PharmSci Lecture 1 Drug Properties/ functional groups
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
physicochemical properties
1. solubility in water/lipids
2. acid/base characteristics
3. conformation, configuration, structure
ADME
absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion
pharmacodynamics vs pharmacokinetics
dynamics= study of drugs and their action on tissues and living organisms
kinetics= ADME of drugs
nonelectrolyte vs electrolyte
non= neutral, un ionized
electrolyte= ionic (weak acid or base)
what can make a hydrogen bond
EN atom (O,N,S,F) and polarized hydrogen
polarized hydrogen
H bound to EN atom
how many hydrogen bonds does S make
2
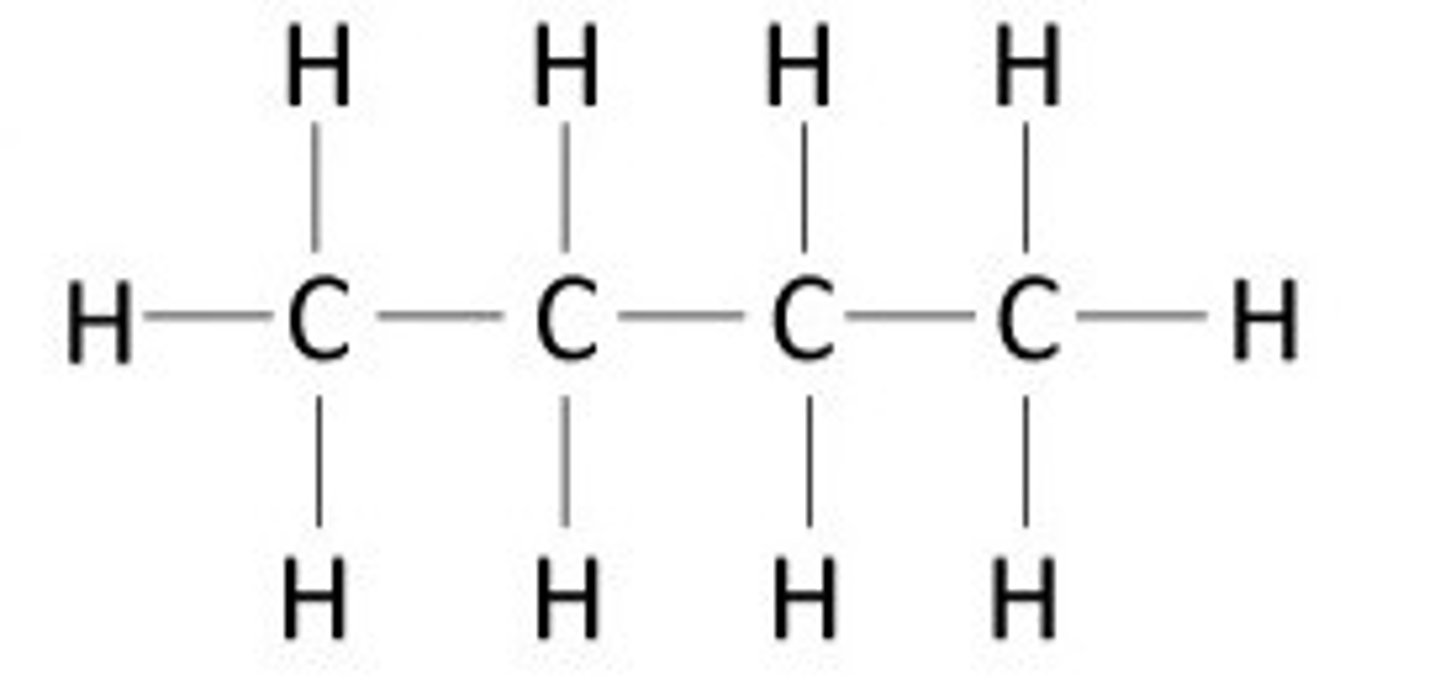
hydrocarbons
NONELECTROLYTE
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
-very FAT soluble
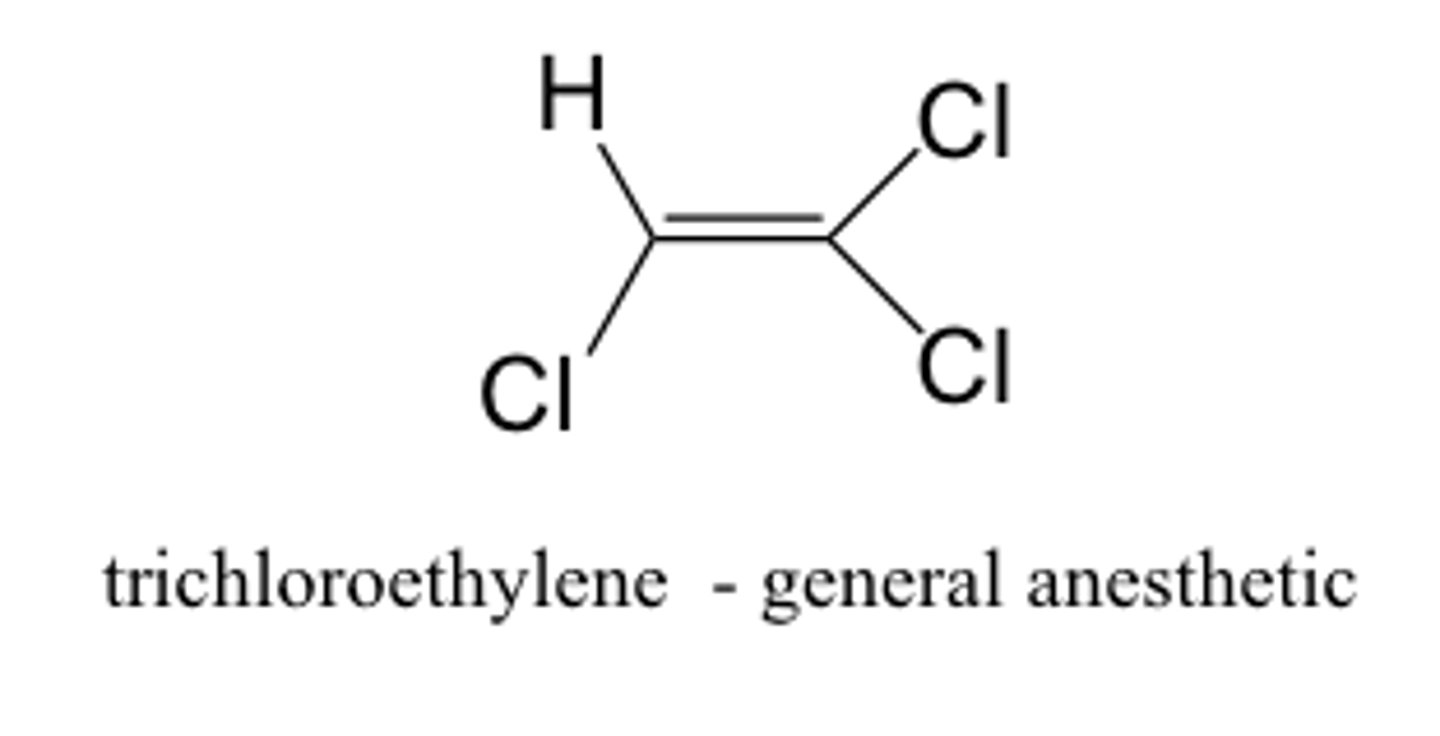
halogenated hydrocarbon
contain C, H, and halides
- FAT soluble
alcohols
NON ELECTROLYTE
R-OH
H bond donor AND acceptor
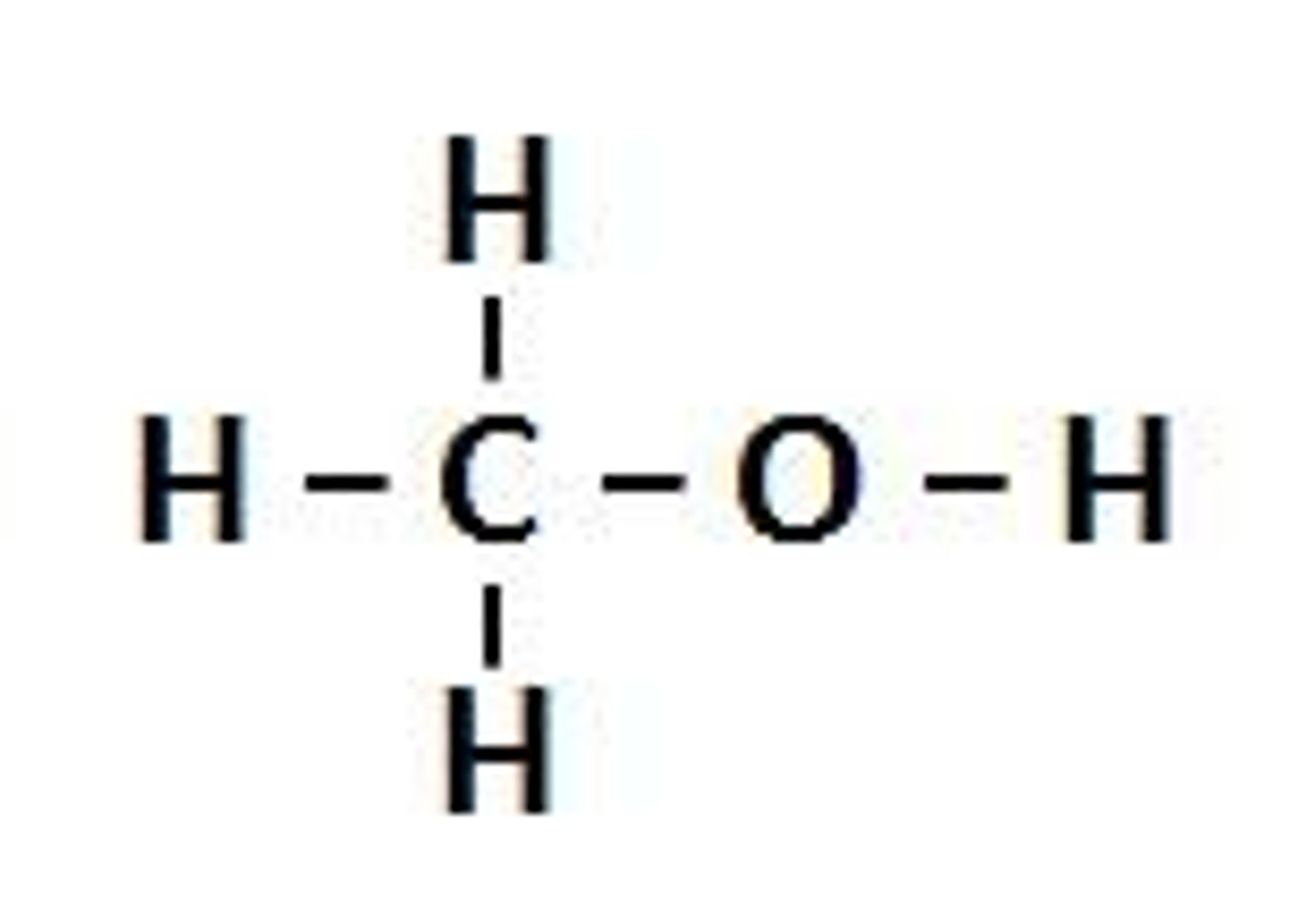
ethers
NON electrolyte
R-O-R

aldehyde
NON electrolyte
CHO
**no H bond donors since H isnt attached to EN atom
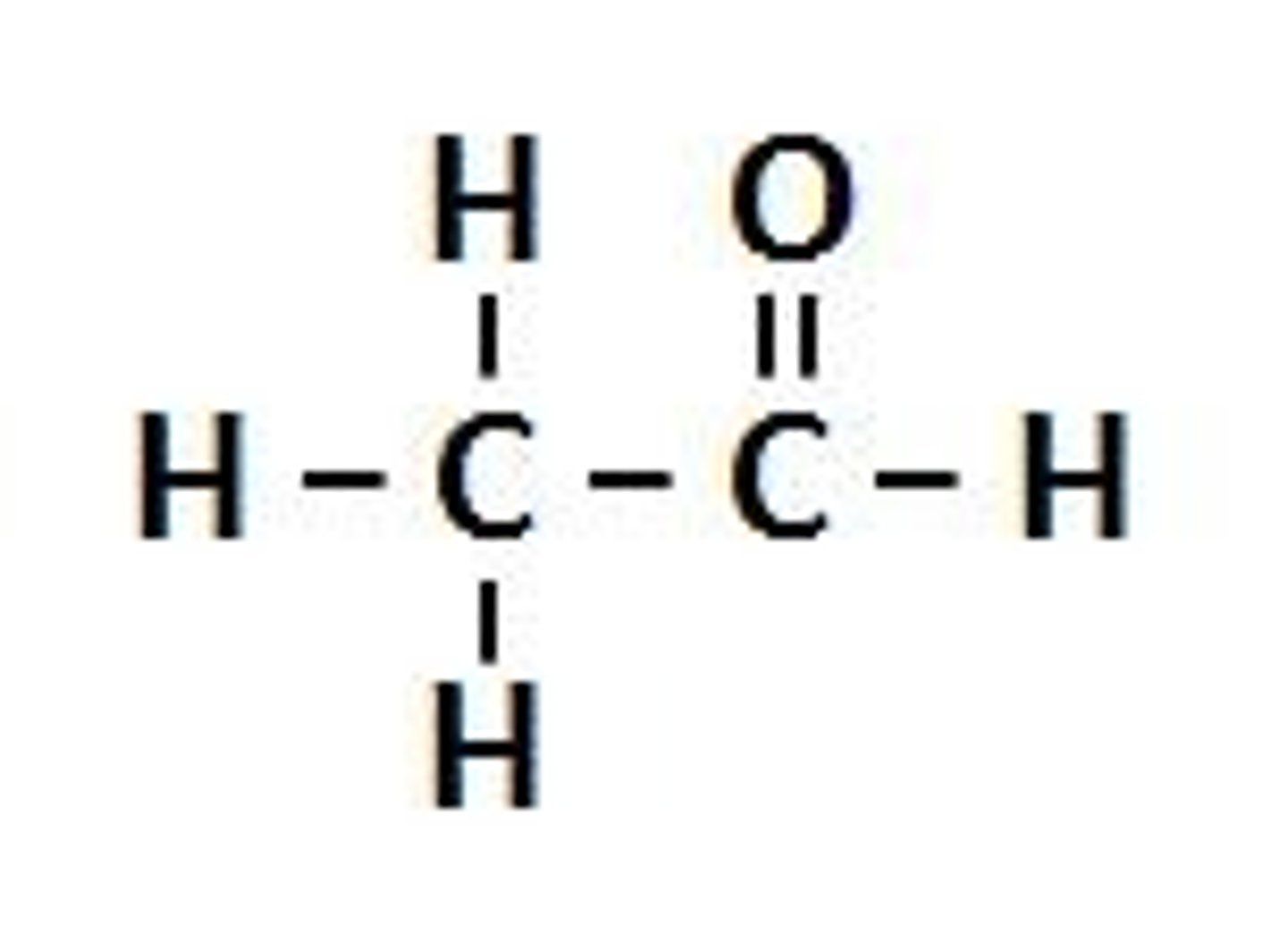
