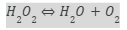Topic 2- Rates of Reaction, Equilibrium and yield, and managing resources
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Steep gradient
Conversion of reactants to products at a rapid rate
Shallow Gradient
Conversion of Reactants to products occurring much slowly
Zero Gradient
Conversion of reactants to products have reached chemical equilibrium.
Slope for a products
Have a positive slope
Increasing
Slope of a reactant
Has a negative slope
decreasing
reducing the number of reactants
What is the collision theory
All partials must collide
All particals must have the correct orientation
All particals must have sufficient energy
Successful collisions
reactants collide in the correct orientation with sufficient energy.
Products are formed
Increase frequency in successful collisions per unit time
Unsuccessful collision
reactants collide in inncore y orientation and or insufficient information.
No products are formed
Decrease frequency in successful collisions per unit time
energy in a exothermic reaction
a net release of energy
Negative
Energy of products is less than energy of reactants
Decrease in heat energy in the system
Energy in a endothermic reaction
absorption of energy
Positive
Energy of products is greater than the energy of reactants
Increase in heat energy
axis in an energy profile diagram
vertical axis: enthalpy of system
Horizontal axis: reaction pathway
What is concentration?
Number of particles per unit volume
Solutions are more concentrated when they have a greater amount of particles per unit of volume.
How does concentration affect the rate of reaction?
increases the number of reacting particles.
increases number of collisions between reacting particles per unit time
increases chance of successful collisions happening.
still needs activation energy and correct orientation.
What is temperature?
measure of average kinetic energy (movement) of particles per unit of time
particles move at higher speeds and collide with greater energy when heat is transferred.
How does Temperature affect the rate of reaction?
Increasing temperature = increase kinetic energy
frequency of collisions between particles increases
amount of reacting particles increases.
increases chance in successful collisions.
What is pressure?
measure of amount of force per unit area
pressure of a gas is increased by reducing the volume of its container.
How does pressure affect the rate of reaction?
increasing the pressure of a gaseous mixture causes particles to be closer, causing frequent collisions.
increases number of collisions per unit time.
increases chance of successful collisions.
What is surface area?
particles collide on the surface of a solid reactant in a chemical reaction.
only particles on surface are available to collide and react with each other.
How does Surface area affect the rate of reaction?
Increases number of surface particles that can react.
increases frequency of collisions between reacting particles.
What is a catalyst?
material that increases the rate of chemical reaction without being consumed
Homogenous: same state of matter as reactants
Heterogenous: Different state as matter as reactants
optimised to minimise the amount of them required whilst optimising efficiency, keeping costs down.
How do catalysts affect the rate of reaction?
provide different reaction pathways that required lower activation energy (Ea)
Reduces activation energy required.
Enthalpy (H)
Measure of heat energy within a system at constant pressure and volume.
change in heat energy is measured at constant pressure in enthalpy change is represented by (ΔH)
What is a system?
Set of substances and energy that is being studied/focuses on
What is a reversible reaction?
reactants collide to form products (forward reaction) and products collide to form reactants (reverse reaction)
What is a irreversible reaction?
proceed in a single direction from reactants to products
Open system
Allows energy and matter to be exchanged with surroundings
container is open
Closed system
only allows energy to be exchanged with surroundings
container is sealed.
what is Equilibrium?
dynamic state in which the forward and backward reaction are ongoing. rate of forward reaction and backward reaction is equal in rate of backward reaction.
In a closed system
state of dynamic equilibrium is reached
Kc equation
if Kc is greater than 1, goes to the left
if Kc is less than 1, goes to the right
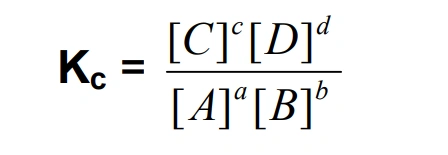
Le Chatelier’s principle
ang changes that affects positions of an equilibrium causes the equilibrium to shift in such way as to partially oppose the effects of the change
system will counteract the change in reaction.
changes so it returns to its nmormal state
Increase concentration of reactant
LCP: decrease concentration of reactants
increase concentration of products
Equilibrium shift to right
Decrease in concentration of the reactant
LCP: increase concentration of reactants
increase in reactants
shifts to left
Increase concentration of products
LCP: Decreasing the concentration of the product
increase in reactants
shits to the left
Decrease in Concentration of the product
LCP: Increasing the concentration of the products
Increase in products
shifts to the right
Equilibrium mixtures are affected by changes in pressure if
The reaction mixture contains gases
Difference in total number of moles of gaseous reactants and products in reaction mixture
Increase of pressure (via decreasing the volume)
LCP: Decreasing the pressure by producing less moles of the gas
Shifts to the side with less moles of gas particles
Decrease of pressure (via increasing the volume)
LCP: Increasing the pressure by producing more moles of the gas (to fill the remaining volume of space)
Shifts to the side with more moles of gas particles
Increase in temperature (Endothermic)
(heat is the reactant)
LCP: Decrease in temperature
Shifts to the right
Decrease in temperature (Endothermic)
(heat is the reactant)
LCP: Increase in temperature
Shifts to the left
Increase in temperature (Exothermic)
(heat is the product)
LCP: Decrease in temperature
Shifts to the left
Decrease in temperature (Exothermic)
(heat is the product)
LCP: Increase in temperature
Shifts to the right
Predict the change that occurred in a system, or whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic, given the effect of the change on the equilibrium position of the system.
Lower temperatures prefer product formation when there is exothermic equilibria, but lower temperatures also reduce the rate of product formation.
The addition of a catalyst can lower the activation energy/temperature
Which is required for a reaction leading to increased rate and yield at the lower temperature.
What is Yield?
amount of the product formed in a chemical reaction
%yield = Actual yield / Theoretical Yield x 100
Exothermic reactions (yield)
favour lower temps
Increase in temp = decrease in yield, but increase in ROR due to kinetic energy, therefore producing less products at a high rate
Endothermic reactions (yield)
favours higher temperatures
Increase in temp = increase in Yield, ROR increases (beneficial for industries) = make more money
Explain the impact of increases in temperature and pressure on manufacturing conditions and costs, and on the environment.
Temperature
Pressure
Reactant concentration
Particle size / surface area
Catalyst
Mixing
Temperature
Raises cost but can increase reaction rate
Pressure
Raises cost but can increase reaction rate
Reactant Concentration
Increases reaction rate
Particle Size & Surface Area
It can increase the rate of reaction
Catalyst
Preparation and Structure
Mixing
Increases the rate of reaction
Explain how use of a catalyst may benefit both the manufacturer and the environment. (Environmental impact )
Advantages: Biodegradable, less pollution
Limitations: Farming may cause soil degradation, water pollution, and pesticide use
Explain how use of a catalyst may benefit both the manufacturer and the environment. (Sustainability )
Advantages: Renewable, lower carbon footprint
Limitations: Large-scale farming can lead to deforestation or loss of biodiversity, large quantities of water required which are often in short supply. Potentially susceptible to climate change.
Explain how use of a catalyst may benefit both the manufacturer and the environment. (Availability)
Advantages: Can be locally sourced, reducing import deficiency
Limitations: Seasonal and geographic factors may limit consistent supply. Reduces land availability for food.
Explain how use of a catalyst may benefit both the manufacturer and the environment. (Energy requirements)
Advantages: lower energy needed for processing
Limitations: Some extraction and refinement processes remain energy-intensive
Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide