CL1 - Breast & Prostate Cancer
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Principles of cancer treatment
aim to kill cancer cells and spare the normal ones
Recent developments to maximise the therapeutic window of cancer treatment
refine chemotherapy schedules
nvoel targeted agents
better supportive medications
immunotherapy
tailoring of treatment to individuals
response predictions
radiotherapy improvements
Settings for chemotherapy
Adjuvant:
following surgery or radiotherapy to reduce risk of recurrence
no way to assess response
continue to planned number of cycles as long as it is tolerated
Metastatic
palliative - to control spread of disease
measure size changes of metastatic lesions
improvement in symptom control and QoL
Neoadjuvant
to shrink tumours before surgery or radiotherapy which improves chance of cure
allows clinical, radiological and pathological response assessments and change to alternative therapy in non-responders
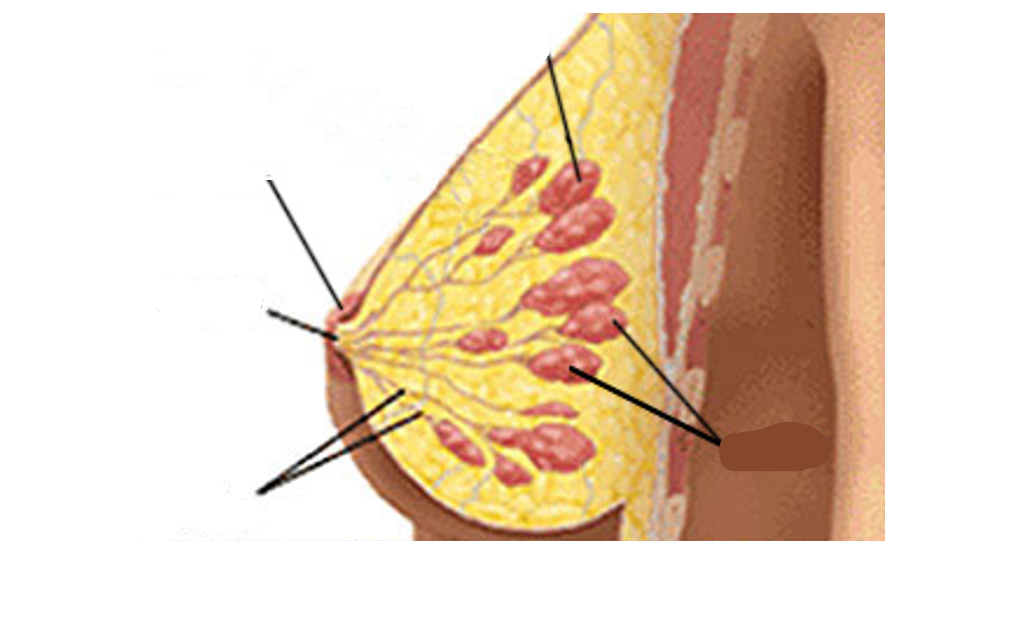
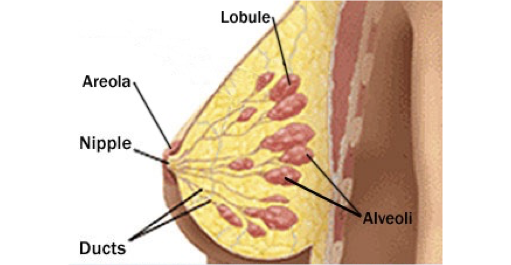
Basic anatomy of the breast
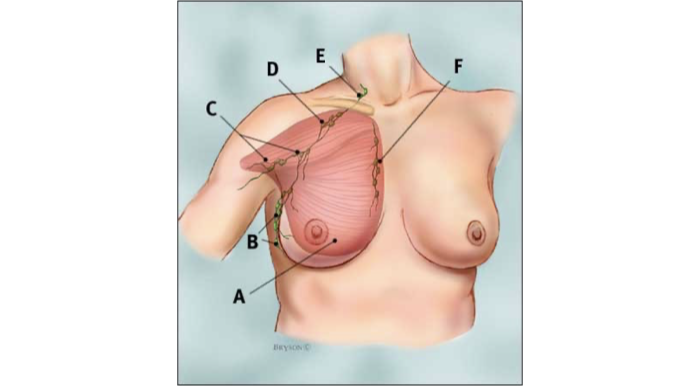
Lymph node areas adjacent to breast
Where the cancer spreads to
A pectoralis major muscle
B axillary lymph nodes: level I
C axillary lymph nodes: level II
D axillary lymph nodes: level III
E supraclavicular lymph nodes
F internal mammary lymph nodes (by the heart so cannot be surgically removed)
How do we assess breast lumps?
