lab final bio
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
interphase
nucleus appears normal, and the cell is performing various cellular functions
unicellular organisms…
can use mitosis for asexual reproduction
why do cells need to divide
growth, differentiation and repair
mitosis
the entire process of nuclear division
cytokinesis
the process of splitting the cytoplasm
when is the dna replicated
s-phase
cancer
disease of the cell cycle
what phase do senescent cells stay in
g0
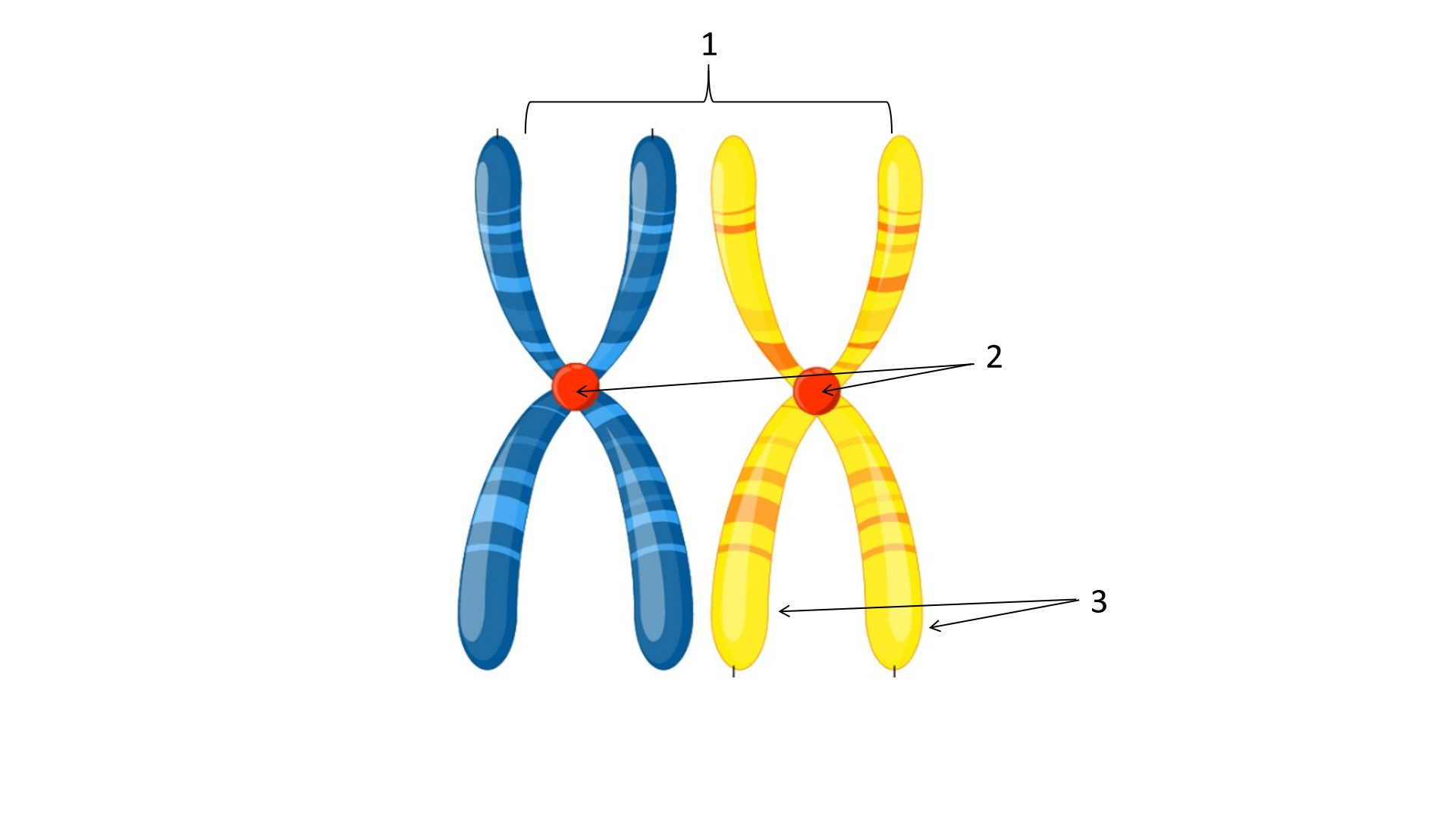
