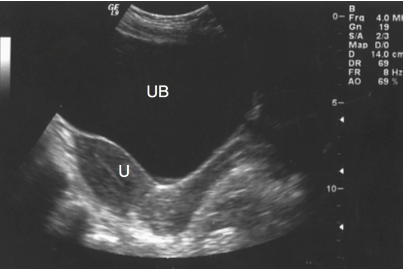
What is the echogenicity of the bladder?
Anechoic
15
New cards
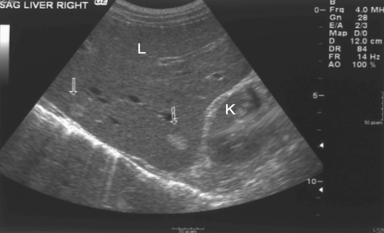
What is the kidney’s echogenicity to the liver?
Isoechoic
16
New cards
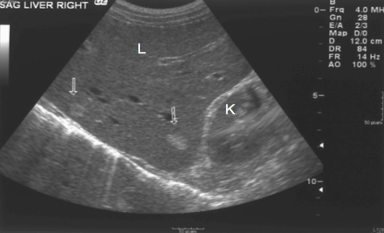
The liver contains two areas (arrows) that are ____________ compared with the rest of the echogenicity of the liver
hyperechoic
17
New cards
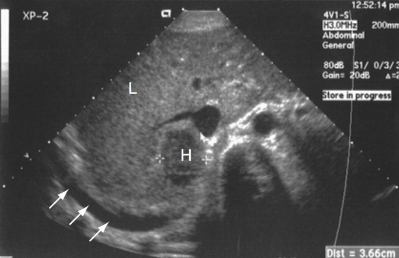
What is the echogenicity of the mass in the liver?
Hypoechoic
18
New cards
Homogeneous organ parenchyma is \__________ in echogenicity
uniform
19
New cards
Inhomogeneous or heterogeneous organ parenchyma is \___________ in echogenicity
not uniform
20
New cards
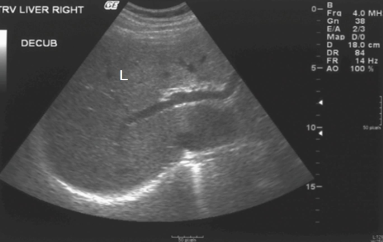
What is the texture of this liver?
Homogeneous (uniform texture)
21
New cards
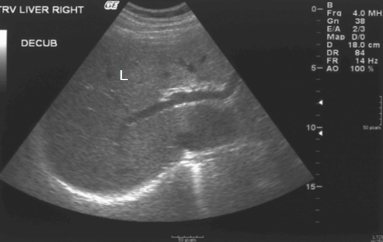
What does the anechoic structures within the liver represent?
vessels & ducts
22
New cards
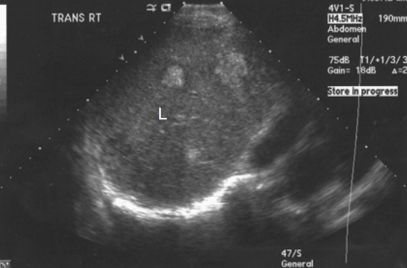
What is the texture of this liver?
Inhomogeneous (not uniform)
23
New cards
Simple cyst
* Reverberation may be seen on the anterior wall of the cysts
* Anechoic (completely)
* Posterior Enhancement
* Smooth walled
(RAPS)
* Anechoic (completely)
* Posterior Enhancement
* Smooth walled
(RAPS)
24
New cards
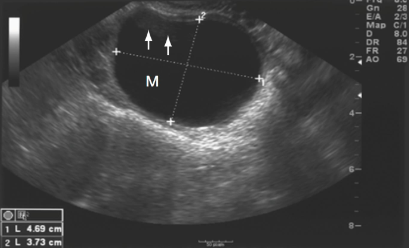
This image displays a
simple cyst
25
New cards
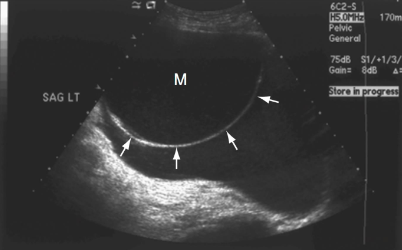
What does the arrows tell you in this image?
Complex cyst bc there is a thin, hair-like structure & septation
26
New cards
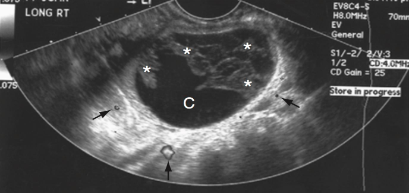
What is this an image of? And how do you know?
