lipari pulmonary function testing
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
normal expiration is ___active/passive?___ process, with flow of air depending on
1.
2.
-passive process
1. elastic recoil
2. airway resistance
what do pulmonary function tests measure?
- airflow obstructions
- lung size restrictions
- decreased gas transfer across alveolar-capillary membrane
what are "abnormal" values in pulmonary function tests based on
- matched to race, age, sex, and height [RASH]
- outside of range based on normal individuals (95% confidence)
therefore, this definition is arbitrary and can misclassify pts
what are the uses of PFTs
1. evaluation: lung disease, chronic cough, dyspnea, chest tightness
2. effects of toxin exposure (dust, chemicals,...)
3. risk stratification before surgery
4. monitoring effectiveness of tx
5. impairment/ disability assessment
t/f: pulmonary function test values are compared to subjects with diagnosed lung function disorders and matched based on race/ethnicity
false. compared to HEALTHY subjects and matched based on race/ethnicity
which reference values does the American Thoracic Society (ATS) recommend
1. GLI for 3-95 years
- gold standard!! multiethnic
2. NHANES III 8-80yrs and Wang equation <8 years
which reference values would you use for a 90 year old patient getting pulmonary function testing done
Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) for 3-95 yrs; multiethnic and most reliable (gold standard!)
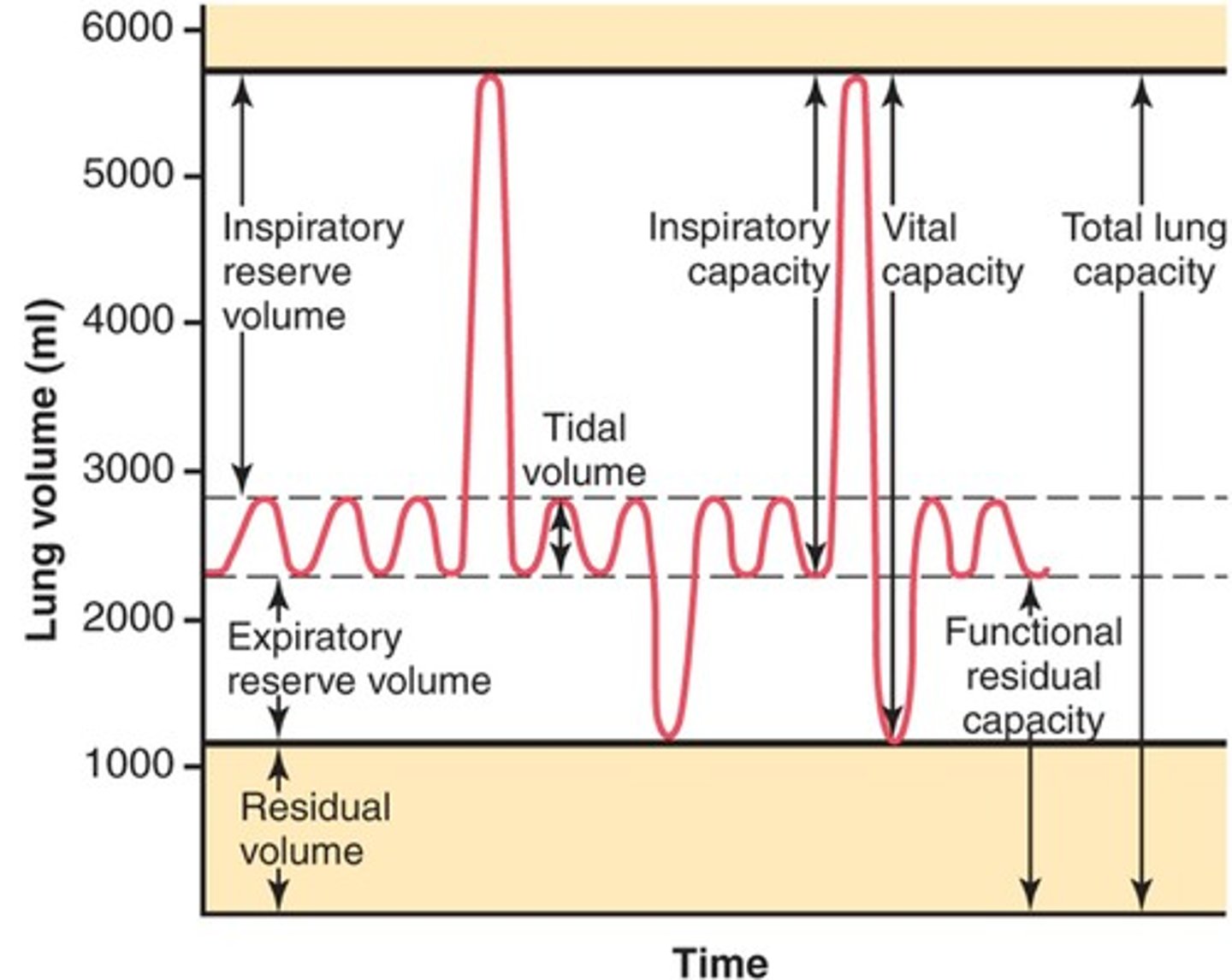
tidal volume
total amount of air exhaled during normal quiet breathing (not forced)
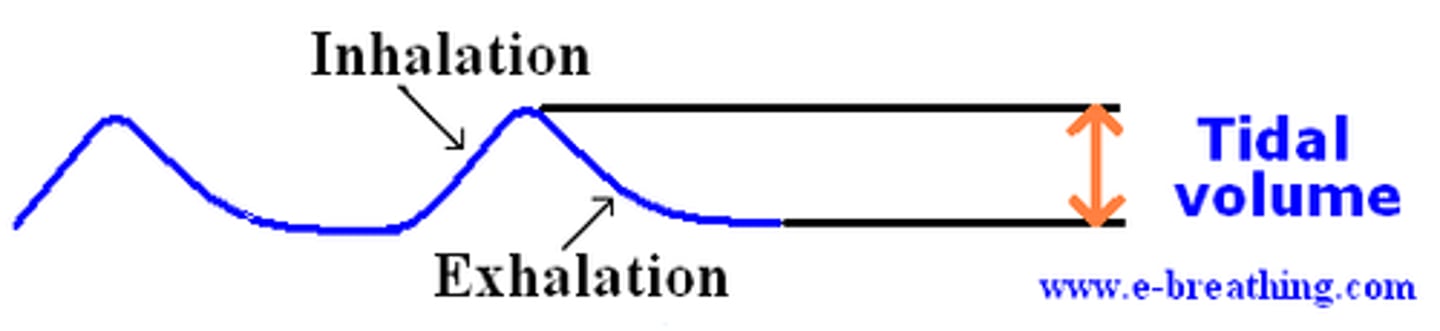
expiratory reserve volume
max air exhaled BELOW tidal volume (below the normal amount you would exhale normally/ forced)

inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
