BILD 1 Midterm 1, BILD 1 Midterm 2, BILD 1 Final COOPER UCSD
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
Characteristics of Life
(ROGERRE) Repro Order Growth Evolution Regulation Response Energy
What is needed for a recessive X-linked trait to be expressed?
1) female needs 2 copies of the allele (homozygous)
2) male needs 1 copy of the allele (hemizygous) (thus more common in males)
first law of thermodynamics
energy in the universe is constant
silent mutations
different nucleotide in DNA but same amino acid in protein
Missence Mutation
when a point mutation results in substituting one amino acid for another
nonsense mutation
changes a normal codon into a stop codon
Biological organization
atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere
second law of thermodynamics
energy conversions increase the disorder of the universe
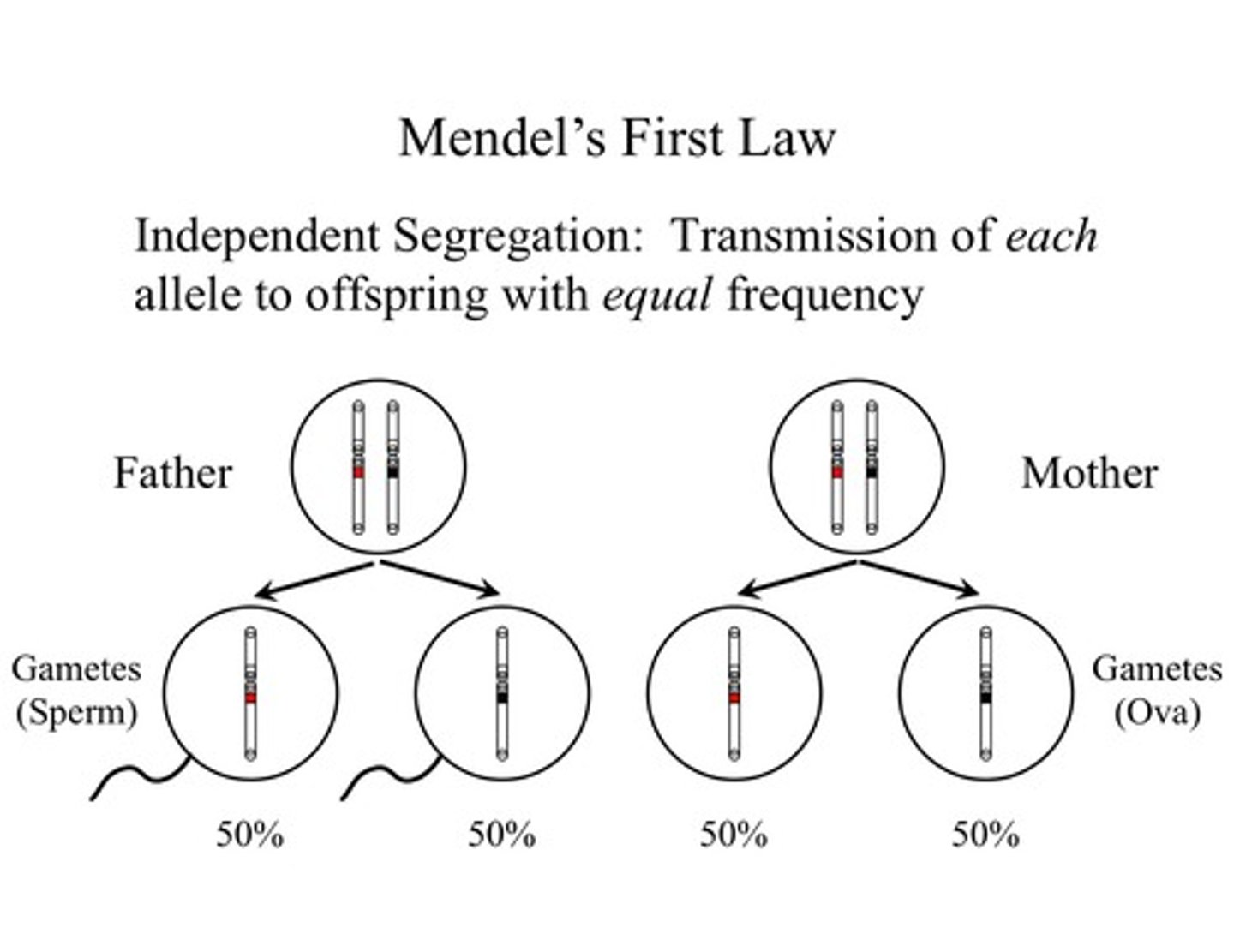
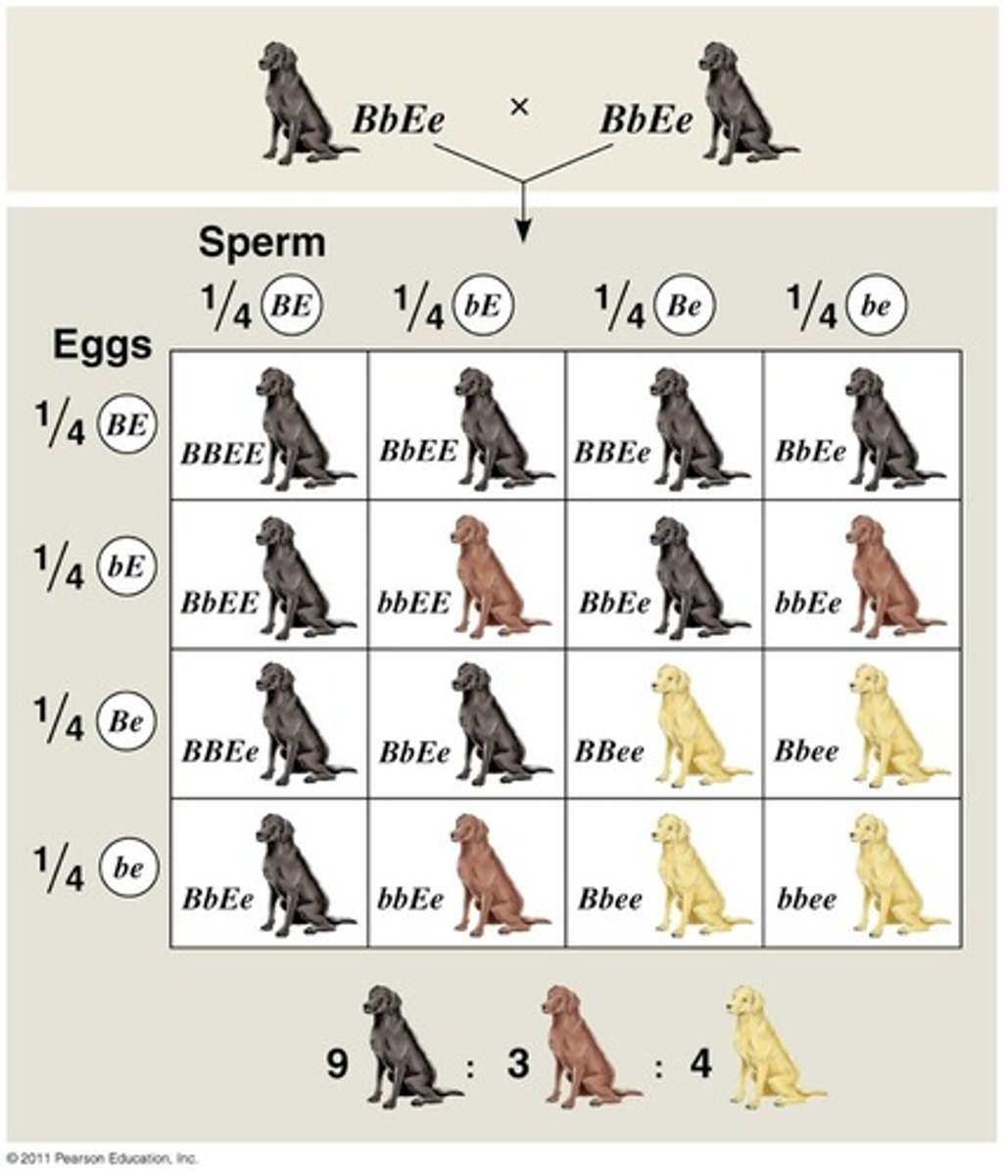
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
endergonic
takes work
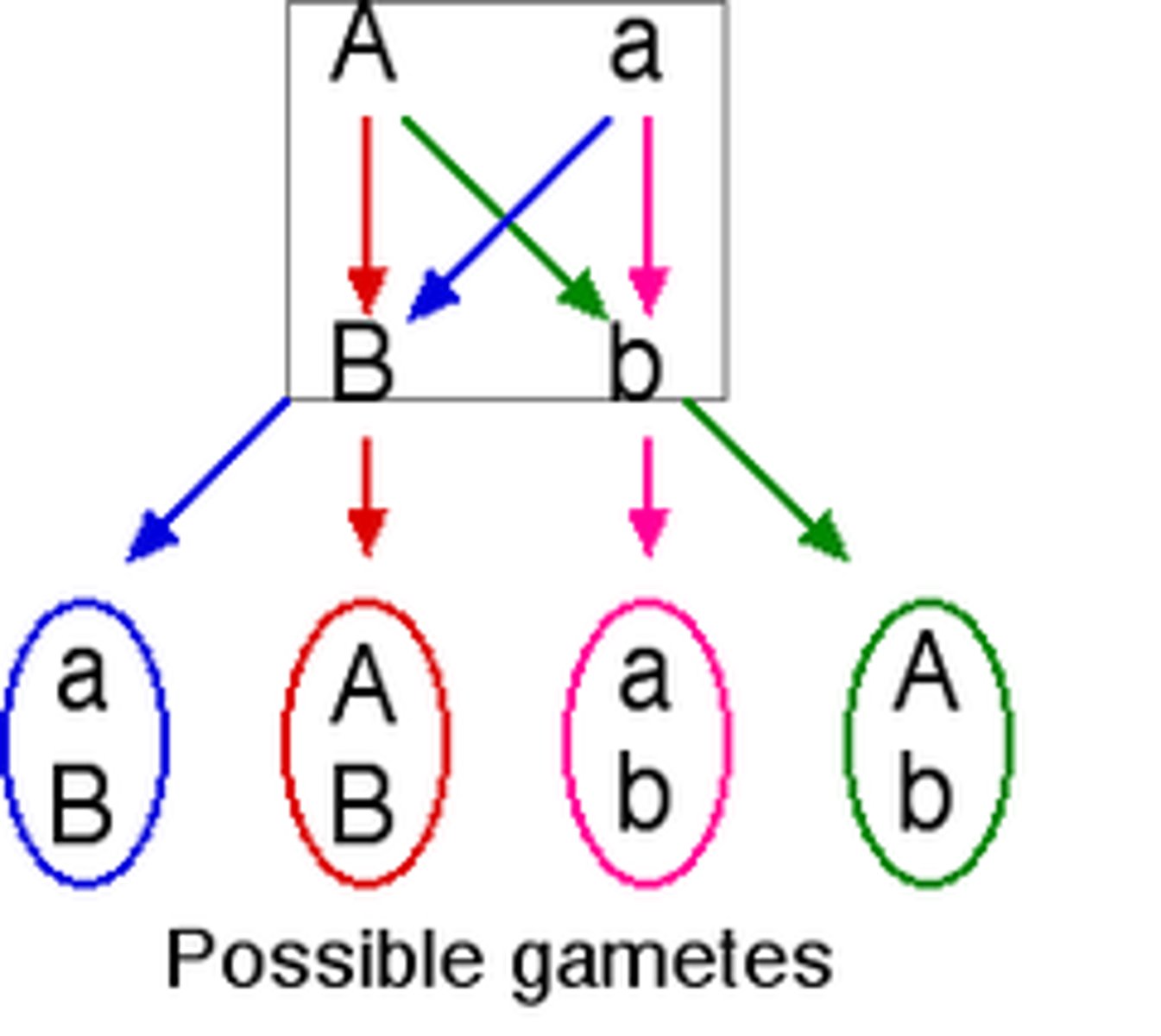
law of independent assortment
Two or more genes assort independently—that is, each pair of alleles segregates independently of any other pair during gamete formation. (only applies to genes on different chromosomes)
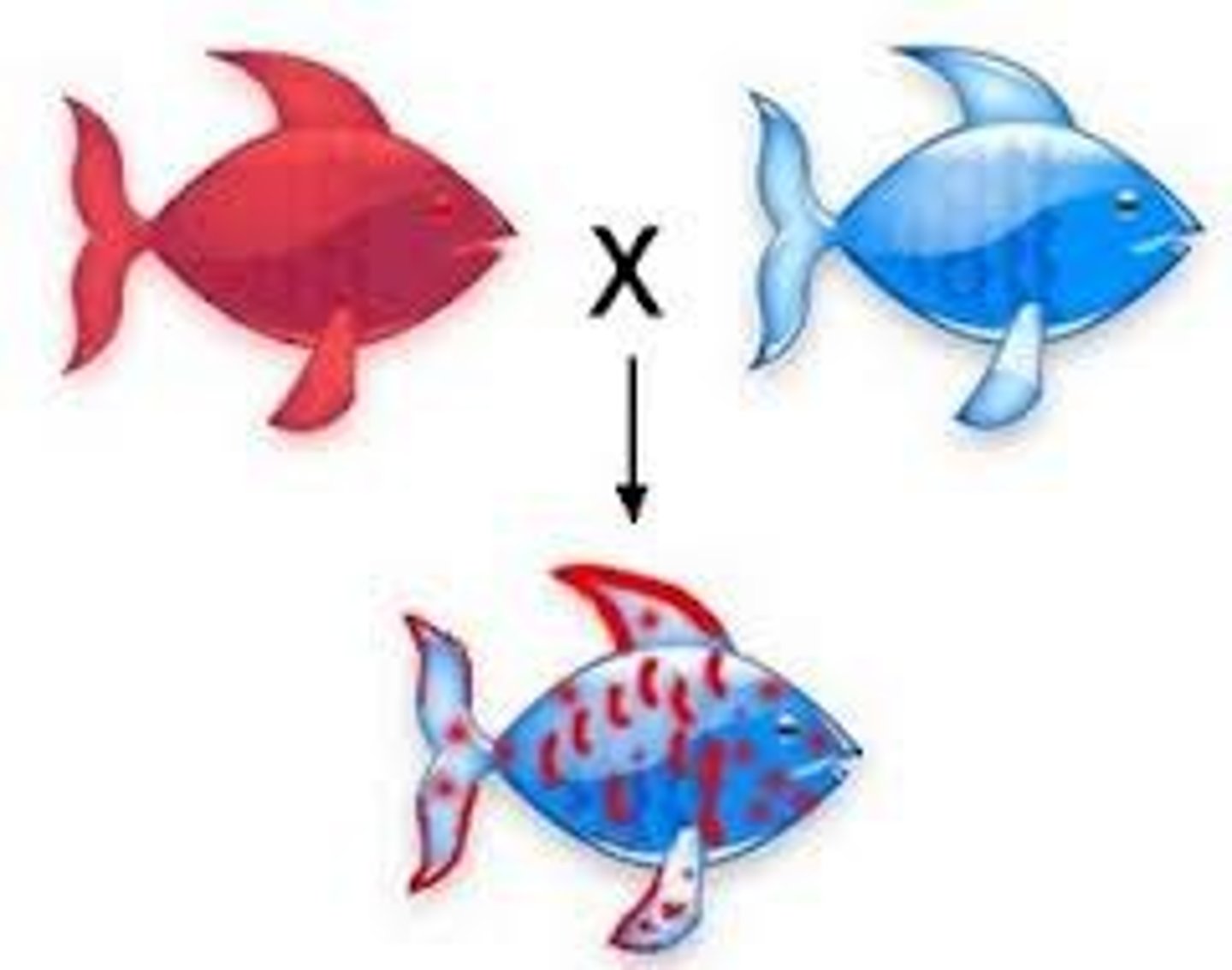
Incomplete Dominance
Phenotype of heterozygous is intermediate between the homozygous dominant and recessive (blended)
Codominance
Phenotype is affected by two different alleles in separate and distinguishable ways
exergonic
releases heat or light
Most Common Elements in Human Body
C, H, N, O
building chemical bonds
inc potential/chemical/stored energy
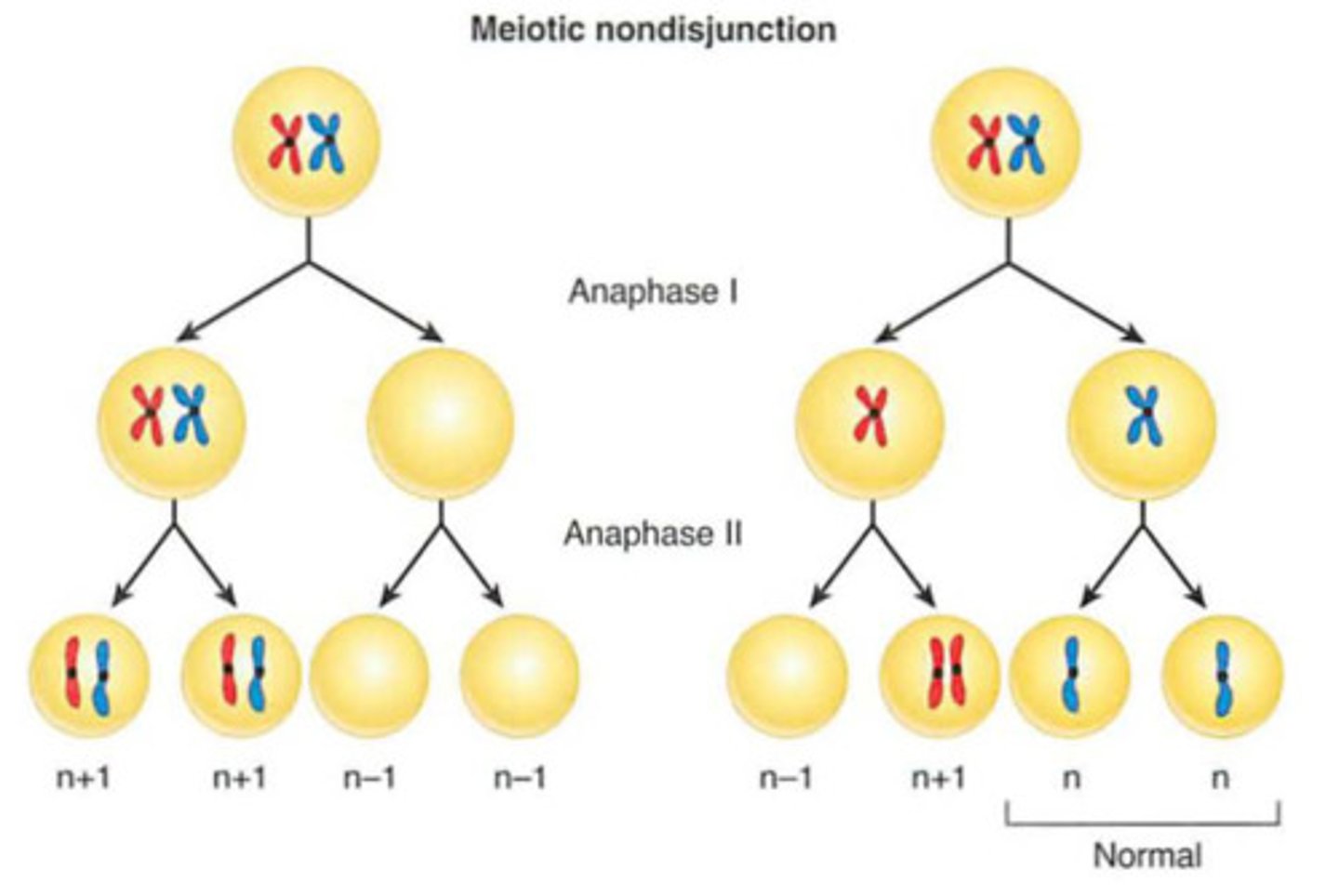
Nondisjunction (and result)
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
Result: 1 gamete receives 2 of the same type of chromosome and the other receives no copy
breaking chemical bonds
inc kinetic energy
Trace Elements in Human Body
Calcium, Phosphorous, Potassium, Sulfur, Sodium, Chlorine, Magnesium
Epistasis
A type of gene interaction in which one gene alters the phenotypic effects of another gene that is independently inherited.