1
sister chromatids
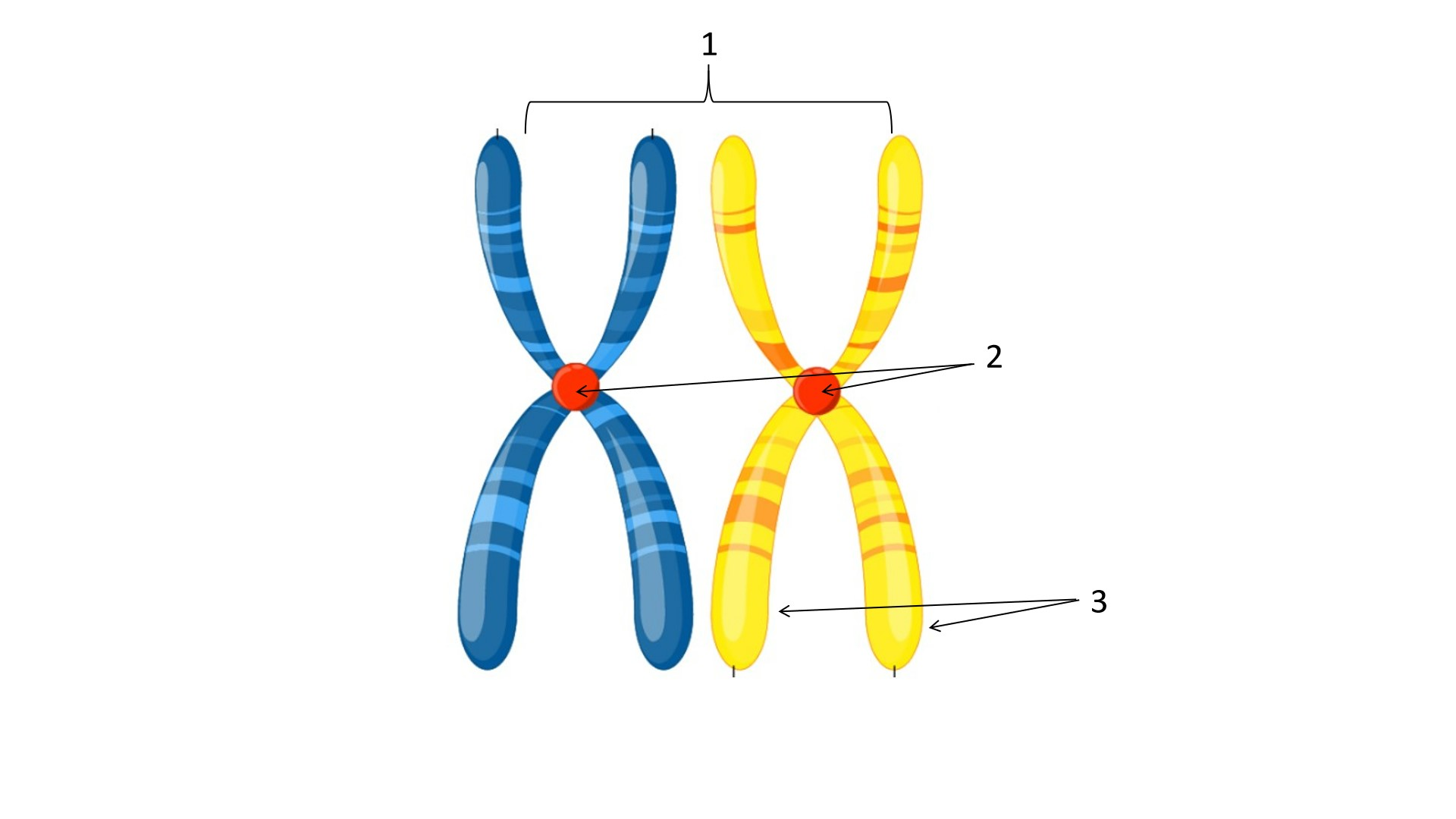
2
centromere
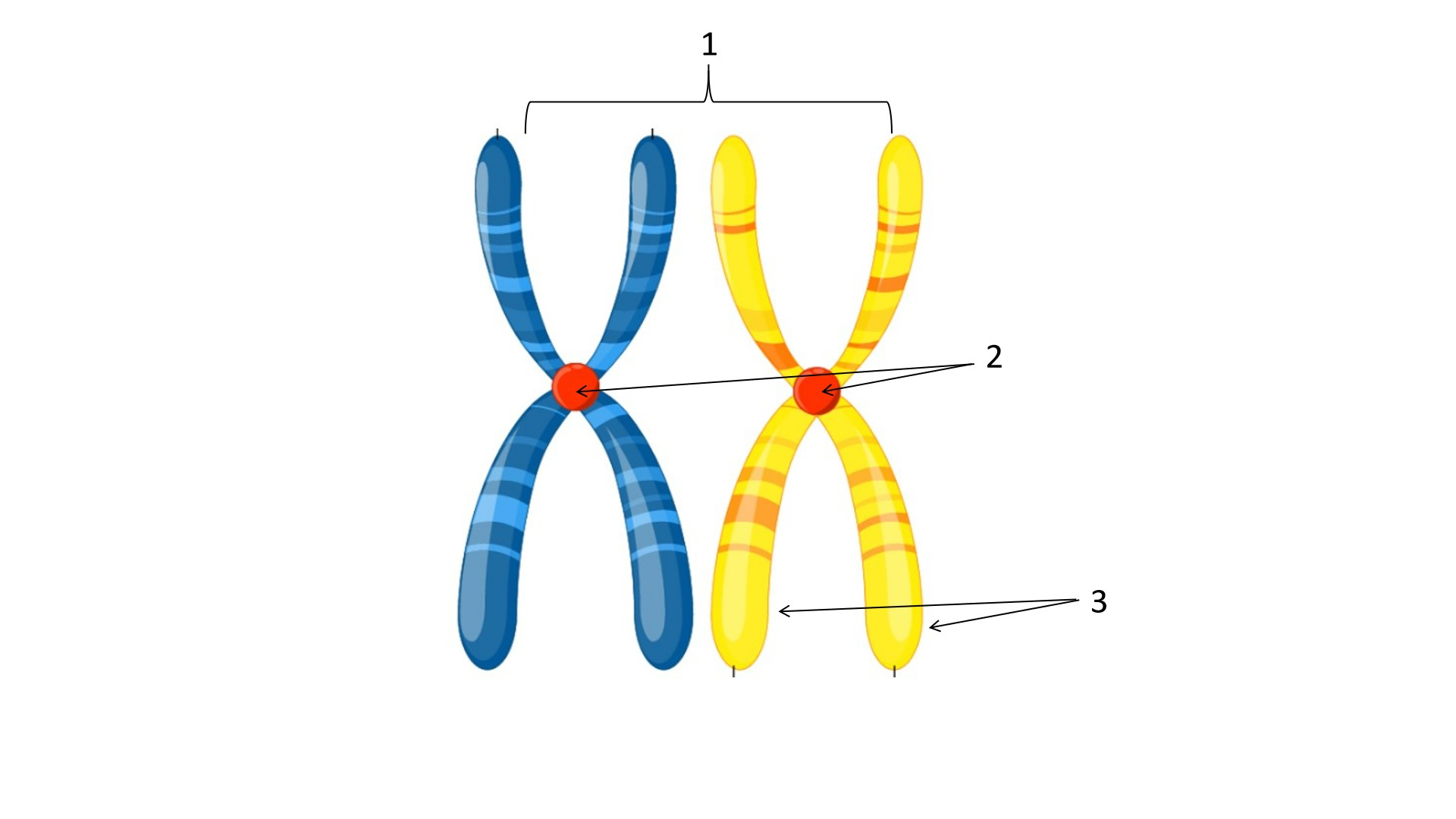
3
telomere
aneuploidy
incorrect number of chromosomes
a spindle is composed of
spindle fibers formed by centrosomes
where are centrosomes located?
