Resistance and Persuasion Exam
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Which (4) definitions of resistance are there?
a reaction against change: I don’t like it, I don’t believe it, I won’t do it
The ability to withstand a persuasive attack
an outcome: not being moved by pressures to change
A motivational state: motivation to oppose and counter pressures to change
What are the 4 stages or reactance theory (Brehm, 1966)?
Freedom (I do what I want)
Threat to freedom (I get told not to do X)
reactance (I want to do X)
restoring freedom (I do X, freedom is restored)
What are some effects of a freedom threat? (replies/ways to resist)
derogate source of (freedom) threat
increase liking for threatened choice
deny existence of threat
exercise different freedom
Which models could exist for the nature of reactance, according to Dillard & Shen (2005) and Rains & Turner (2005)
purely cognitive
purely affective
cognitive and affective (distinct effects → dual-process)
cognitive and affective (linear effects)
cognitive and affective (intertwined effects)
Explain Politeness theory
People have a negative and positive face. Language is impolite when it violates one or both of these face wants
Positive face: fundamental need for approval, acceptance, and being viewed as competent
Negative face: fundamental need for autonomy and independence
Resistance to persuasion is a defensive reaction to an unjustified relational claim → threatening one or both aspects of face
How can language cause a face threat? And when is this risk smaller?
Forceful language is threatening → controlling, but also demeaning anyone who does not agree
Forceful messages are less likely to be viewed as a face threat when the source has greater/legitimate power, or the situation requires it (requires maximum efficiency)
What is persuasion knowledge (PK)?
Consumers’ knowledge and beliefs regarding marketers’ persuasion goals and attempts, as well as their underlying motives and tactics, and how persuasion works
Draw the persuasion knowledge model
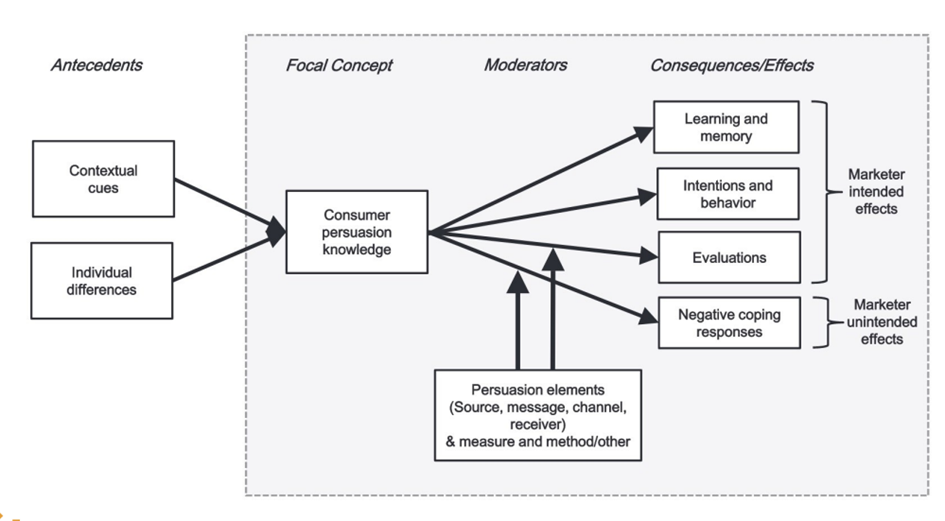
What is advertising literacy?
an individual’s knowledge of and skills related to advertising. Works as a filter or radar, enabling consumers to critically evaluate ads
What is the difference between dispositional and situational advertising literacy?
Dispositional advertising literacy:
advertising related knowledge and skills
available all the time
associative networks of information nodes
Has a cognitive, affective, and moral dimension
Situational advertising literacy:
applying dispositional advertising literacy when confronted with an ad
Activating associative network
Two-step process → change of meaning
recognizing persuasive attempt
critical reflection of this attempt (compined action of cognitive, affective, and moral advertising literacy)
Coping skills is the stop and think response that is the crucial connection between dispositional and situational advertising literacy
What are ways one could solve cognitive dissonance?
avoidance
suppression
denial
cognitive reappraisal
What is the difference bertween reactance and dissonance?
reactance is psychological response to autonomy/freedom threat, while dissonance is psychological response to self-integrity threat
Which 8 strategies for resisting attitude change are there?
attitude bolstering
counterarguing
assertions of confidence
social validation
selective exposure
source derogation
negative affect
derogating persuasive tactic
Which resisting strategy is most effective?
Counterarguing → effortful resistance seems most effective
BUT using multiple (additive resistance index) simultaneously is better
What do Valli & Nai (2023) mean with intertwined effects?
Individuals are expected to engage in multiple resistance processes/strategies simultaneously
Which resistance strategies become more effective through cognitive elaboration?
counterarguing, derogation of persuasive tactic, social validation, negative affect, and the intertwined resistance index
What is the ACE typology of Fransen et al. (2015)?