anabolic
simple to complex substances (building up)
Ions
Atoms with more/less electrons than protons
catabolic
complex to simple substances (breaking down)
Valence Electrons
- Chemical behavior of an atom is determined by its valence electrons
- First shell: 2 electrons
- Second shell: 8 electrons
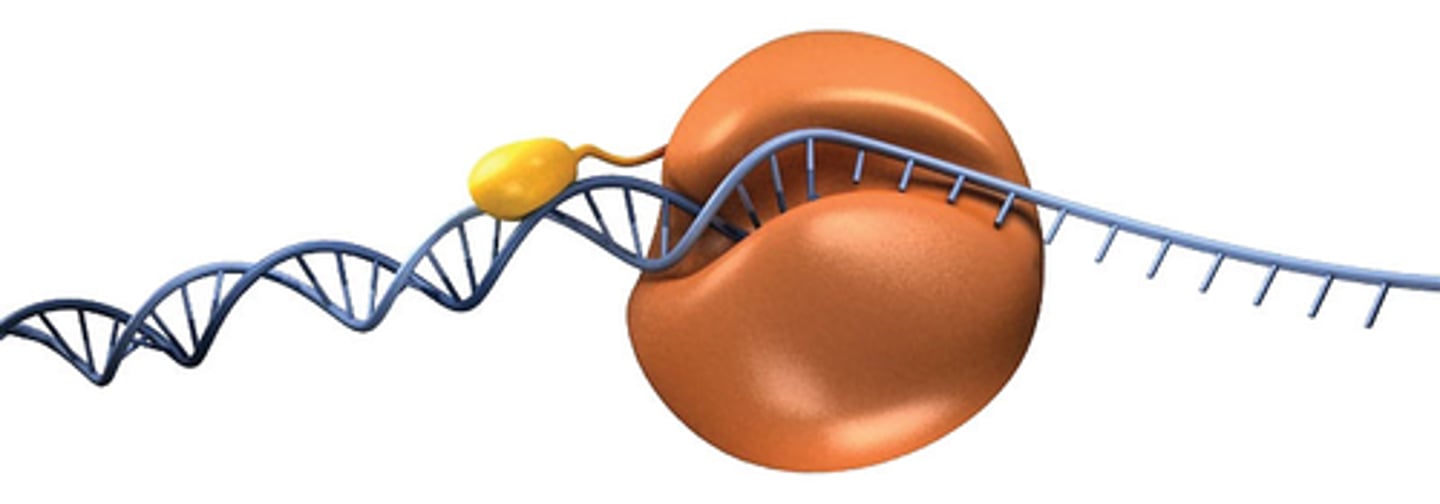
Helicase
Enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks
energy coupling
use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one
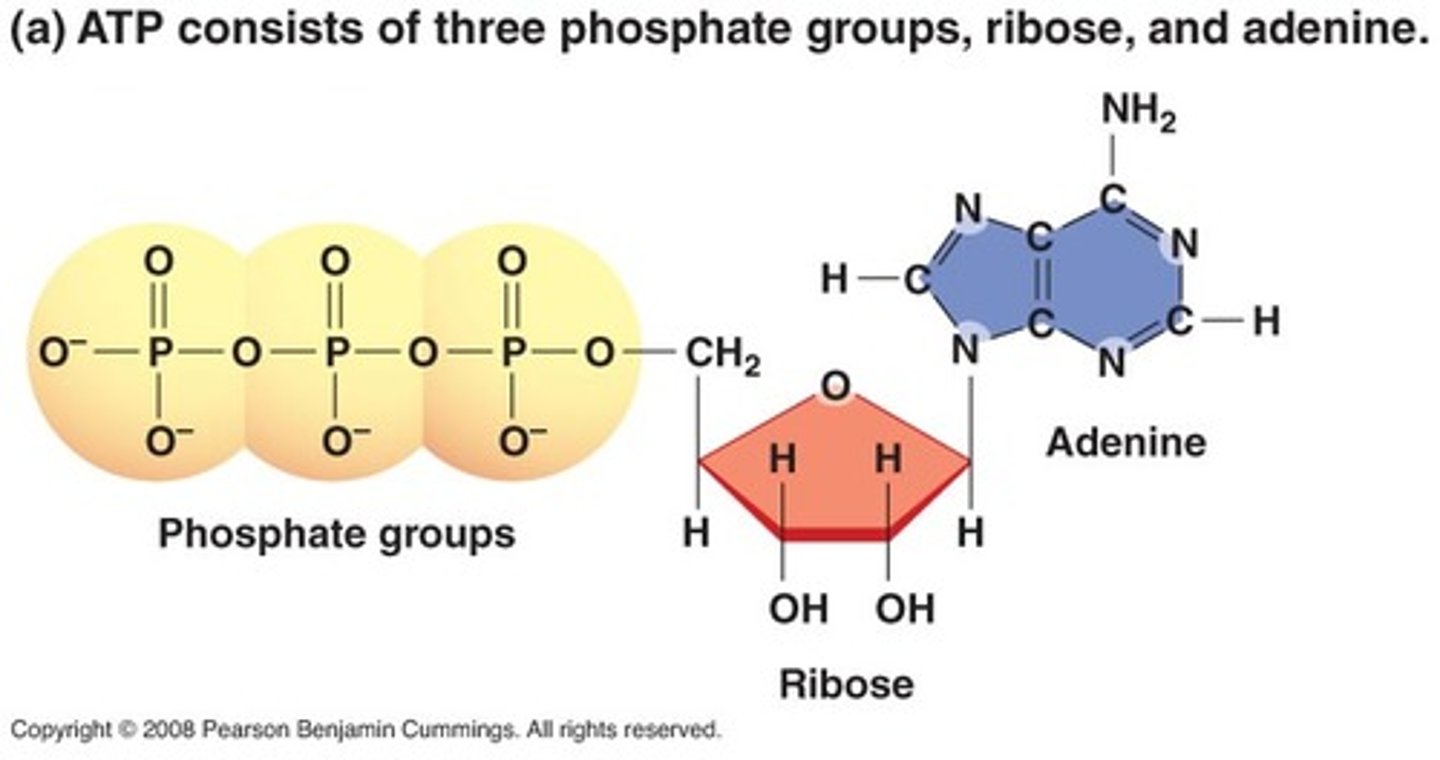
ATP
phosphate groups, sugar, nitrogenous base
hydrolyze to get ADP
phosphates don't want to be next to each other so neg charges repel each other and are held by a covalent bond; when this bond breaks, it releases a ton of energy
Solution
liquid that is a homogenous mixture of substances
enzyme
catalytic protein
optimum activity at 37*C (body temp) and a pH around neutrality
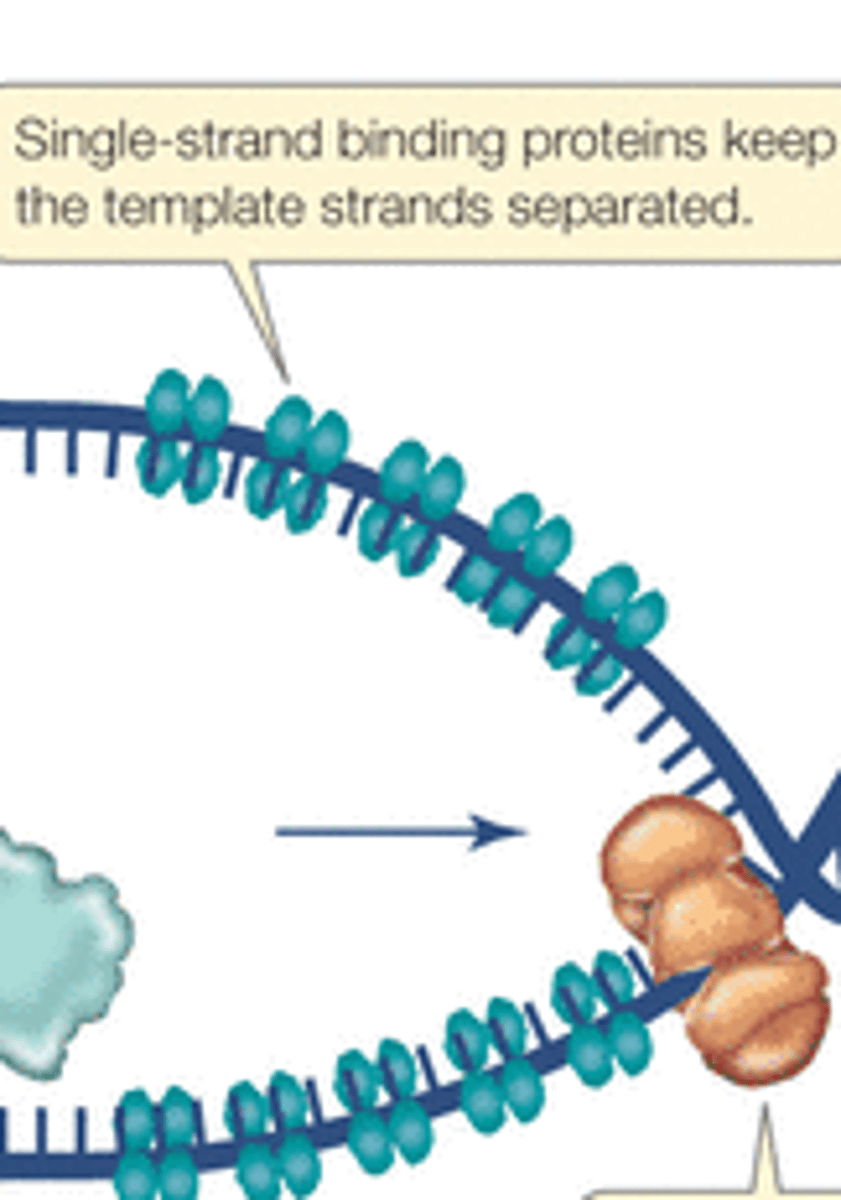
Single strand binding proteins
hold DNA strands apart
Solute
Substance that is dissolved
catalyst
chemical agent that speeds up a reaction w/o being consumed
Solvent
Dissolving agent (usually water)
cellular respiration
exergonic
transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to ATP
produces 30-38 ATP from each glucose
40% efficient, other 60% is heat that maintains the body temp
Semi conservative replication
Each half of an original DNA molecule serves as a template for a new strand, and the two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.
Hydrophilic
High affinity for water (polar, N, O)
oxidation
loses electrons, or is oxidized
getting smaller
Topoisomerase
A protein that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork by twisting and rejoining DNA strands
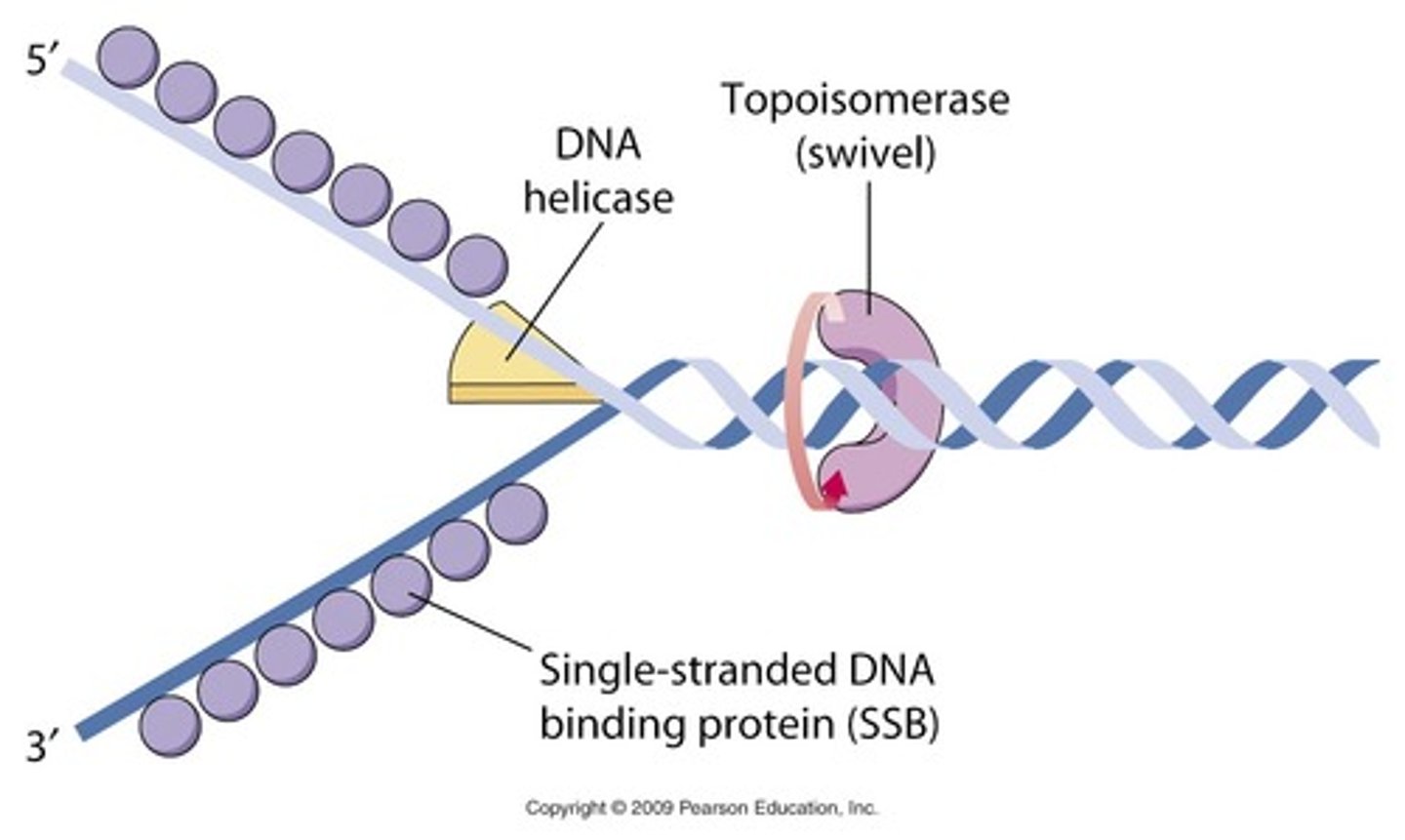
What aspects of genomes and cell structure makes DNA replication more complicated in eukaryotes than prokaryotes?
- circular vs. linear DNA
- prokaryotes don't have a nucleus
- prokaryotes have 1 chromosome; humans have 46
- DNA in eukaryotes is tightly condensed instead of floating around
- one vs. many origins of replication
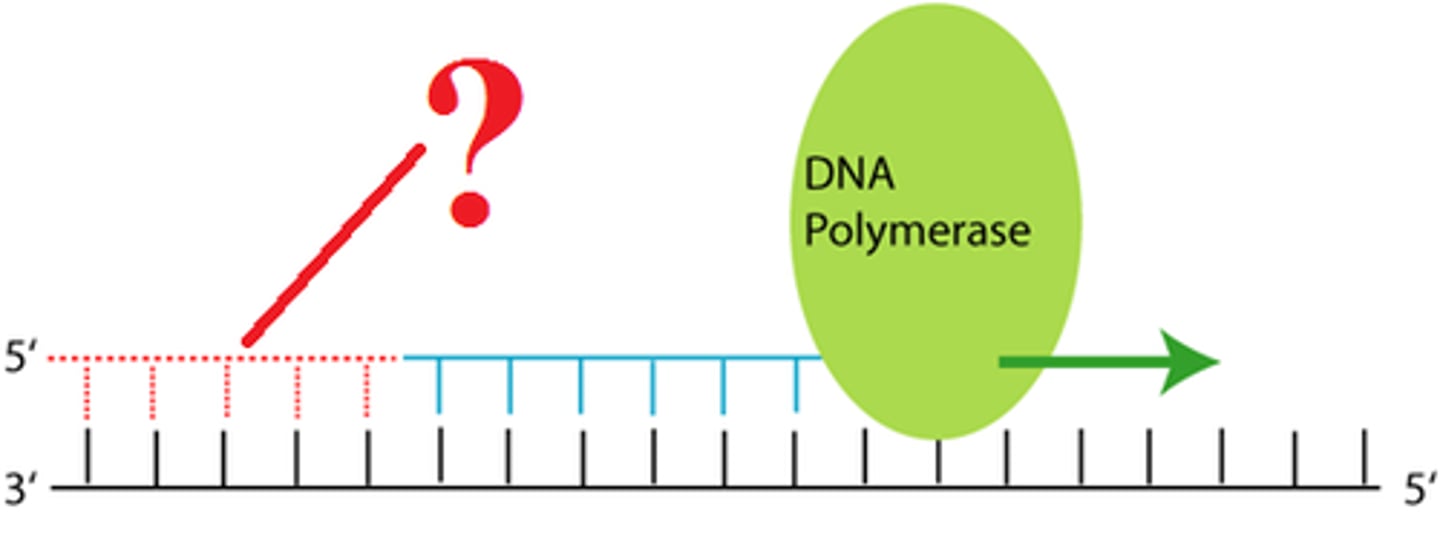
RNA primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
DNA polymerase require a primer to which they can add nucleotides
reduction
gains electrons, or is reduced (amount of positive charge is reduced)
Hydrophobic
No affinity for water (nonpolar, C, H)
Primase
makes a short RNA molecule (~10 base pairs) that creates a small double stranded section
cellular respiration stages (4)
1. glycolysis
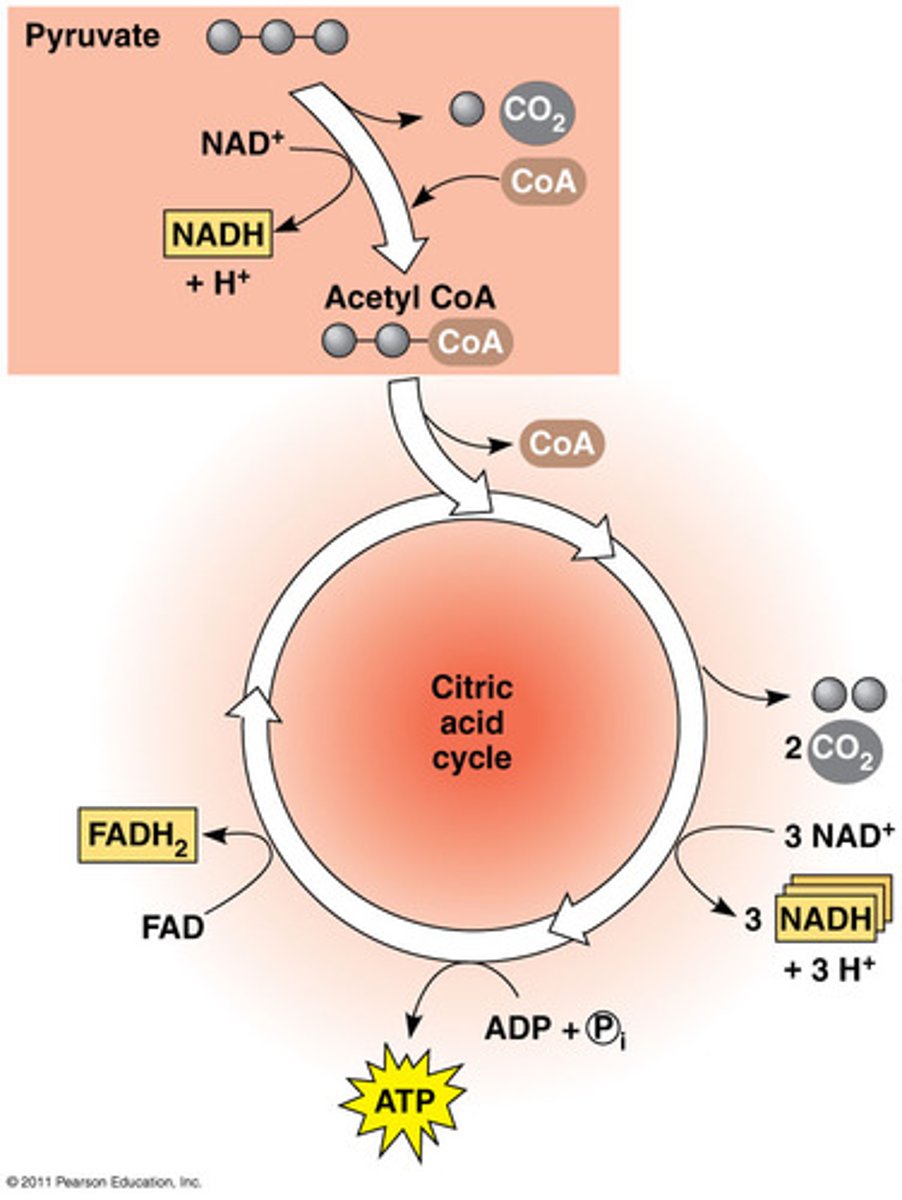
2. pyruvate => Acetyl CoA
3. citric acid cycle (aka Krebs)
4. oxidative phosphorylation (aka electron transport chain)
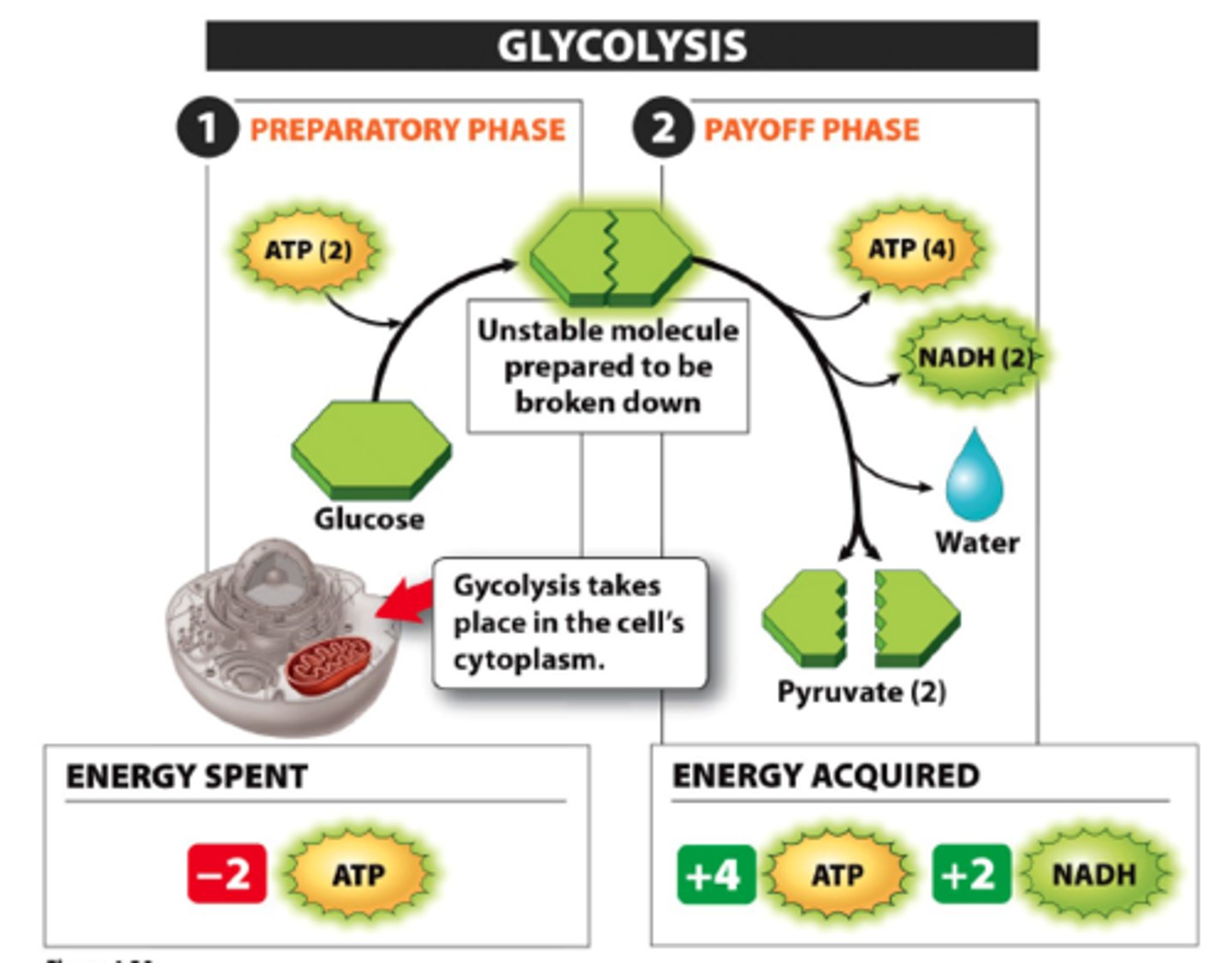
glycolysis
where: cytosol
inputs: glucose, 2 ATP
Substrate level phosphorylation
outputs: 2 pyruvate, 4 ATP, 2 NADH
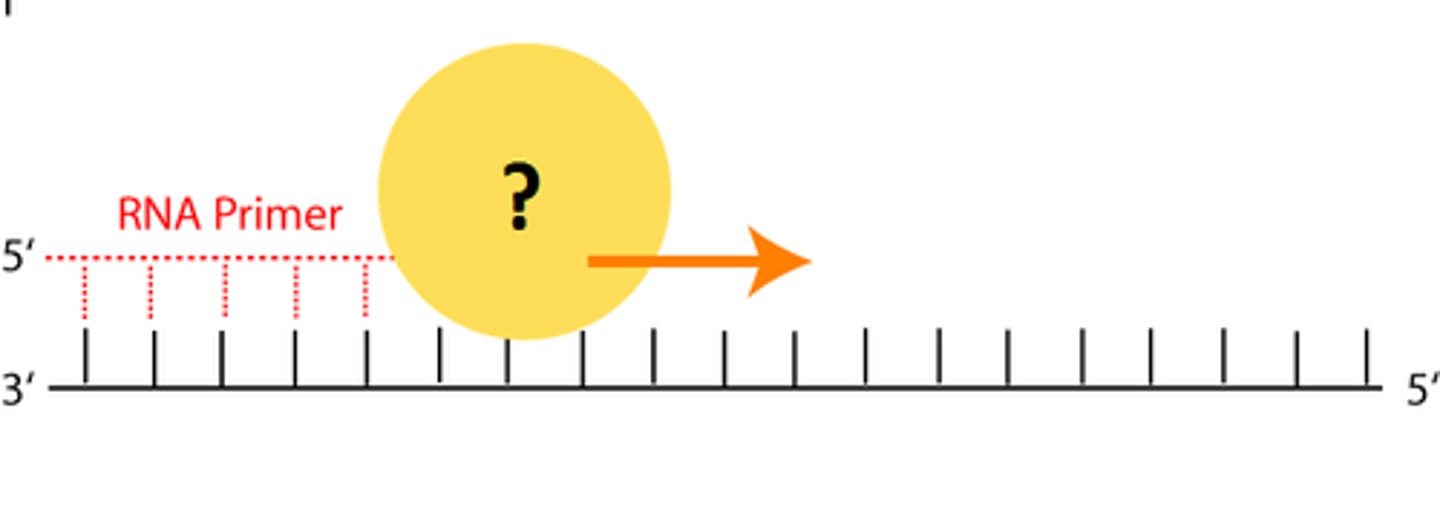
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA at replication fork
DNA ligase
Joins DNA together to make one continuous strand

krebs cycle
where: mitochondria
inputs: 2 pyruvate - 2 CoA
Substrate level phosphorylation
outputs: 6 CO2 + 2 ATP + 8 NADH (2 FADH2)
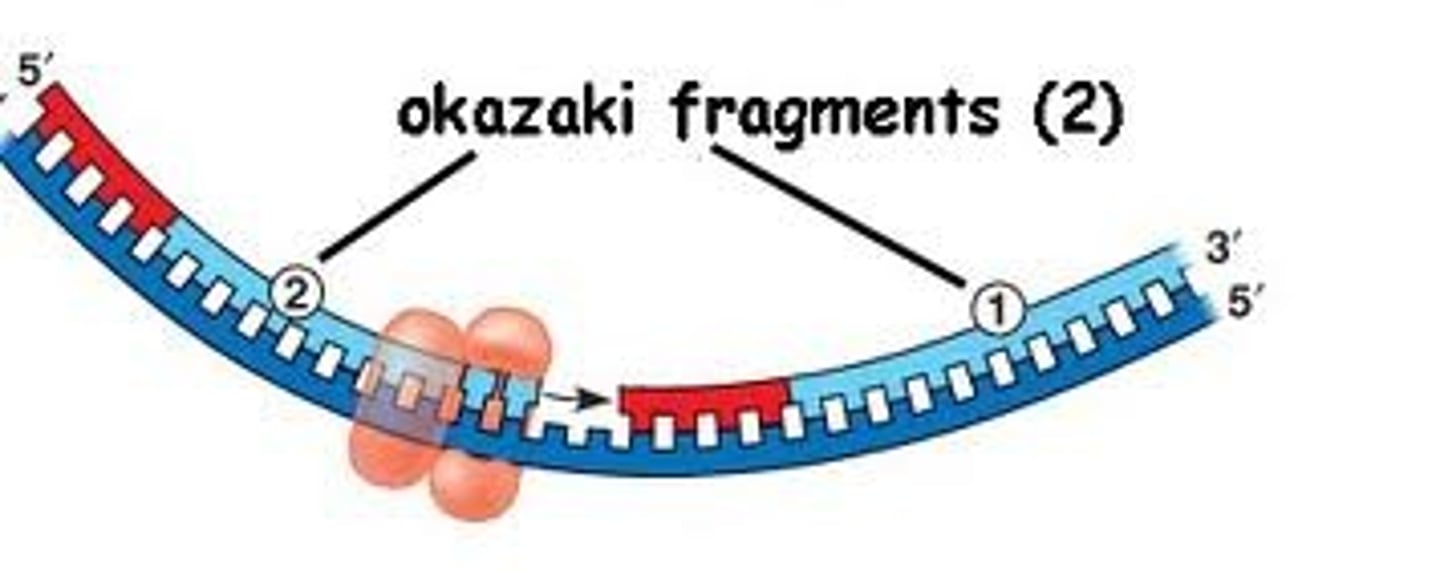
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
DNA polymerase I
replaces RNA primer with DNA
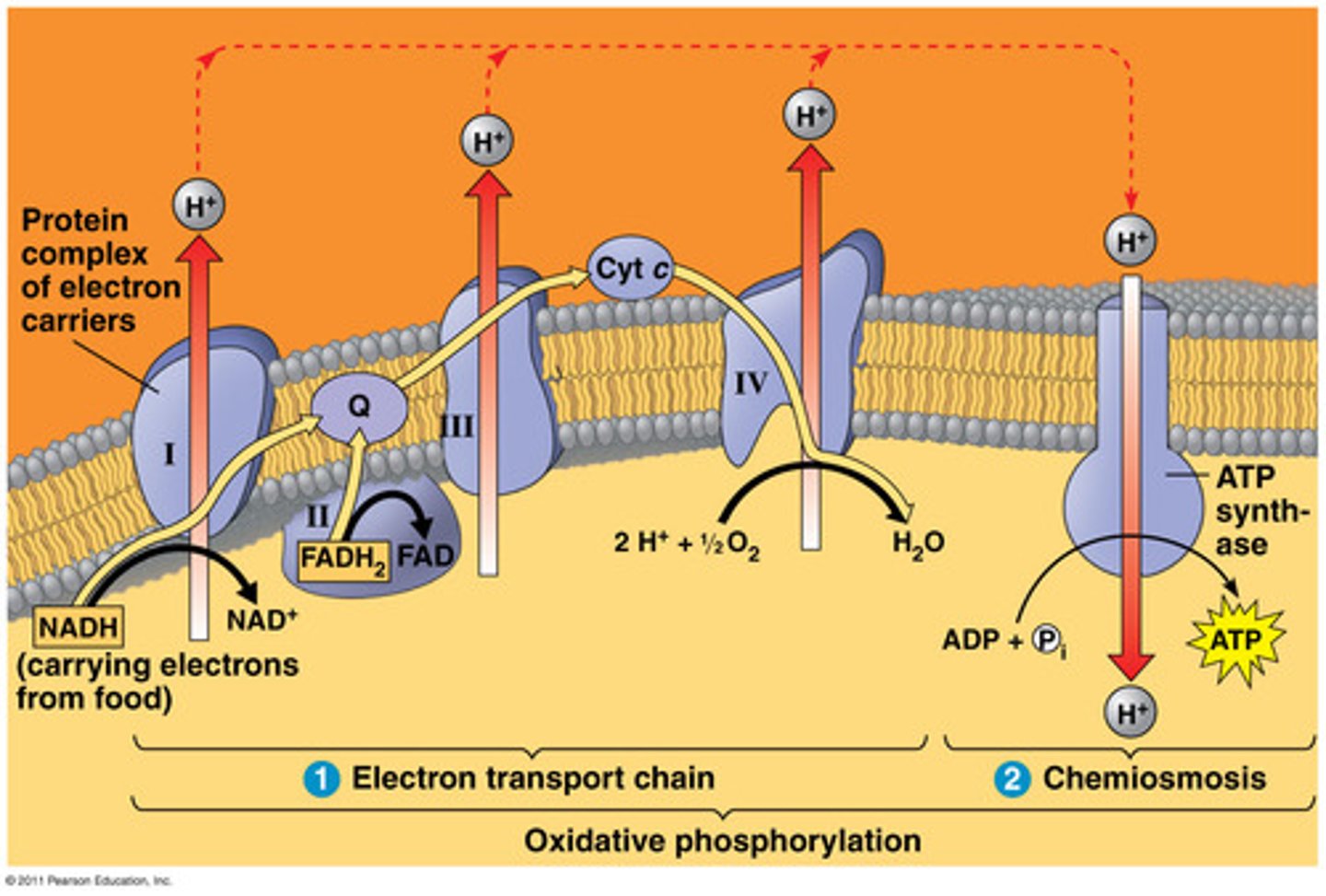
electron transport chain
where: inner mitochondrial membrane
inputs: NADH, FADH2, O2
outputs: Lots of ATP, H2O
DNA polymerase III
makes new DNA strand by adding nucleotides one at a time to the 3' end
fermentation
anaerobic energy-generating process
alcohol: uses yeast to produce ethanol
lactic acid: converts pyruvate to lactate (or lactic acid); can only use for short periods of time
autotrophs
living things that make their own food w/o using organic molecules derived from any other living thing
photoautotrophs use light to produce
take energy and sunlight and convert it to chemical energy stored in organic molecules
ex: most plants, algae, and other protists, some prokaryotes
Strength of Bonds
Hydrogen
Ionic
Covalent
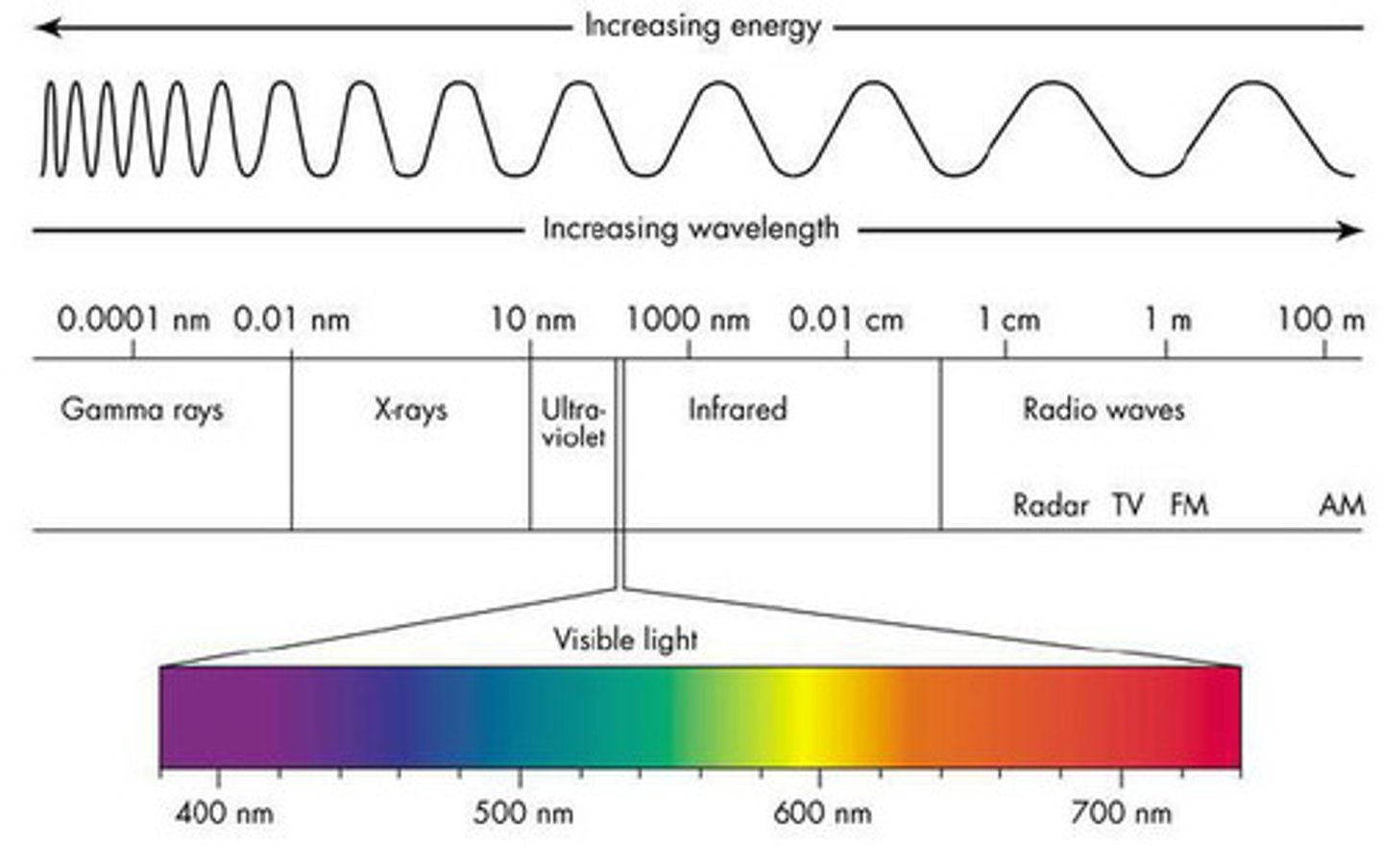
color is a light wave
lowest is purple, highest is red
white reflects all light
black absorbs all color
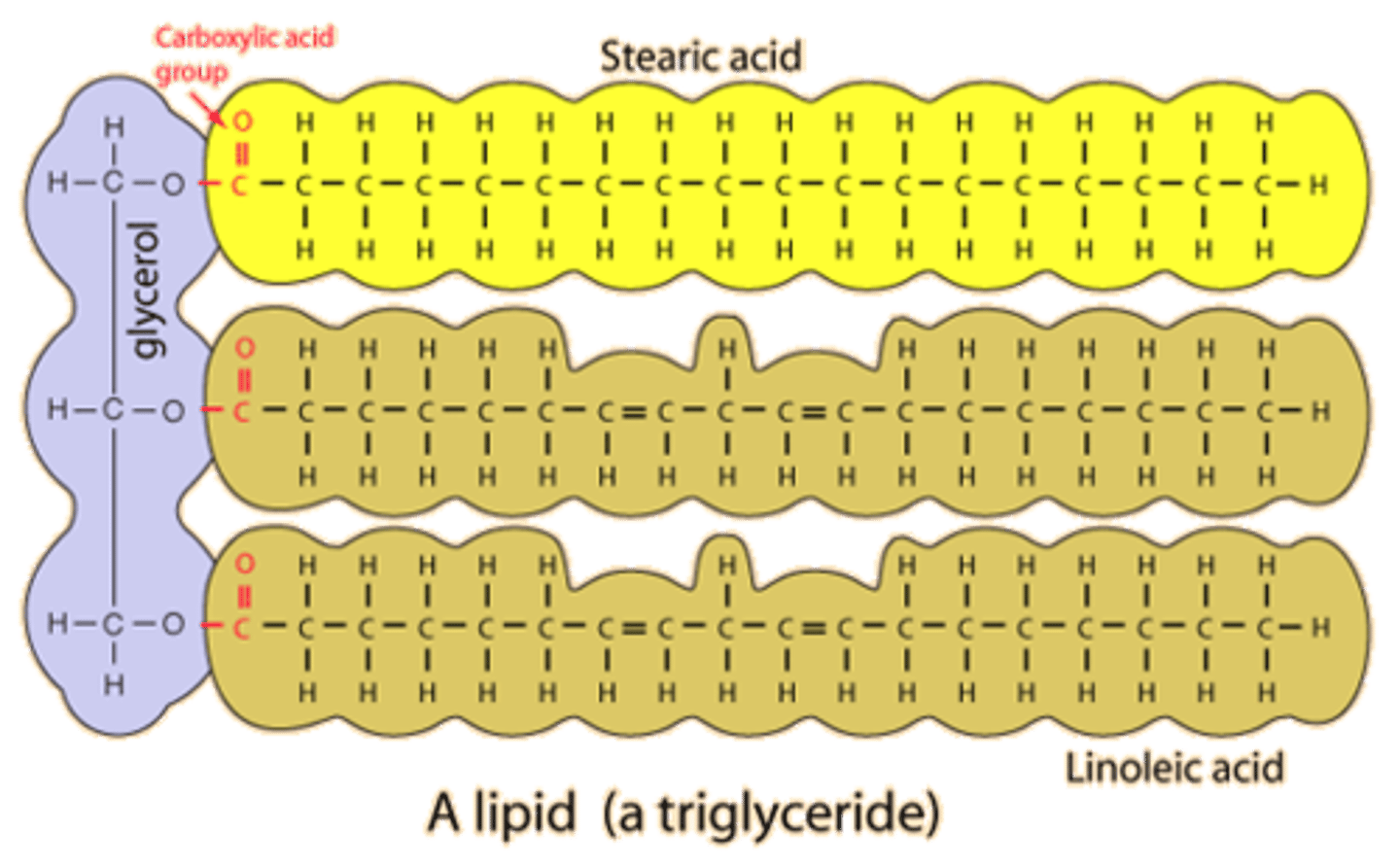
Lipids
- Water insoluble (long hydrocarbon chains)
- Important in energy storage
- Contain twice as much energy as a polysaccharide
- Made of glycerol and fatty acids
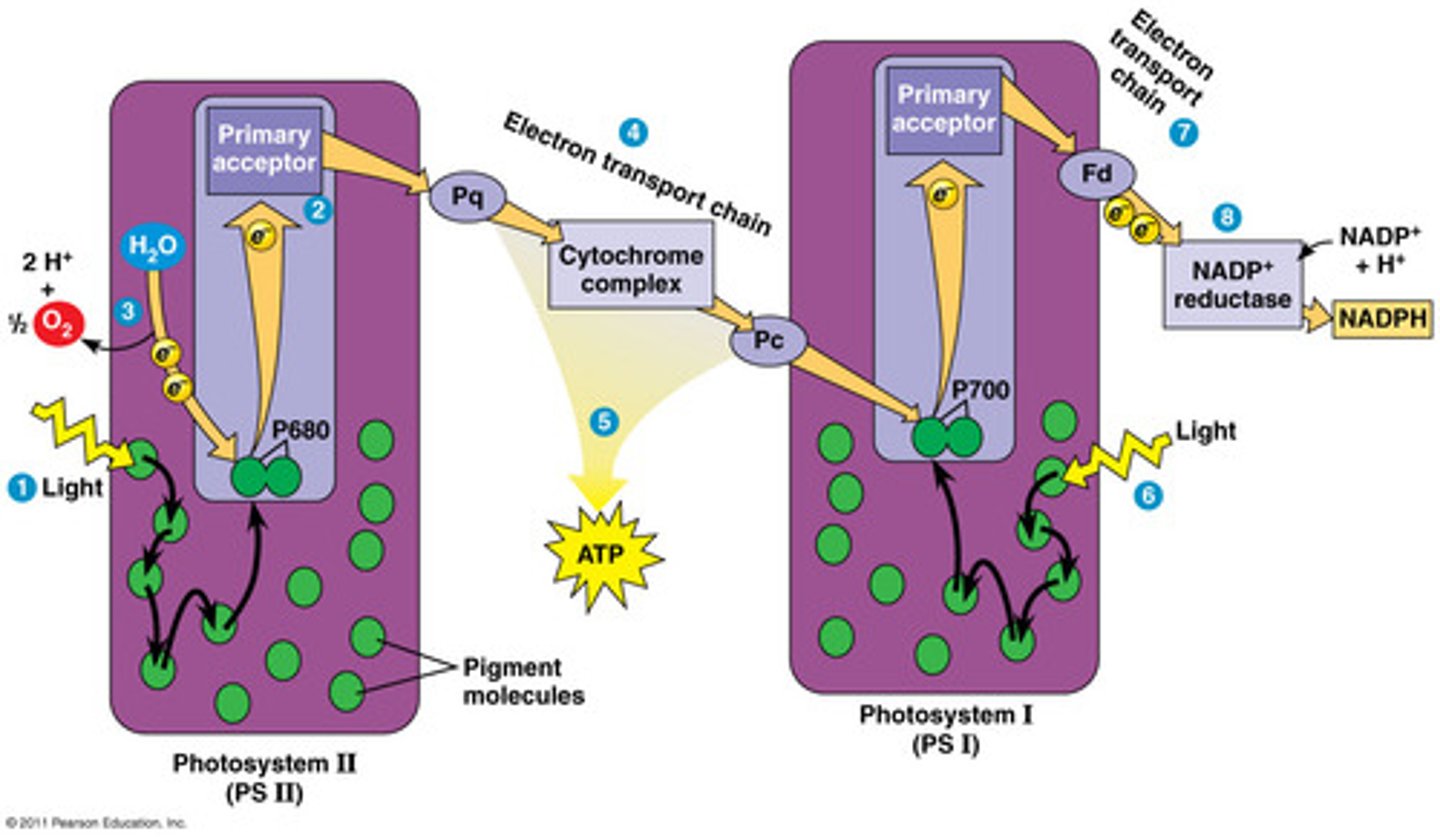
pigments in chloroplasts
- absorb light (capturing solar power)
- causing release of electrons which jump to a higher energy level (excited) then drop back down (ground) whilst releasing excess energy
- photon excites a chlorophyll, excites an electron, releases wavelengths
Photosystem II
Photon will hit
Get passed from chlorophyll to chlorophyll
Will funnel into one center chlorophyl
Goes into one electron
Photosystem II gives its electron to the transport chain and then its given to photosystem I
Photosystem needs a new electron
Gets a water molecule and gets an electron
Oxygen → byproduct
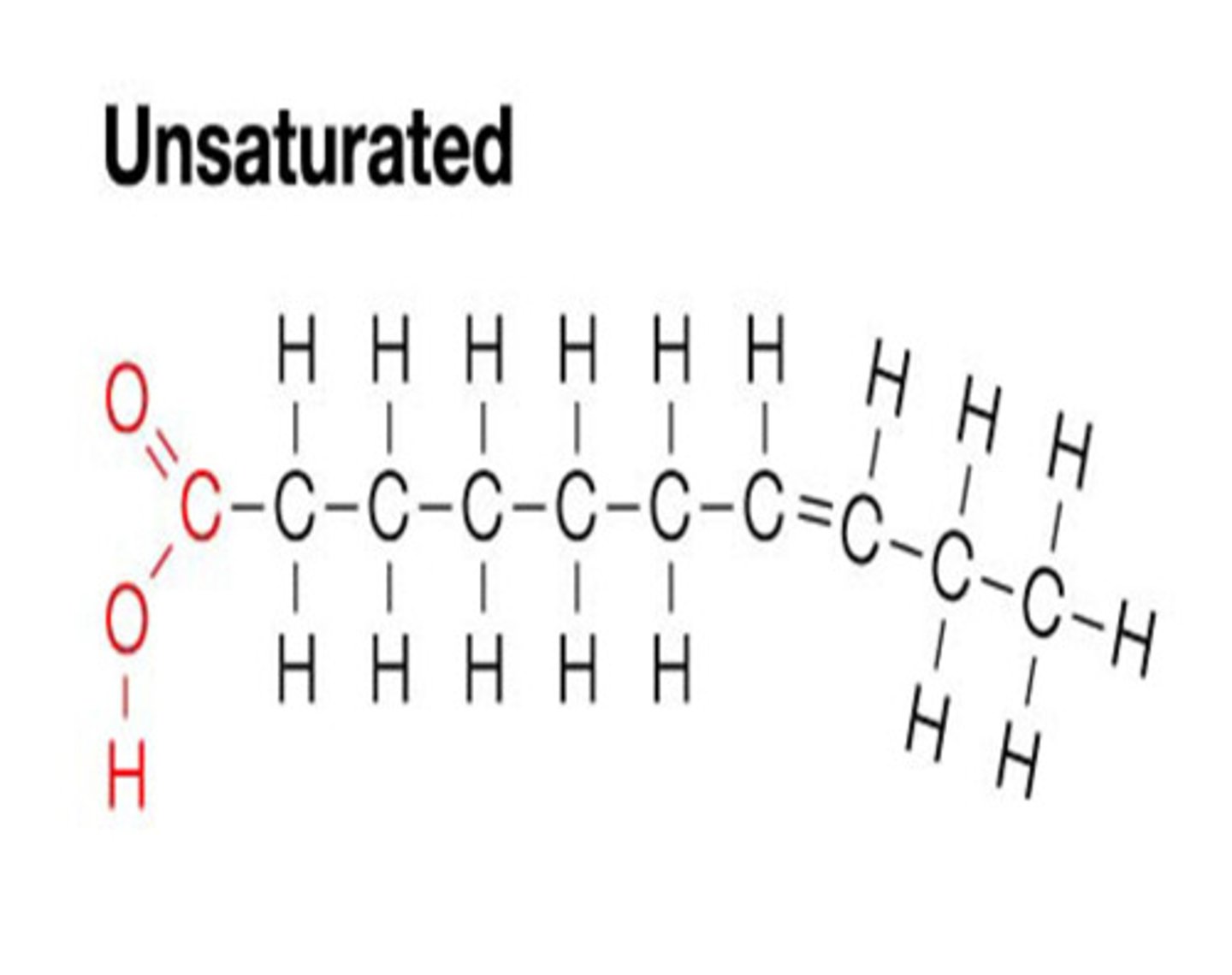
Unsaturated Fats
- Double bond in one of the hydrocarbon chains
- Doubles bonds do not allow for the max number of hydrogens to bond to the carbon
- Liquid at room temperature
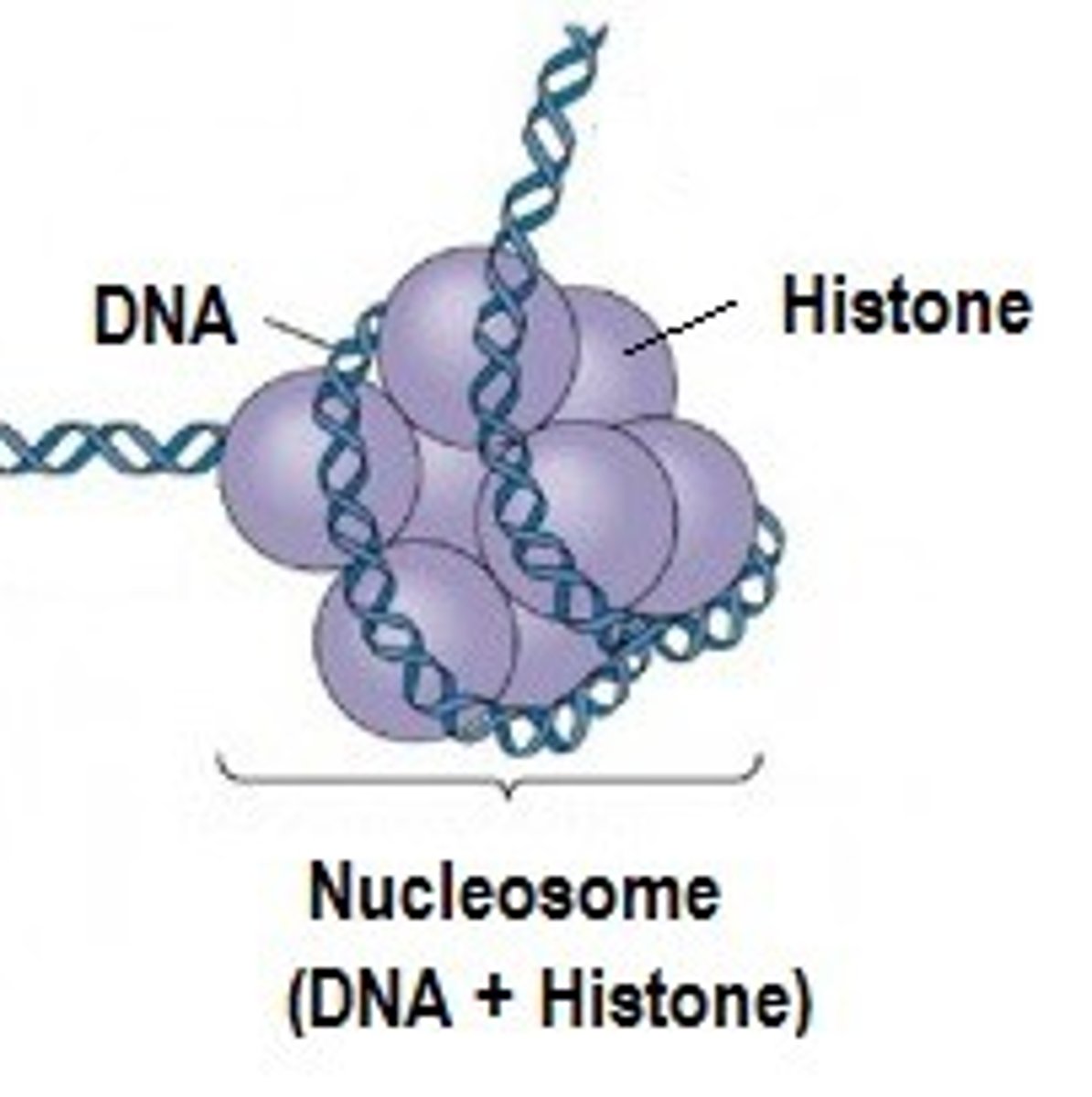
Histones
Responsible for the first level of DNA packing in chromatin
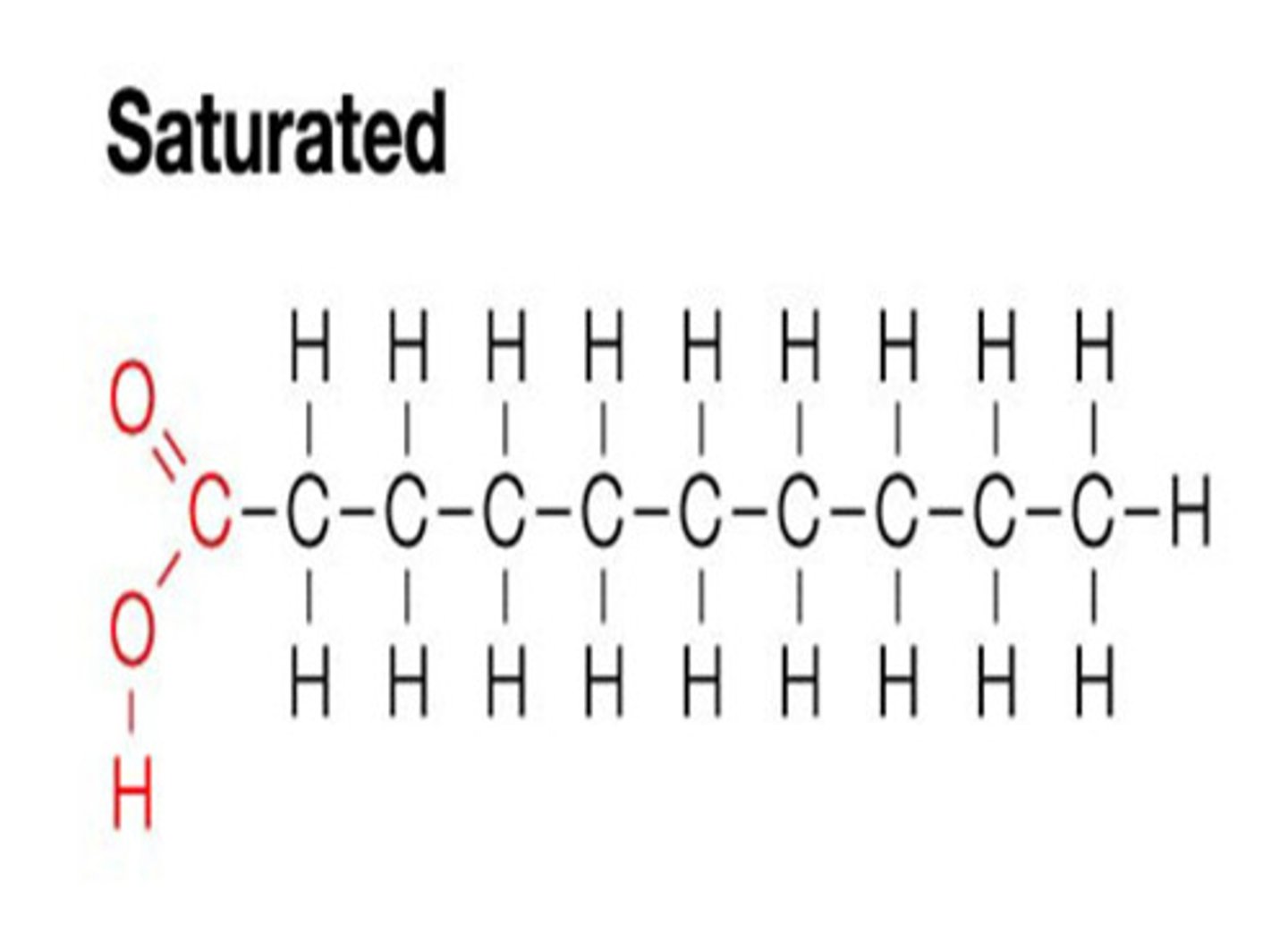
Saturated Fats
- Do not have double bonds and are complete "saturated (with hydrogens)"
- Packs together more tightly (no bend)
-Solid at room temp
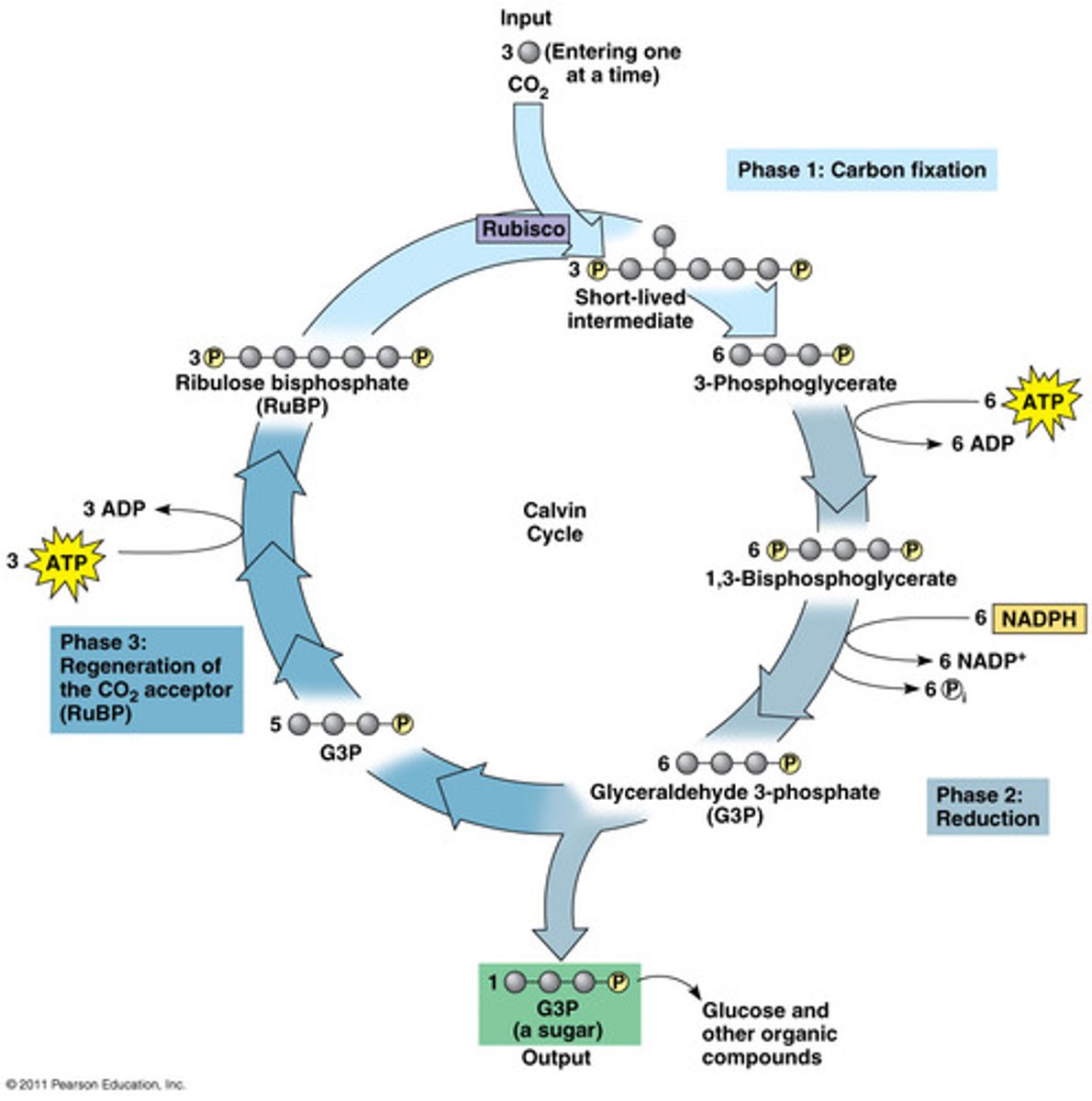
calvin cycle
RUBISCO
converting CO2 to sugars
input: CO2, ATP, NAPDH
output: sugars
plant stomata
pores on the bottom of plant leaves that are open to air
in hot climates, CR4 and CAM close this off to reduce water loss
C4 use spatial separation of steps to inc CO2
CAM use temportal (time) separation of steps to inc CO2
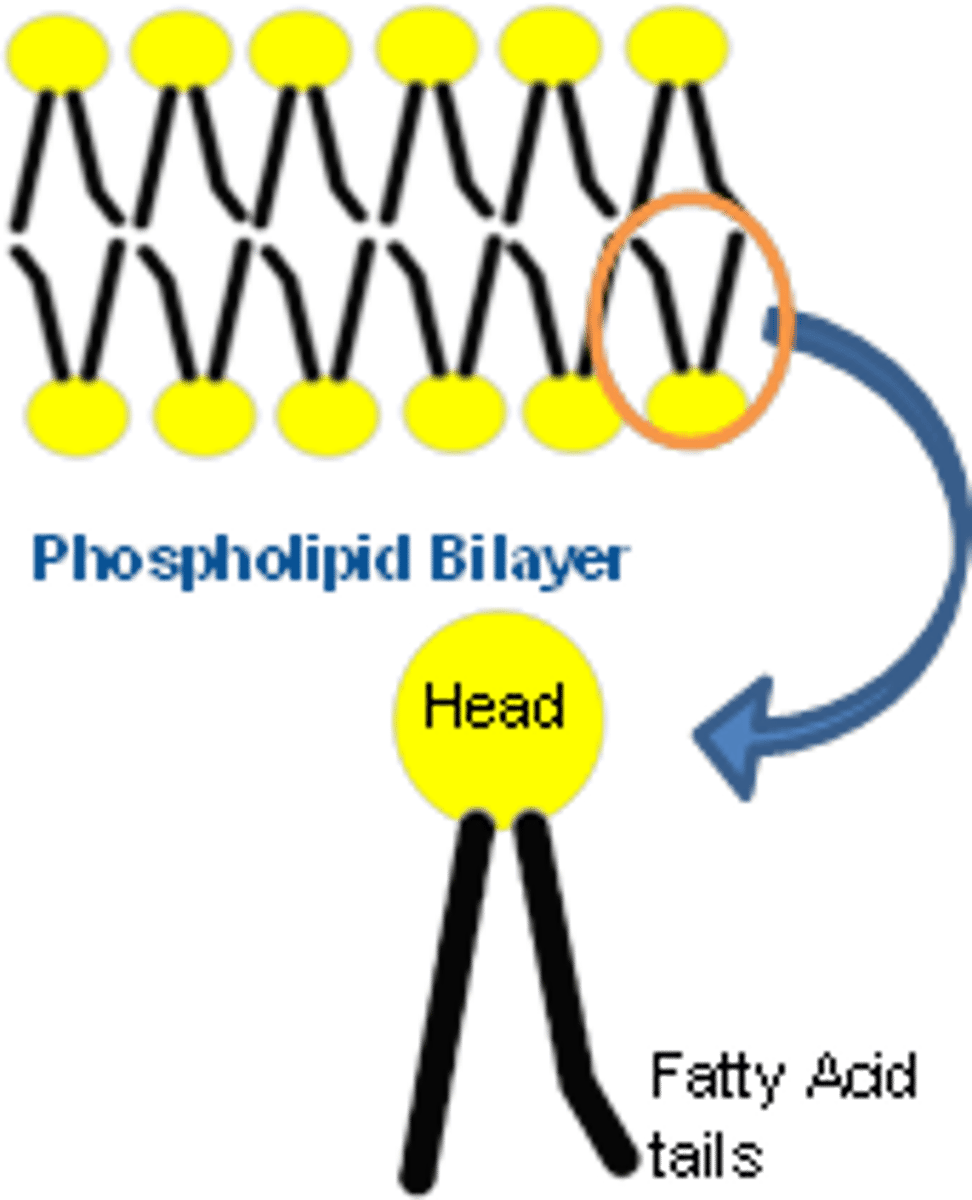
Phospholipids
-Structurally similar to fats
- Hydrophilic heads: Contact with water of environment and internal part of the cell
- Hydrophobic tails: Band in the center of the bilayer
- Polar/phosphate head and 2 non polar fatty acid chains
- Makes up cell membrane
- Amphipathic
gene
A DNA sequence that is expressed to form a functional product: either RNA or polypeptide
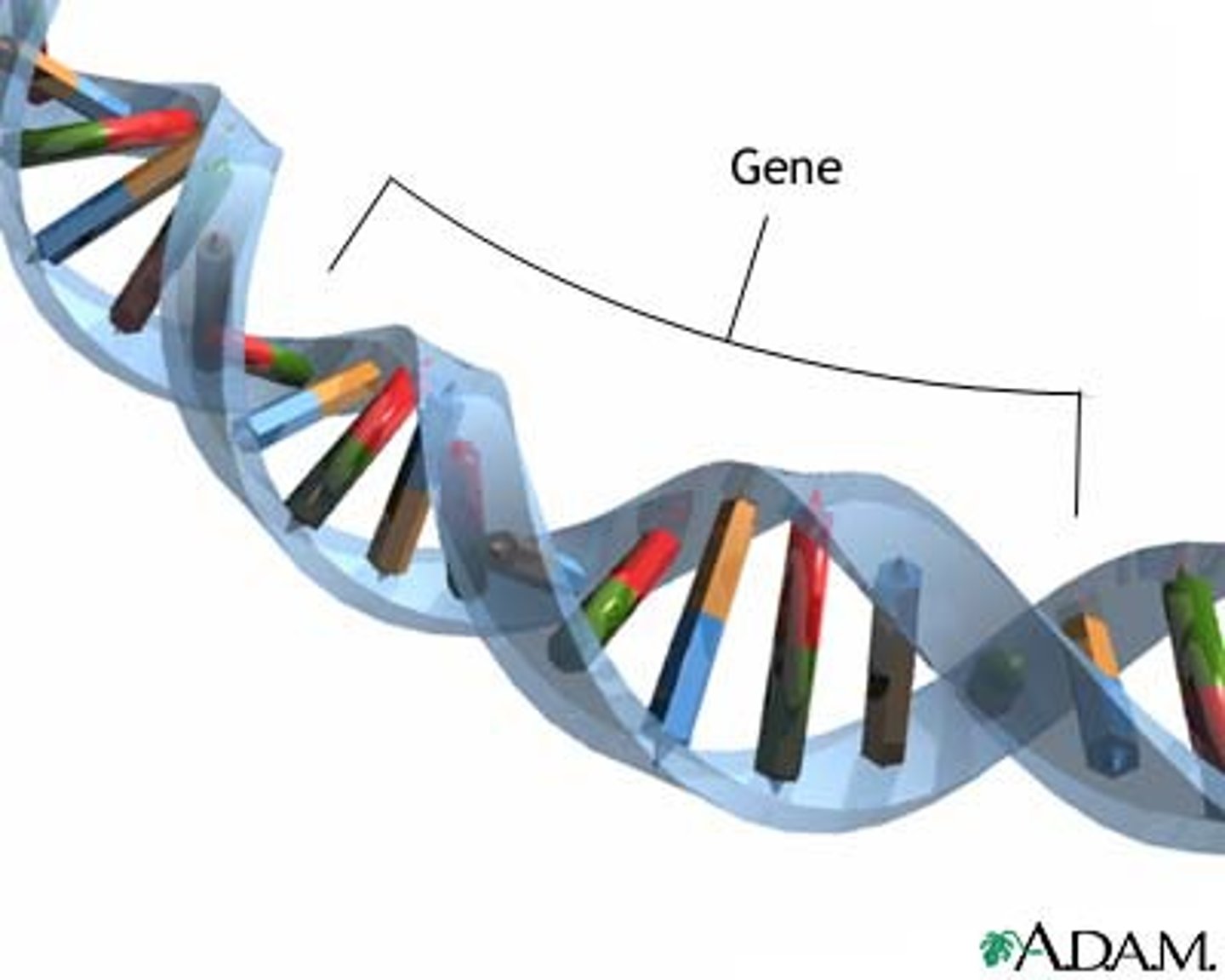
asexual reproduction
offspring identical to original, inherit all genes from one parent