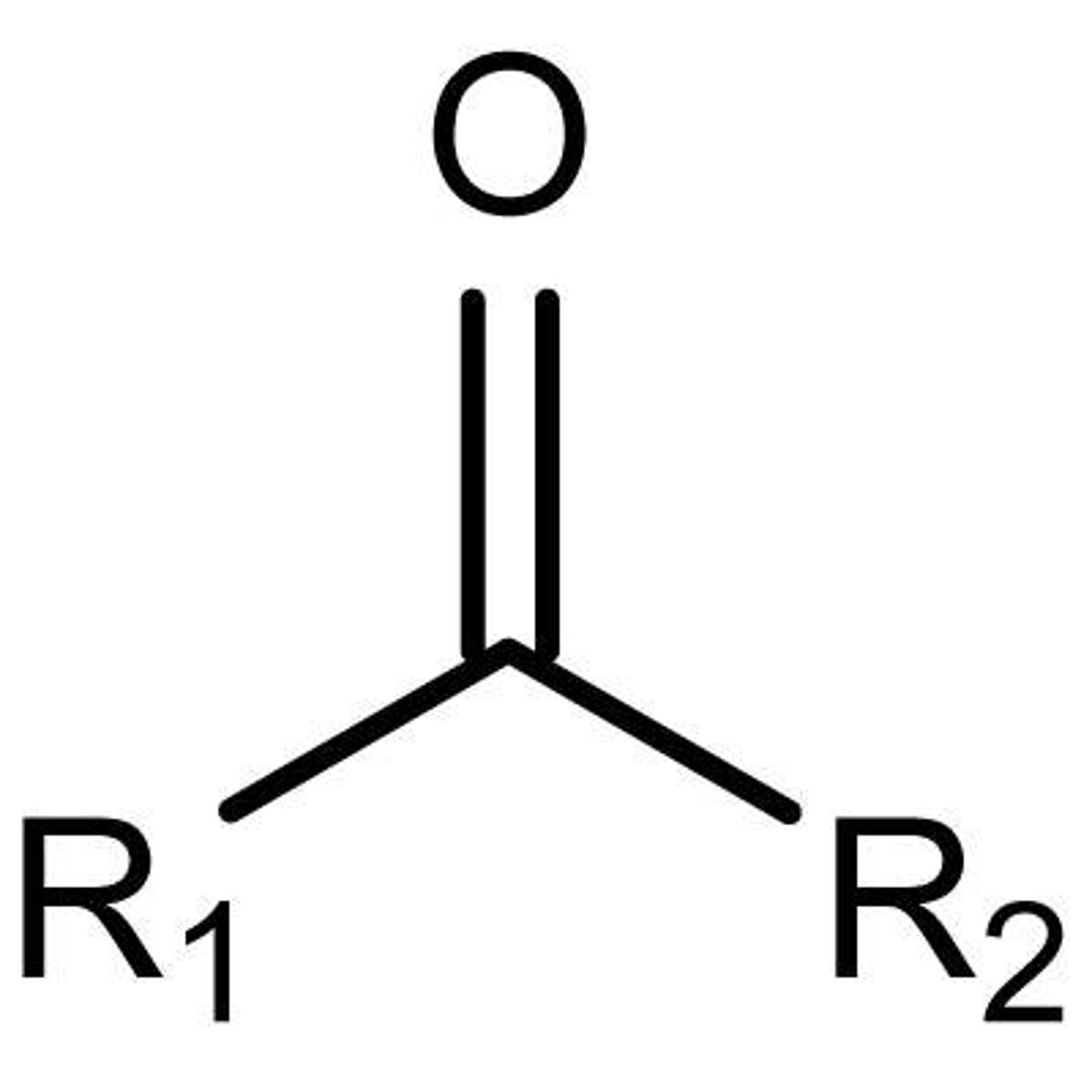
ketone
NON electrolyte
R-C=O-R
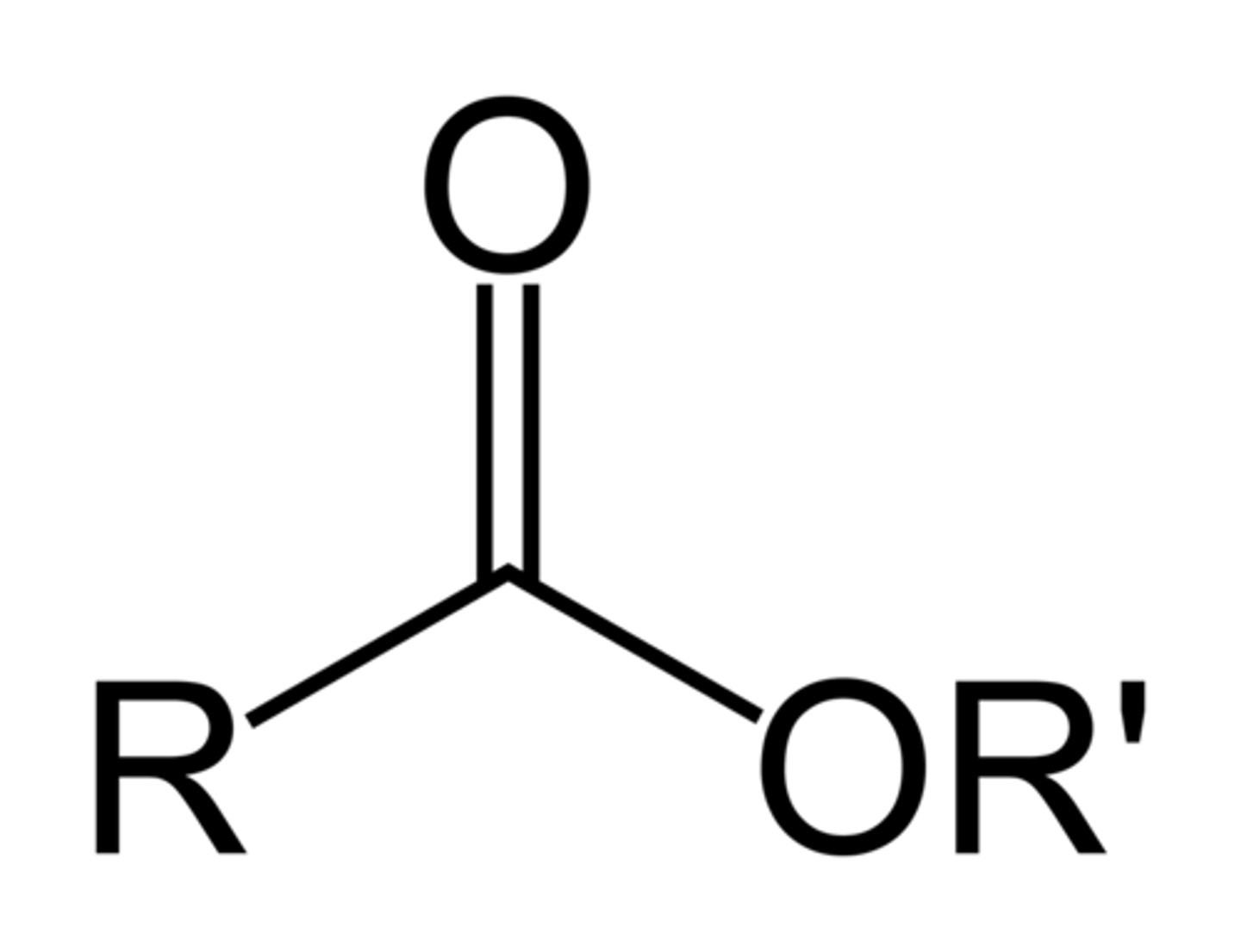
esters
NON electrolyte
formed by reacting OH with carboxylic acid
R-C=O
|
OR
Nitric Acid Esters
alcohol + nitric/nitrous acid
OH + HNO3 => C-ONO2
OH + HNO2 => C- ONO
NON electrolyte
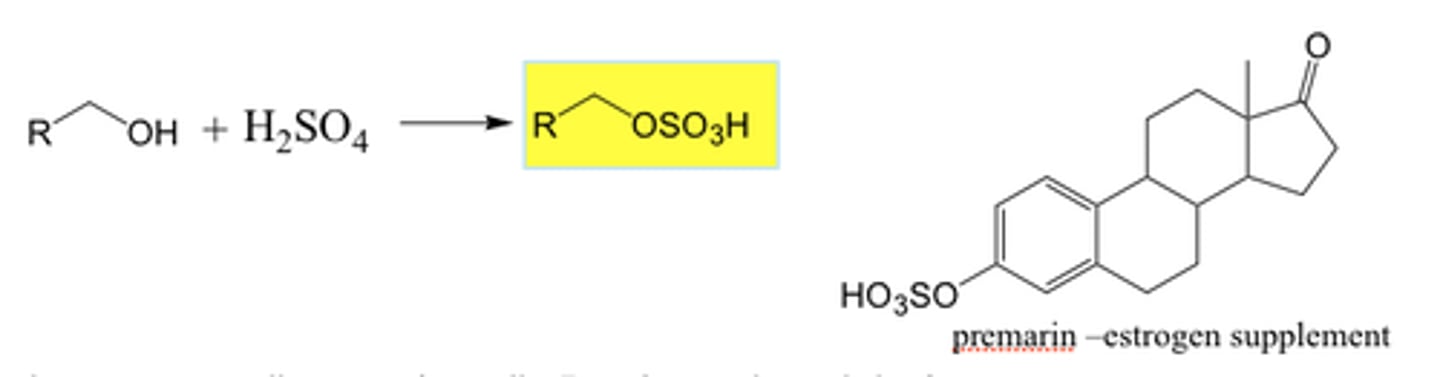
Sulfuric Acid Ester
OH + H2SO4 -> C-OSO3H
NON electrolyte
lactone
NON electrolyte
Cyclic ester
O-C=O MUST be in ring
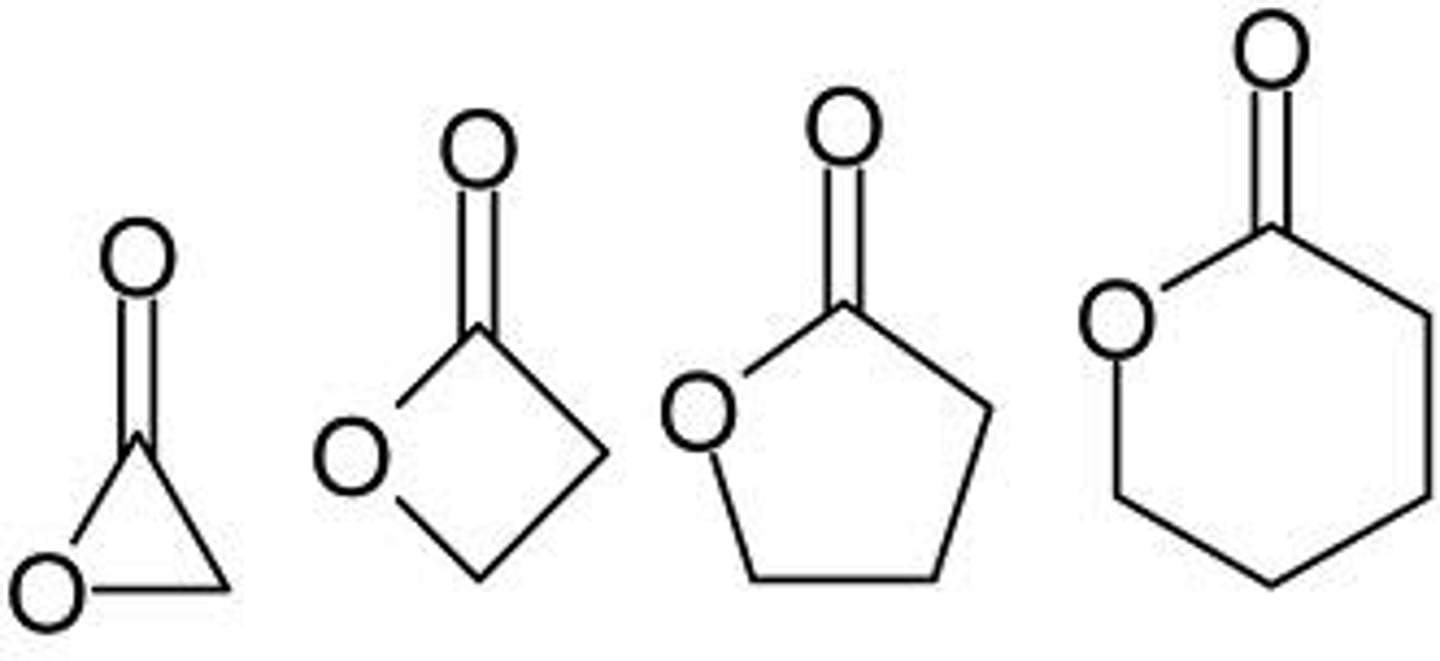
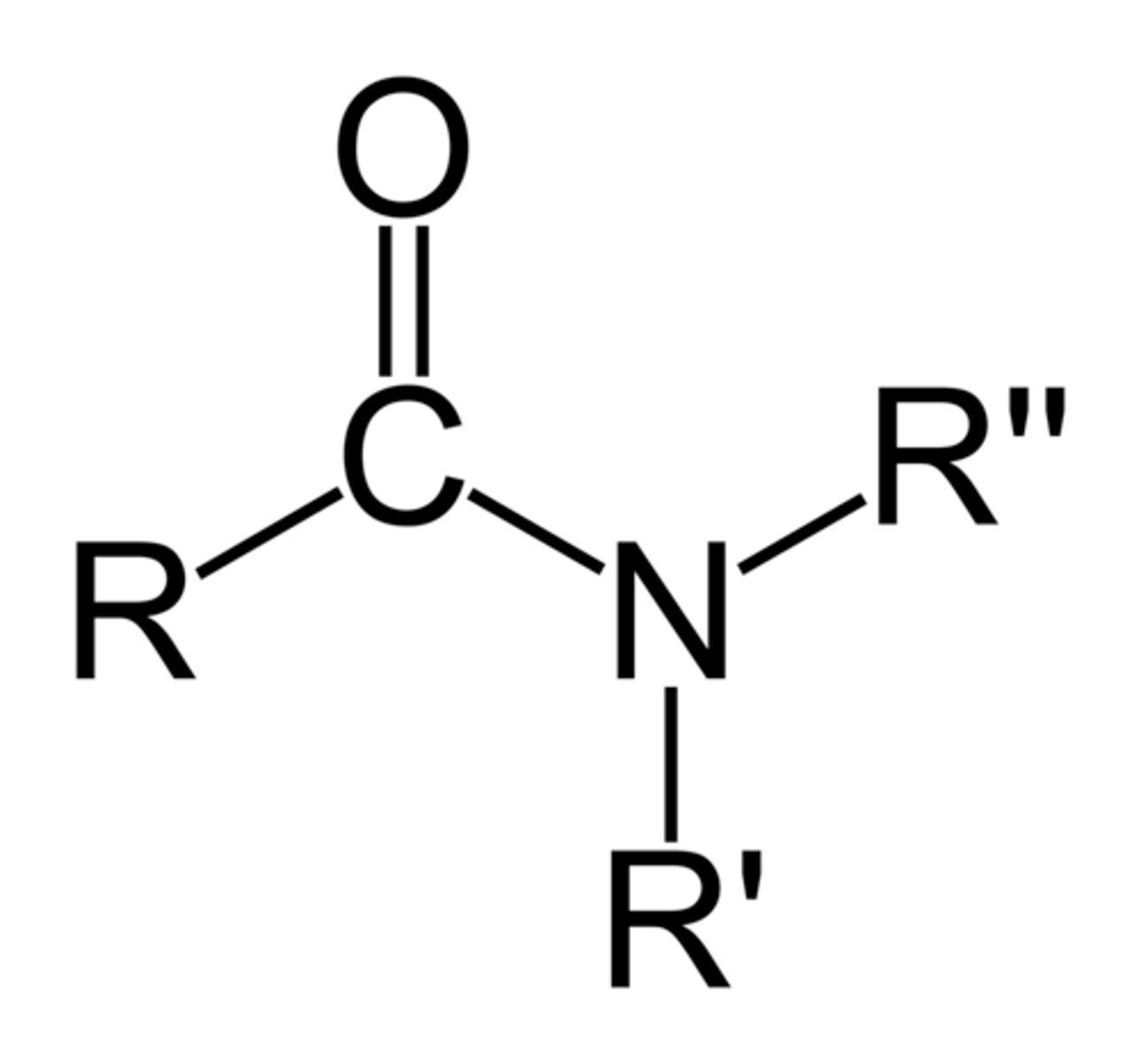
amide
NON electrolyte
N attached to carbonyl
primary, secondary, tertiary
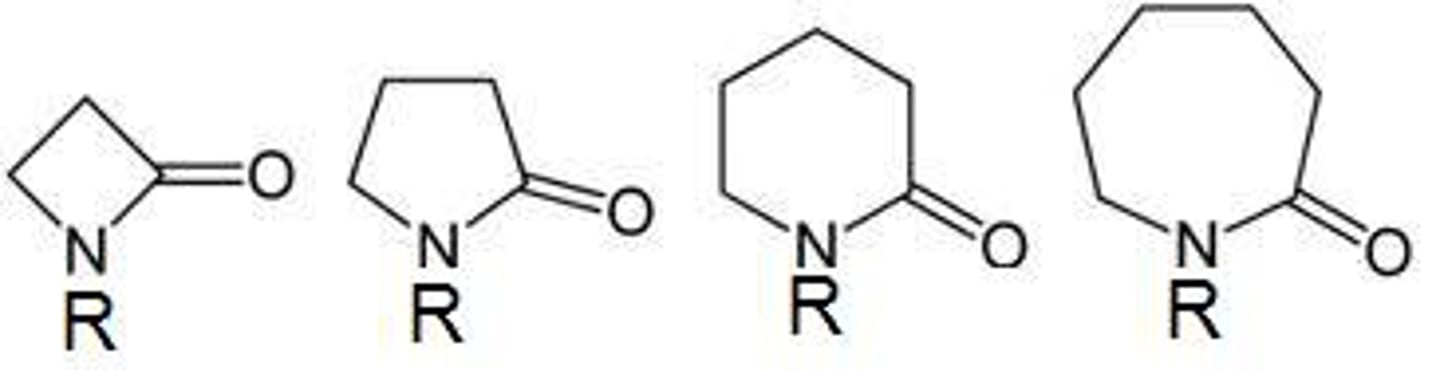
lactam
cyclic amide
NON electrolyte
O=C-N must be in ring
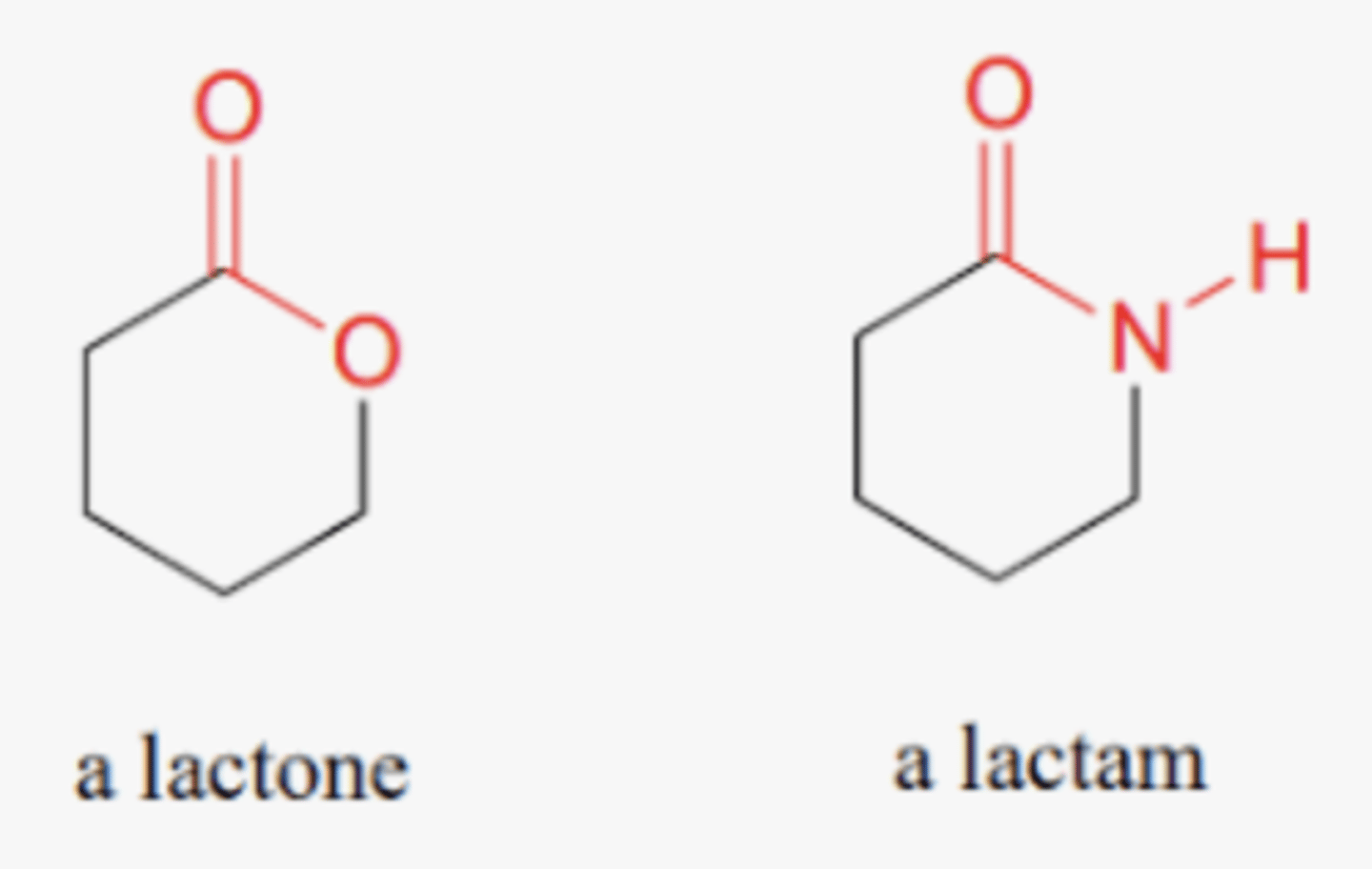
lactone vs lactam
lactone- cyclic ester
lactam- cyclic amide
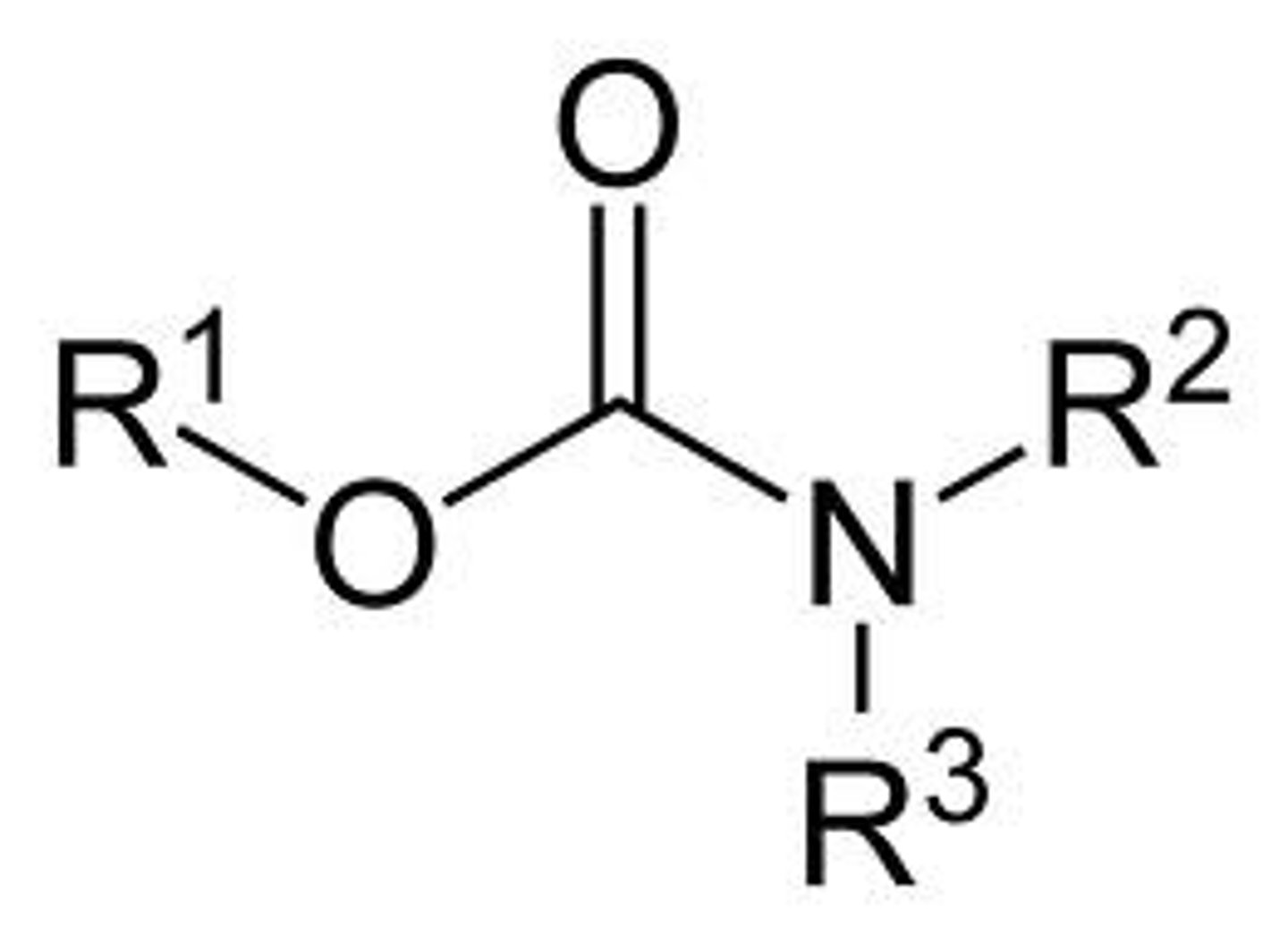
carbamate
carbonyl with OR and N
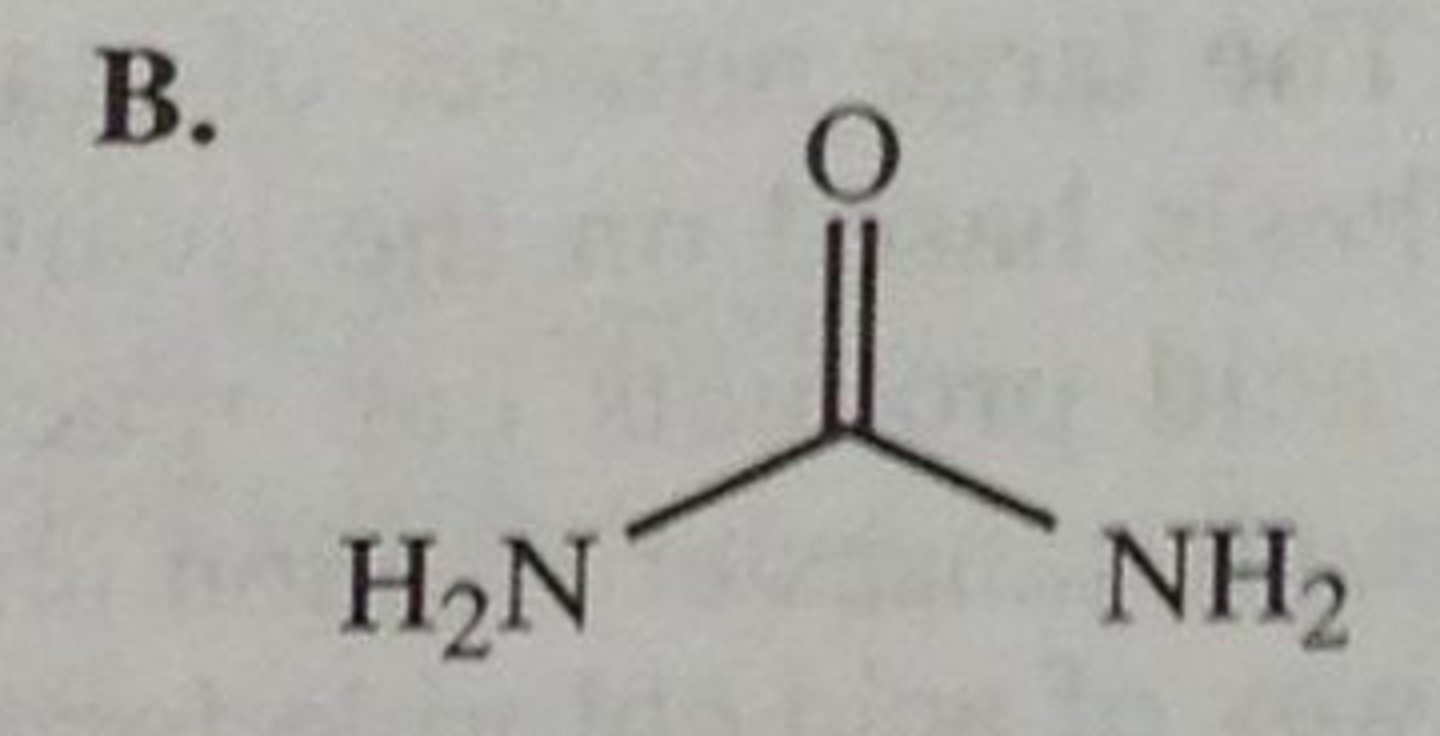
urea
carbonyl with 2 Ns
NON electrolyte
primary, secondary, tertiary
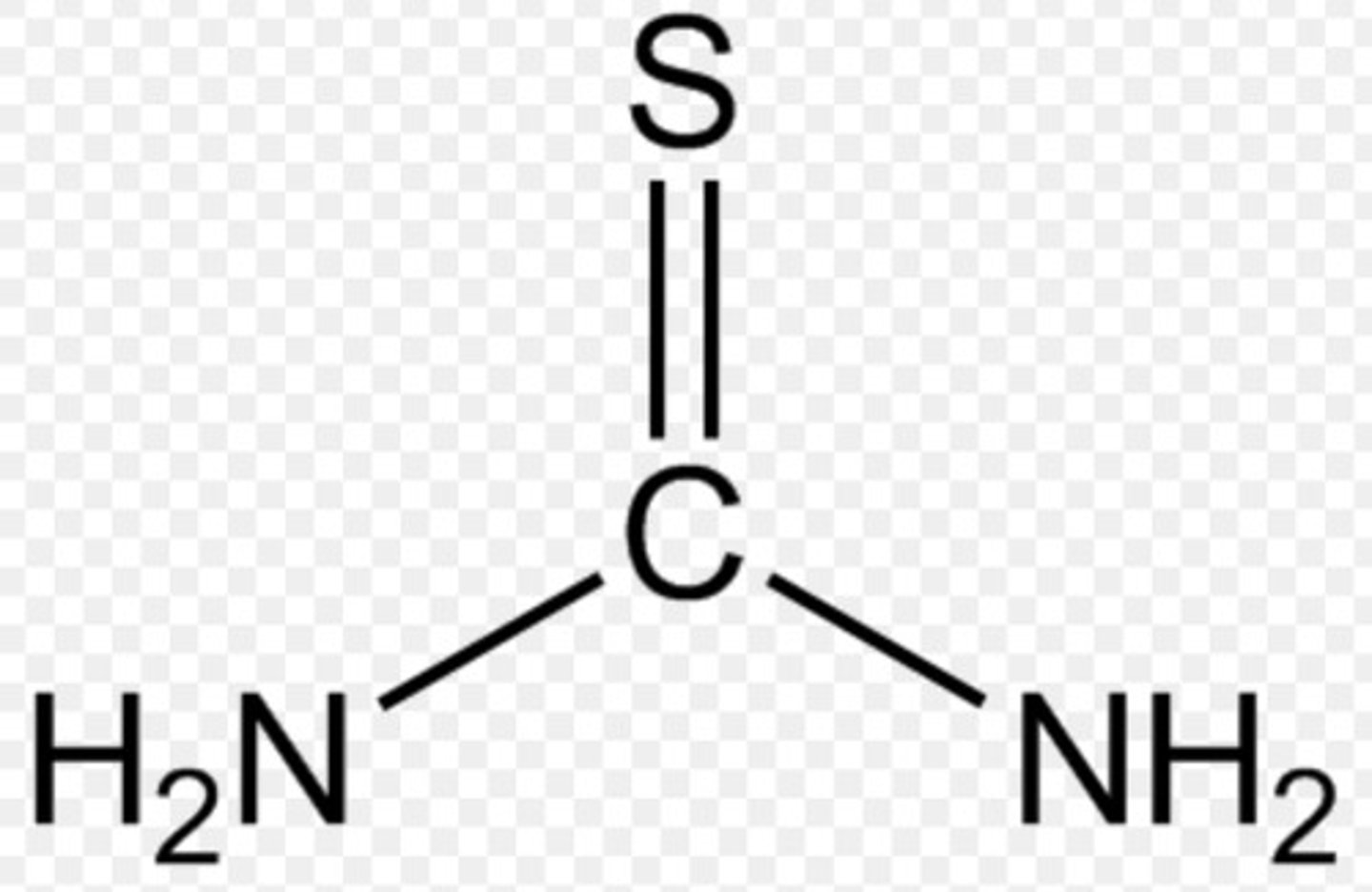
thiourea
urea but C=S, not C=O
NON electrolyte
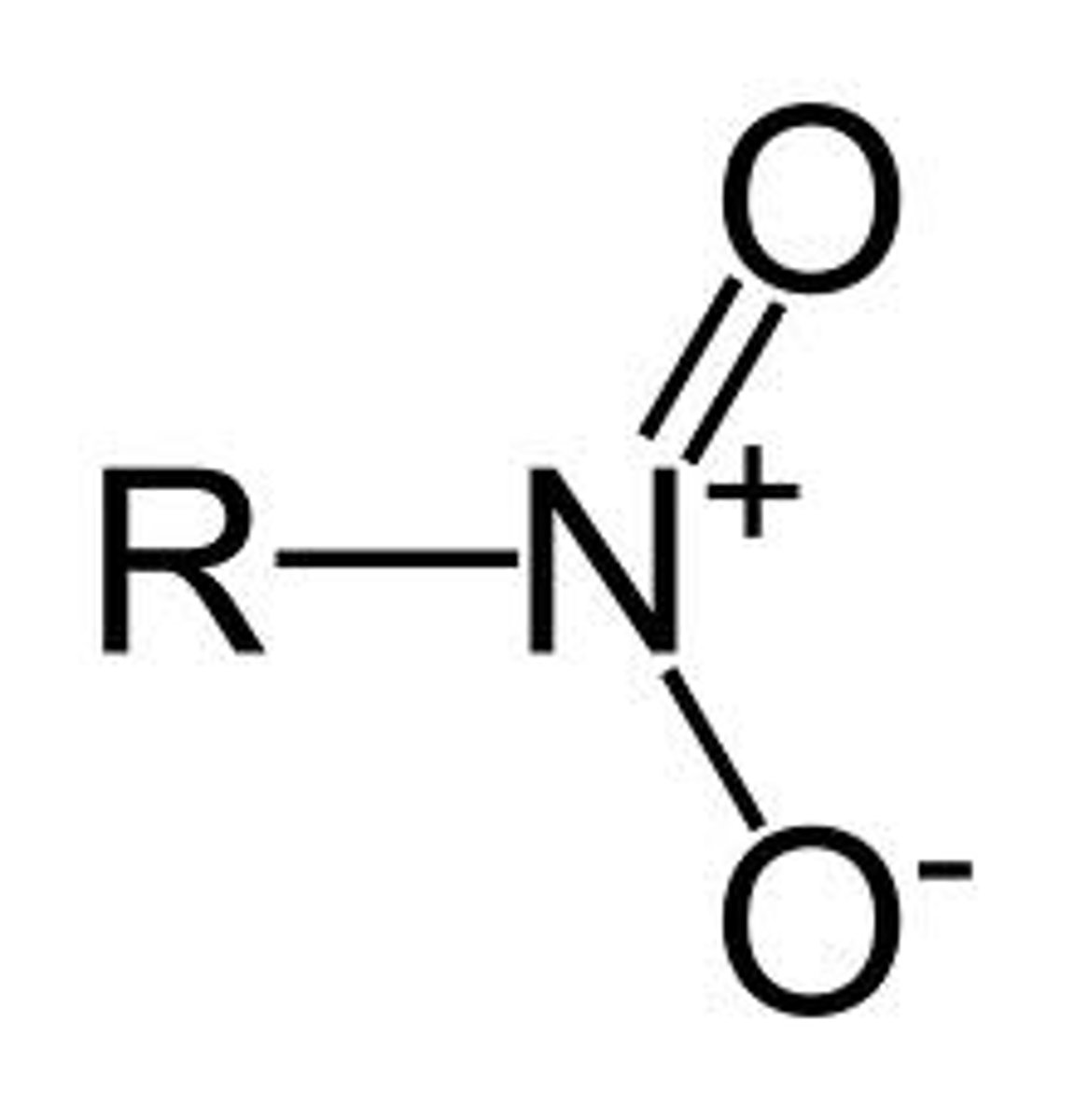
Nitro
NO2-