the poles of the spindle
aster
array of fibers
cytokinesis in animal cells forms a
cleavage furrow
cytokinesis in plant cells forms
a cell plate
contractile ring
band of actin filaments
meiosis
nuclear division of gametes
tetrad
two pairs of homologous chromosomes
synapsis
homologues pair up
interkenesis
short period of time between meiosis I and II
spermatogenesis
the production of sperm
oogenesis
the production of eggs
haploid cells
have 1 copy of each chromosome
reductive division
first meiosis division
sources of genetic variation
crossing over, independent assortment, random fertilization
when does crossing over happen
prophase I
how many different ways can chromosomes arrange
2²³
germ cell
starts meiosis
genotype
refers to an individuals genes
phenotype
refers to a persons physical appearance
dihybrid cross ratio
9:3:3:1
scientific word for flies
drosophila
autosomes
non sex determination chromosomes
biotechnology
the use of natural biological systems to create a product or achieve some other end desired by human
genetic engineering
modification of an organisms genes
protein synthesis
gene expression
transcription
happens in nucleus during interphase, stimulated by transcription factors, done by rna polymerase
translation
happens in cytosol during interphase, coordinated by an rRNA
stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
start codon
AUG
how many codons are there within RNA?
64
How many amino acids do codons code for
20
DNA is said to have
a triplet code
every three bases is called
a codon
each RNA has one particular tRNA amino acid at one end what a specific _ at the other
anticodon
what is the process called where charged DNA molecules migrate across a span of gel because they are placed ina powerful electrical field?
electrophoresis
4 micro evolution forces
natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutations
the theory of evolution broadly describes
genetic change in populations
what is the tendency to produce more offspring than competing individuals
fitness