The additional volume of air that can be inhaled with maximum effort after normal inspiration
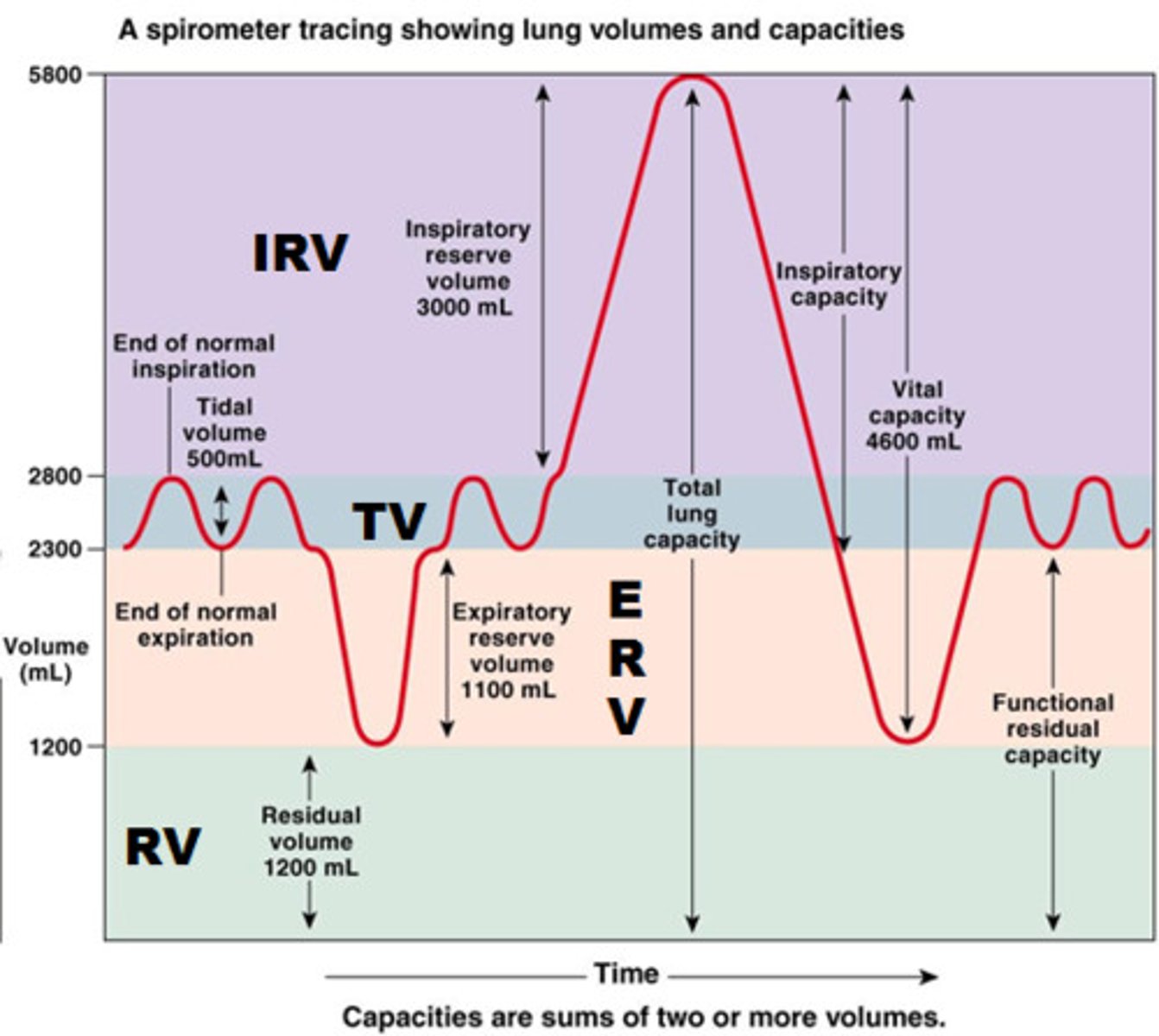
residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a maximum forced exhalation (the amount of air left to prevent lungs from collapsing)
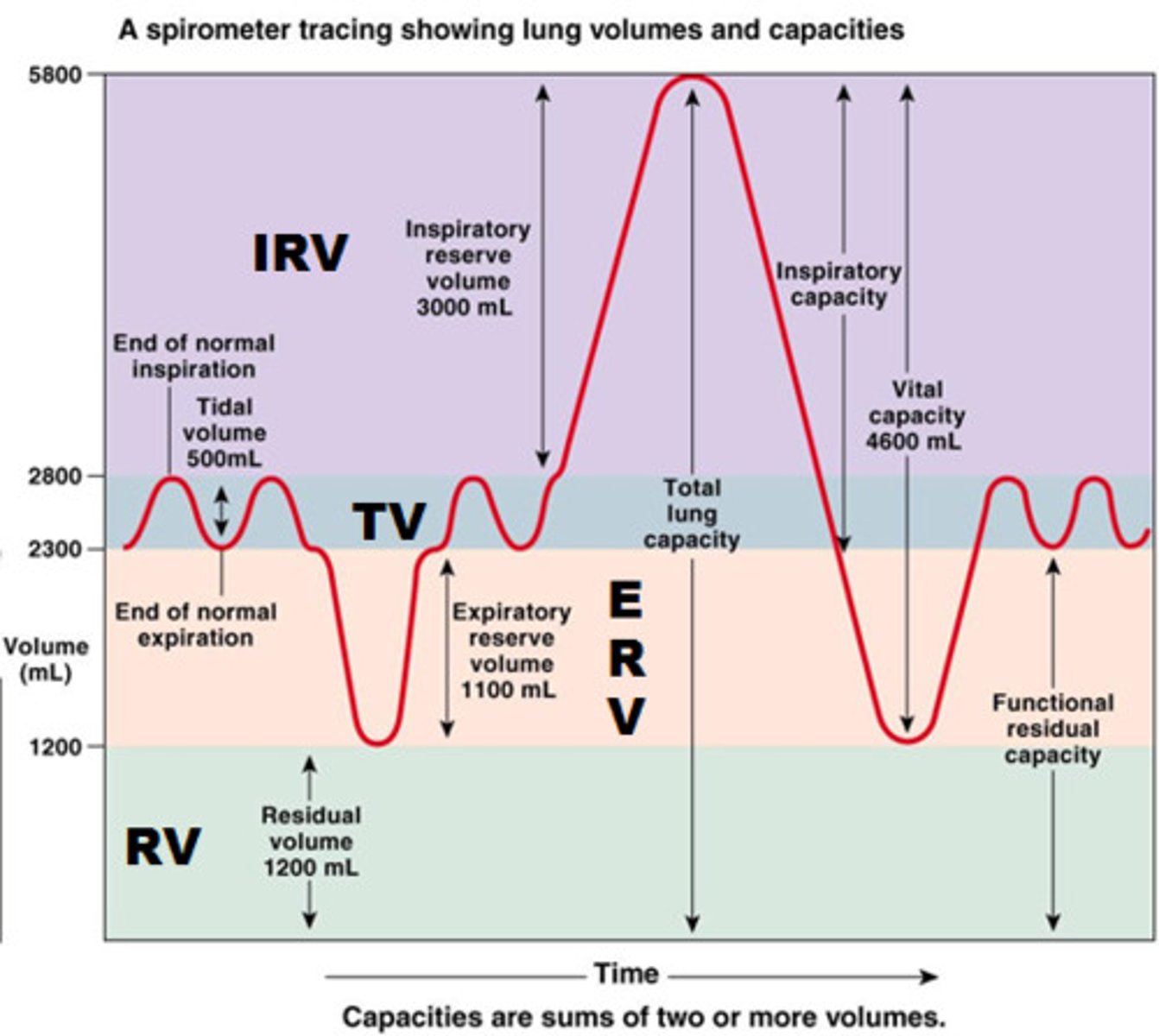
summarize and explain TV, IRV, ERV, and RV (summary)
tidal: how much air you exhale when normally breathing
erv: extra air you can forcefully exhale after a normal exhale
irv: extra air you can forcefully inhale after normal inhale
rv: air that always stays in your lungs after you fully exhale—this prevents lung collapse
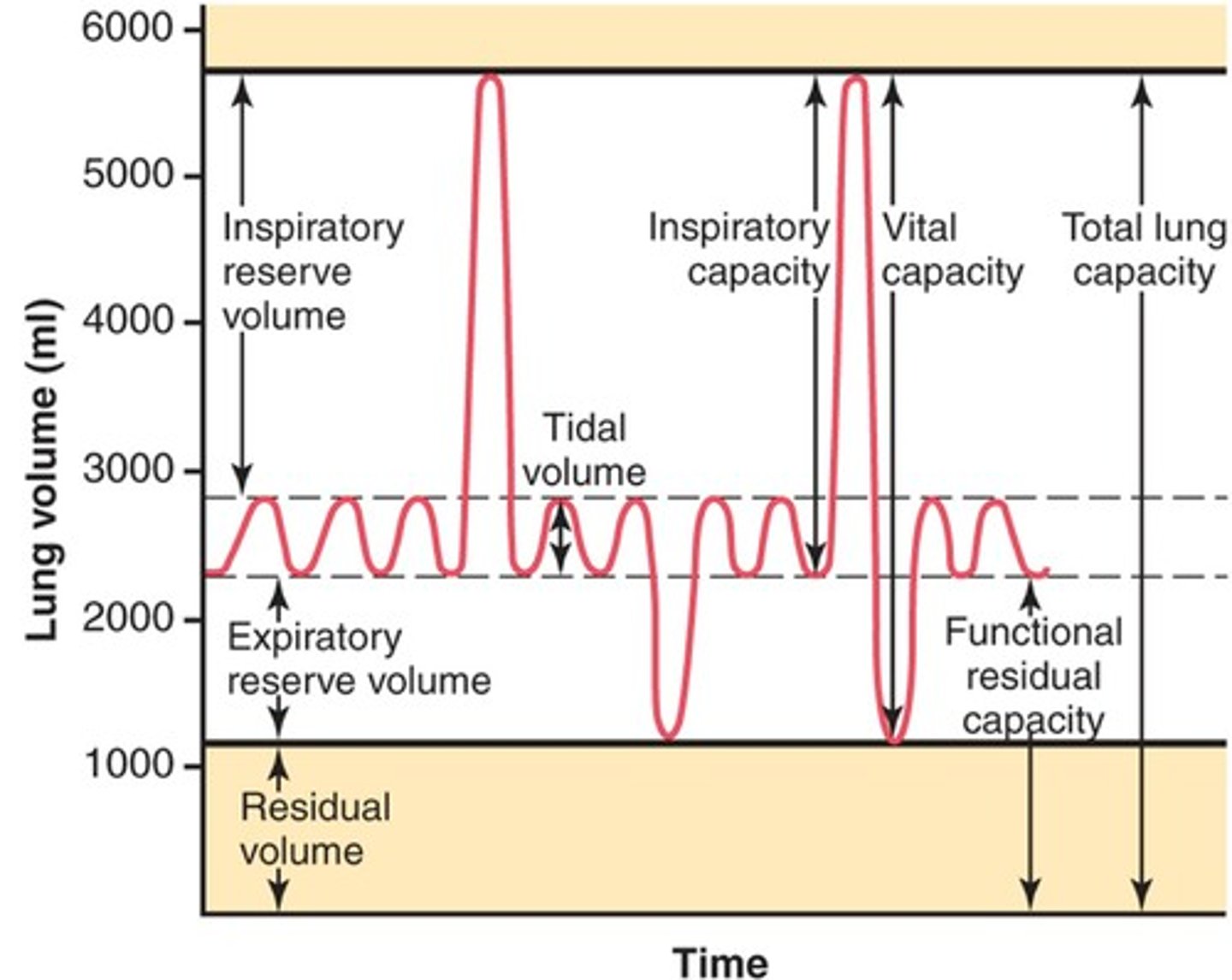
functional residual capacity (FRC)
volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal tidal volume expiration (ERV + RV)

functional residual capacity (FRC) is ___% of total lung capacity (TLC)
40%
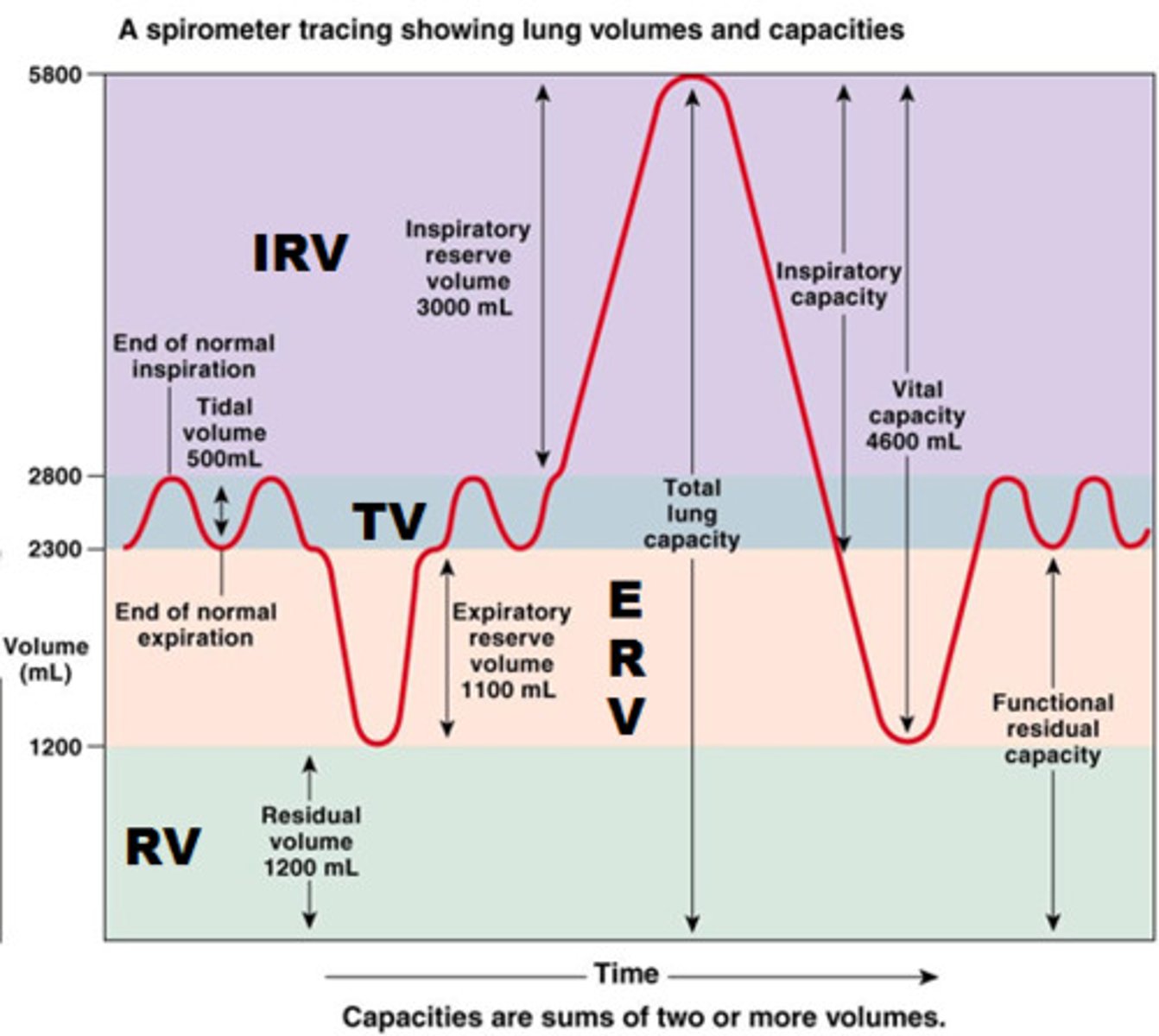
inspiratory capacity (IC)
max volume of air inhaled after a normal exhale
(TV + IRV)
compare FRC to IC
- both add up to make up your total lung capacity (TLC)
FRC is what stays in your lungs after you exhale normally
IC is how much you can inhale from that same point
TV + IRV =
IC
vital capacity (VC)
amount of air exhaled after a maximal inspiration (75% of TLC)
VC = IRV + TV + ERV
vital capacity is ___% of total lung capacity
75%
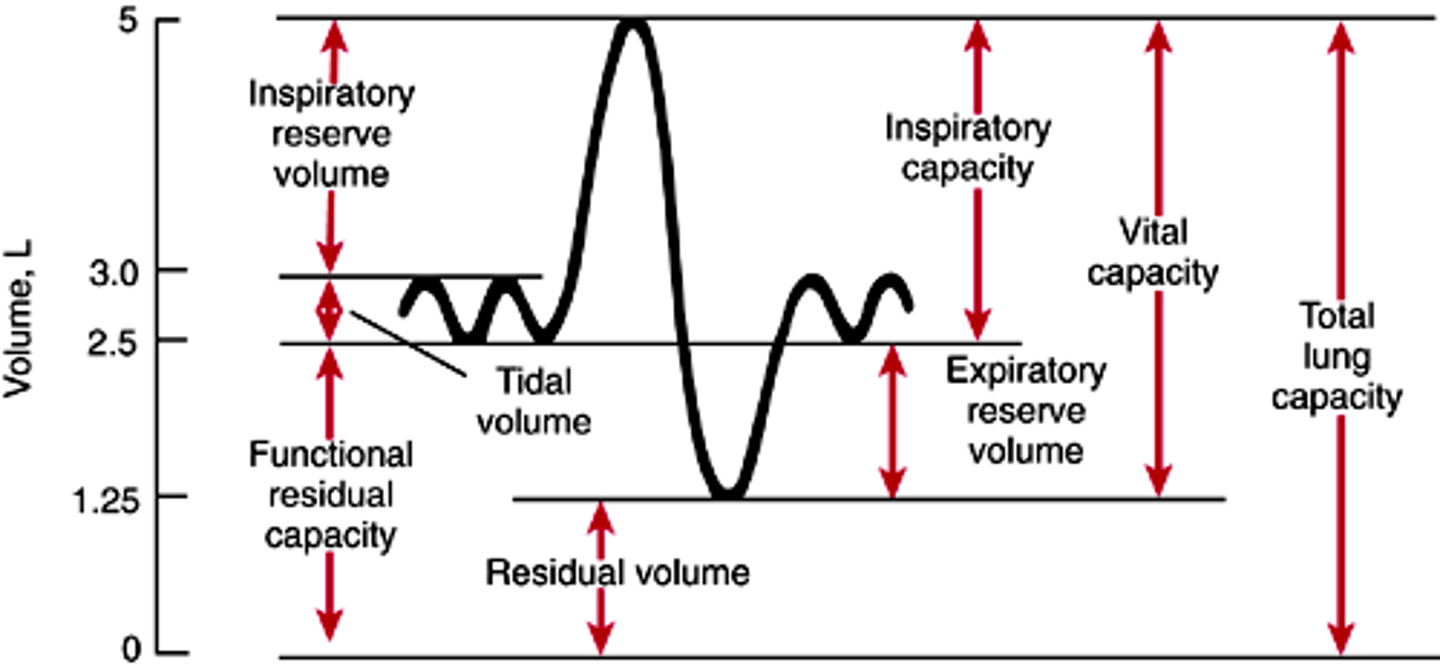
2 ways to measure vital capacity
1. forced vital capacity (FVC)
- measured on forced expiration
2. slow vital capacity
- measured over 30+ second exhale
- normal range restrictive disorder unlikely
total lung capacity (TLC)
volume of air after maximal inspiration
TLC = IRV + TV + ERV + RV
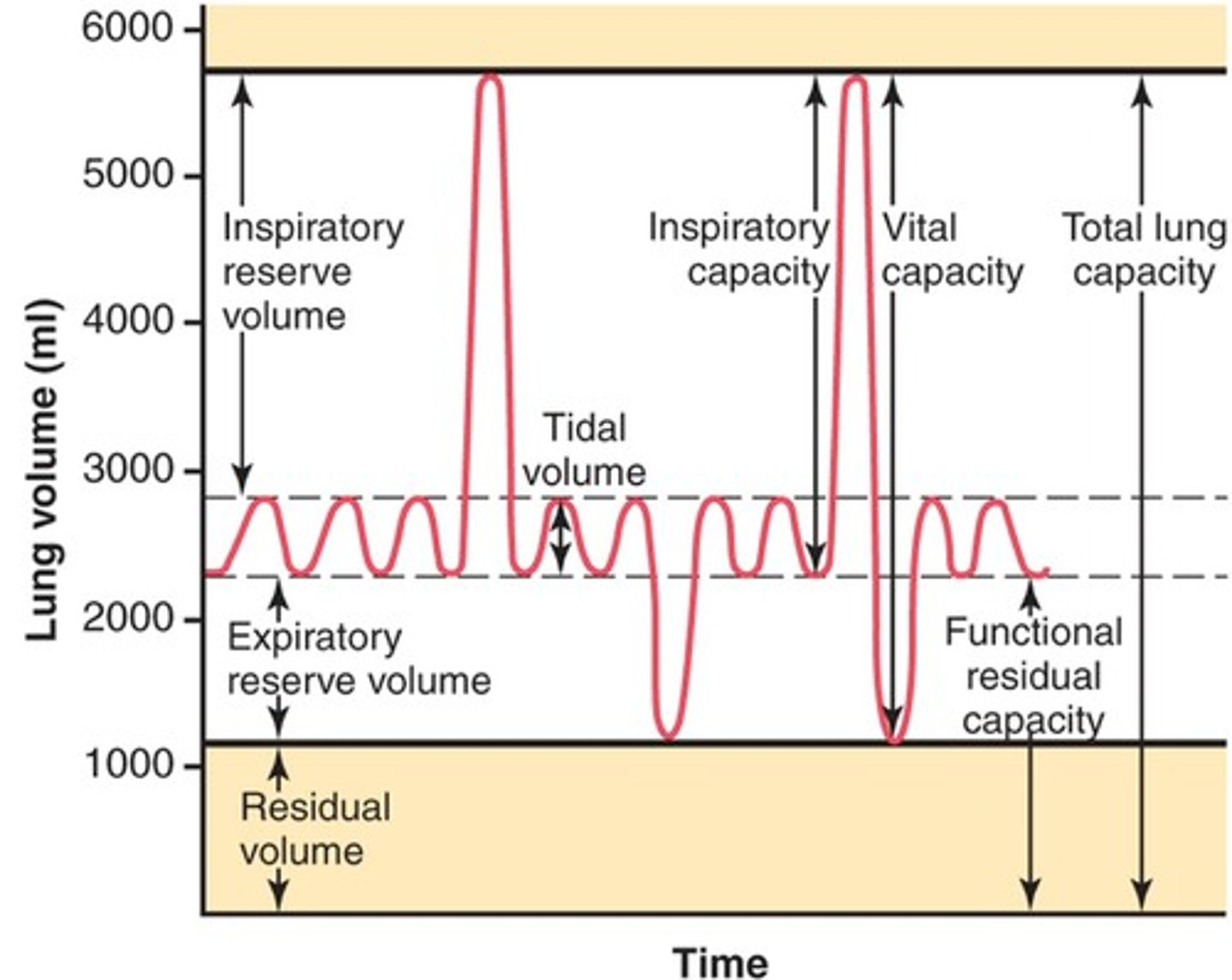
t/f: RV is only measured indirectly
true. it is the amount that is left in the lungs so we cant really take it out and measure it
t/f: restrictive lung diseases will show an increase in TLC