NON electrolyte, but has slightly positive and slightly negative poles
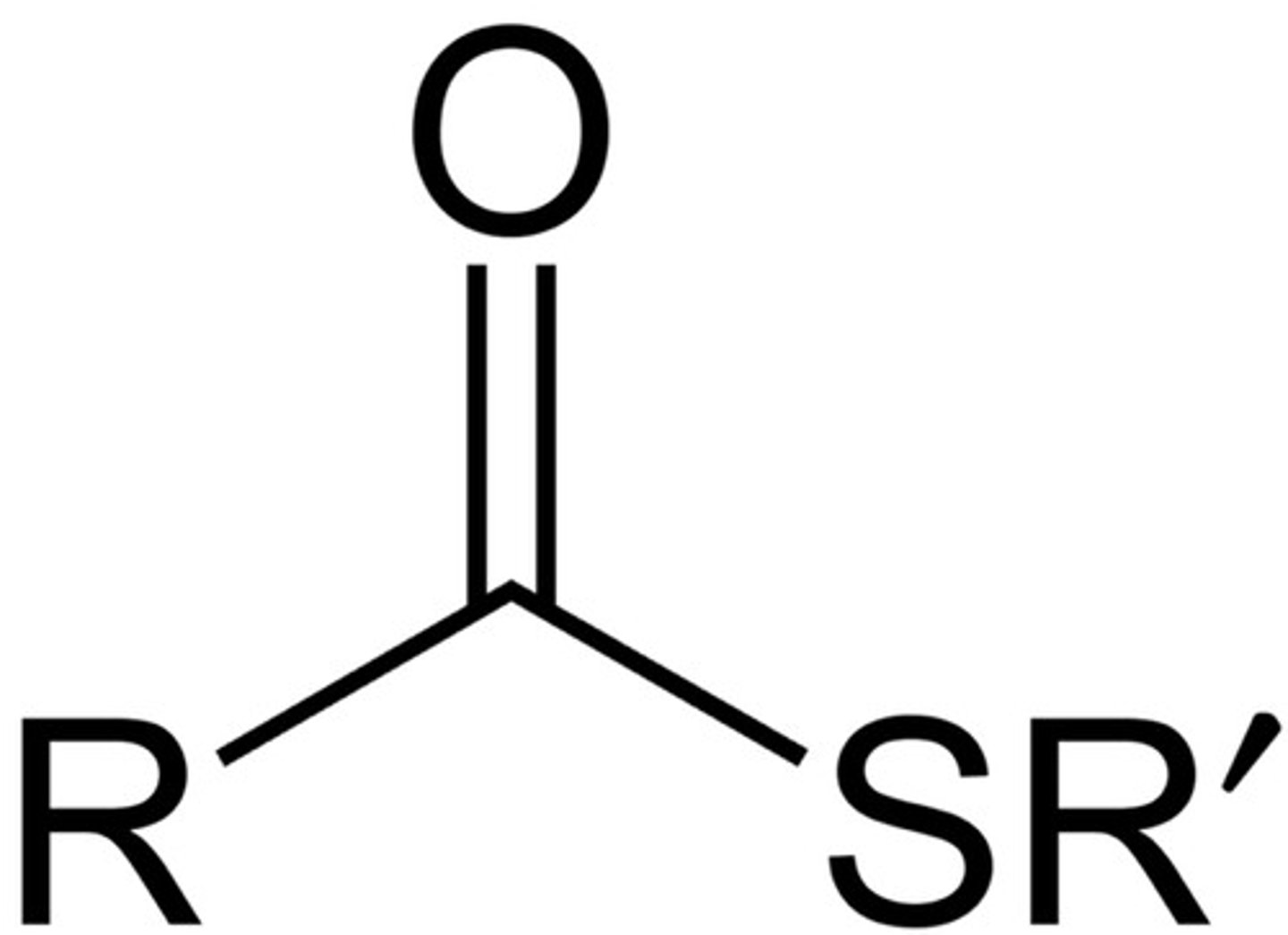
Thioester
R-C(=O)-S-R
like ester, but has S, not O
NON electrolyte
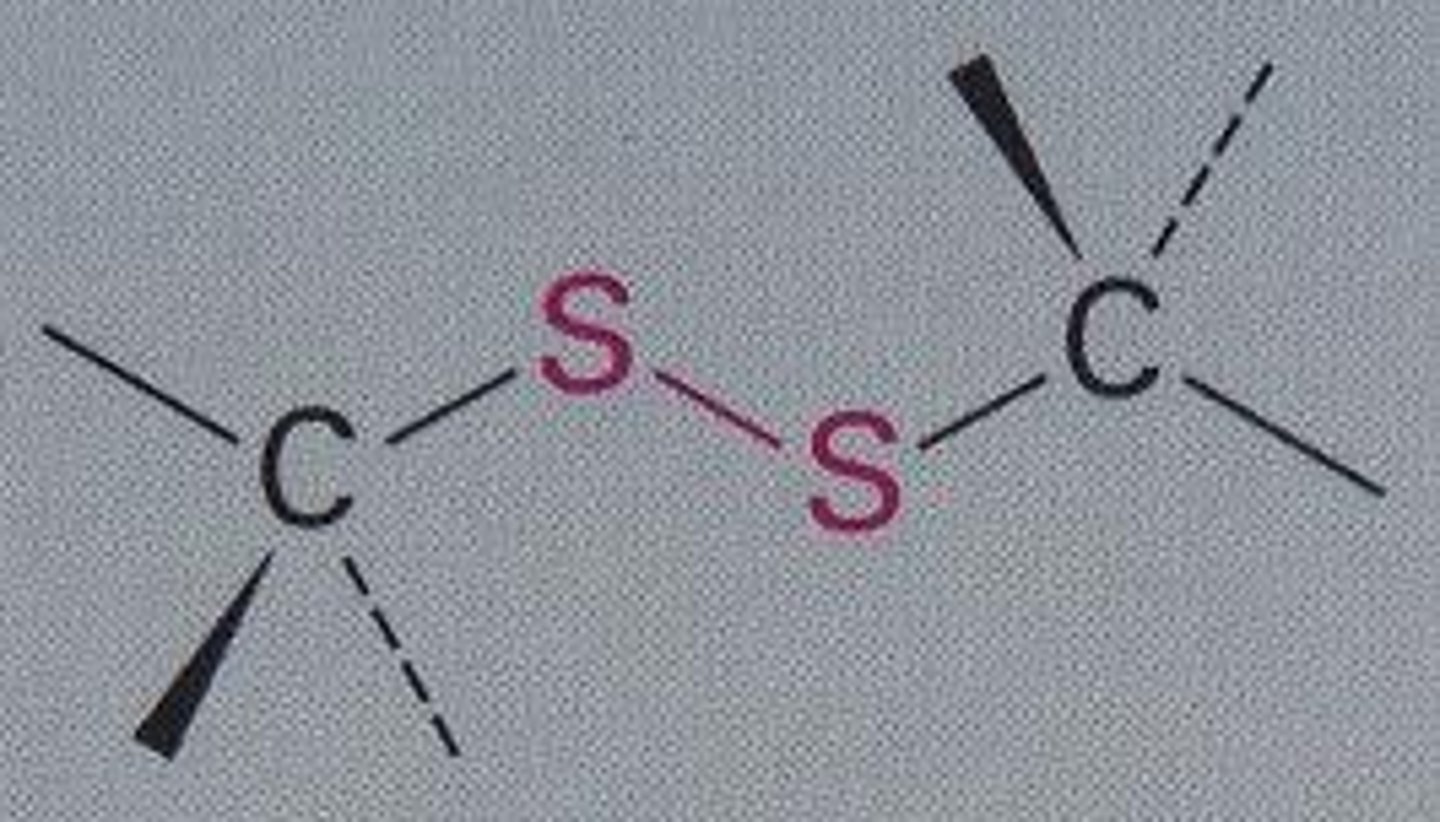
disulfide
R-S-S-R
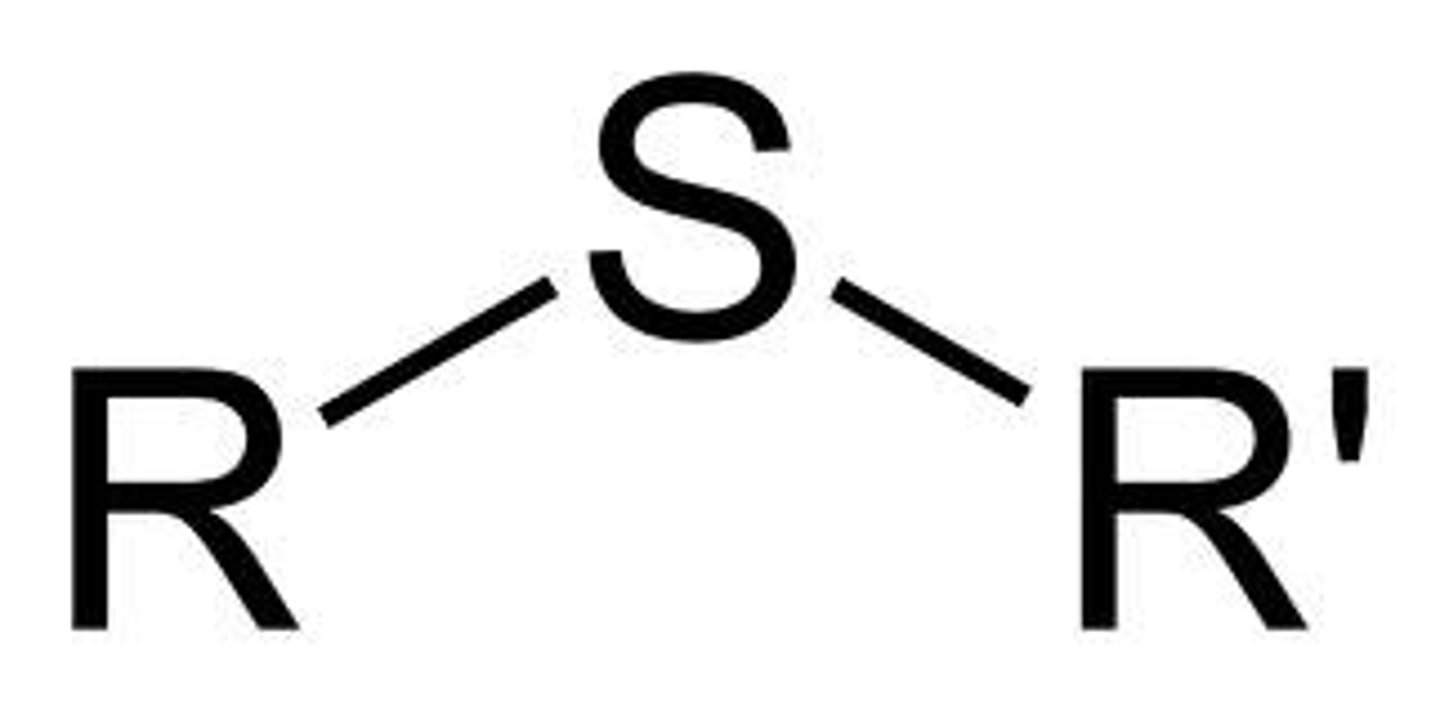
thiol ether
R-S-R
pKa is a measure of
the tendency to give up a proton (acid strength)
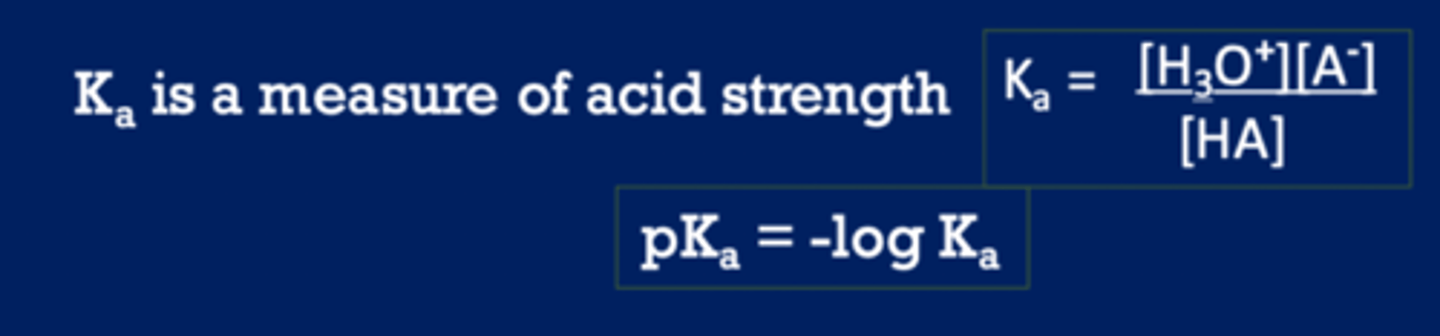
as pKa decreases, the ________ the acid
stronger (easier to give up H)
which is a weaker acid?
Acid A= pKA= 10
Acid B= pKa= 1
B-> pkA 10 is weaker
(higher pKa= weaker acid)
can pKa tell you if something is an acid or base?
no. it only tells you how strong of an acid something is
phenols
1. acids with pKa 8-10
aromatic OH
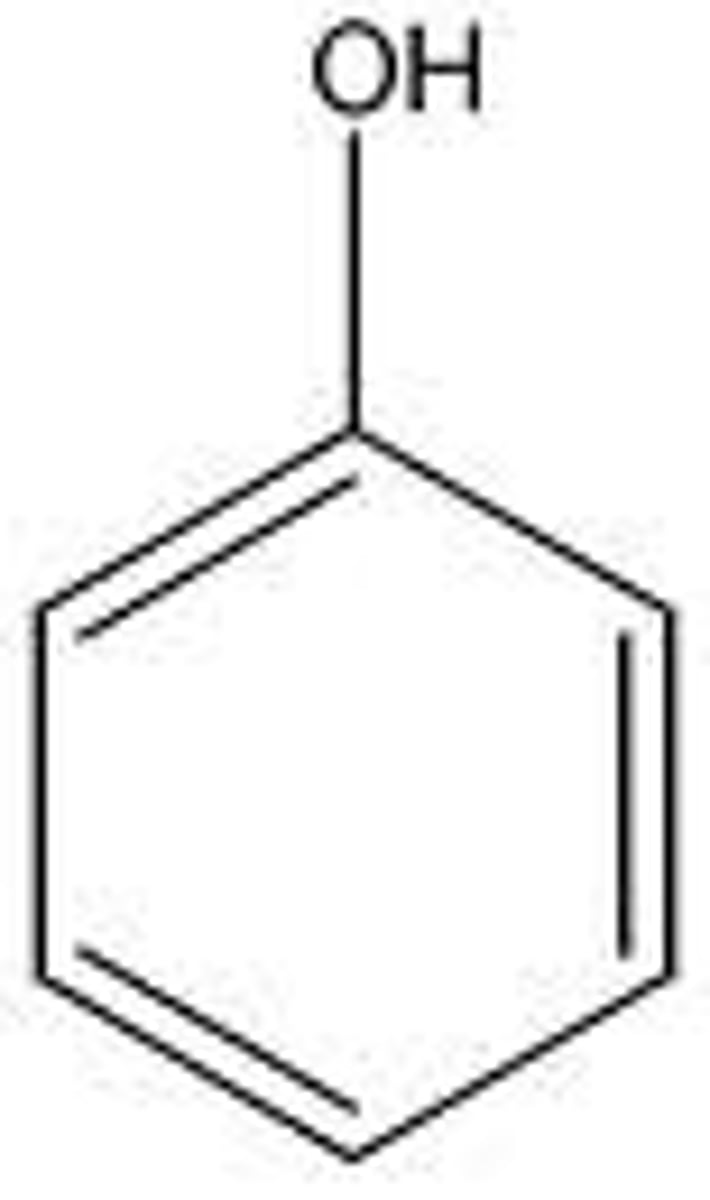
why is phenol an acid but an alcohol is not?
aromatic ring in phenols contributes to resonance making it more stable and able to give up a proton
carboxylic acids
1. acids with pKa 3-5
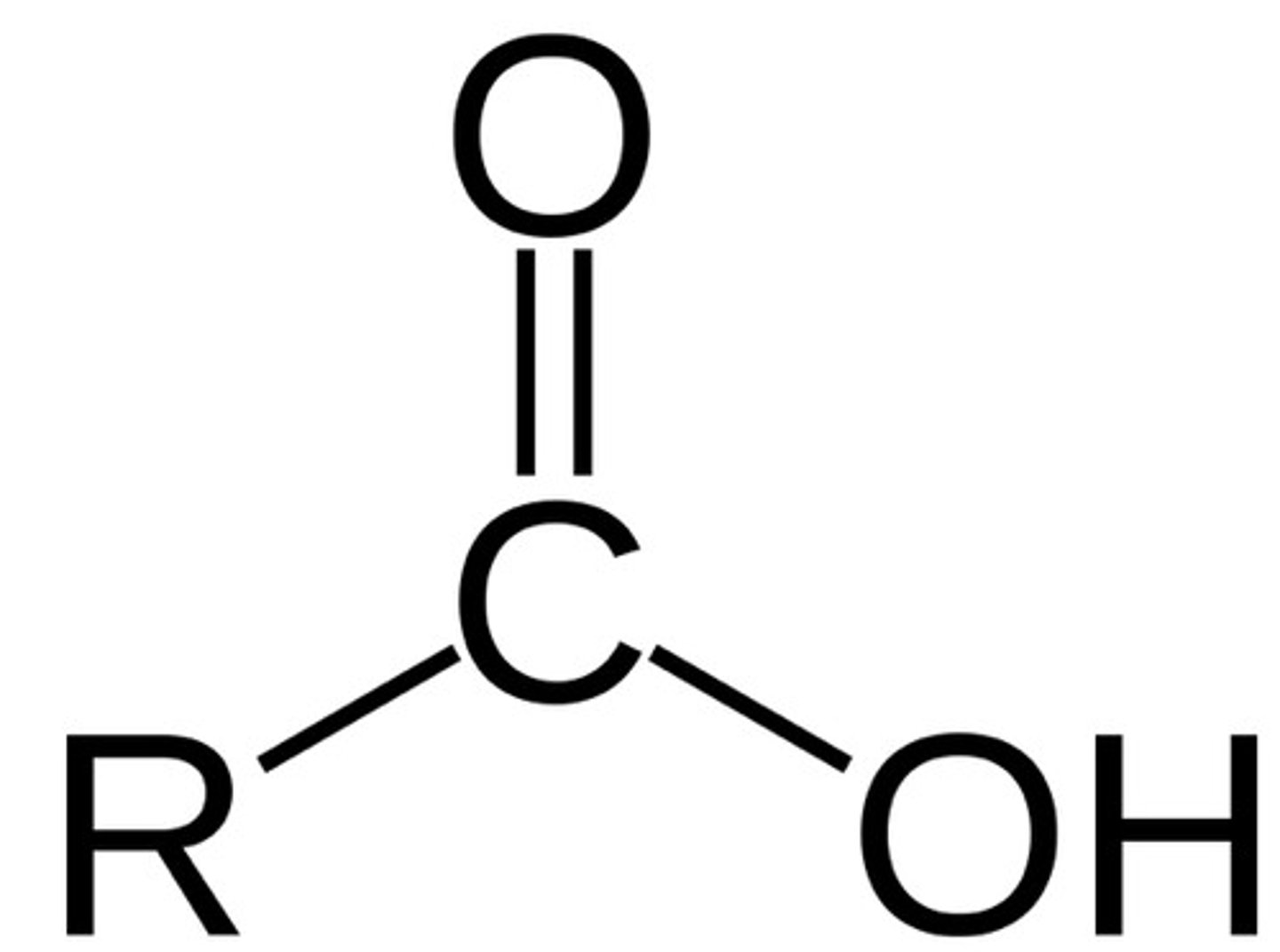
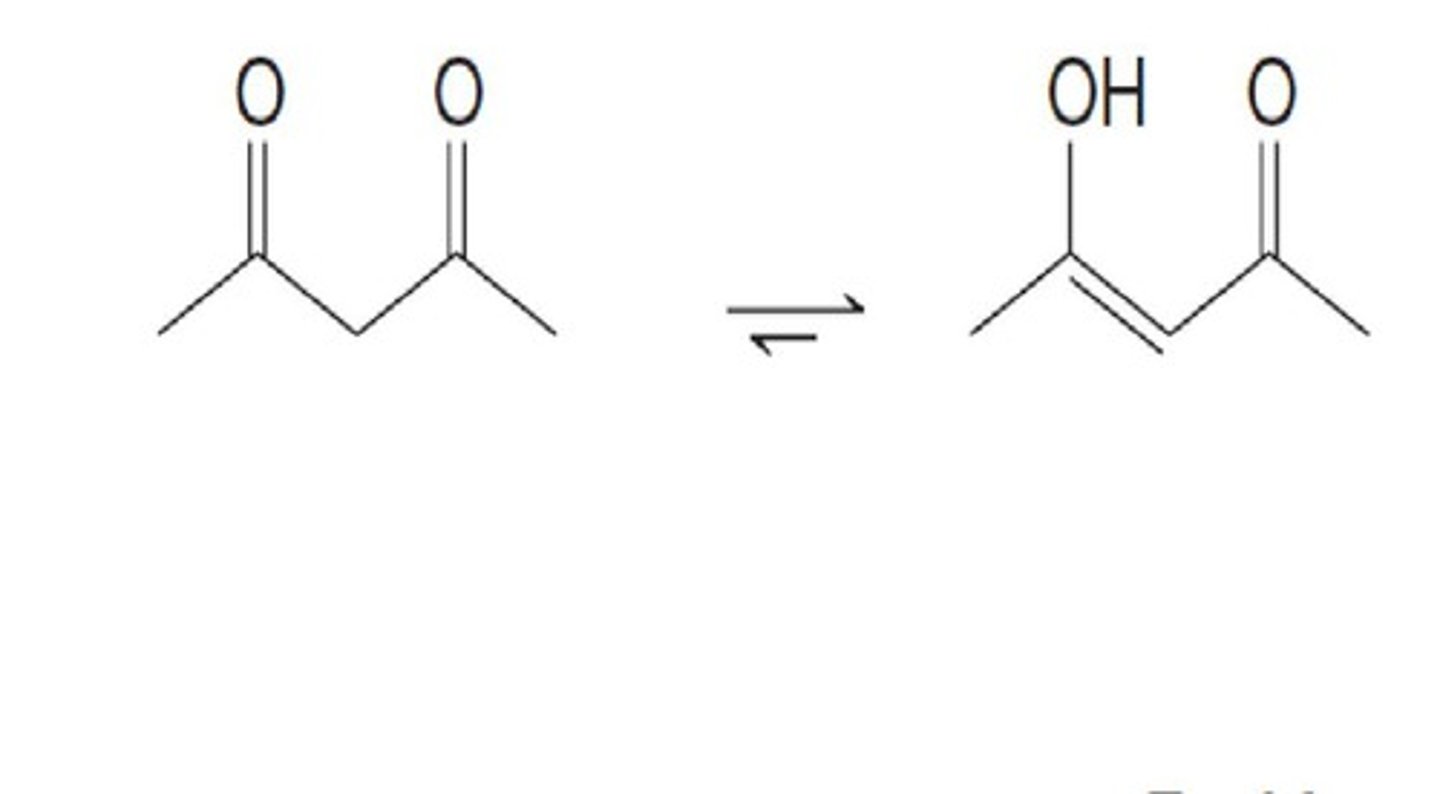
B-dicarbonyl compounds
1. Acids with pKa 3-5
* can be keto or enol form
is the acidic proton in B-dicarbonyl compounds an H bond donor?