history and examination
mammography
ultrasound
MRI
DCE-MRI
Distant staging
bone scan
CT chest/abdomen/pelvis
PET/CT
Staging for Cancer
T: Size of Tumour
N: Rate of Lymph nodes spread
M: Metastases
Tis
Carcinoma in situ - pre-invasive disease
Primary Tumour Staging (T)
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1: tumour 2cm or smaller in greatest diameter
T2: Tumour is > 2cm but not > 5cm
T3: Tumour is > 5cm
T4: extension to skill or chest wall
Regional Lymph Nodes (N)
N0: no regional lymph node metastasis
N1: Metastasis in 1-3 axillary lymph node(s)
N2: Metastasis in 4-9 axillary lymph node(s) or radiologically involved interanl mammary nodes
N3: Metastasis in 10 or more axillary nodes or ipsilateral infraclavicular lymph nodes
Metastases measure of
Mx: not evaluated
M0: no distant metastases
M1: distant metastases
What do we look out for on pathology reports?
Tumour type
IDC/ILC/papillary/tubular etc
Associated DCIS/LCIS
Size
Grade (1-3)
Margins
Lymphovascular invasion
Nodes
Extracapsular spread
ER/PgR/HER2 receptor status
Pathological type of breast cancer
Invasive ductal carcinoma - most common type
Invasive lobular carcinoma
more likely multifocal/bilateral
less likely to present with define lump
more likely to spread to unusual sites
but often low grade and more elderly population
similar long term outcomes
Role of cell surface receptors
cellular receptors are responsible for translating signals from outside the cell into signals within the cell
these have effects such as growth, proliferation and cell survival
can be inappropriately activated in cancer causing the spread and growth of cancer cells
Cell surface receptors in breast cancer
ER - oestrogen receptor
PR - progesterone receptor
Her-2 receptor - overexpressed in ~20% of breast cancers and is associated with more aggressive cancers/poorer prognosis
Why is Her-2 ER negative?
Oestrogen suppresses Her-2 expression and her-2 is overexpressed in cancer
Endocrine therapy
ER positive tumours are more susceptible to endocrine therapy
can cause less side effects
More convenient than chemotherapy
Lack of cross-resistance
Types of endocrine therapies
Tamoxifen
Aromatase inhibitors - anastrozole, letrozole, exemestane
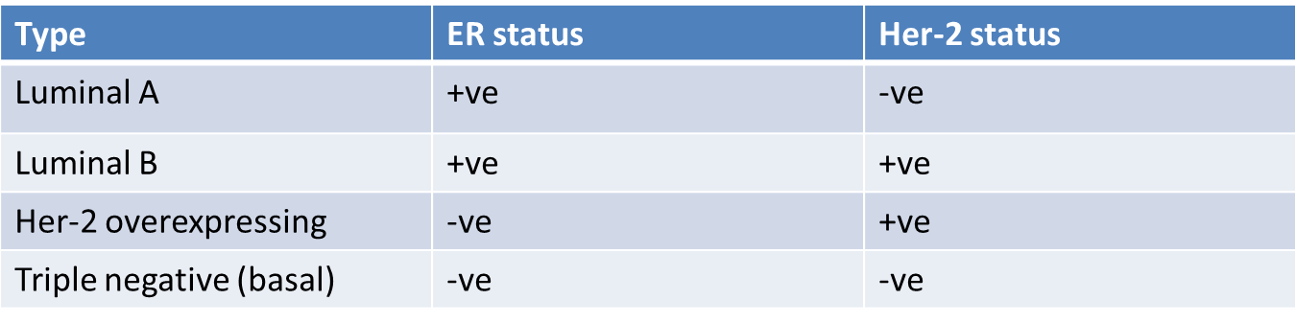
Types of Cancers and their ER responsiveness
Adjunvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
gives absolute survival benefit of around 1-15% depending on patient and tumour characteristics
The combinations have changed over the last 10-15 years
CMF
FEC
TAC/FEC-T
PREDICT BREAST
A programme used to predict the benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy
Inputs data such as:
pt age
grade of tumour
ER responsiveness
Helps make the decision to whether chemotherapy is beneficial when you also consider the SE
Genomic Sequencing
Used to predict the benefit of chemo by sending off a sample of the tumour
multiple genes examined
comes up with score for risk of recurrence score
less than 11 = low risk
11-25 means intermediate risk
> 25 means high risk of recurrence
used to predict benefit from chemo but made as prognostic marker initially so the high risk could also be in general and not relating to chemo
Initially was only used in node negative but now also being used in node positive patients
Abemaciclib
cdk 4/6 inhibitor
given alongside endocrine treatment
used to double the effect of treatment in metastatic setting
~2 year improvement in survival
Issues with Abemaciclib
toxicity (causes quite a lot of diarrhoea)
more ANC (absolute neutrophil count)? less nact (neoadjuvant chemo therapy)
Will pts get a CDK4/6i upon relapse as well?