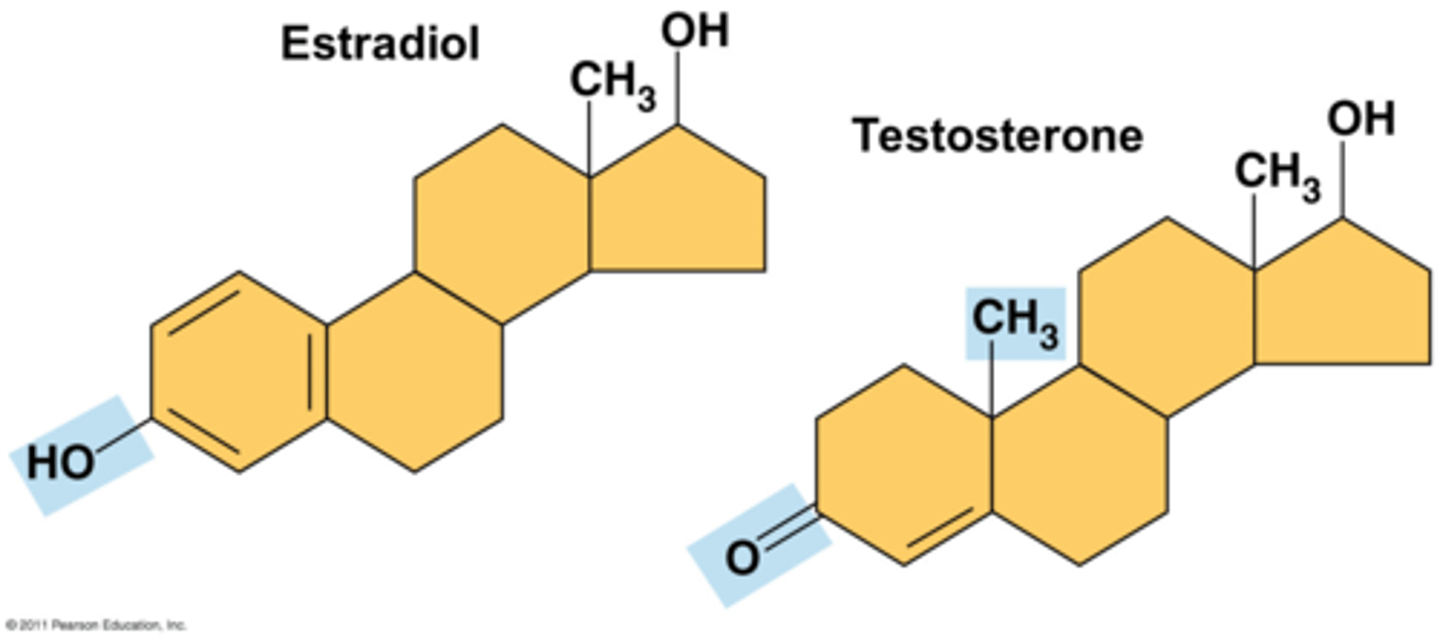
Steroids
- Lipids composed of 4
fused rings
- Hormones
- Testosterone and Estradiol
Leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
Lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments (joined together by DNA ligase), each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
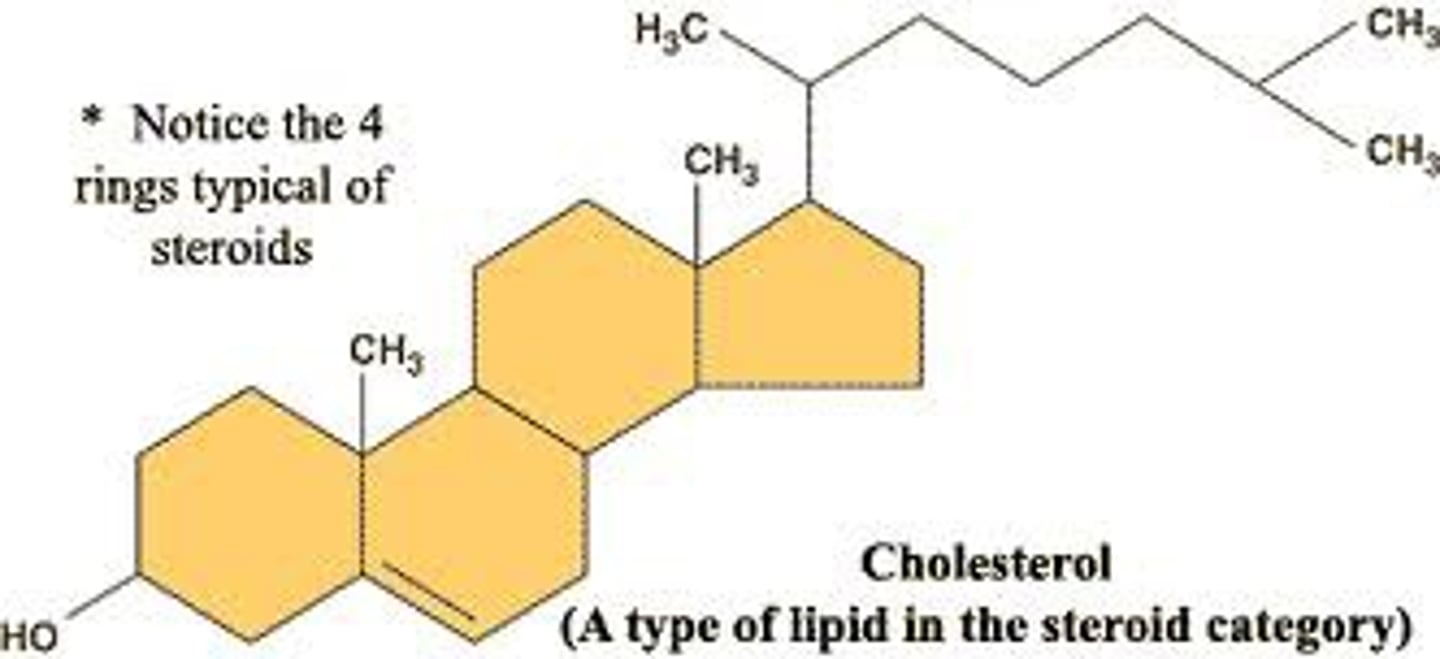
Cholesterol
- Example of a steroid that plays significant role in structure of cell membrane
- 4 rings
- LDL and HDL
sexual reproduction
offspring similar to parents, but show some variation
inherit unique sets of genes from two parents
Gene expression
The process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and translation
chromosomes
each chromosome appears as two sister chromatids, containing identical DNA molecules
chromatids are connected, but once they split, they are no longer chromatids and are two indiv chromosomes
Transcription +product
Synthesis of RNA using information in DNA
Produces mRNA
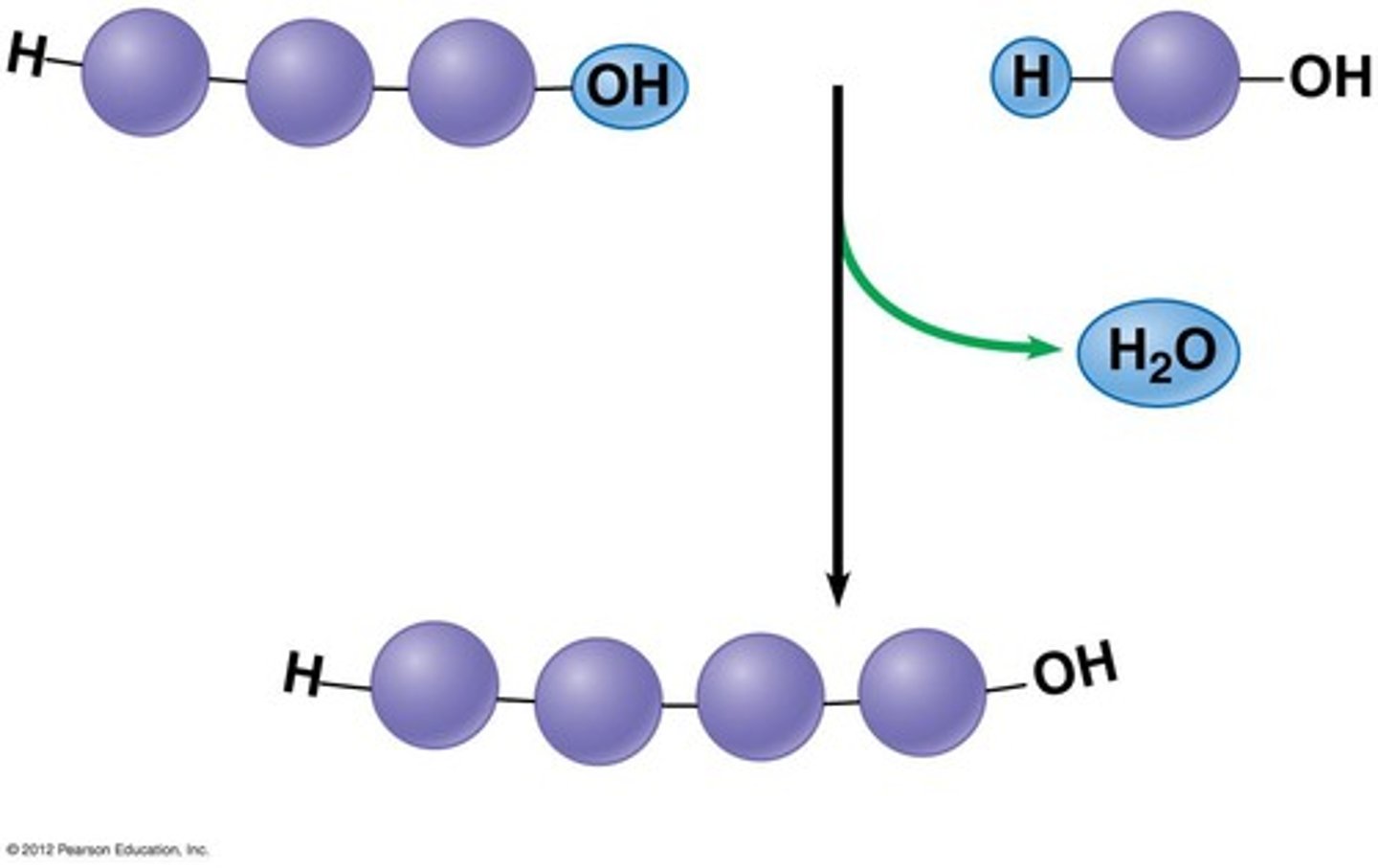
Dehydration Reaction
Build polymer out of monomer subunits and produces water
cell cycle
G0: period of no growth, cell not actively progressing into mitosis
G1: growth
S: DNA synthesis
G2: growth
M: splitting
Translation +site
Synthesis of a polypeptide using the information in the mRNA
Ribosomes are the site (ribosomes found on rough ER and in the cytoplasm)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jnP8_1eIfgo
What separates transcription and translation in eukaryotic cells?