no, it is not attached to an EN atom
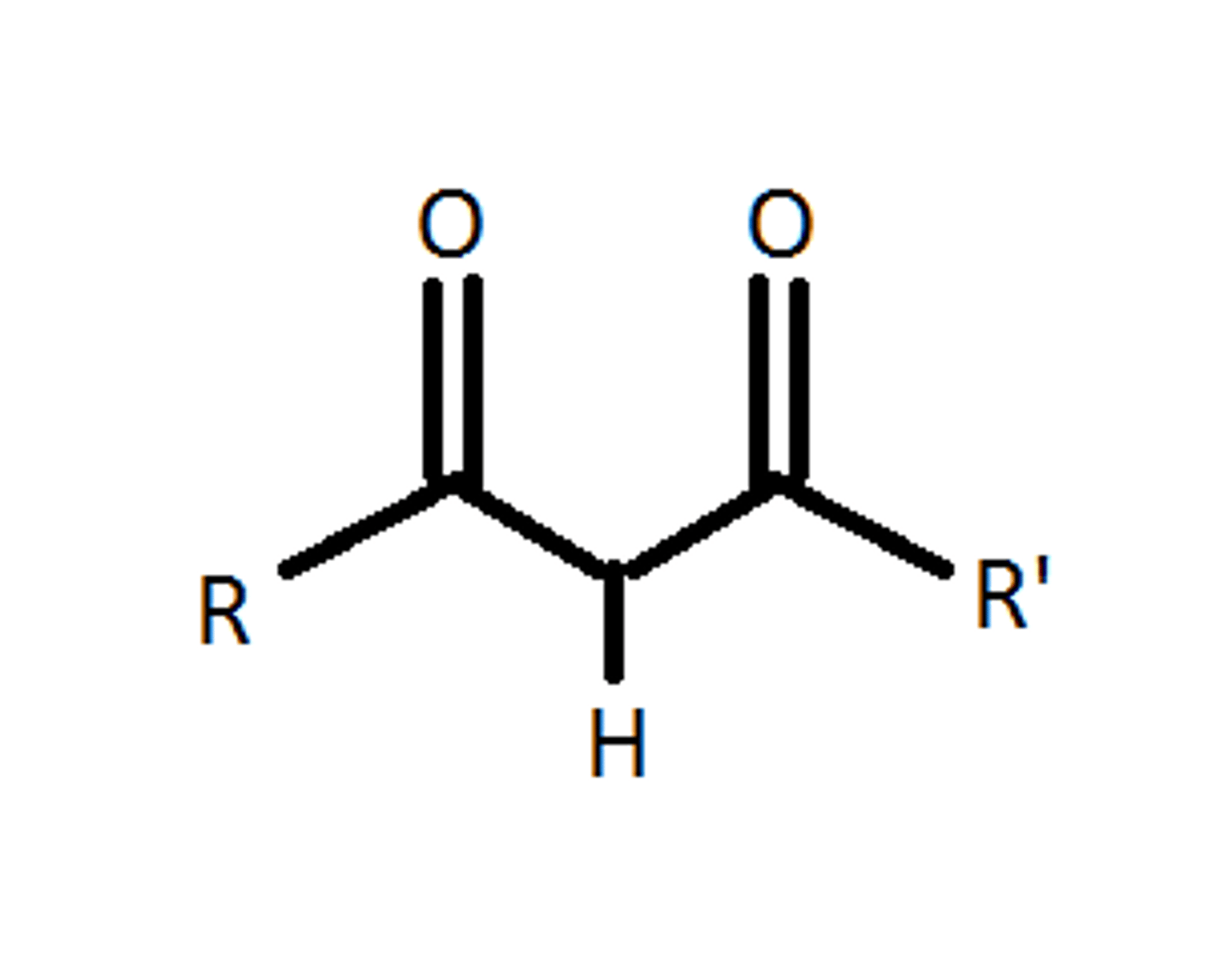
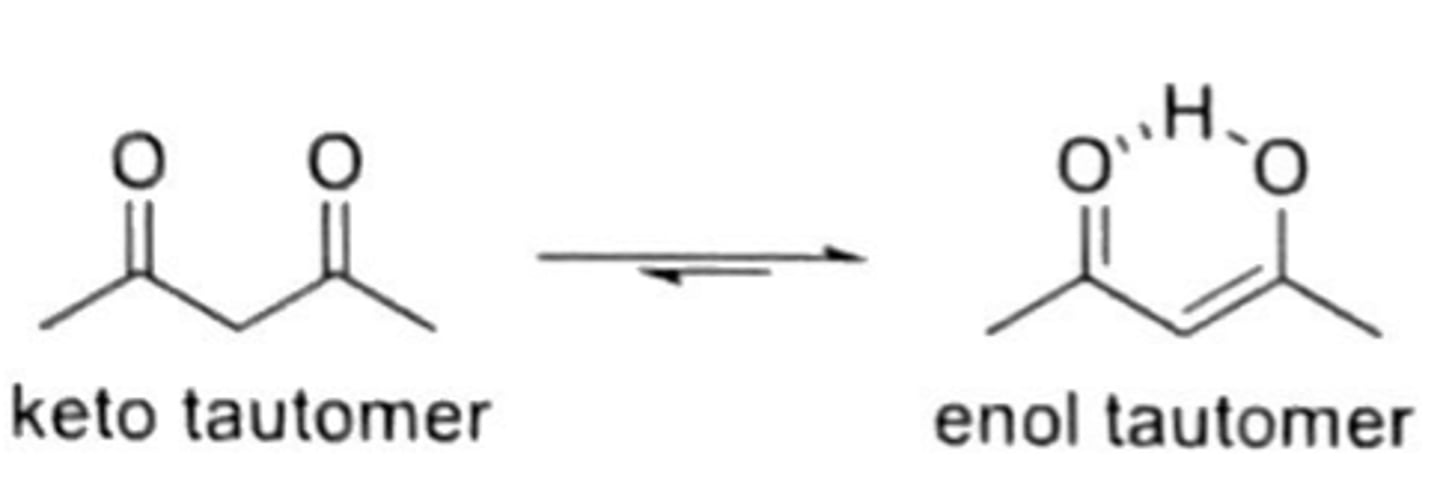
keto-enol
aldehydes and ketones exist in both keto form (more common) and enol form (less common)
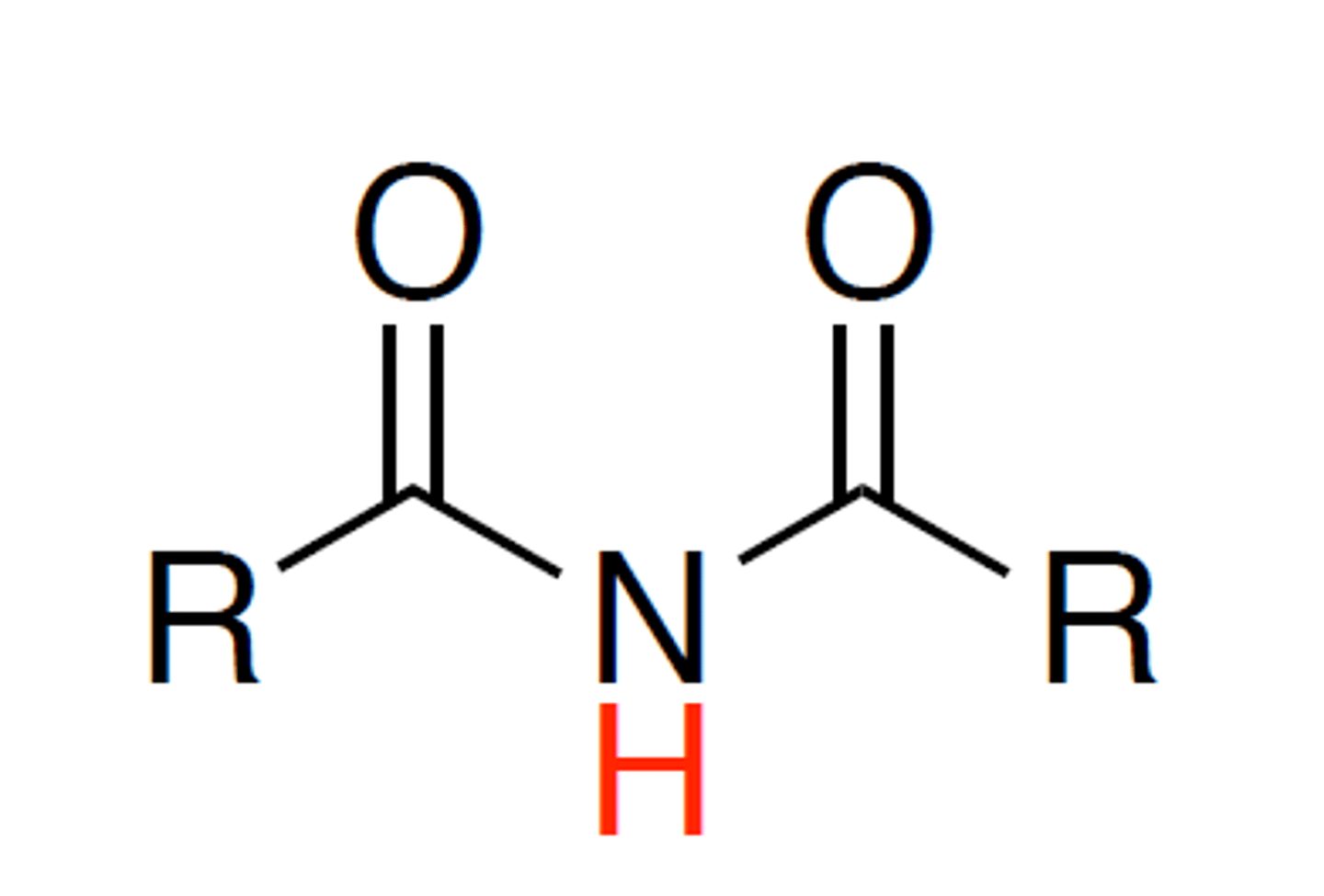
imide
1. acid with pKa 9-11
like B-dicarbonyl but NH not CH
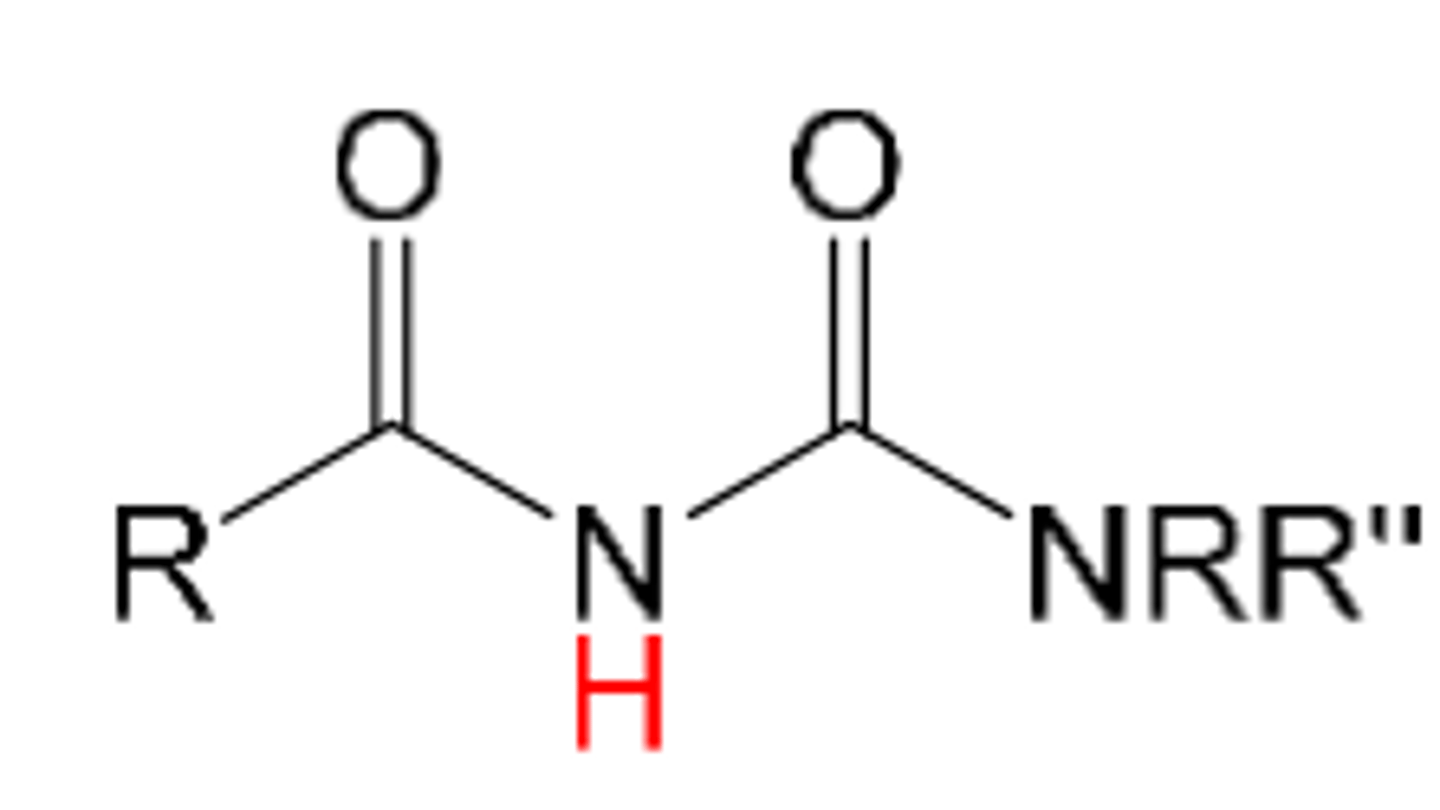
acylurea
1. acid with pKa= 9-11
like an imide but carbonyl is attached to another N
sulfonamide
1. acid with pKA= 9-11
H on N is acidic

N-arylsulfonamide
sulfonamide attached to aromatic ring
stronger acid with pKa= 5-6
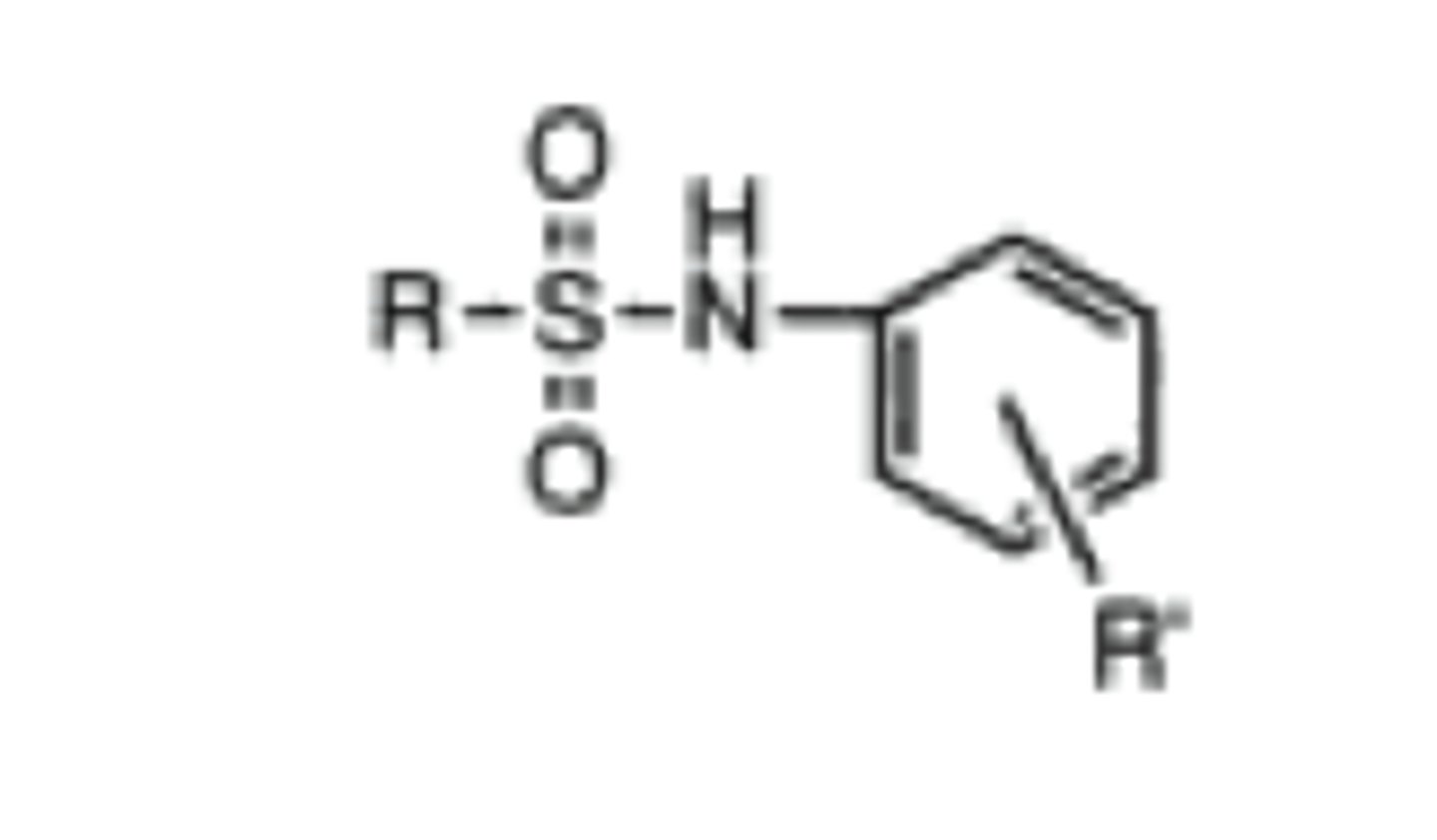
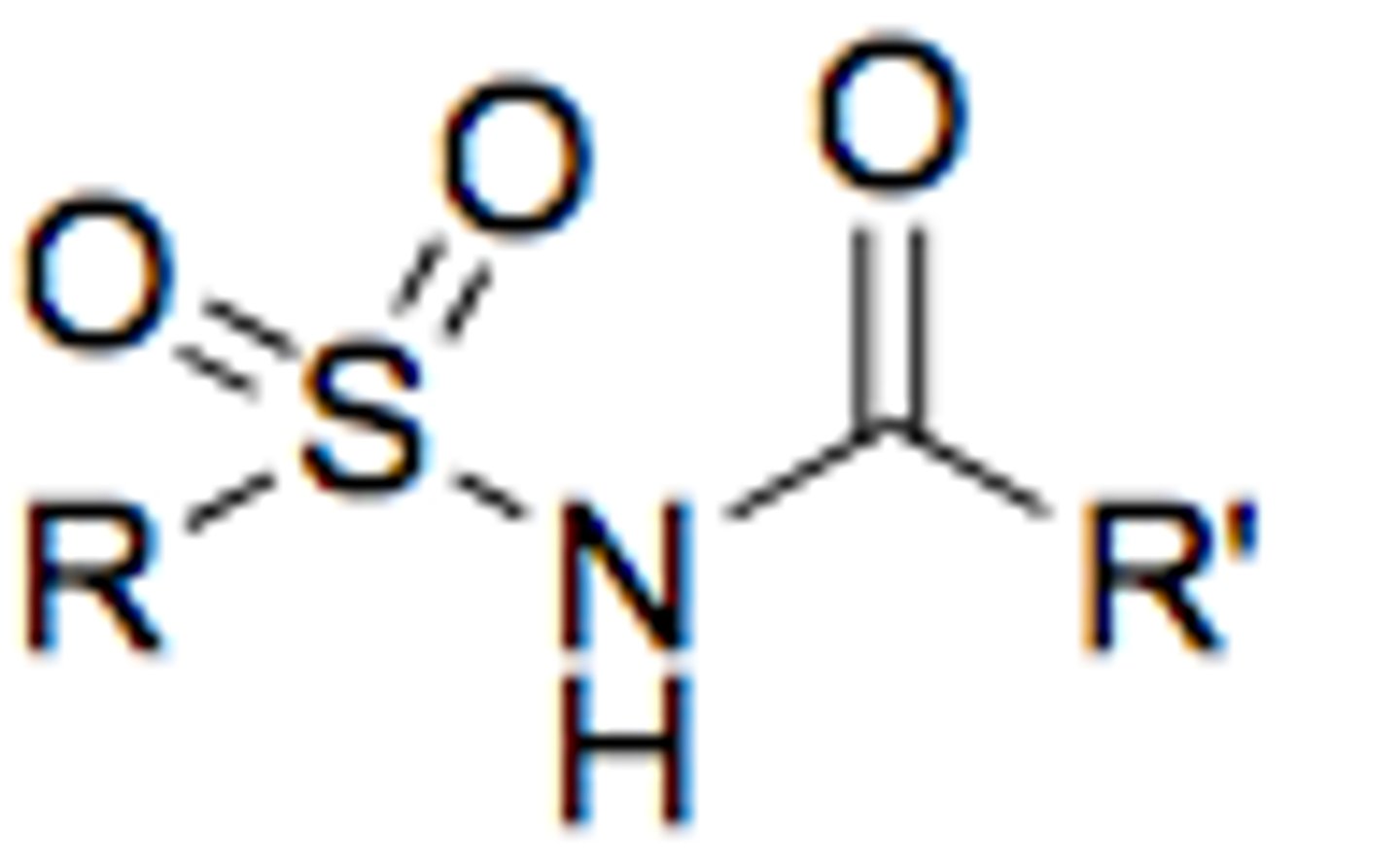
sulfonimide
more acidic than sulfonamide with pKa= 5-6
like sulfonamide but N attached to carbonyl
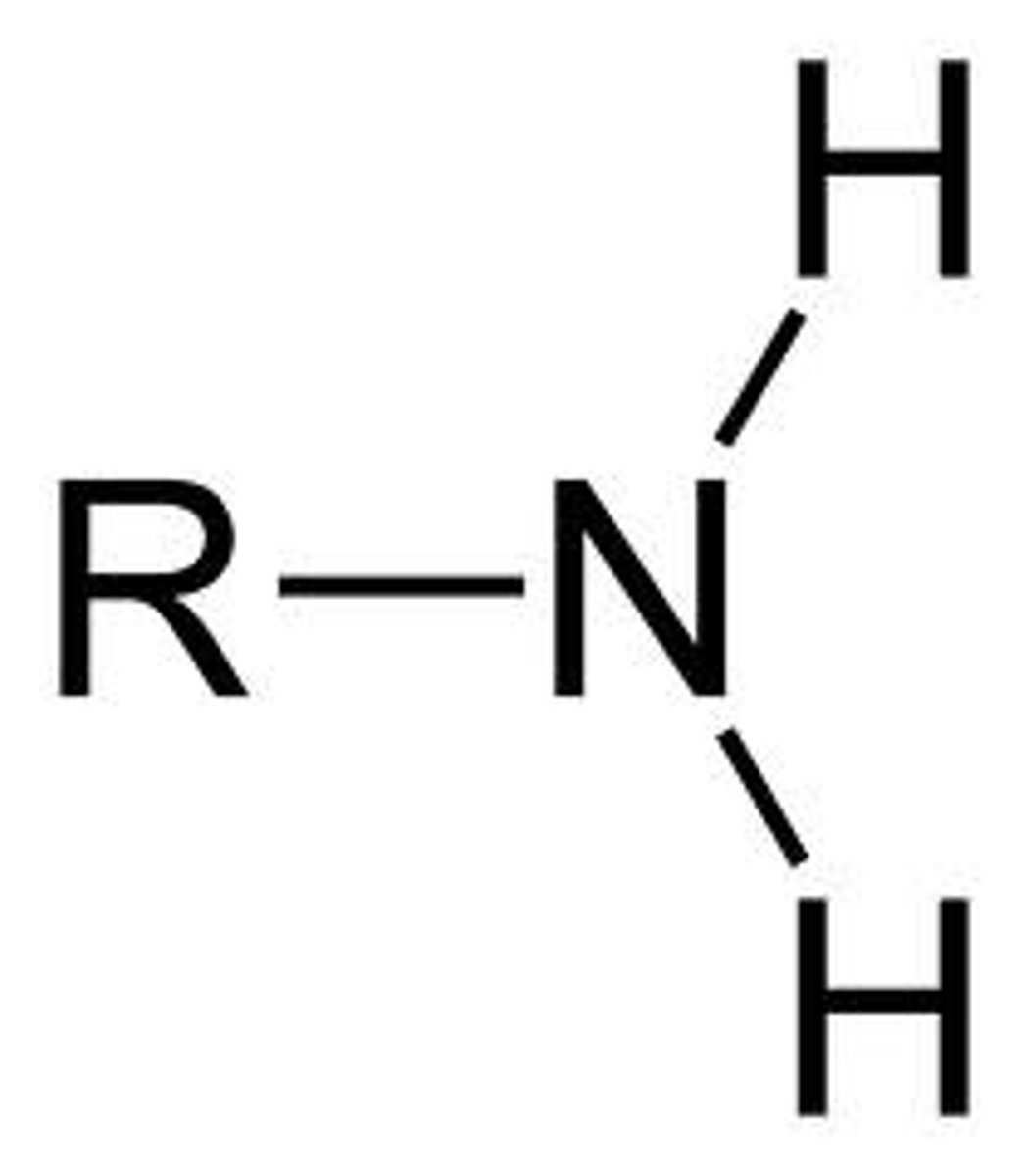
amino
BASE electrolyte group with pKa= 9-11
NH2
can be aliphatic or aromatic