Complex cyst bc there are multiple loculations/compartments
27
New cards
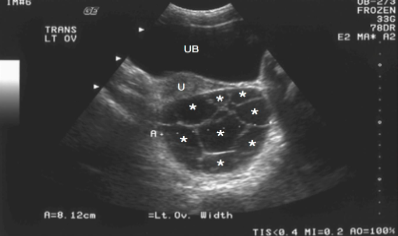
This image displays a
Complex cyst
28
New cards
Solid mass
* Homogeneous or inhomogeneous (heterogeneous)
* Hypoechoic or hyperechoic
* May attenuate sound partially or completely (poor transonicity)
\
(Anything but anechoic)
* Hypoechoic or hyperechoic
* May attenuate sound partially or completely (poor transonicity)
\
(Anything but anechoic)
29
New cards
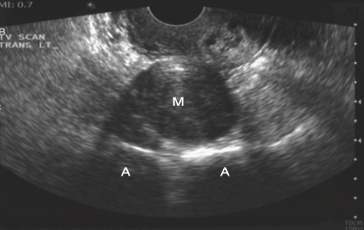
This image displays a
Hypoechoic solid mass
30
New cards
Complex cyst
* Smooth-walled, Anechoic, Posterior enhancement
* Septations that appear echogenic
* Fluid-fluid layers
* Multiocular compartments
* Internal echos
* Calcification
* Septations that appear echogenic
* Fluid-fluid layers
* Multiocular compartments
* Internal echos
* Calcification
31
New cards
In complex cysts, septations appear as
Echogenic hair-like strands
32
New cards
In complex cysts, internal echoes may indicate
hemorrhage or infection
33
New cards
In complex cysts, fluid-filled layers may represent
blood, fluid, or fat layers
34
New cards
In complex cysts, calcification appear as
highly reflective echoes (hyperechoic) w/ posterior shadowing
35
New cards
What plane runs perpendicular to the sagittal plane?
coronal/frontal
36
New cards
In \________ view markers points to the patient right side
transverse
37
New cards
In \_________ view markers points to the patients head
longitudinal
38
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is sagittal (longitudinal) the top of the picture is _________
anterior
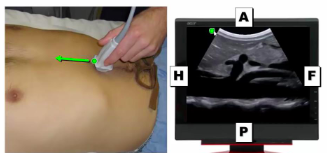
39
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is sagittal (longitudinal) the bottom of the picture is _________
posterior
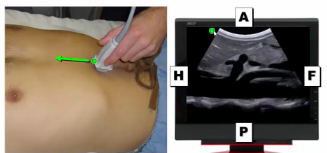
40
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is sagittal (longitudinal) the left of the image is _________
cephalic (towards head)
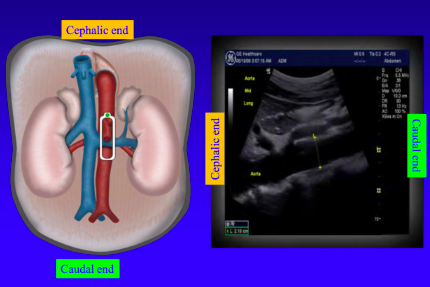
41
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is sagittal(longitudinal) the right of the picture is _________
caudal (towards feet)
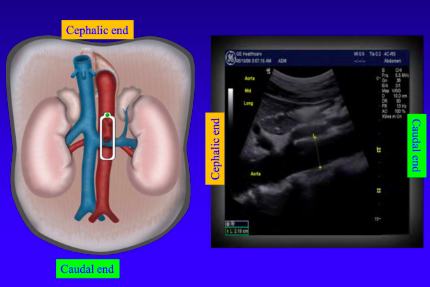
42
New cards
The probe marker is towards the patient's \__________ when the probe orientation is sagittal
head
43
New cards
The probe marker is towards the patient's \__________ when the probe orientation is transverse
right
44
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is transverse (cross-sectional) the top of the picture is _____
anterior
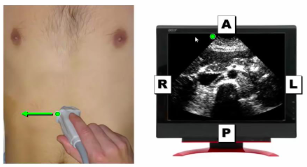
45
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is transverse (cross-sectional) the bottom of the picture is ______
posterior
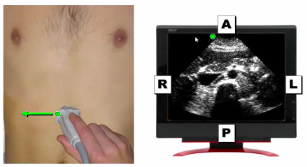
46
New cards
When the ultrasound probe is transverse (cross-sectional) the left of the picture is ______
lateral (right)
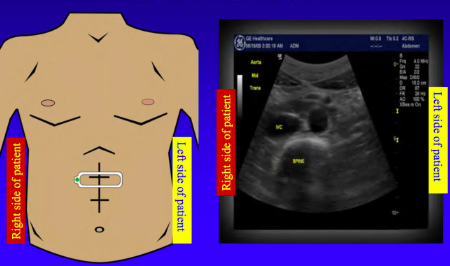
47
New cards
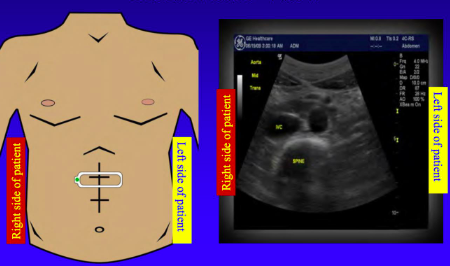
When the ultrasound probe is transverse (cross-sectional) the right of the picture is _______
medial (left)
48
New cards
body cavities
spaces within the body that contain, protect, and support internal organs
49
New cards
What are the 2 principal cavities?