the proportion of individuals in a certain category relative to the total number of individuals considered
frequency
P=
2(BB)+(Bb)/2(total population)
factors such as temperatures and predation that affect organisms and result in selective reproduction of phenotypes
selection pressures
chlamydomona
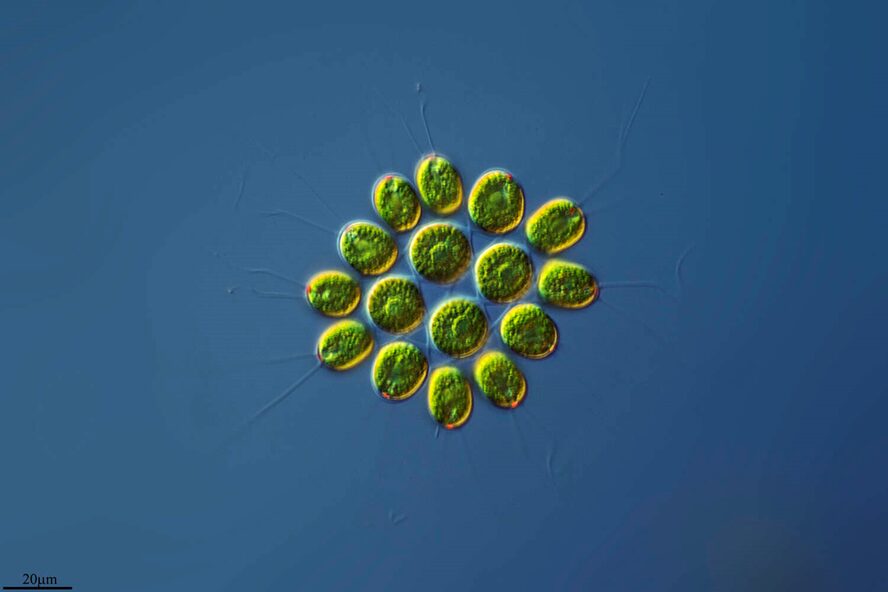
gonium
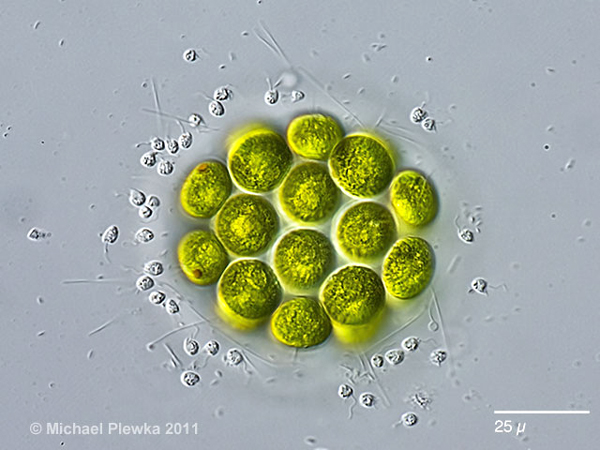
pandorina
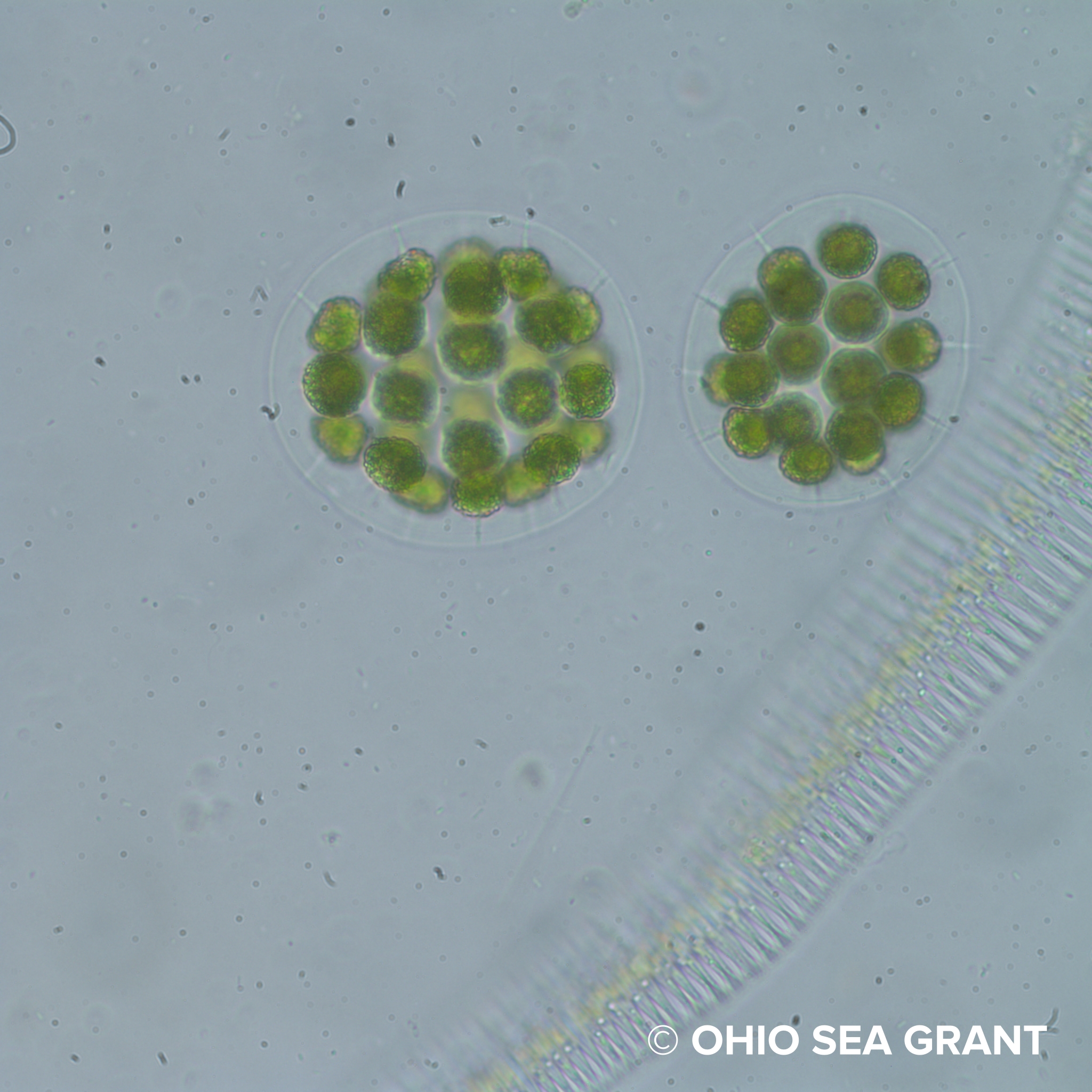
eudorina
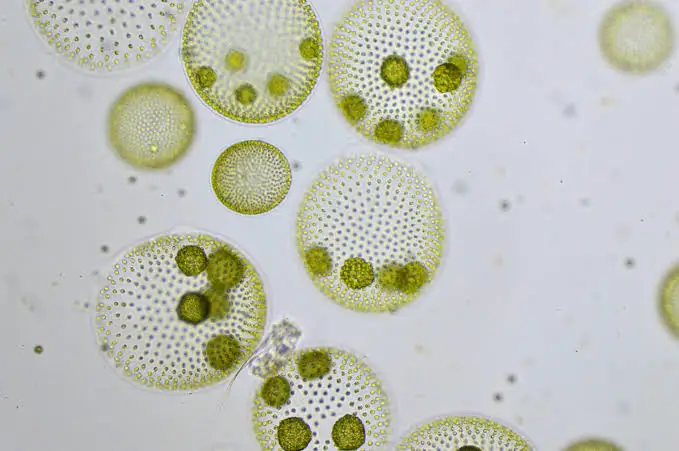
volvox
Hardy-Weinberg equation
P²+2PQ+Q²=1
hardy-weinberg conditions
no mutations, random mating, no gene flow (migration), a very large population size, and no natural selection
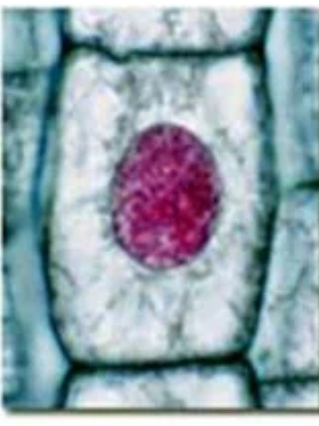
prophase
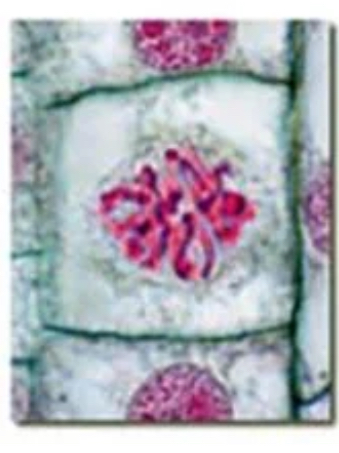
prometaphase
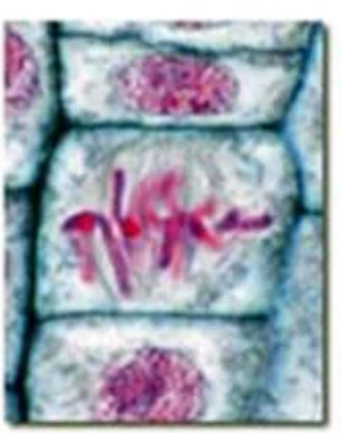
metaphase
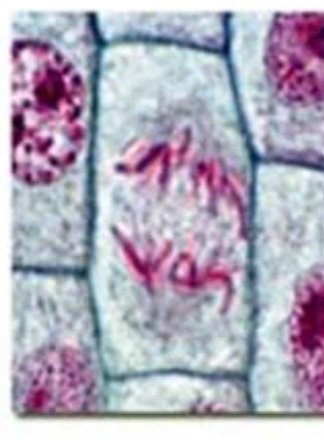
anaphase
telophase
Why do we dissect other vertebrates
because of homology
gene flow
migration
recombinant chromosomes
chromosomes that have crossed over
p²
Frequency AA
2pm
frequency of Aa
q²
frequency of a