acid form of amino group
NH3+
guanidino
BASE electrolyte group
pKa= 12
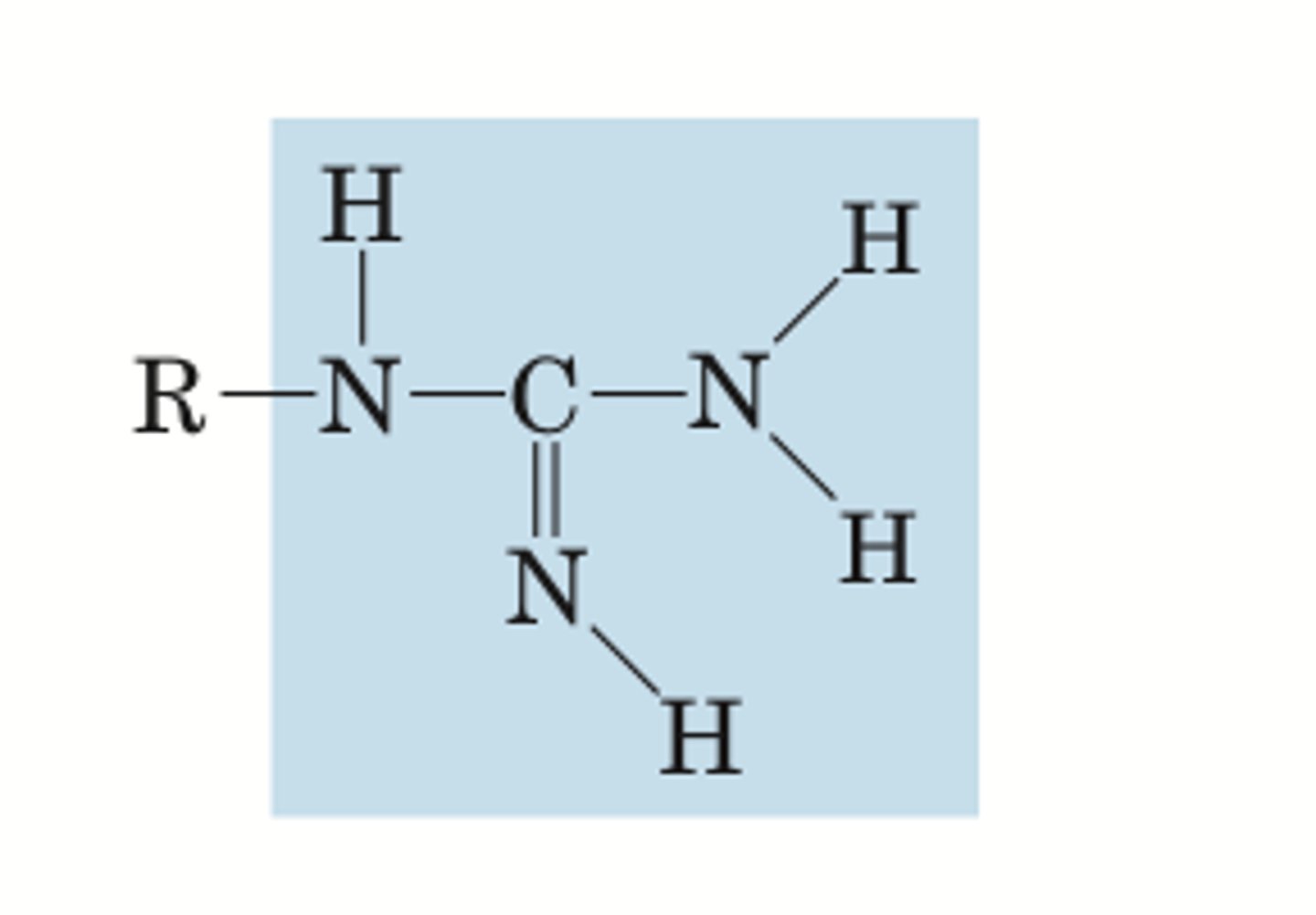
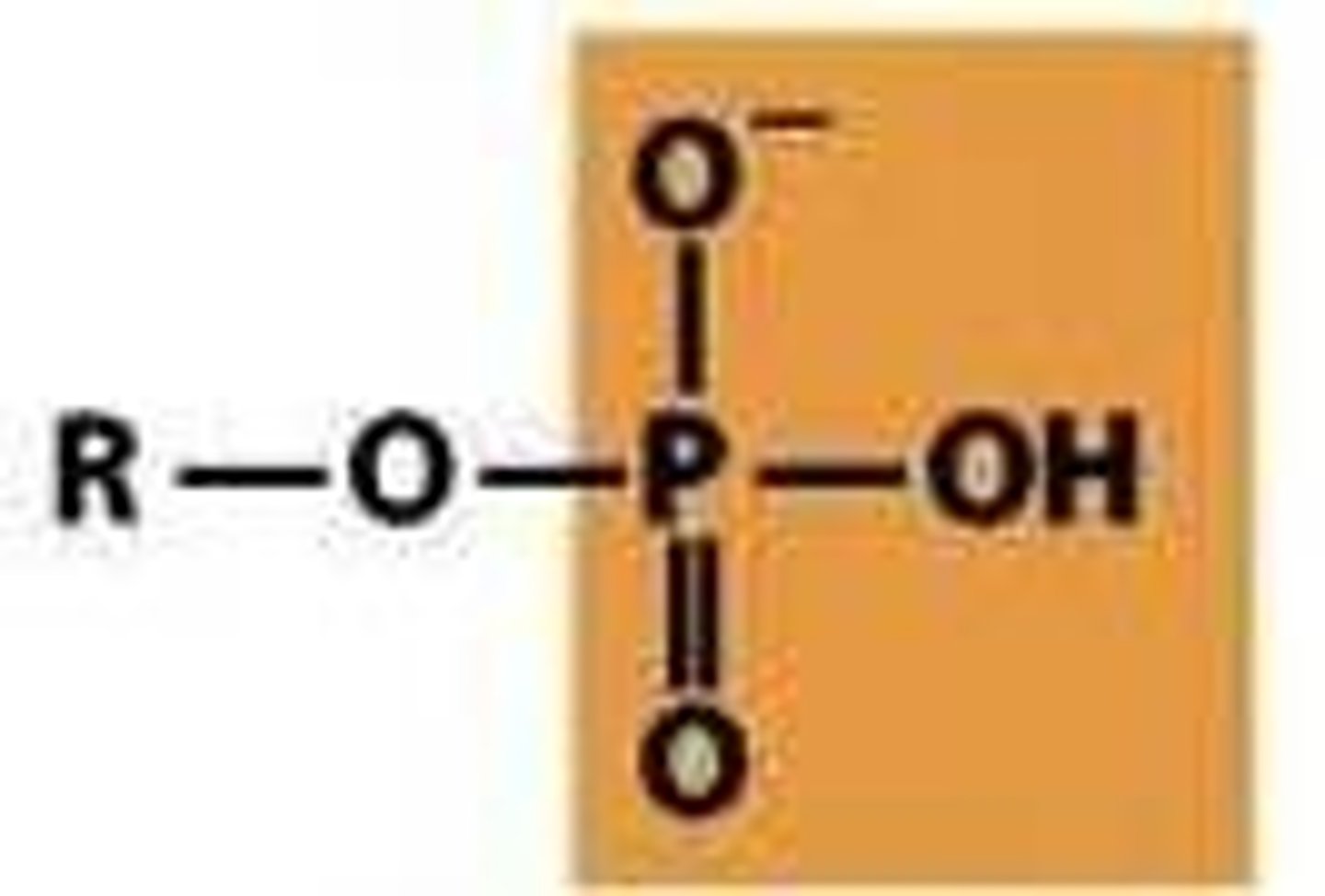
phosphoryl
acidic with
pKa1= 2-3
pKa2= 6-7
thiol
acid with pKa= 10
R-SH
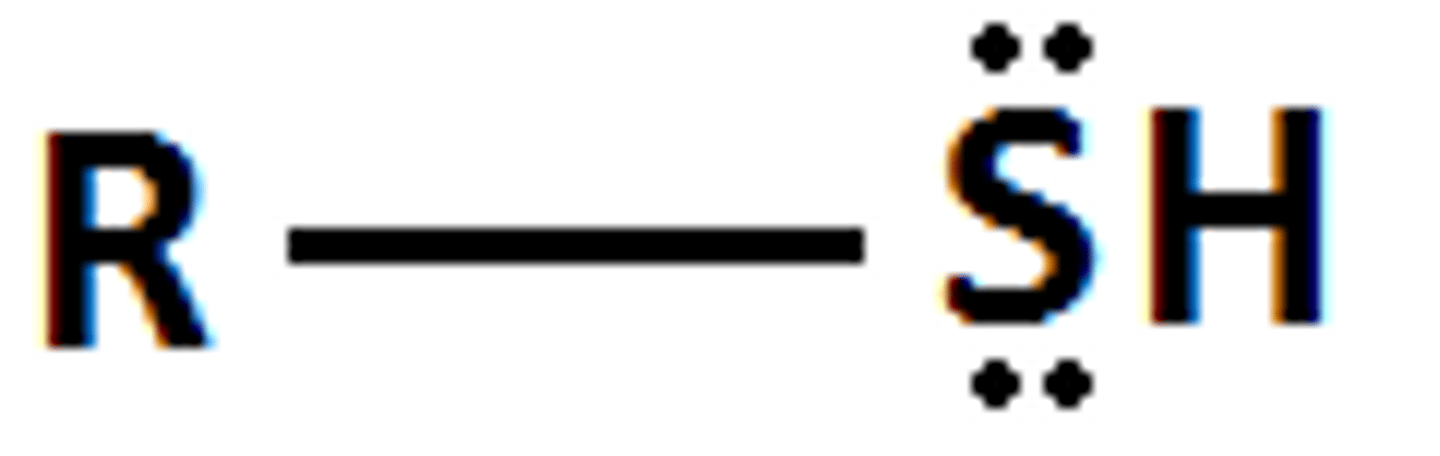
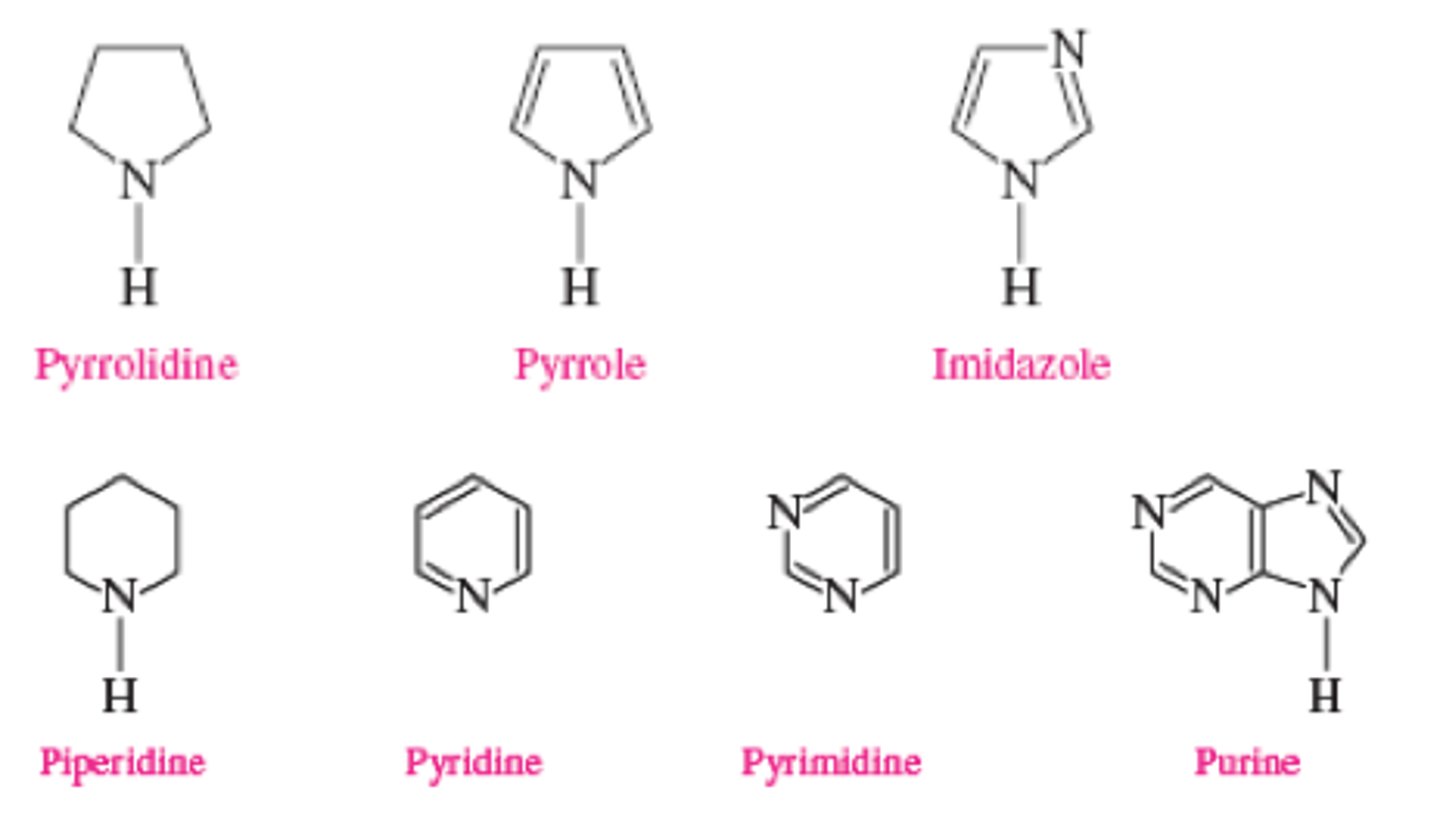
what are heterocycles
A ring structure that contains at least one atom that is not carbon (heteroatoms)
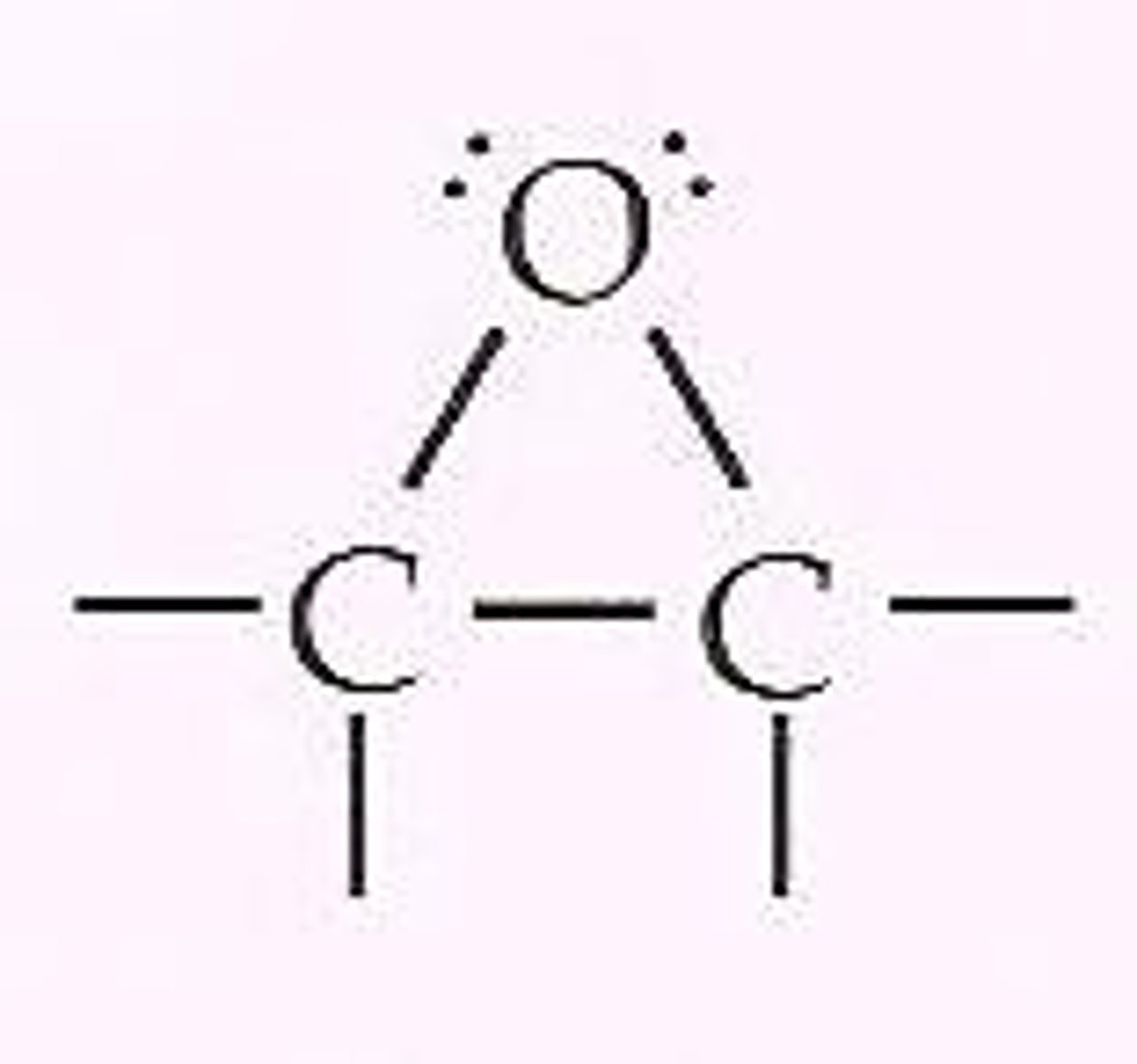
epoxide
aziridine
(like epoxide but NH)

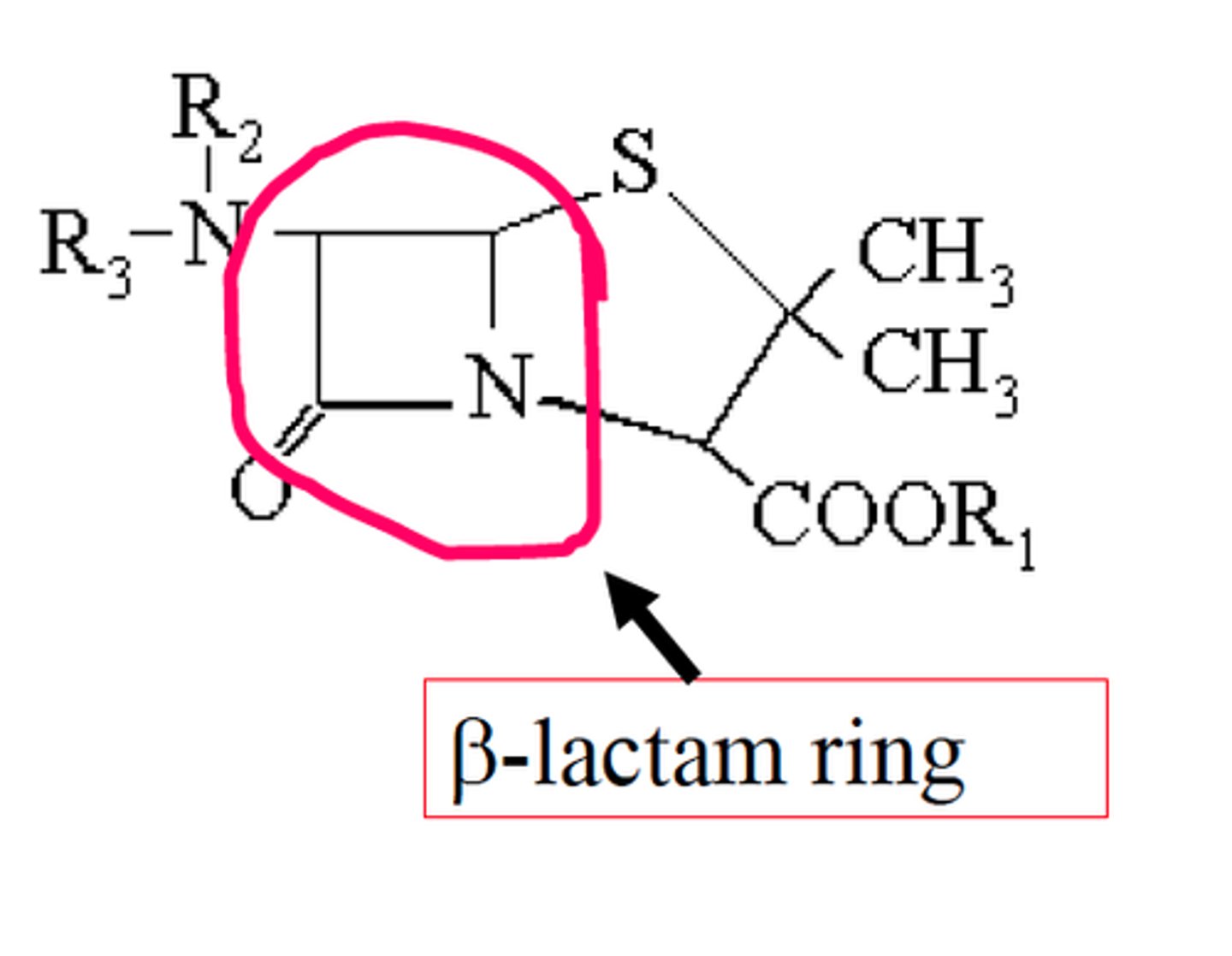
B-lactam
4 membered lactam ring
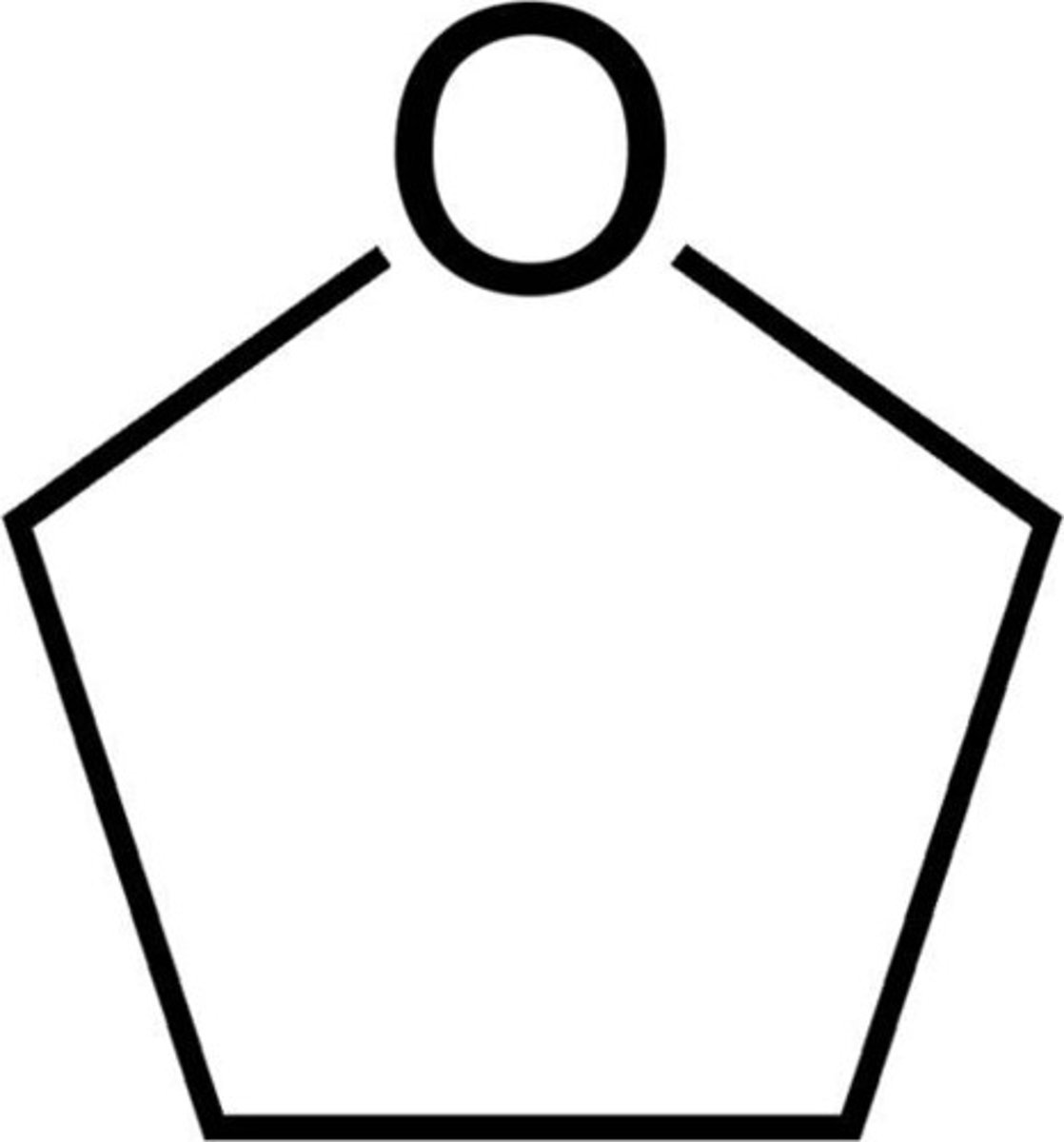
tetrahydrofuran
4 carbons and 1 O
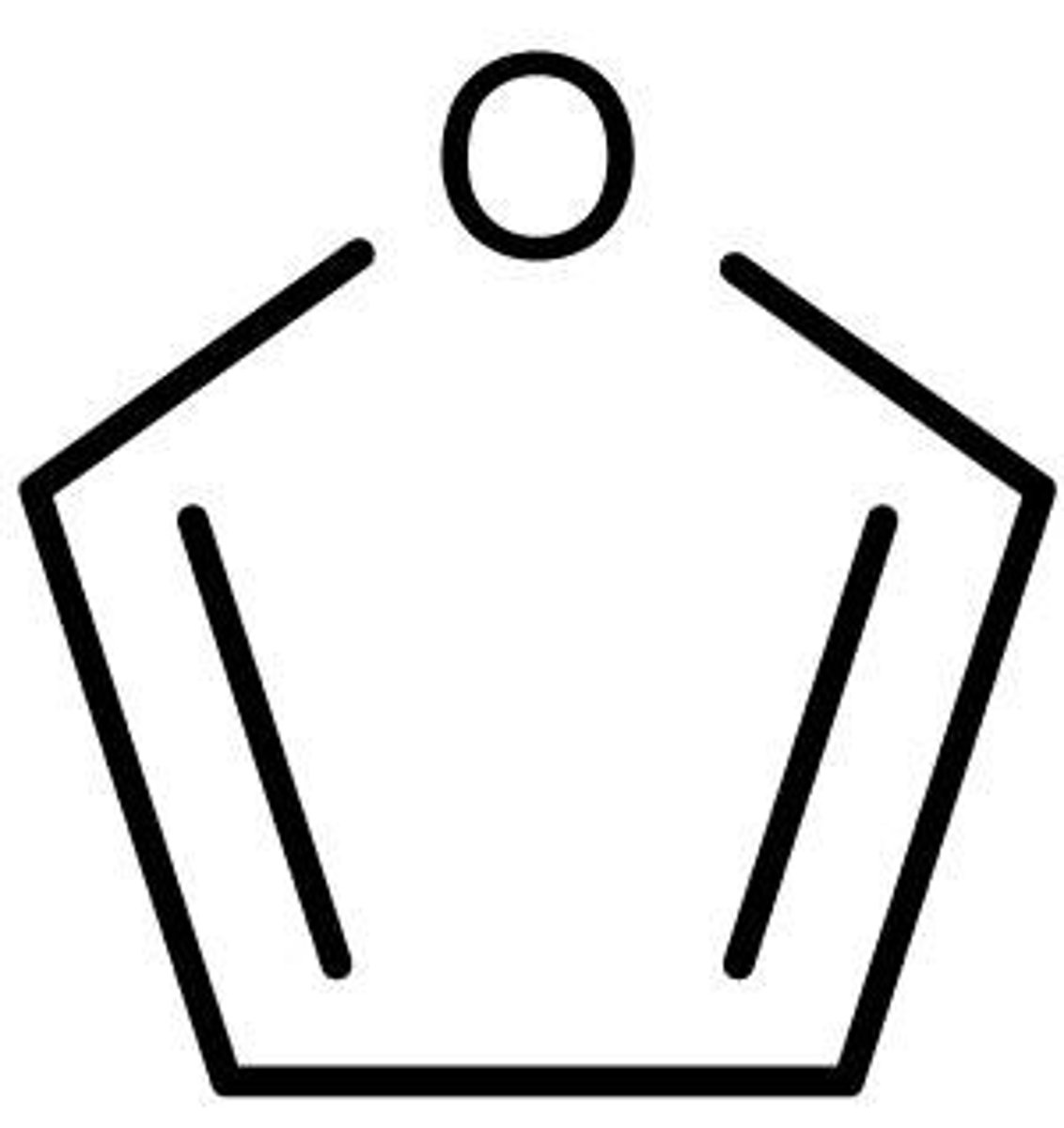
furan
five-membered oxygen heterocyclic aromatic
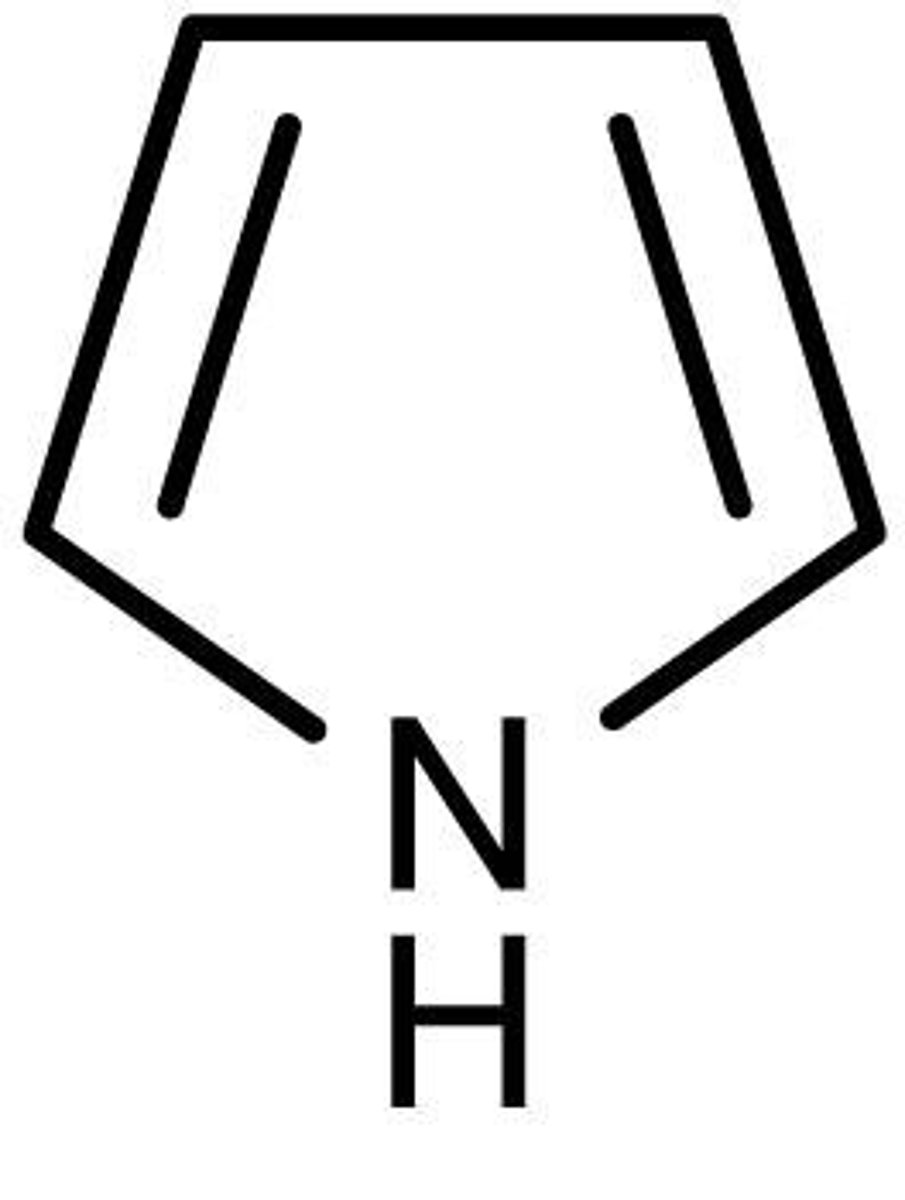
pyrrole
five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic aromatic