2 years of additional appointments and pharmacy input
Anti-Her2 directed therapy
Trastuzumab
3-weekly infusions or SC
usually given until progression
well tolerated but can cause infusion reactions/cardiac effects
Pertuzumab
HER2 dimerisation ibhibitor
improves PFS (progression free survival) alongside docetaxel/trastuzumab in 1st line
Kadcyla
TDM1
conjugate of trastuzumab and chemotherapy molecule
what is NACT with pembrolizumab?
Neoadjuvant chemo therpay with pembrolizumab
used to treat triple negative breast cancer
seen a higher PCR (pathological complete response)
Use of NACT with pembrolizumab
longer infusion time in neoadjuvunt setting and additional 9 adjuvant treatments
clinic time is roughly doubles due to new pt consultation time and due to complex toxicity management
quite toxic
Metastatic disease
incurable so the aim is to control and prevent symptoms
significant gains in PFS and OS (overall survival)
most patients sequence through 5-6 lines of therapy over a number of years
similar drugs to adjuvant setting
chemo
endocrine therapy
anti-HER2 therapy
New agents:
Cdk4/6 inhibitors
mTOR inhibitors
Trastuzumab Deruztecan
New drug
Her 2 antibody + molecule of chemotherapy attached via linker molecule
targeted chemotherapy so reduced generalised chemo toxicity
Sacituzumab govetican
New drug
Used in triply negative/hormone postive cancers
antibody conjugate: trop-2 antibody + topoisomerase inhibitor
used for advanced breast cancer after 2 or more therapies with at least one of them being intended for advanced disease
Diagnosing Prostate Cancer
usually through raised PSA blood test
may or may not have symptoms:
bladder frequency
nocturia
terminal dribbling/poor stream
digital rectal examination
MRI scan
transrectal biopsy
Early detection of prostate cancer
PSA screening and digital-rectal exams can help with early detection and treatment
Prostate cancer pathology
PSA level
number of biopsy cores involved
percentage of tissue involved
extracapsular extension/seminal vesicle involvement (stage T3a/b)
lymph node spread (on scans)
gleason grade:
two added scores of 1-5
subjective
minimum for cancer 3+3=6
Radical Treatment Options
For localised disease
Surgery
open
laparoscopic
robot-assisted
Radiptherapy
external beam radiotherapy
conformal
IMRT
IGRT
LDR brachytherapy
HDR brachytherapy
Active surveillance
Watchful waiting
External beam photon therapy
targeted treatment
20 doses over 4 weeks
side effects: bowel, bladder and fatigue
Metastatic prostate cancer
Most common spread is to bones
Backbone of treatment is testosterone suppression and blockade e.g.
LHRHa
Anti-androgens
New endocrine therapies: abiraterone, enzalutamide, daralutamide
Chemotherapy
Docetaxel
Cabazitaxel
Radium 223
Coping with cancer in the future (NHS)
Increasing role of independent prescribers
decision makers
impact on oncology clinics
room capacity
Better horizon planning of impact of new drugs on service
ideally centralised
lots of work to get accurate estimates
impractical to submit business cases for each drug/indication
Reorganisation of outpatient clinic slots
Work with RCR/RCP on training and recruitment
Sensible use of treatments
elderly and cdki
genomic predictive testing in adjuvant setting
later lines of mBC treatments