The nuclear envelope
interphase
cytoplasmic contents double
in nucleus, chromosomes duplicate during the S phase (can't visibly see chromosomes yet)
Monomer of nucleic acids
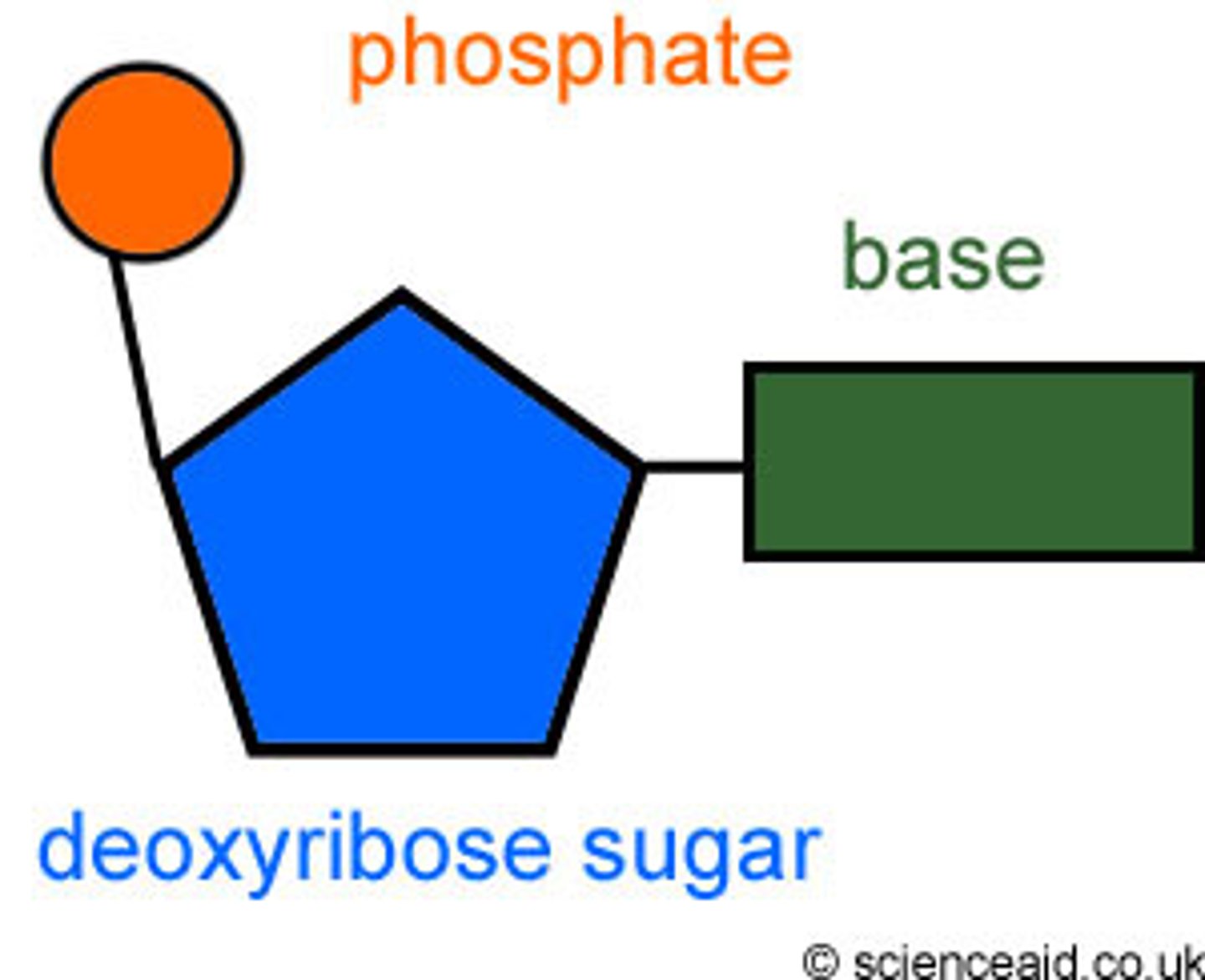
Nucleotides
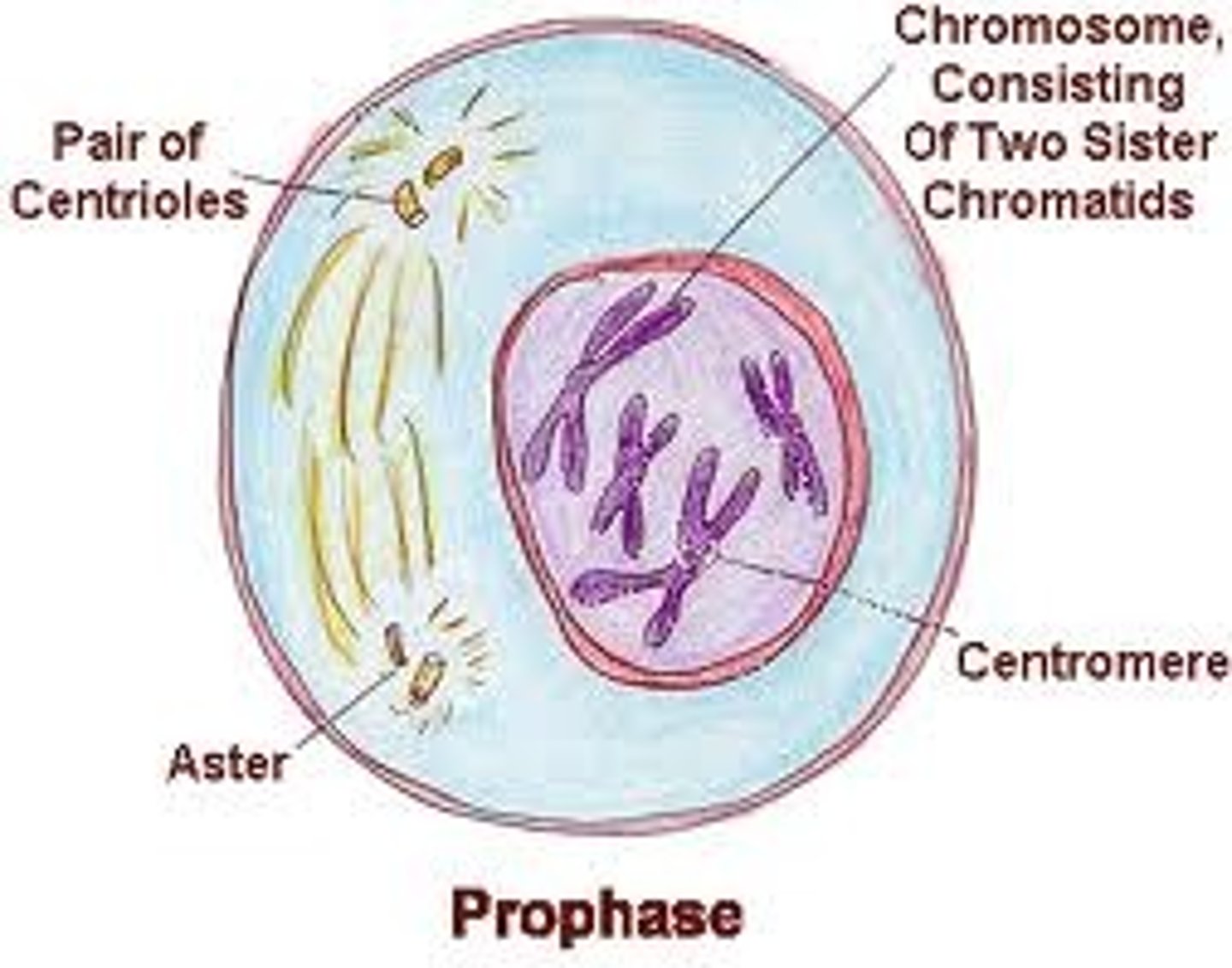
mitosis prophase
see chromosomes/two sister chromatids
start to see cytoskeleton elements responsible for pulling cells apart (centrosomes)
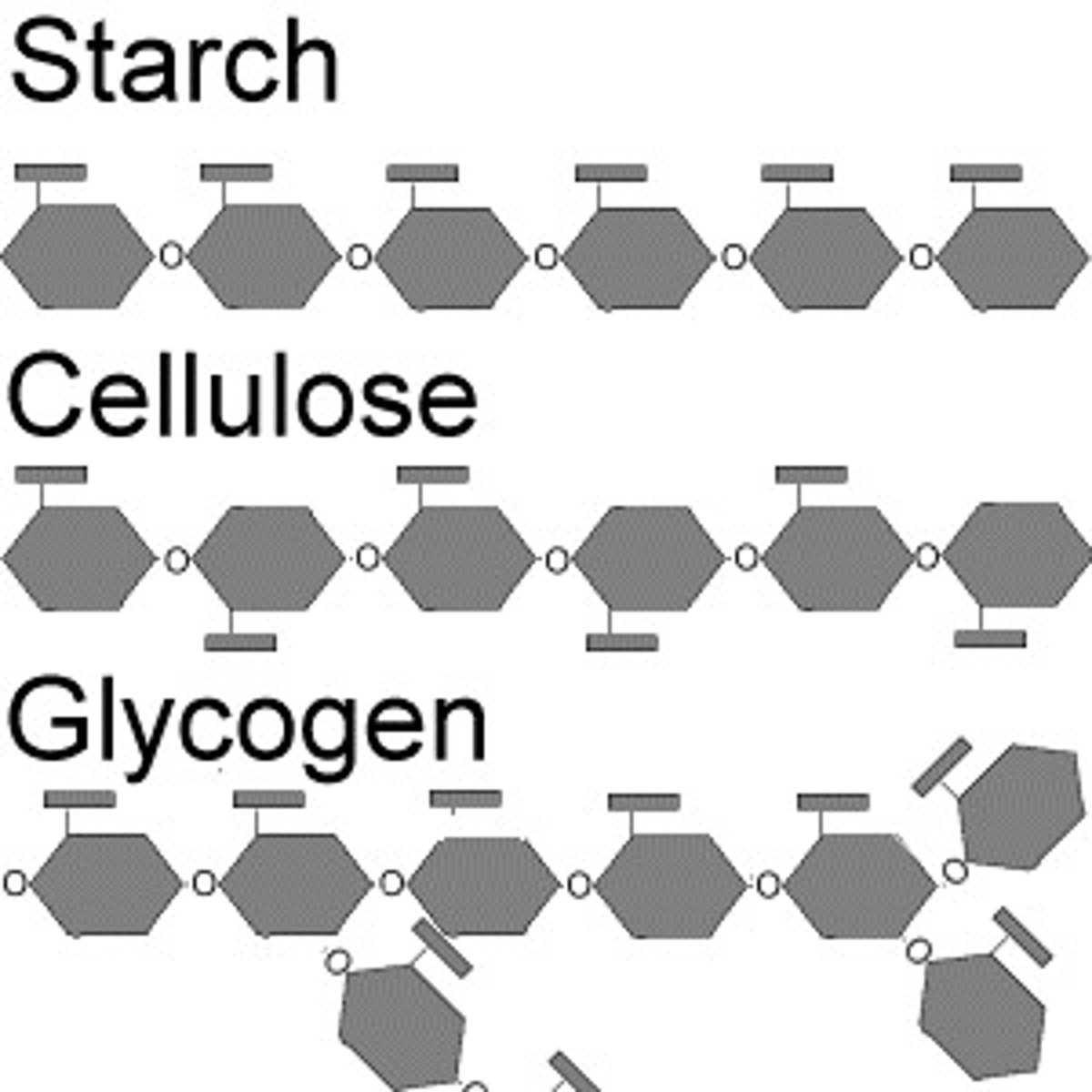
Carbohydrates
- Sugar (-ose) = simple (monomer)
- Starches = complex (polymer)
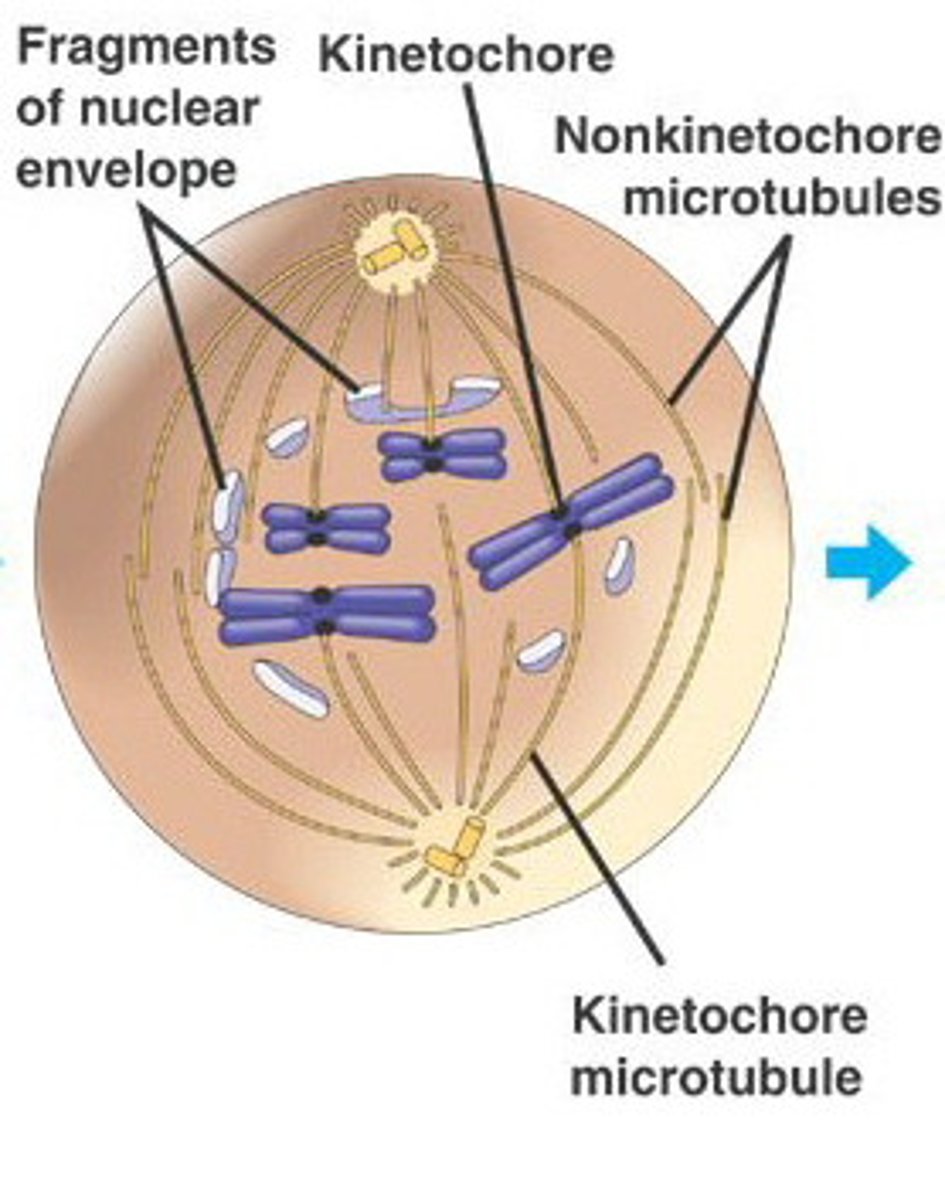
mitosis prometaphase
break apart nuclear membrane (no nucleus)
microtubules connect to individual chromosomes through kinetochore