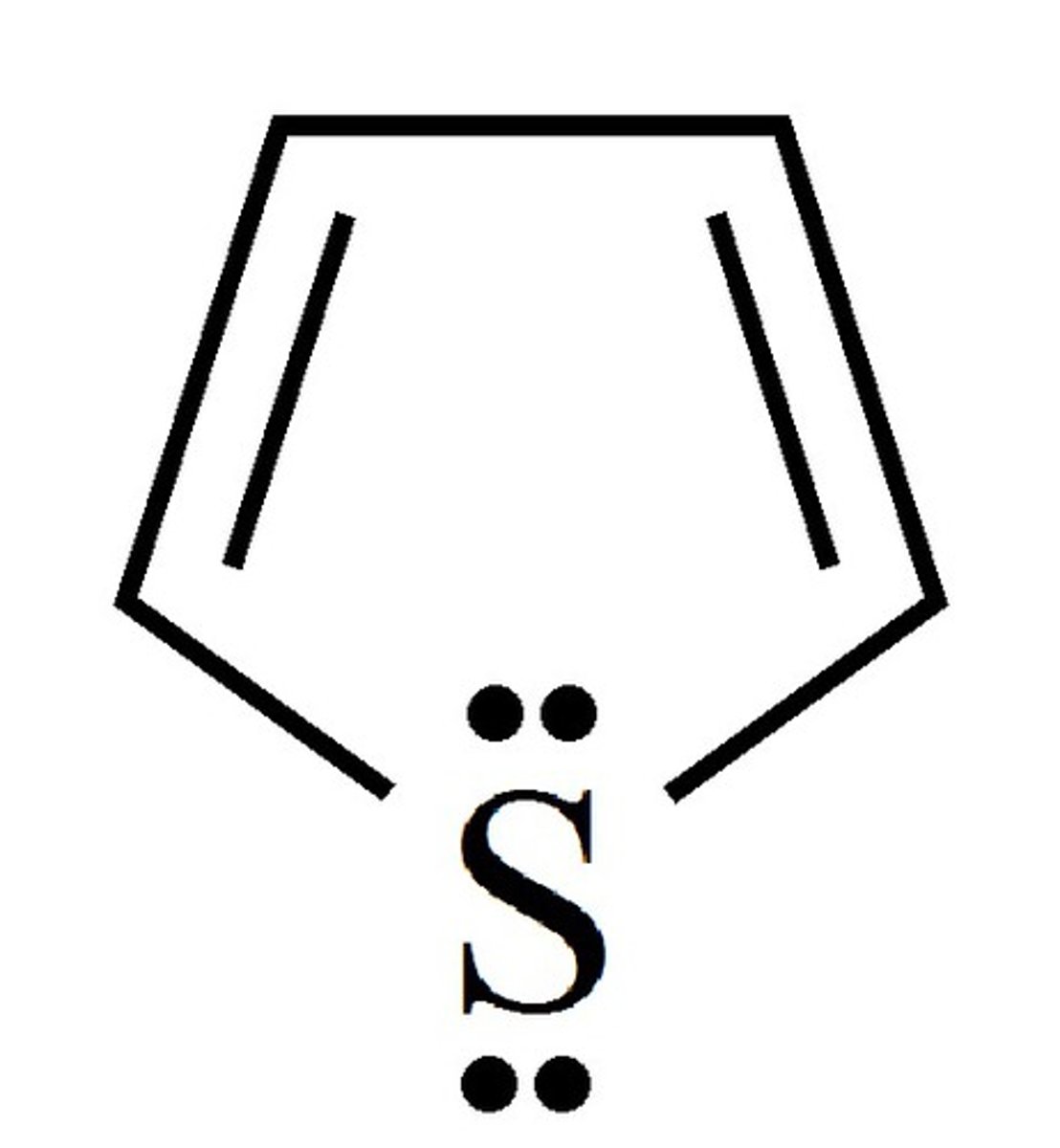
thiophene
5 membered aromatic ring with sulfur
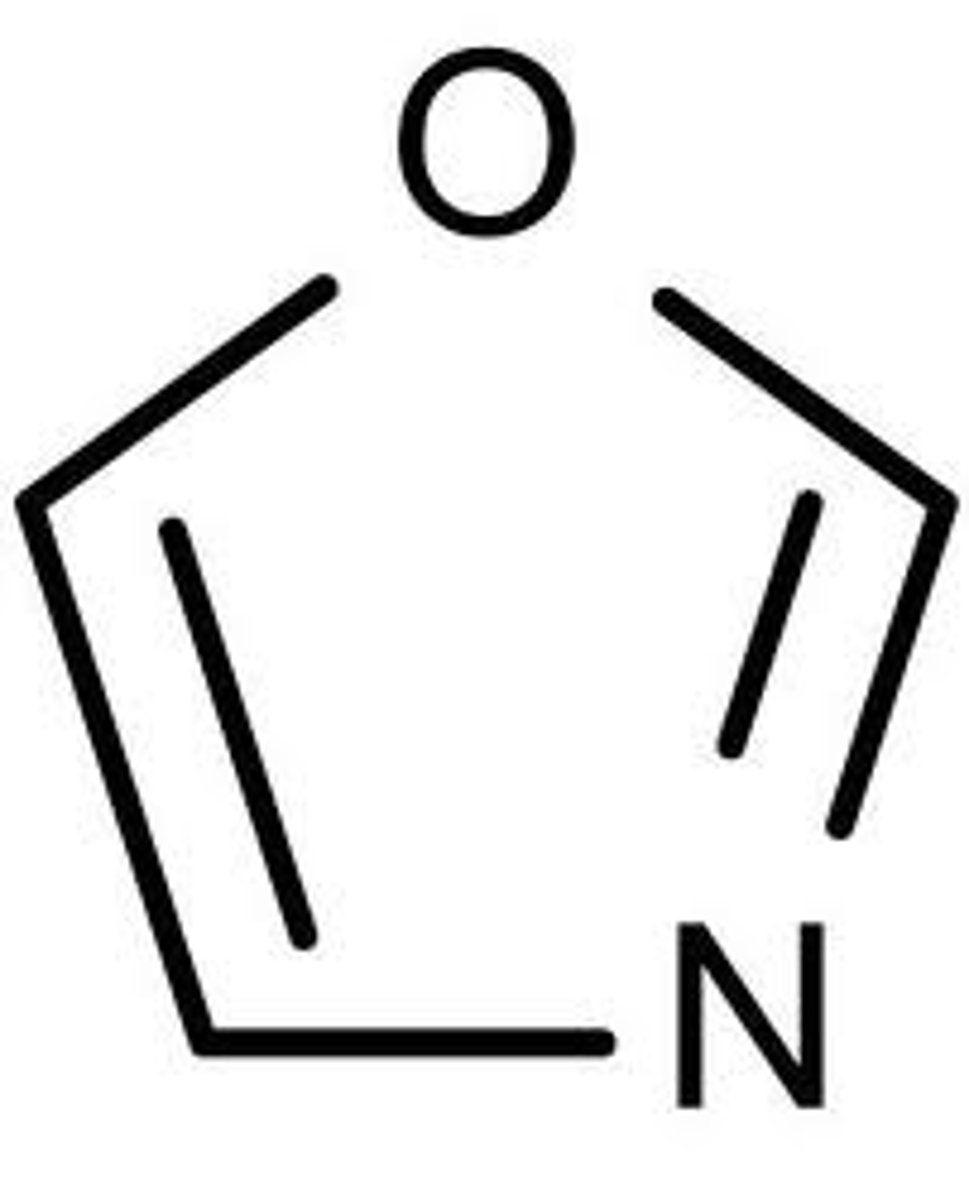
oxazole
5 membered, with O-C=N
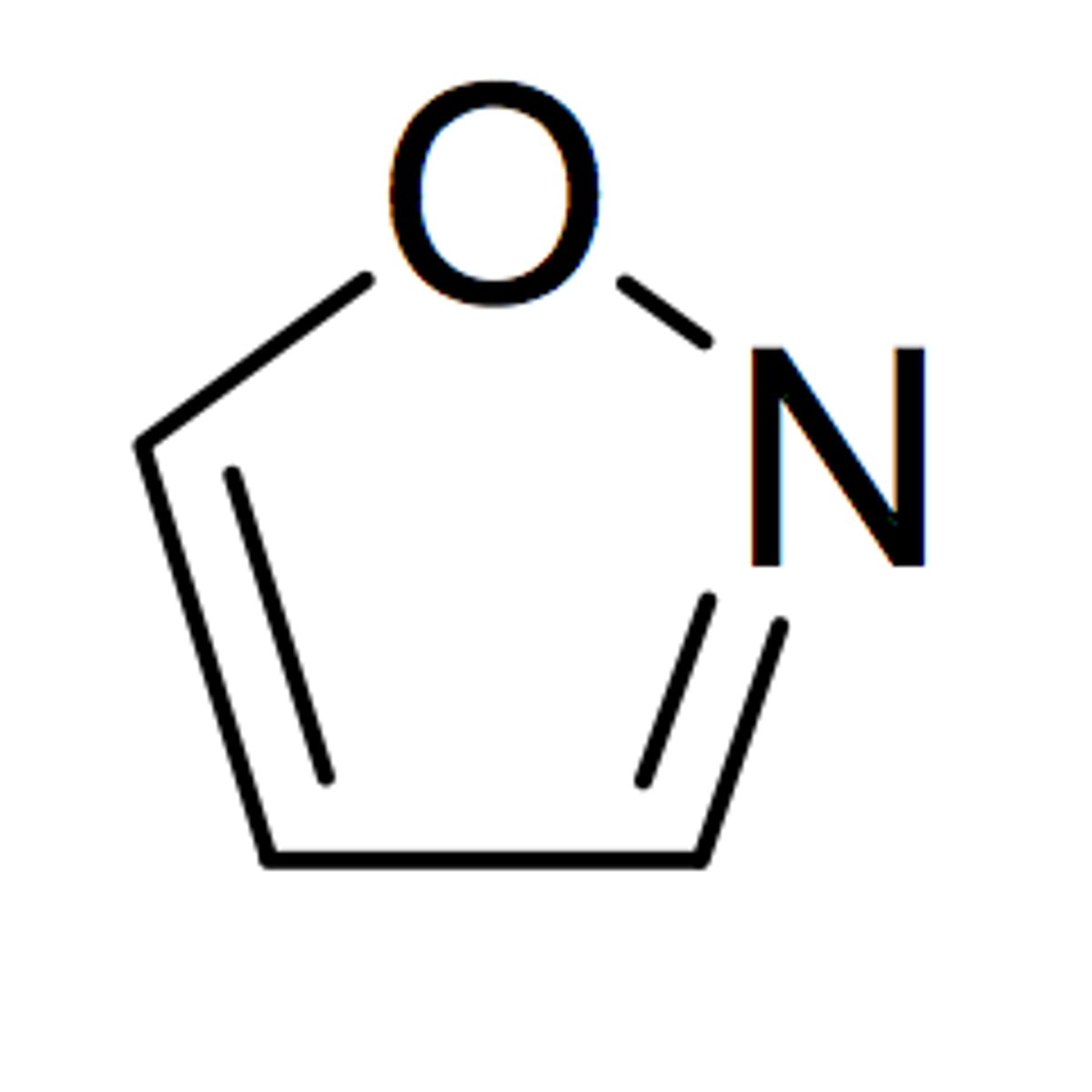
isooxazole
5 membered with O-N=C
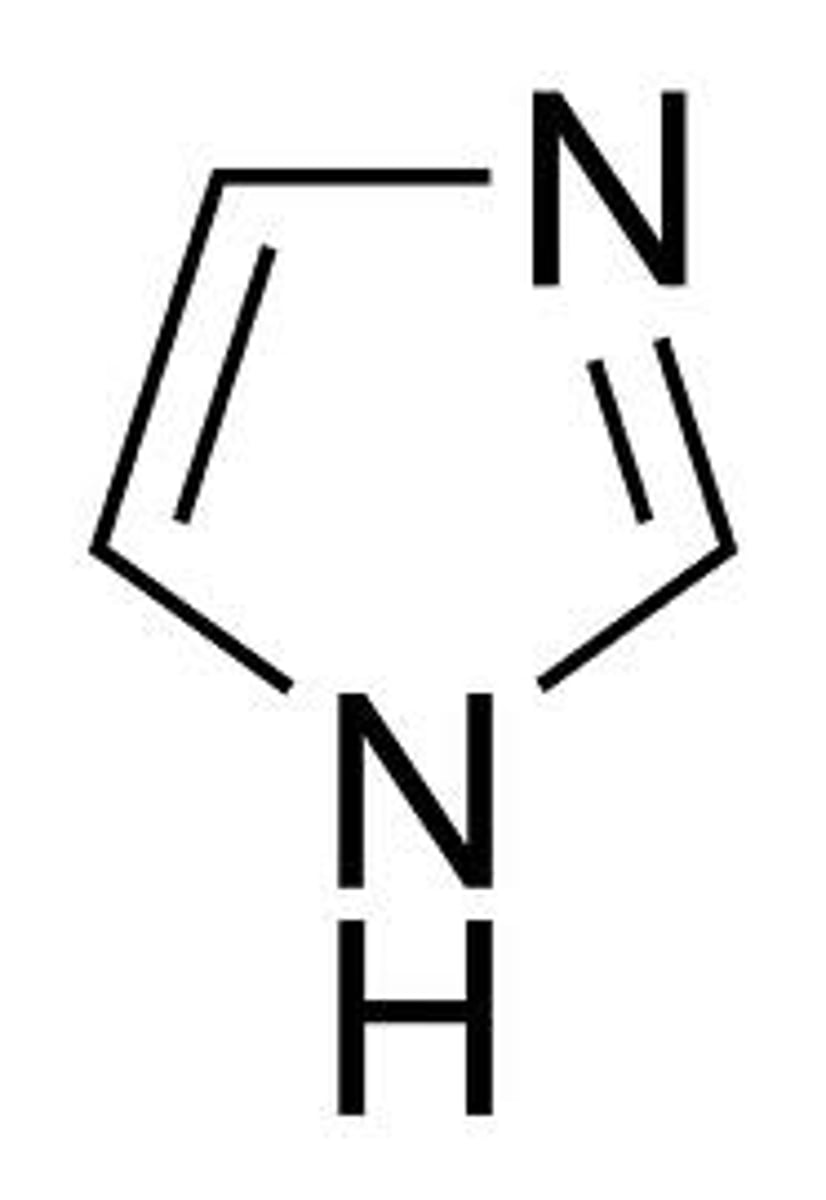
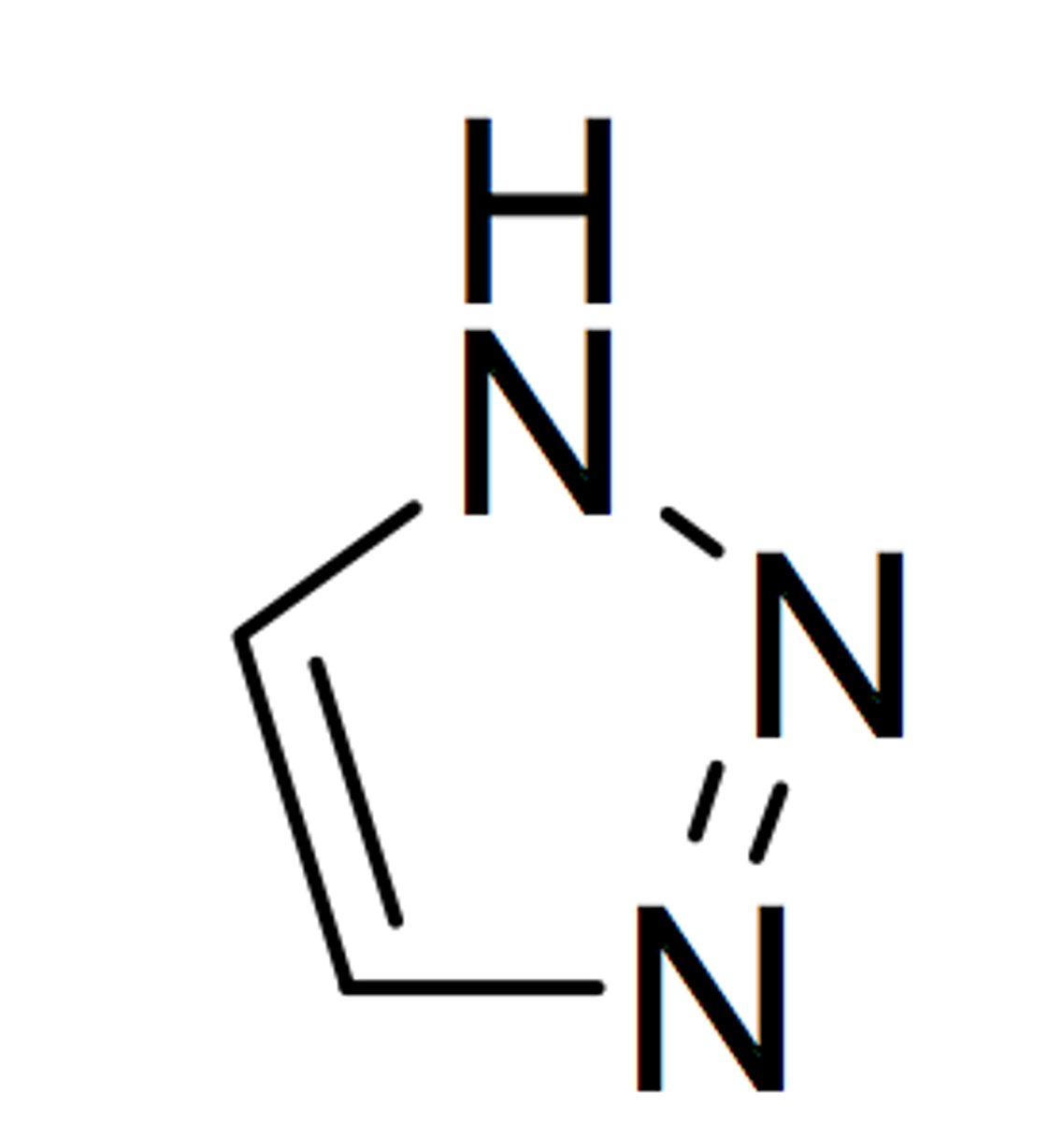
imidazole
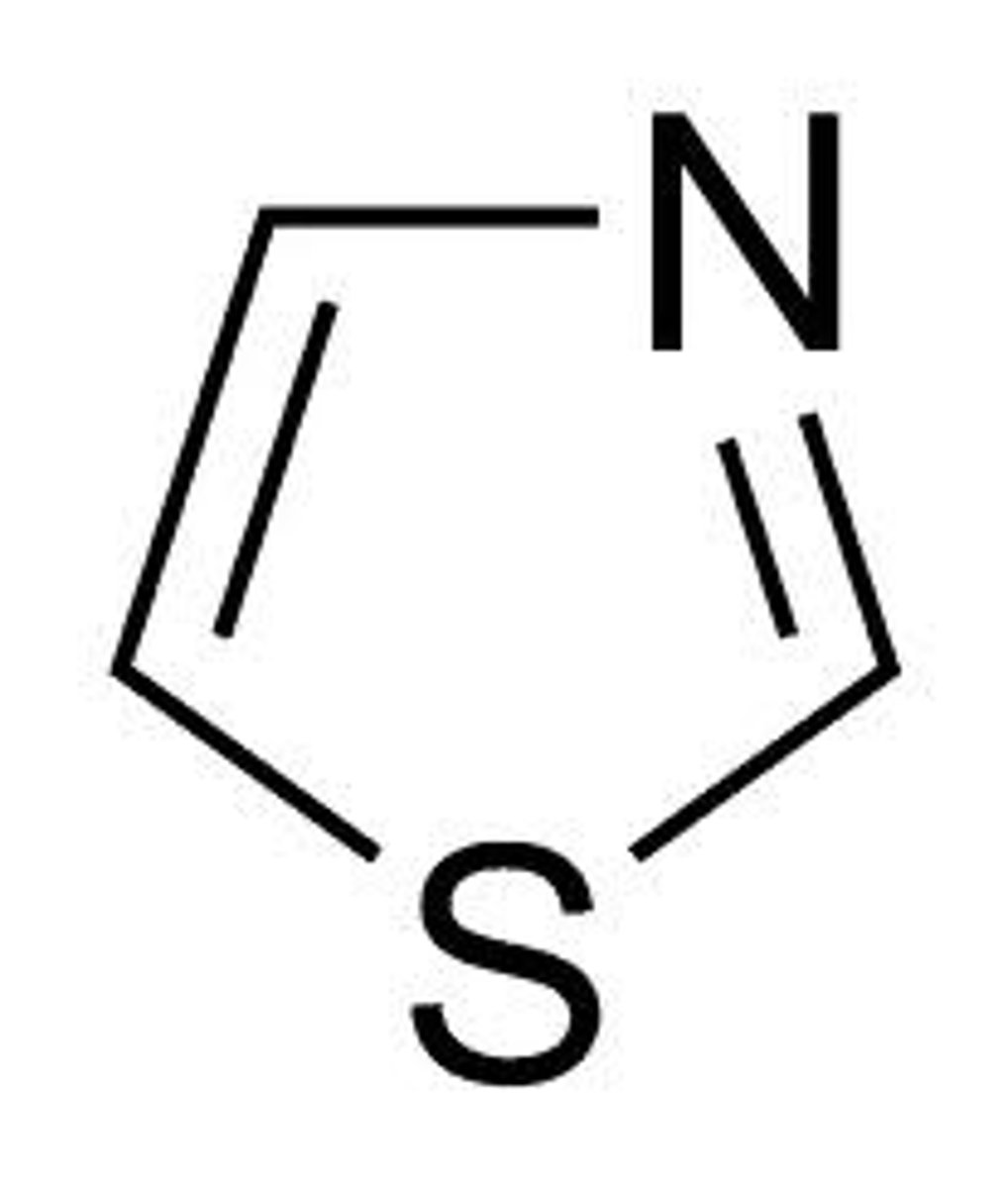
thiazole
like azoles but S
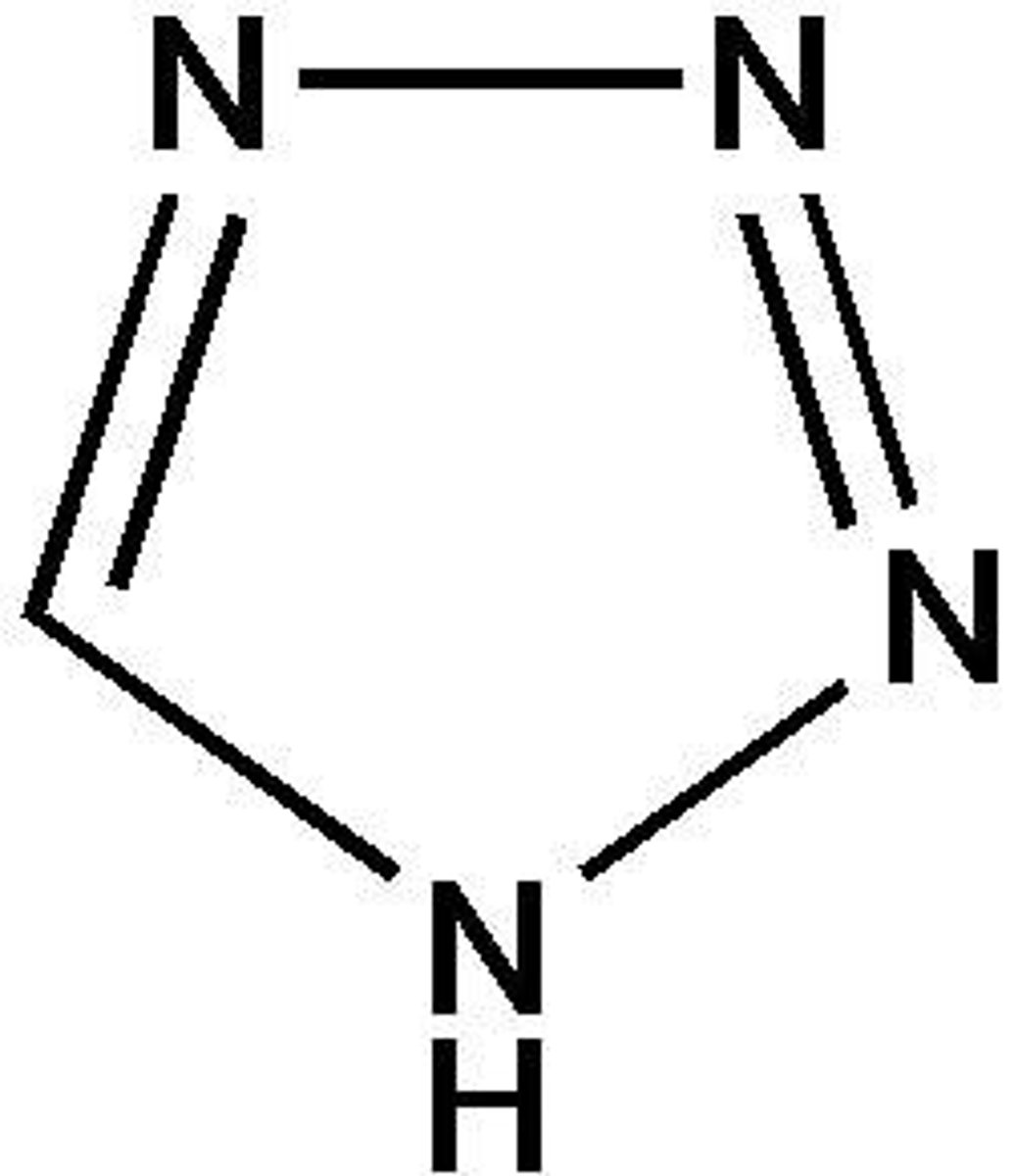
1,2,3-triazole
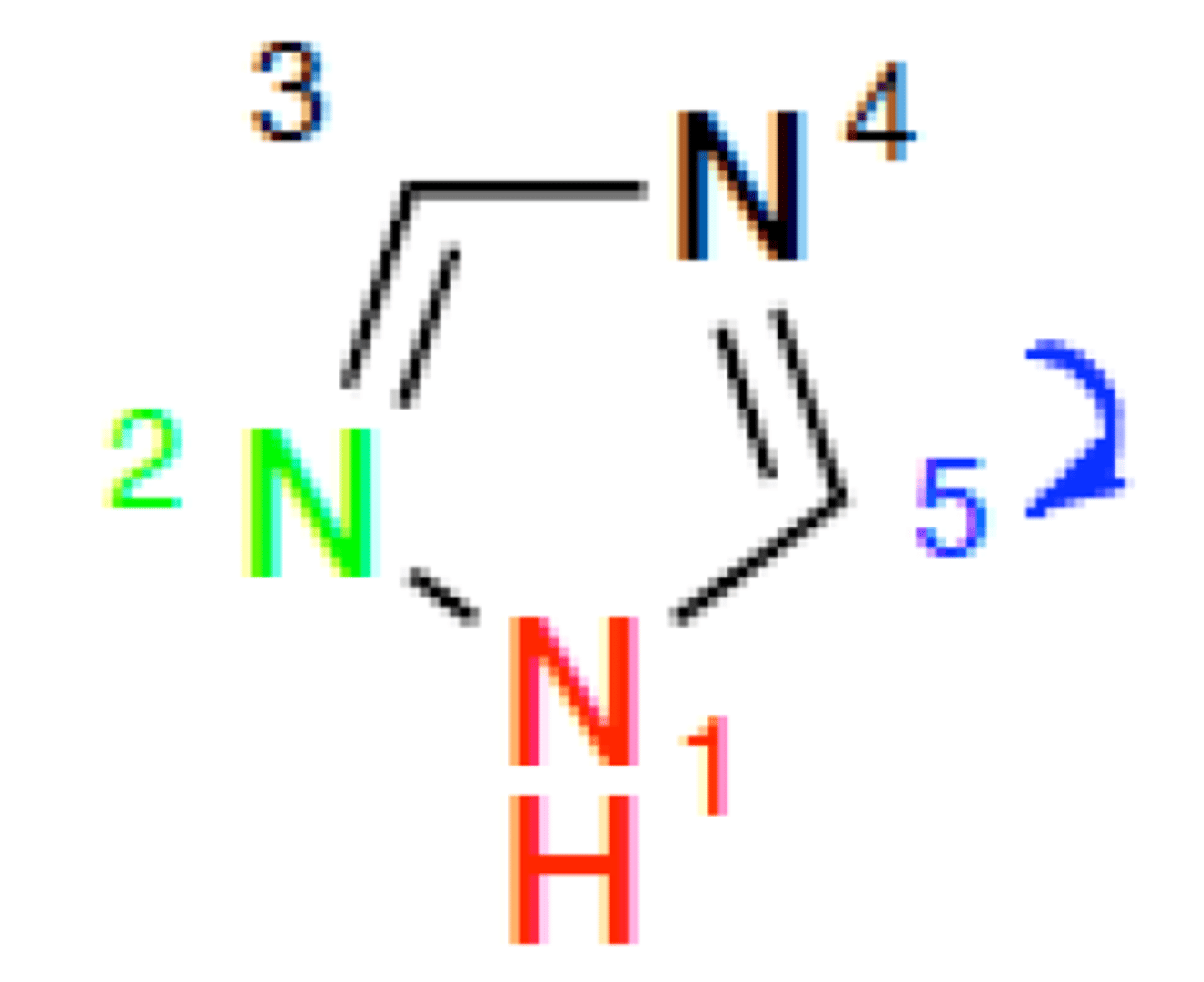
1,2,4- triazole
tetrazole
pyridine
6 membered aromatic N
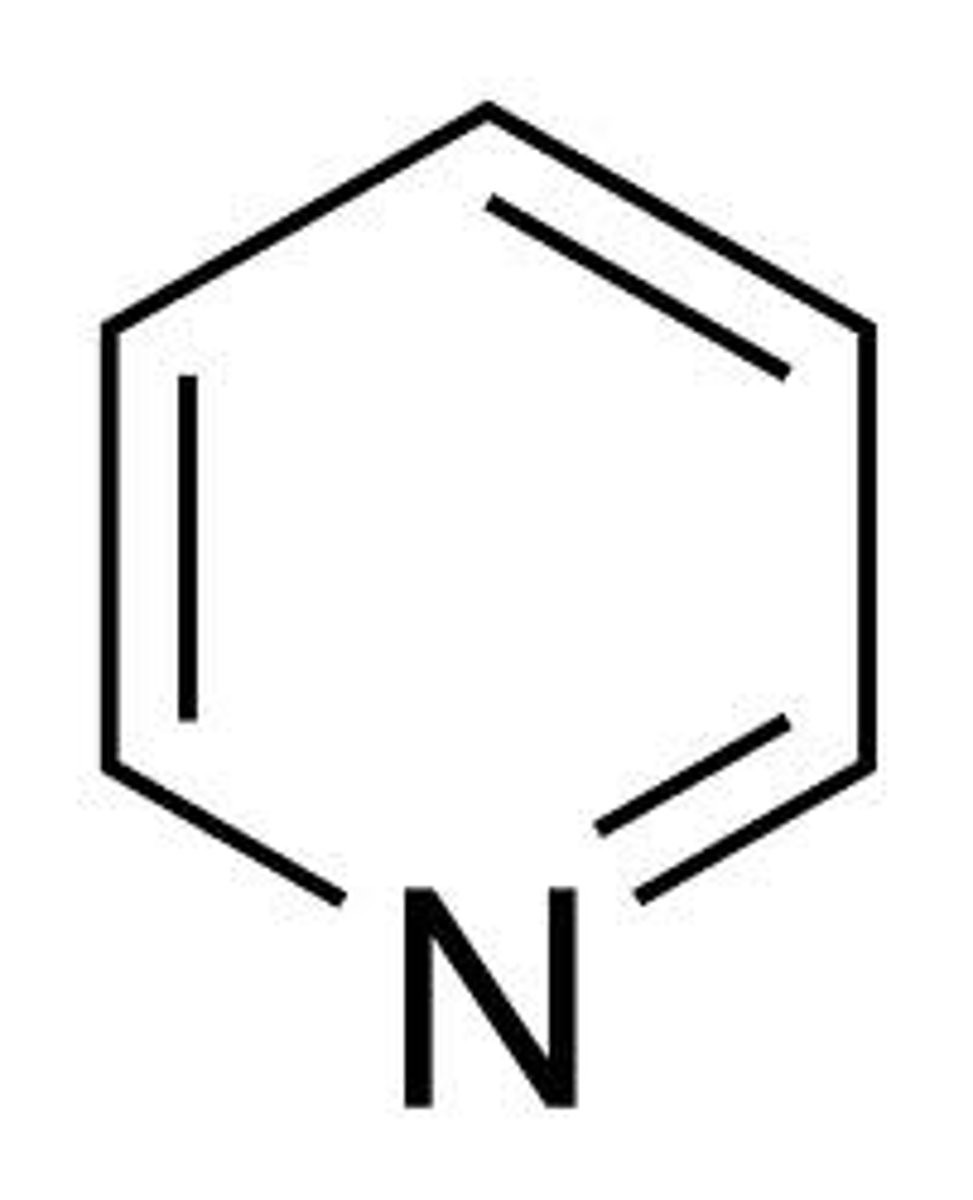
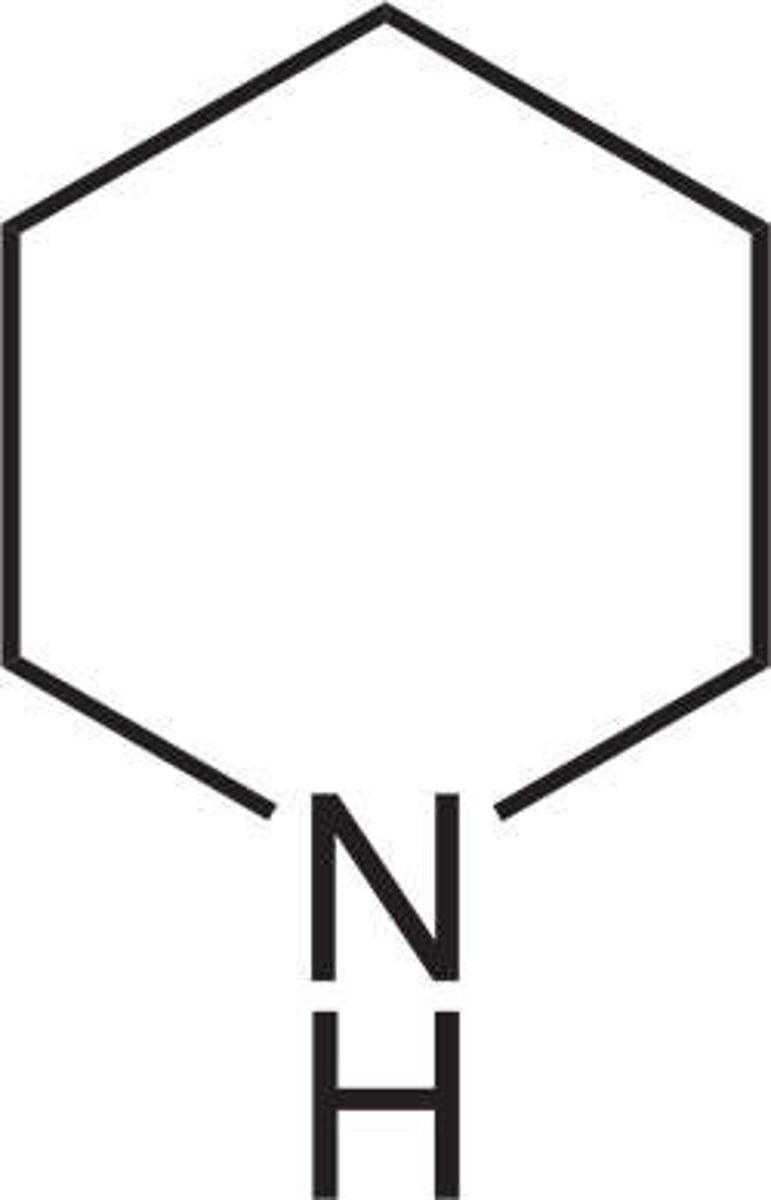
piperidine
like pyridine but NOT aromatic
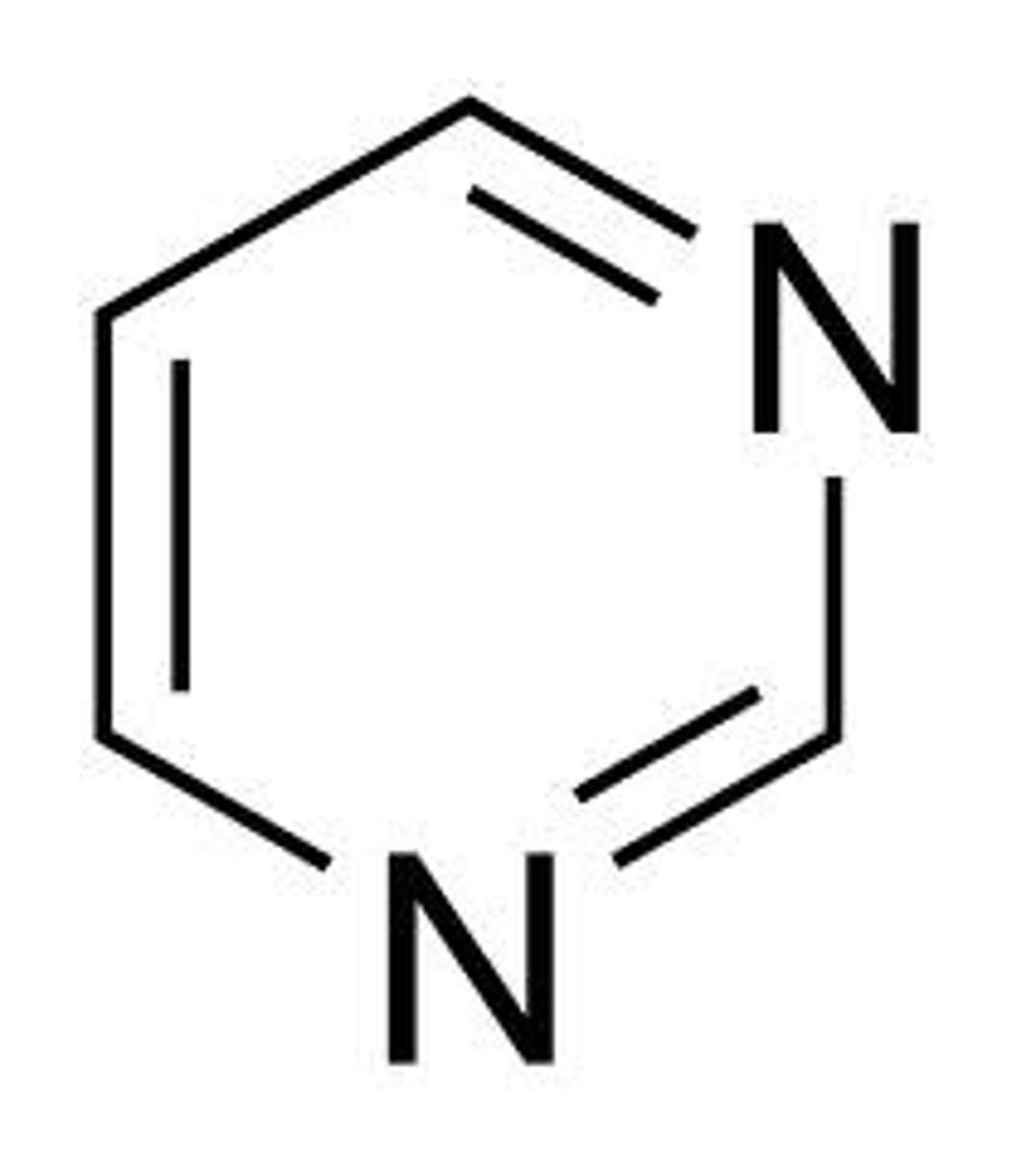
pyrimidine
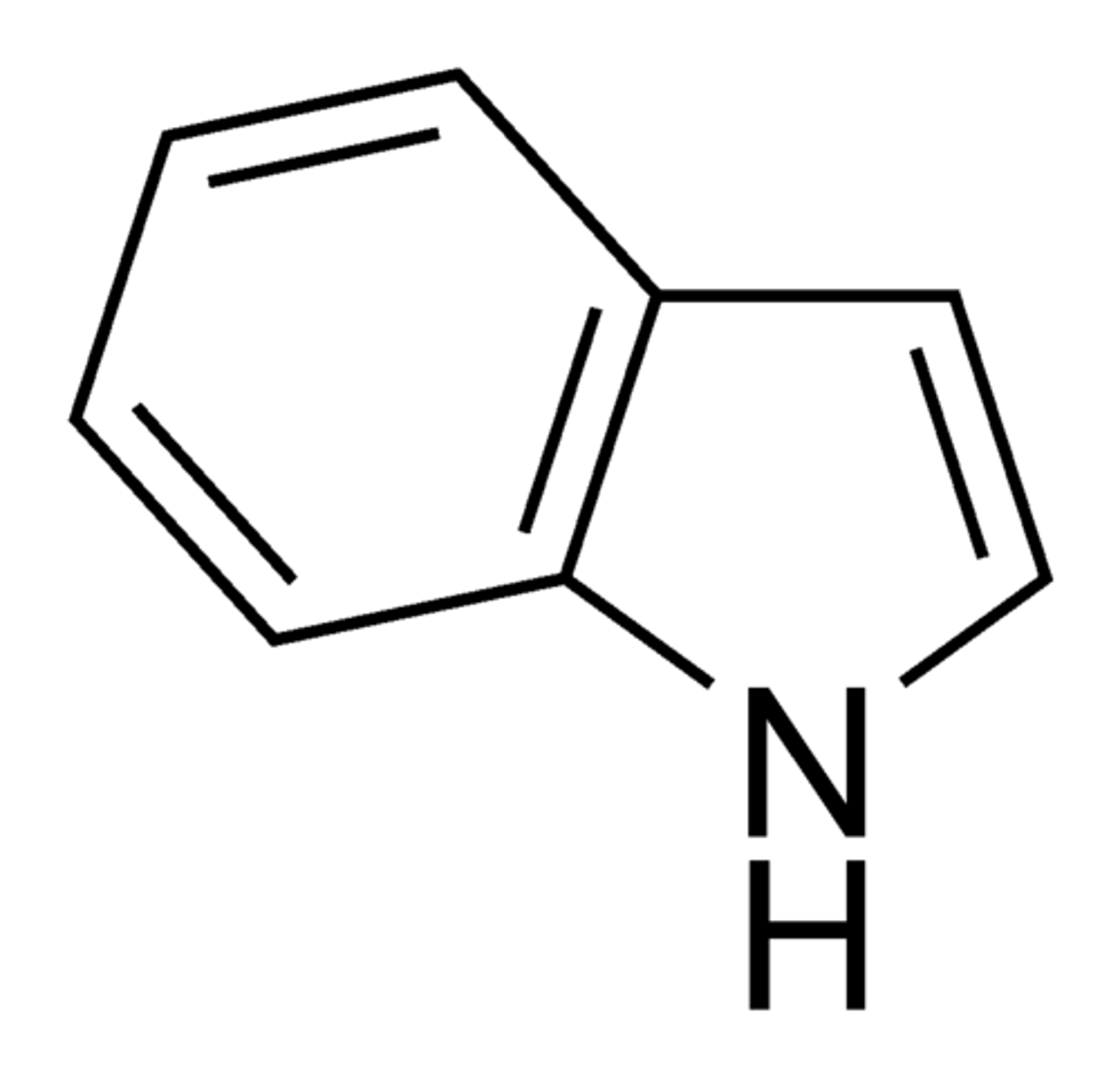
indole
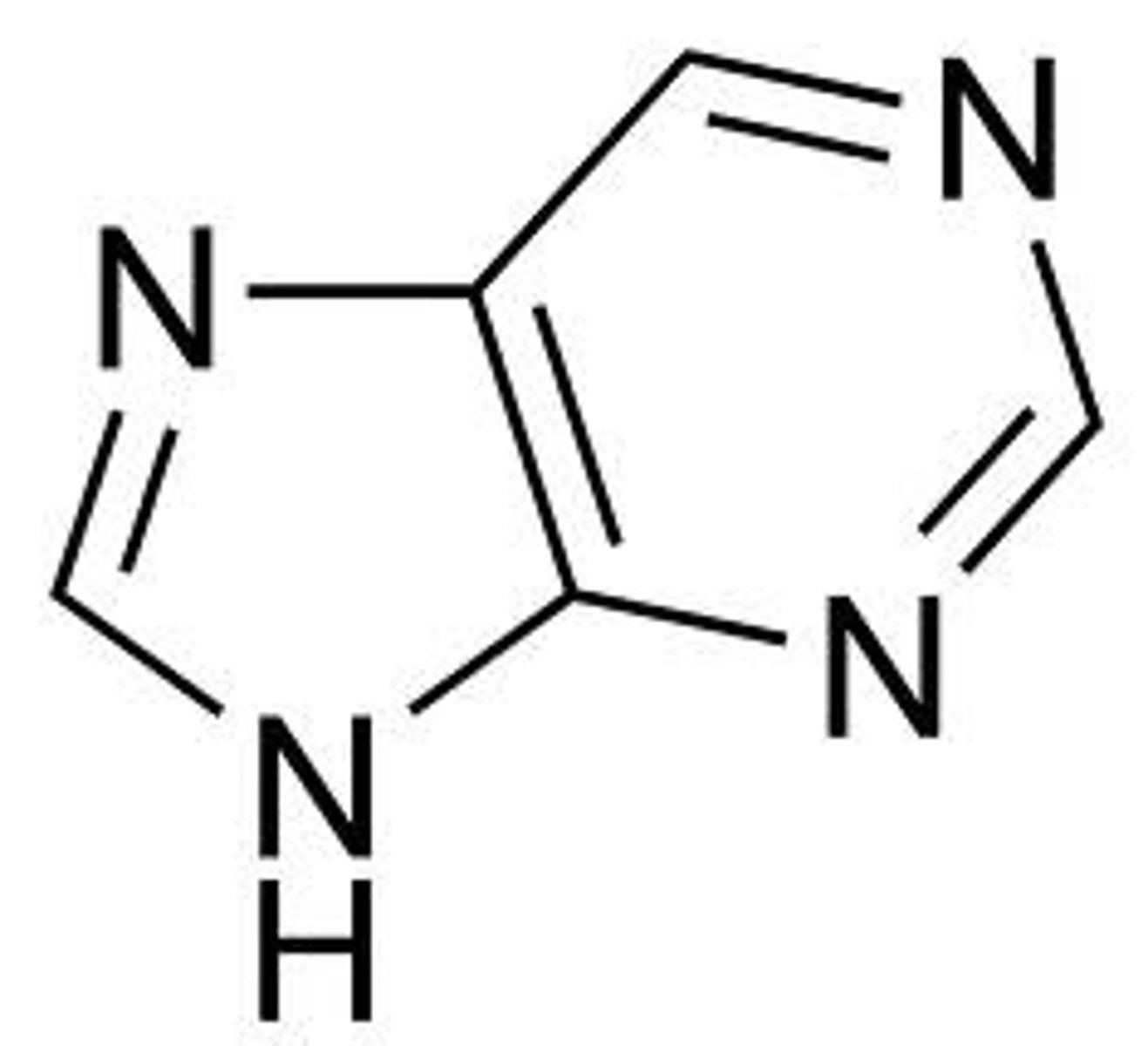
purine
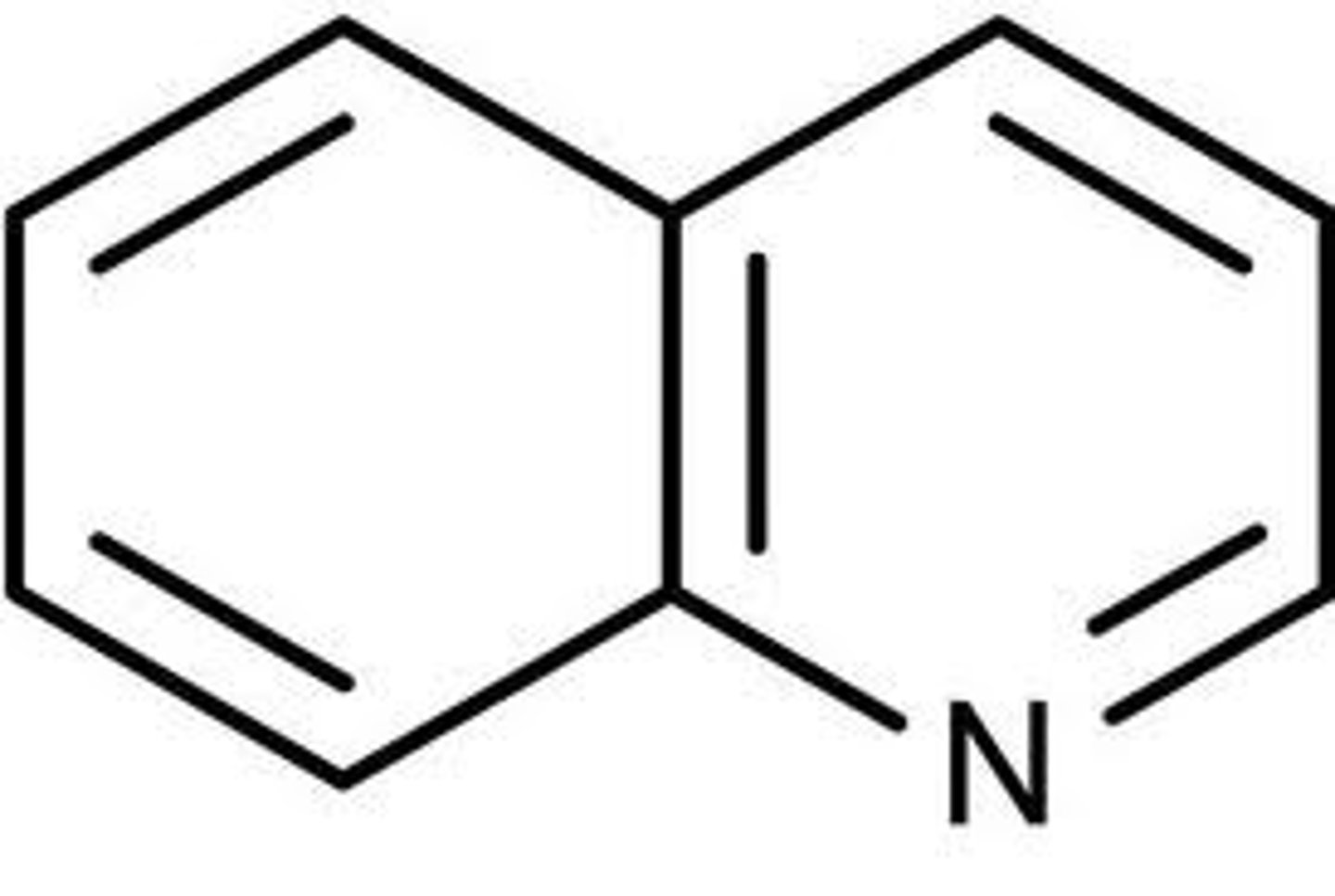
quinoline
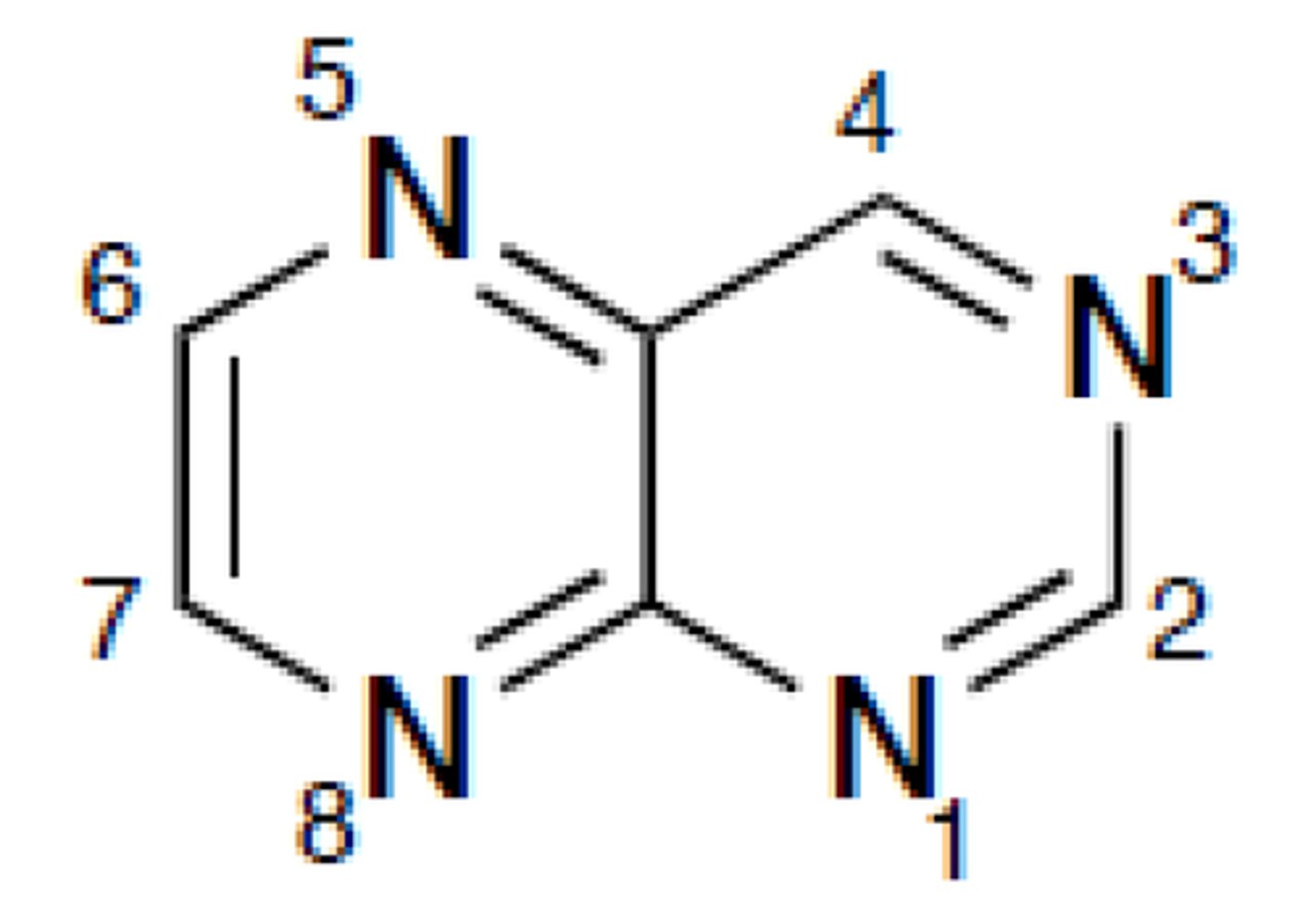