false. reduction in TLC bc cant get air into lungs due to restriction when inhaling
vital capacity + _________ = TLC
functional residual capacity + _________ = TLC
IRV + ERV + reserve volume + __________ = TLC
vital capacity + reserve volume = TLC
functional residual capacity + inspiratory capacity = TLC
IRV + ERV + reserve volume + tidal volume = TLC
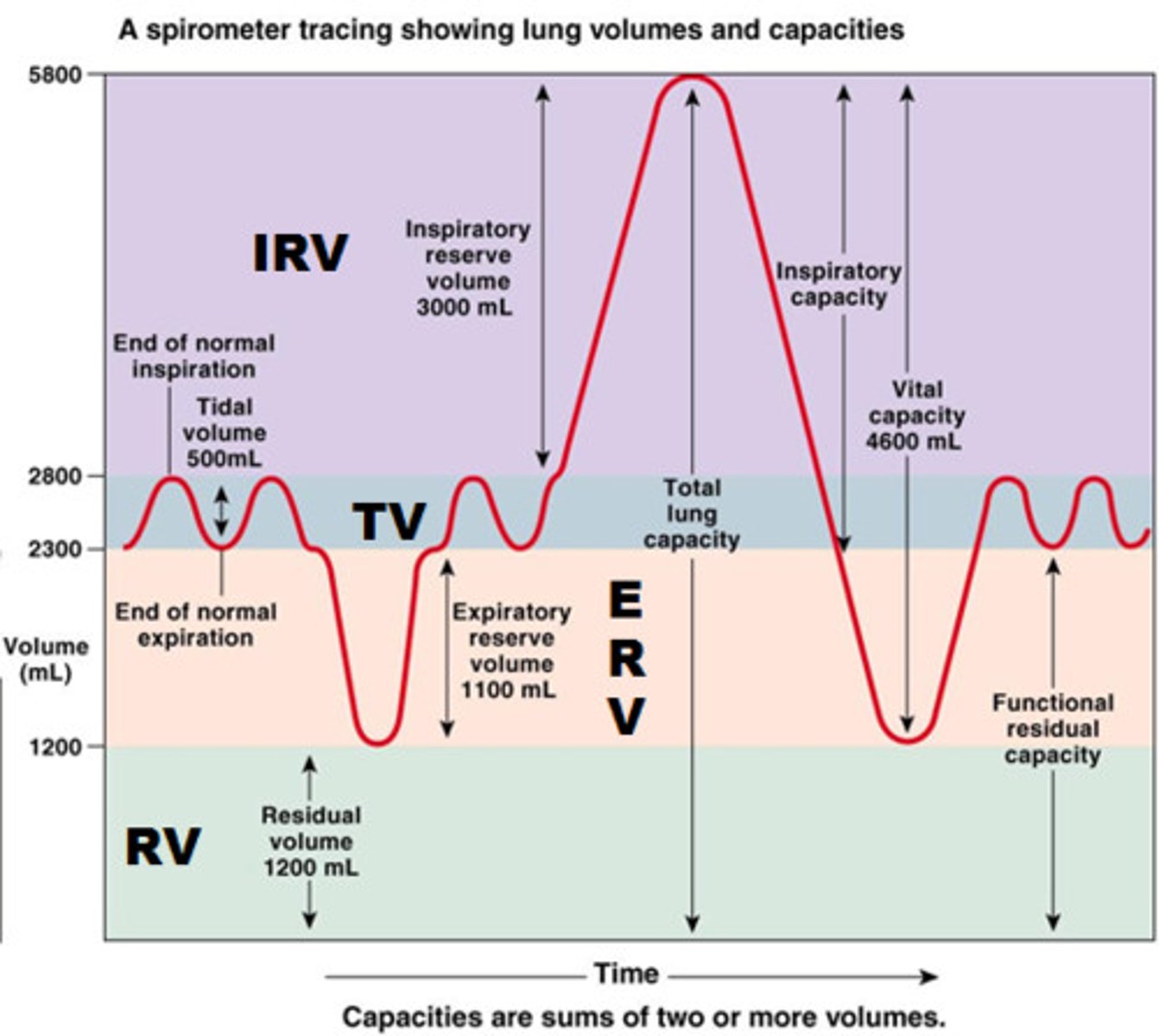
forced vital capacity (FVC)
measurement of the amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled from the lungs after the deepest inhalation

what is FEV1 and what does it convey and depend on
FEV1: amount of air exhaled during the 1st second of FVC maneuver
- conveys info on obstruction
- depends on volume of air in lungs and effort when exhaling
- can be lowered by a decrease in TLC or lack of effort
FEV1 can be lowered by
obstructions, decrease in TLC, lack of effort
why do we use FEV1/FVC instead of just FEV1?