Categorises resistance strategies:
Avoidance
Contesting → actively refuting the message by challenging it
Empowering → reassuring the self or one’s existing attitude
Which 2 tactics are there to promote attitudinal or behavioral change?
increase approach forces with Alpha strategies
decrease avoidance forces with Omega strategies
(Some strategies (e.g. humor) use both strategies!)
Which 7 types of omega strategies are there?
sidestep resistance
address resistance directly
consume resistance
distract resistance
disrupt resistance
use resistance to promote change
address resistance indirectly (taking away the need to be resistant)
Which omega strategies with with which ACE typology category?
Avoidance:
sidestep resistance
Contesting
address resistance directly
consume resistance
distract resistance
disrupt resistance
Empowering
use resistance to promote change
address resistance indirectly
When is it most useful to use self-persuasion?
when a direct persuasion attempt is likely to fail
because important attitudes, habitual behavior, or difficult lifestyle changes are concerned
People don’t see the need to change/are not intrinsically motivated
When the target group knows it’s important, but just doesn’t act upon it → confronting people with own hypocrisy (evoke cognitive dissonance)
When to use narrative persuasion?
To neutralise avoidance → sender and persuasive intent disguised
to neutralise contesting → source derogation and counterarguing are inhibited
to neutralise empowering → involvement with characters can evoke vicarious self-persuasion, increase perceived vulnerability and self-efficacy, and change social norms and outcome expectancies
Make sure your narrative matches your target group though! Not all narrative are succesful in avoiding resistance
How does humor reduce resistance?
Both through creating positive affect (affective model) and distraction (cognitive model)
What is often an issue with sex(ual) appeals?
They’re so succesful that the reader/viewer doesn’t pay attention to the ad message anymore
What are the 4 stages of parasocial relationships?
initiation (first impression)
experimentation (several interactions)
intensification (establishment of relationship)
integration/bonding (maintenance of relationship)
What is the difference between parasocial interactions (PSIs) and parasocial relationships (PSRs)?
PSI: short, non-reciprocal interactions with media personalities
PSR: Long-term, cross-situation relationship with media personalities that develop over time
How does PSR neutralise resistance (Breves et al.)?
trustworthiness → less reactance/counterarguing → more persuasion
Which two types of persuasion knowledge are there according to Youn and Kim (2019)?
Conceptual and attitudinal
Conceptual persuasion knowledge: perception of a persuasive intent
Attitudinal persuasion knowledge: deceptive intent
How do disclosures affect persuasion knowledge?
Increases conceptual persuasion knowledge, but decreases attitudinal persuasion knowledge, because less feeling of deceit
→ balances each other out
Explain inoculation theory (McGuire, 1970)
People can build up resistance against unwanted persuasion attempts through prebunking → vaccine for persuasion
forewarning (hey your beliefs might be challenged)
refutational preemption (they might say A, but B is actually true/that is false because)
Which 6 degrees of manipulation were used in the Get Bad News Game?
discrediting opponents
appealing to emotion
polarizing audiences
impersonation
floating conspiracy theories
trolling
Which defensive responses to health messages belong to contesting, bolstering, cognitive reappraisal, biased processing, suppression, and avoidance, according to Fransen (2023)?
Contesting:
counterarguing
denial
source derogation
message derogation
Bolstering
attitude bolstering
social validation
Cognitive reappraisal:
fatalism
risk normalization
religiosity
downward social comparison
Biased processing:
weighting attributes
reducing impact
optimism bias
Suppression:
hiding fear
alcohol/drug abuse
Avoidance:
physical avoidance
cognitive avoidance
(mechanical avoidance?)
On which 4 major elements depends whether/how consumers activate/apply their persuasion knowledge?
source, message, channel, and receiver
Which information processing stages do children go through?
limited processors (under 7) → can’t properly process information yet
Cued processors (7-11) → need help (through cues) to initiate info processing
Strategic processors (12+) → have strategies to process information
Which 3 stages do children go through regarding interpersonal influence tactics knowledge?
Learning the concept of self-interest
Developing a conception of relationship
Understanding social welfare concepts → judgement of appropriateness based on altruism and moral rightness
Through which 3 stages of content knowledge do children go?
perceptual (3-7)
Analytical (7-11)
Reflective (11-16)
How can advertising literacy be operationalised according to a cognitive perspective?
- Recognise advertising
- Understand its selling intent
- Understand its persuasive intent
- Understand its persuasive tactics
- Recognize the source of advertising
- Identify the audiences an advertisement is targeted toward
- Next to a cognitive component, a moral one can also be distinguished, which is about the ability to morally evaluate the appropriateness of the advertisement and format.
- A third component of dispositional advertising literacy is the affective or attitudinal dimension, which is about the importance of emotion regulation to counterbalance the affective reactions evoked by the persuasive messages.
What is the difference between narrative empathy and narrative sympathy?
Narrative empathy: perspective-taking and vicarious experiences (identification)
Narrative sympathy: caring for characters’ predicaments without identifying or empathizing with them.
Both have been argued to facilitate persuasion by distracting attention from persuasive intent and suppressing resistance.