DT- Unit 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Human Factors
The combination of ergonomics and anthropometrics
What are the aims of Human Factors?
Reduce stress and fatigue on people, as they will be able to do things faster,
more easily, more safely and make fewer mistakes (reduce errors)
Increase safety
Increase ease of use
Enhance operational comfort
Improve system performance, reliability and maintenance
What is Ergonomics?
Application of scientific information concerning the relationship of human beings to the design of objects, systems and environments.
What do we mean by the term physical ergonomics?
Physical ergonomics mainly focuses on work-related topics such as posture, workspace layout, material handling, repetitive movements, injuries from repetitive strain, muscle and joint problems, and workplace safety.
The aspect of ergonomics that deals with body measurements, particularly those of size, strength and physical capacity.
cognitive ergonomics
Mental processes like perception, memory, reasoning, and motor responses influence how people interact with each other and with different parts of a system.
organisational ergonomics
communication, work design, shift (work hours) management, crew resource management, teamwork, virtual organizations, telework, and quality management.
Anthropometric data
It is sub-classified as Static Data and Dynamic Data.
Structural Anthropometric data
Static Data (also known as Structural data) is measurements taken while while the subject is in a fixed or standard position, e.g. height, arm length.
Static data is much easier to gather, as people are asked to remain still while measurements are taken.
functional Anthropometric data
Dynamic Data (also known as Functional data) is measurements taken during physical activities, e.g. crawling height, overhead reach and a range of upper body movements.
Dynamic data involves people carrying out tasks. People carry out tasks in many different ways. While static data is more reliable, dynamic data is often more useful.
What tools can be used to collect Anthropometric Data?
Sliding Callipers,Cloth Tape, Sitting height meters, Stadiometer
clearance in Human Factors?
Physical space between 2 objects
This is especially important when designing emergency exits and safety hatches
reach in Human Factors?
Also known as the workspace envelope. A 'workspace envelope' is a 3-dimensional space within which you carry out physical work activities when you are at a fixed location.
Workspace envelopes should be designed for the 5th percentile of the user population, which means that 95% of users will be able to reach everything placed within the envelope.
reach in Human Factors
also known as the workspace envelope.
Why does a designer need to consider adjustability when designing seating?
Certain products tend to be available in different sizes or with adjustability built in as there really is no ‘one size fits all’.
Explain what is meant by the range of sizes versus adjustability
Clothing comes in a range of sizes. For manufacturers to make clothing fit every individualvariancewouldnotbeeconomically possible,thusittendstocomeinarange of sizes based on percentile ranges. Children’s car seats are adjustable to allow for a range of sizes and a growing child.
What is an ergonome and when are they used? and Pro and Con
2D scaled physical anthropometric model based on a specific percentile human forms
Its human-shaped models based on average body sizes from specific percentiles. They are used in drawings to help designers see how people will interact with an object or space, making sure everything fits well and is comfortable to use.
What is a manikin
3D model of the human body
Ergonomes help show how different body parts fit in a space, like how a person sits at a desk. Full-size manikins cost more than ergonomes but give a more accurate idea of how comfortable and practical a design is in real life.
What is Cognitive psychology
concerned with mental processes, such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, as they affect interactions among humans and other elements of a system.
What is a Nominal Data Scale
Nominal means ‘by name’. Used in classification or division of objects into discrete groups. Each of which is identified with a name.
What is an Ordinal Data Scale
Deals with the order or position of items. Words, letters, symbols or numbers arranged in a hierarchical order
What are examples of Psychological factors
Smell, sound, light, taste, texture, temp, value (perceived prestige)
What is the Human information processing systems
Human information-processing systems, considering inputs, processes (sensory, central and motor) and outputs.
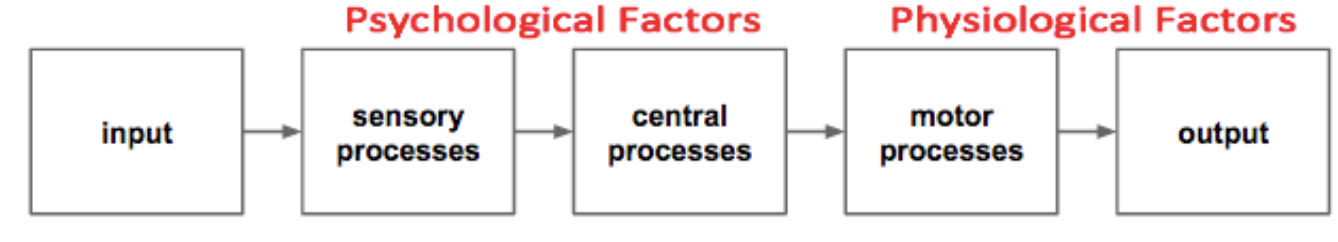
What are possible ways of optimizing environmental factors to maximize workplace performance?
Lighting: best lighting is natural lighting or low frequency/brightness depending on task.
Thermal comfort: Male and Female have different body temperature. Having the right temperature air/humidity and flow of air/circulation to get best work performance.
Working space: Space, working envelope, safe
Noise: Protection of excessive noise (above 85 decibels)
Vibration: Machines, etc. create vibration and sound and can be annoying
What are some perception effects in products?
The whole is seen rather than the sum of its parts.
Physiological factors concerned with
bodily tolerances (how much can the body withstand) such as comfort and fatigue
Physical ergonomics concerned with
concerned with human anatomy, and some of the anthropometric, physiological and biomechanical characteristics as they relate to physical activity
What is Fatigue
tired they react in different ways. Fatigue is the temporary diminishment of performance
What is Comfort
physiological factors that inform design decisions and can affect users
How can designing ergonomically enhanced work environments and products have advantages for the employer and employee
Healthy Workforce: Instead of workers adjusting to standard tools and equipment, ergonomics promotes product designing based on human body structure and requirements.
Enhanced Productivity: A healthy workforce translates to enhanced productivity. Easy to use equipment keeps the work momentum going on for longer durations.
Reduced Number of Sick Days Reported: When workers don’t get sick or injured from their job, they take fewer days off. This means more days of work and fewer sick days.
biomechanics in human factors
includes the research and analysis of the mechanics (operation of our muscles, joints, tendons, etc.) of our human body
Biomechanics in human factor design deals with four key criteria:
Force
Repetition
Duration
Posture
FEA- Finite element analysis
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a way of predicting how something behaves under stress, temperature, or other physical effects. Engineers use it to simulate real-world behavior before actually building something.