- more sensitive
- independent of patient's size or TLC
- measures airway obstruction with or without restriction
whats a normal fev1/fvc? obstruction?
normal: >75%
obstruction: <70-75%
diagnosis if <70%
what is peak expiratory flow
fastest airflow rate reached during exhalation (FVC)
describe the proper way to take a peak flow measurement
1. have patient STAND and INHALE deeply
2. blow into peak flow meter as fast as possible
3. write down number shown on meter
- repeat twice (best of 3 total)
describe what DLCO is (diffusing lung capacity for carbon monoxide) & how you know if its abnormal
pt takes single breath of CO and enters lungs-> binds to HgB
- if there is NO CO in their exhalation= no abnormality
- if there IS CO in their exhalation= abnormal (bc of decreased gas transfer, the CO didnt diffuse onto hgb properly and was instead exhaled)
t/f: an abnormal diffusing lung capacity for carbon monoxide would show no CO in a patient's exhale
false. abnormal test WOULD show CO since bad gas transfer led to it still being in lungs
common conditions that reduce diffusing lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO)
anything where gas transfer from alveoli to blood is impaired
- lung resection
- emphysema
- interstitial lung disease
normal spirometry and lung volumes with reduced DLCO can suggest
- pulmonary vascular disease
- anemia
- early interstitial lung disease
when are arterial blood gases assessed
- hypoxemia
- hypercapnia (CO2 retention)
- acid-base disorders
what is an A-a gradient
Difference in partial pressure of oxygen between alveoli and arterial blood; used to measure pulmonary gas exchange quality
what can a normal A-a gradient and hypoxemia indicate
alveolar hypoventilation (ex: sedative overdose)
(low inspired oxygen rather than issues with gas exchange)
what is FeNO? why is it used?
Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO)
- measures eosinophilic airway inflammation
-used to assess patients' adherence to therapy or if they need more ICS therapy
a low feno (<____ppm) indicates ____________ response to ICS
a high feno (>____ppm) indicates ____________ response to ICS
low <25ppm: decreased response to ICS
high >50ppm: increased response to ICS (bc high eosinophilic inflammation)
spirometry measures all lung volumes and capacities (including Fev1) EXCEPT
RV (residual volume; never directly measured)
FRC (left in lungs after normal exhale-> erv + rv)
TLC (all lung volume sum; need rv)
t/f: spirometry is the most widely available PFT and is used to define the degree of restrictive lung diseases
false. obstructive lung disease
spirometry IS the most widely available pft, but it cannot directly measure rv, frc, and tlc—which are essential for diagnosing restrictive lung disease
instead, it may show characteristics in restrictive diseases
since spirometry cannot measure TLC, which tests can?
- helium dilution
- nitrogen washout
- body plethysmography
- chest xray measurement (planimetry)
which 2 curves are produced in spirometry
volume vs time
flow rate vs volume
which PFT is the most widely available, useful, and can be done in 15-20 mins
spirometry
t/f: obstructive lung diseases are characterized by a lower capacity to move air through airways and into the lungs
false. out of lungs (restrictive is into lungs)
mechanisms of obstructions in obstructive lung diseases
- mucosal factors (secretions, edema,inflammation)
- smooth muscle constriction
- loss of elastic support
- collapse of airways
identify whether the following are increased, decreased, or normal in obstructive lung disease
FVC
FEV1
FEV1/FVC
fvc= normal (exhaled total is normal)
fev1= low (low in first second)
fev1/fvc= low (normal is 70+)
which spirometry measurements define an obstructive process
low FEV1 and low FEV1/FVC
which 3 diseases are commonly associated with obstruction
asthma, emphysema, chronic bronchitis
obstructive vs restrictive lung disease characteristics
obstructive: defined by low fev1 and low fev1/fvc!!
- low FEV and FEV1/FEV ratio [fvc is normal]
- cannot get air out of lungs
restrictive: defined by low TLC!!
- FEV1/FEV ratio is normal or higher
- low FVC and low FEV1
- cannot get air into lungs
identify whether the following are increased, decreased, or normal in restrictive lung disease
FVC
FEV1
FEV1/FVC
FVC= low
FEV1= low
FEV1/FVC= normal or higher(70+)
t/f: restrictive lung diseases are characterized by an inability to move air into the lungs and have a reduction in all expiratory volumes
true
what are restrictive processes defined by
lower tlc (total lung capacity)
- normal flow-loop curve
- shortened height and width
describe the changes to a flow-loop curve in restrictive diseases
- shape remains normal (pattern of inspiration and expiration is unchanged)
- shortened height and width:
mild<80%
moderate <65%
severe <50%
common diseases associated with restriction
parenchymal inflammation, fibrosis, alveolar filling, chest wall deformity, neuromuscular conditions, poor effort
normal fev1/fvc
over 70-75%
t/f: normal spirometry values are age dependant
true. lower values in older patients, higher in younger pts
would you expect to see high or lower fev1/fvc in elderly? kids? kids w asthma?
older= lower
kids= higher
kids with asthma= <85%
t/f: healthy athletic subjects may have a low fev1/fvc, and normal fev1 and normal FVC
true. may indicate health or mild asthma
- must use judgement or give bronchodilator challenge
a FEV 1 of ____ indicates moderate obstruction
a FEV1 of ______ indicates severe obstruction
<60: moderate
<40%: severe
t/f: a fev6 may be used instead of fev1
true
what is an acute bronchodilator response characterized by? (fev1)
increase in FEV1 >12% and >0.2L
(mostly seen in asthma)
compare asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema in terms of FEV1, FEV1/FVC, airway resistance, and response to bronchodilators
-low FEV1 in all
- low FEV1/FVC in all
- increased airway resistance in asthma and chronic bronchitis (not emphysema)
- large response to bronchodilators mainly in asthma!!! low in chronic bronchitis and emphysema (about 20% may have tho)
what can be a potential differential in asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema
-increased airway resistance in asthma and chronic bronchitis (not emphysema)
- large response to bronchodilators mainly only asthma
t/f: mainly asthma pts have hyper-reactive airways, but some patients with COPD may as well, suggesting worse prognosis and accelerated decline in FEV1
true
asthma may be diagnosed by demonstrating hyperresponsiveness to provocative agents such as
methacholine
histamine
distilled water
cold air
exercise
a positive hyperreactivity asthma test would display
decline FEV >20% AND reversibility of obstruction to bronchodilators
[can be used on pts with no wheezing and normal PFTs]
summary of obstructive lung disease vs restrictive lung disease
FVC
FEV1
FEV1/FVC
TLC
RV/TLC
airway resistance
FVC: normal in OLD, low in RLD
FEV1: low in both
FEV1/FVC: low in OLD, normal or high in RLD
TLC: normal or high in OLD, low in RLD
RV/TLC: normal or high in both
airway resistance: high in OLD, normal in RLD
which pulmonary functions values are the same in obstructive and restrictive lung diseases
FEV1 (low)
RV/TLC (normal or high)
FEV1 and FEV1/FVC can be used to diagnose ______ and suggest _______
diagnose obstructions, suggest restrictions
use TLC to diagnose restriction using 4 methods:
helium dilution, nitrogen washout, body plethysmography, chest xray measurement (planimetry)
what are 2 minor tests used to assess lung function based on general fitness
1. 6 minute walk test: walk pre determined route, see how much distance is covered
2. harvard step test: step up and down 20 inch step, last 5 minutes, 1 minute rest, measure recovery heart rate (lower hr= better fitness)