dorsal & ventral
50
New cards
Dorsal cavity contains
cranial cavity and spinal cavity
51
New cards
Ventral cavity contains
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
52
New cards
abdominal quadrants
RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
53
New cards
SSALT
size, shape, acoustics, location, transonicity
54
New cards
What are the measurements you need for organs?
length, width, depth
55
New cards
Gain knob
controls overall brightness of the image
56
New cards
Time Gain Compensation (TGC)
allows adjustment of image brightness at selective depth
57
New cards
depth knob
Allows adjustment of the depth of field of view
58
New cards
focus knob
allows focus of ultrasound beam to area of interest
59
New cards
How should a patient prepare for a general abdominal exam?
fasting (NPO) for 8-12 hrs
60
New cards
NPO
Nulla Para Ora - Nothing by mouth
61
New cards
Why NPO?
Minimizes abdominal gas which can blur ultrasound image
62
New cards
Why is patient positioning important?
* easier to visualize a target organ
* brings area of interest closer to probe
* minimize gas in patient to allow better image
* brings area of interest closer to probe
* minimize gas in patient to allow better image
63
New cards
supine
lying on back (face up)
64
New cards
prone
lying face down
65
New cards
decubital
lying on the side
66
New cards
left lateral decubital
lying on the left side
67
New cards
right lateral decubital
lying on the right side
68
New cards
oblique
halfway on the side
69
New cards
Ultrasound transducers convert \__________ energy to \___________ energy
mechanical; electrical
70
New cards
What are the most commonly used ultrasound transducers?
sector & linear
71
New cards
How are images displayed with linear transducers?
rectangle or parallelogram
72
New cards
The size of the field of view in linear transducers is
equal in both near and far field
73
New cards
Linear transducers are optimal for
superficial structures (ex: testes)
74
New cards
How are images displayed with sector transducers?
wedge or pie-shaped section
75
New cards
The field of view with sector transducer is
wider in the far field than in near field
76
New cards
Sector traducers are commonly used for
routine abdominal & pelvic imaging
77
New cards
Linear and sector transducers have a range of frequencies generally varying from
2.0 to 12.0 MHz
78
New cards
Transducer selection is based on
type of exam & patient's body
79
New cards
Low-frequency traducers have a frequency of
2.0 MHz
80
New cards
Low-frequency traducers have a sector format that results in
increased sound penetration but with loss of resolution
81
New cards
Low-frequency transducers are suitable for
abdominal & pelvic exams, obese patients
82
New cards
Medium-frequency transducers have a frequency range of
3.0 - 5.0 MHz
83
New cards
What is the format of medium-frequency transducers?
generally sector
84
New cards
Some 5.0 MHz medium-frequency transducers are in what formats?
both linear & sector
85
New cards
Medium-frequency sector transducers are suitable for imaging
most adults
86
New cards
What is the frequency range of high-frequency transducers?
7.0 - 12.0 MHz
87
New cards
Format of high-frequency transducers
linear or sector
88
New cards
High-frequency transducers results in
increased resolution but w/ reduced penetration
89
New cards
High-frequency transducer **sector probes** are suitable for
pediatric patients
90
New cards
High-frequency **linear probes** are best suitable for
imaging superficial structures
91
New cards
In the upper abdomen, sonographers should find a
good acoustic window through which to transmit the sound beam (ex: healthy liver is an excellent window)
92
New cards
Movements of transducers (transducer manipultations)
sliding, tilting, rotating, angling
93
New cards
sliding
movement of transducer from one location to another
94
New cards
tiling
angling transducer from side to side
95
New cards
rotating
turning 90 degrees to change image from sagittal to transverse view
96
New cards
angling
same as tilting
97
New cards
Focal point
a control that has one or more toggle buttons
98
New cards
Focal point allows the operator to
choose the level at which the ultrasound beam is focused to increase resolution at specific points
99
New cards
The focal point control should be set at the
most posterior aspect of the organ or structure being imaged
100
New cards
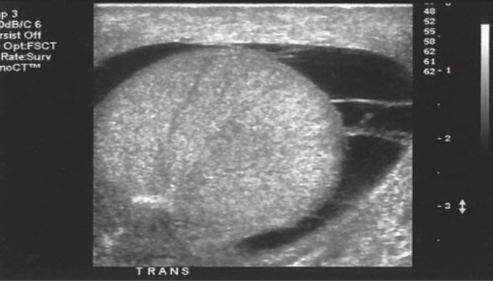
What is the transducer display in this image?
linear (rectangle)