pteridine
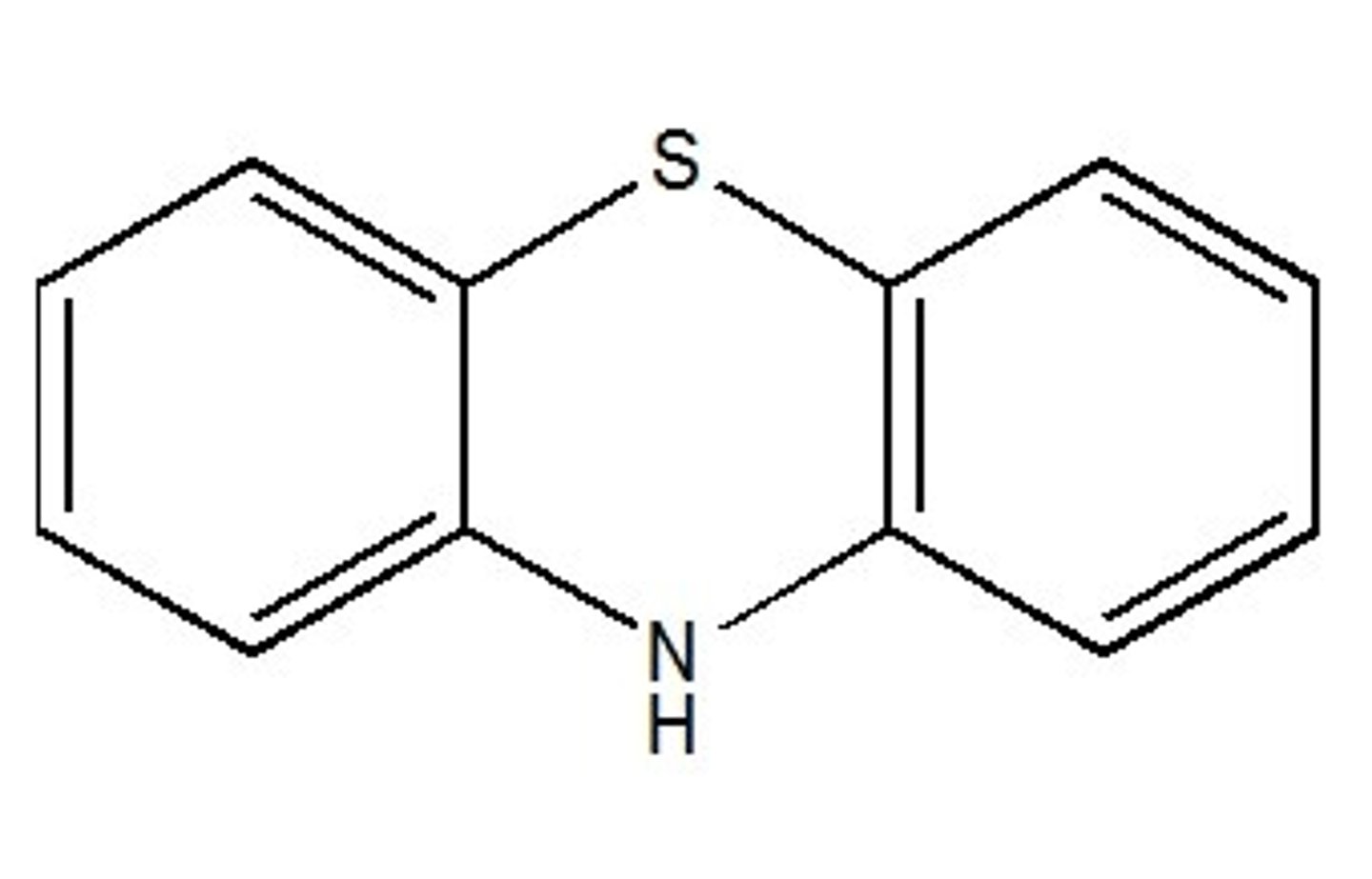
phenothiazine
acridine
Huckel's rule
If a compound has planar, monocyclic rings with 4n+2 pi electrons (n being any integer, including 0), it is by definition an aromatic compound.
pi electrons must be continuous

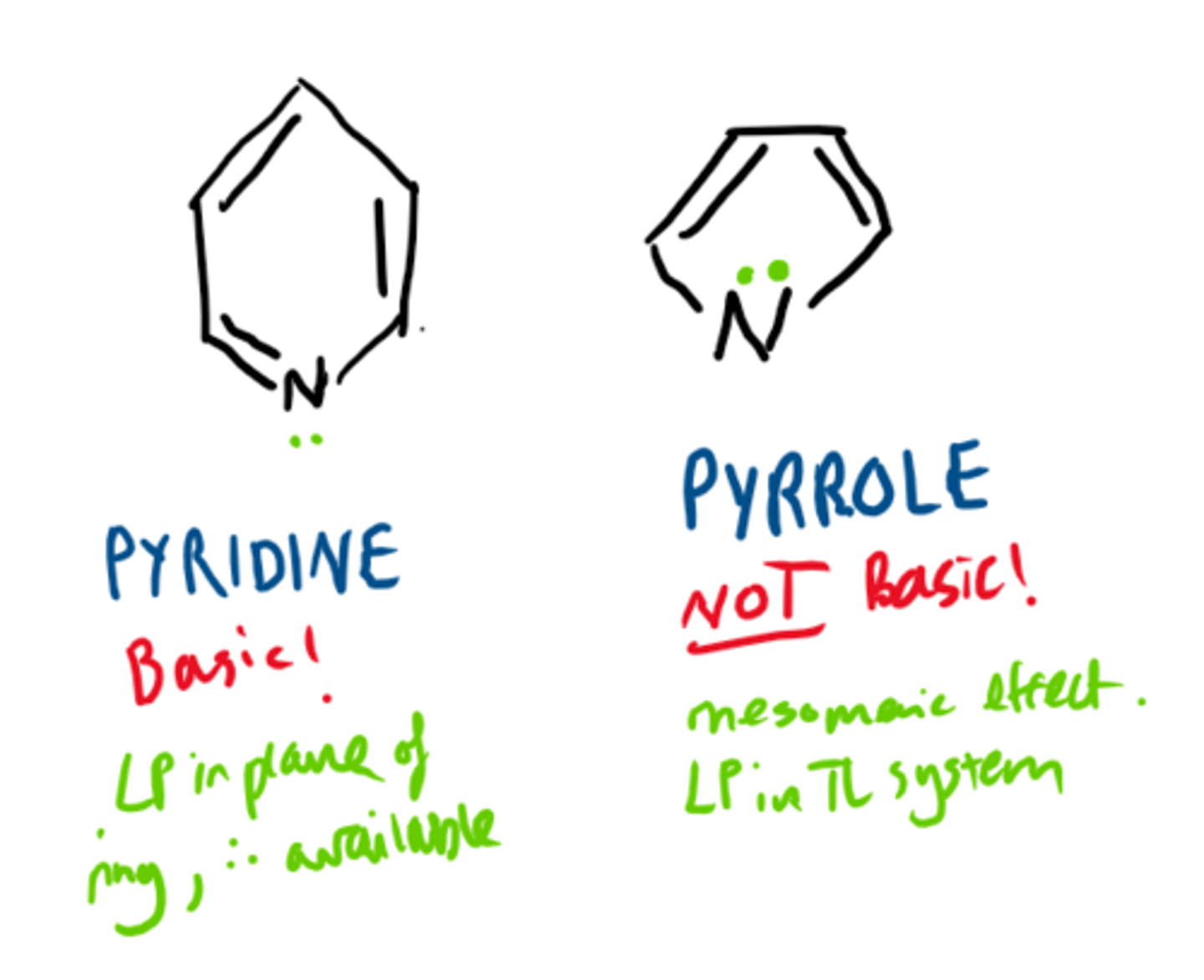
how do you know if an aromatic N ring has available lone pairs?
if there are 6pi electrons in ring then N's lone pair will not be used (ex: pyridine)
If there are 4pi electrons in ring then one of N's lone pairs will be used, therefore it cannot H bond (ex: pyrrole)
compounds that dissolve in water are termed ______
hydrophilic
can water dissolve polar or non polar molecules
polar (like dissolves like)
compound that do not dissolve in water are termed
hydrophobic
do hydrophobic or hydrophilic compounds cross membranes
hydrophobic
compounds that have a mix of hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups are called
amphipathic
are most drugs hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or both?
they are both-> amphipathic
water solubility is a competition between ________ interactions. explain
intermolecular interactions
= more interactions with water= more soluble (ex:salt)
= less interactions/ crystal packing= less soluble (ex:oil)
more H bonds in a molecule means it is __________ water soluble
more
charged molecules are more ____(hydrophobic or hydrophilic)______ than uncharged molecules
hydrophilic
(charged molecules are polar, water is polar)
can uncharged or charged molecules cross membranes
uncharged= hydrophobic= cross membrane
4 intermolecular forces contributing to water solubility
1. ionization state= high dielectric constant
2. hydrogen bonds
3. dipole-dipole
4. entropic