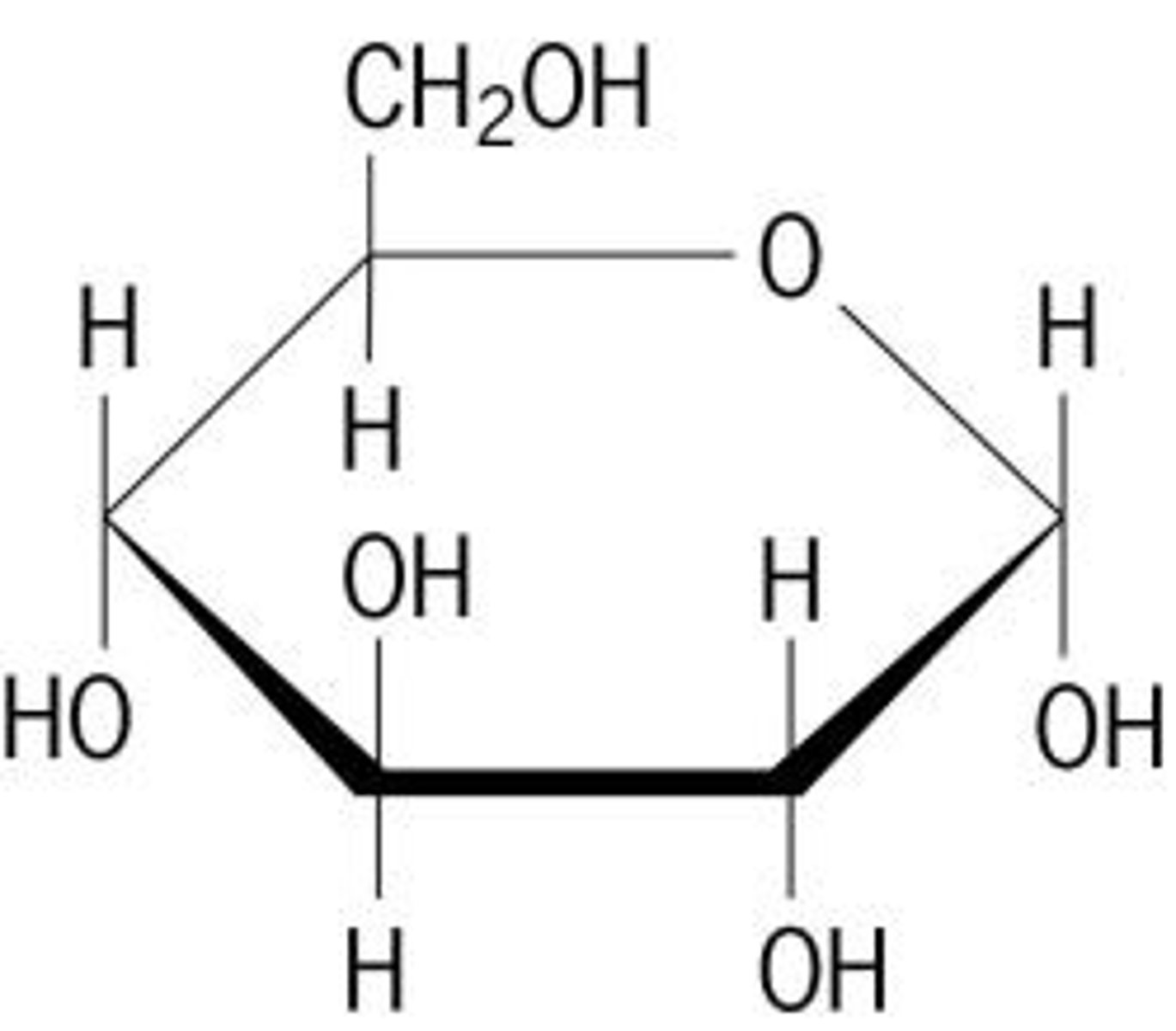
Sugar monomers (Monosaccharides)
- Can be linked together to form polysaccharides
- CH2O
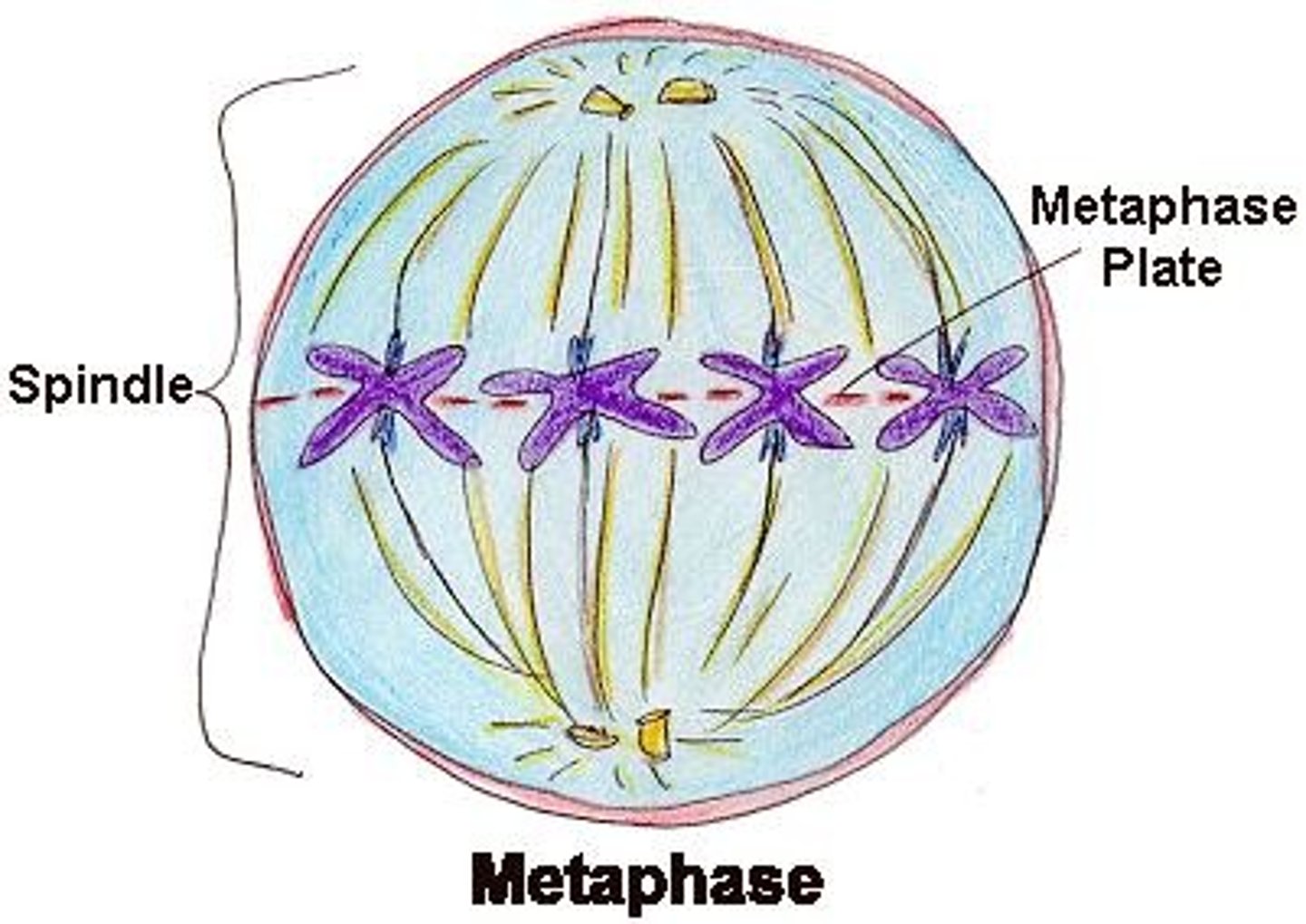
mitosis metaphase
connected chromosomes all line up on plate
Primary transcript
The initial RNA transcript from any gene prior to processing
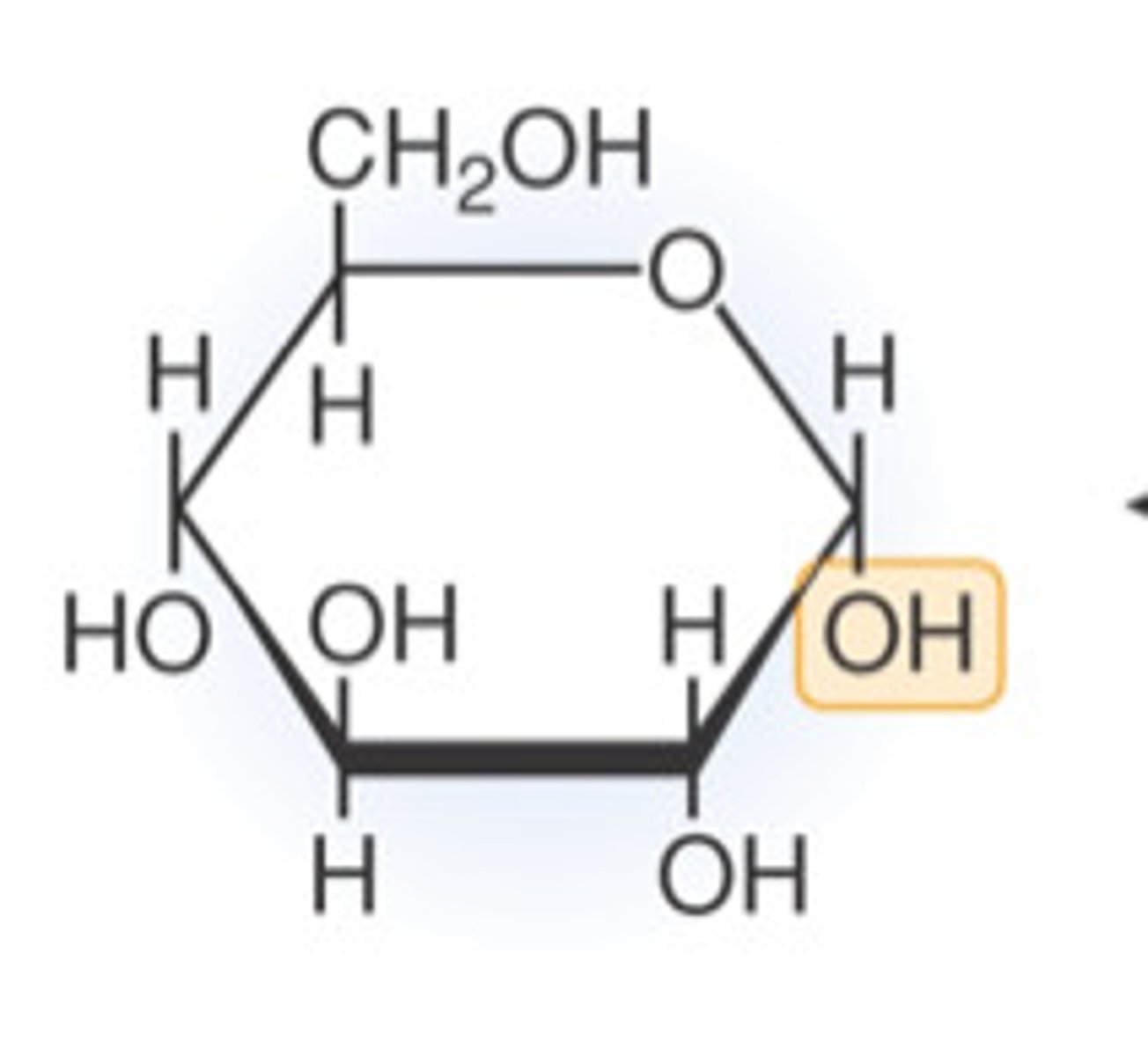
Glucose
- Blood sugar
- Essential energy source
Central dogma
Concept that cells are governed by a cellular chain of command:
DNA → RNA → Protein
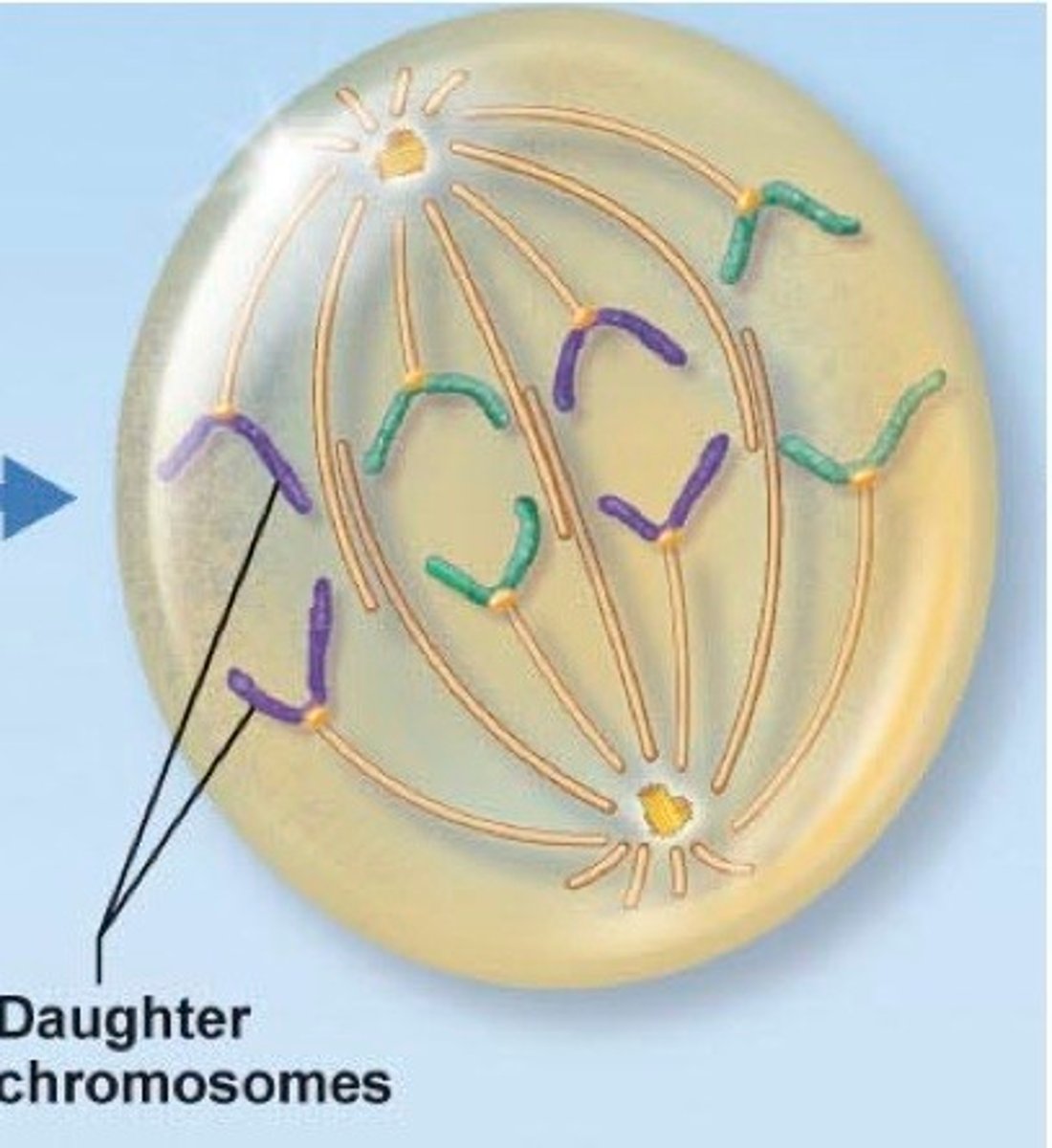
mitosis anaphase
separation (kinetochore eats at microtubule)
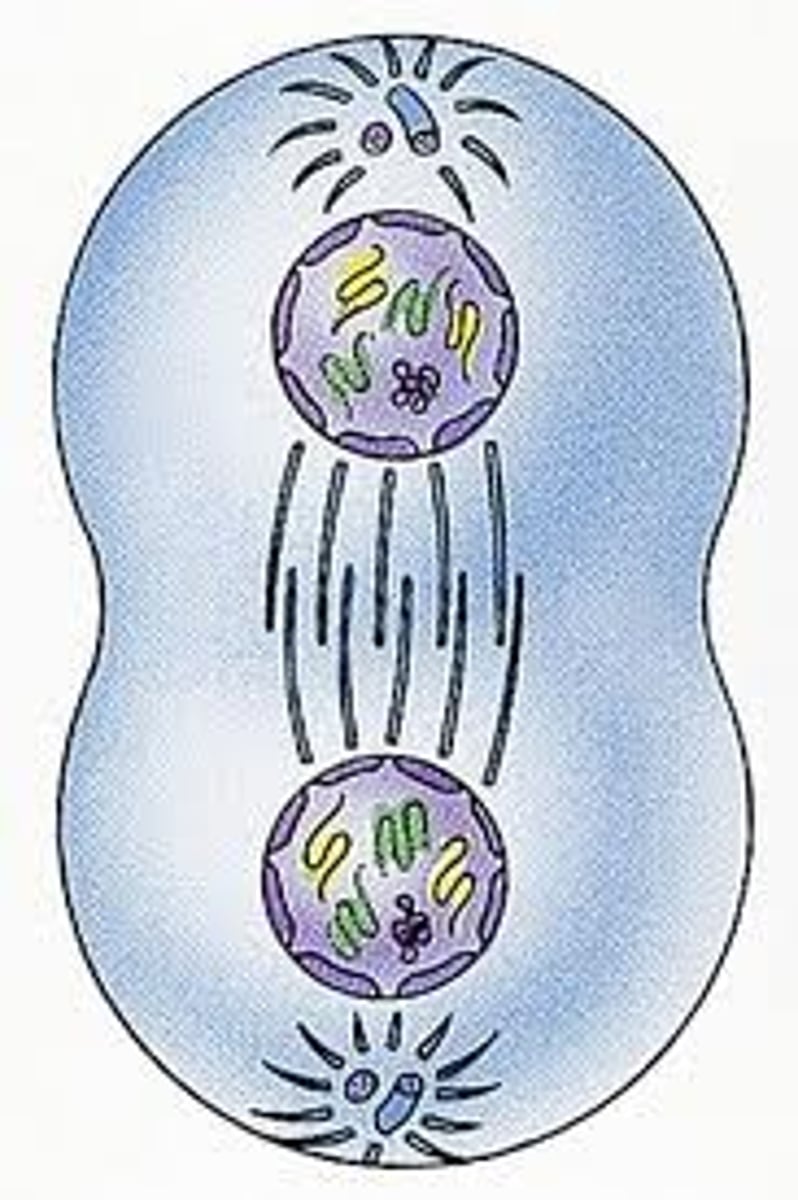
mitosis telophase
reformation of new nuclear membranes
Fructose
- Sweetest of sugars
- Fruit
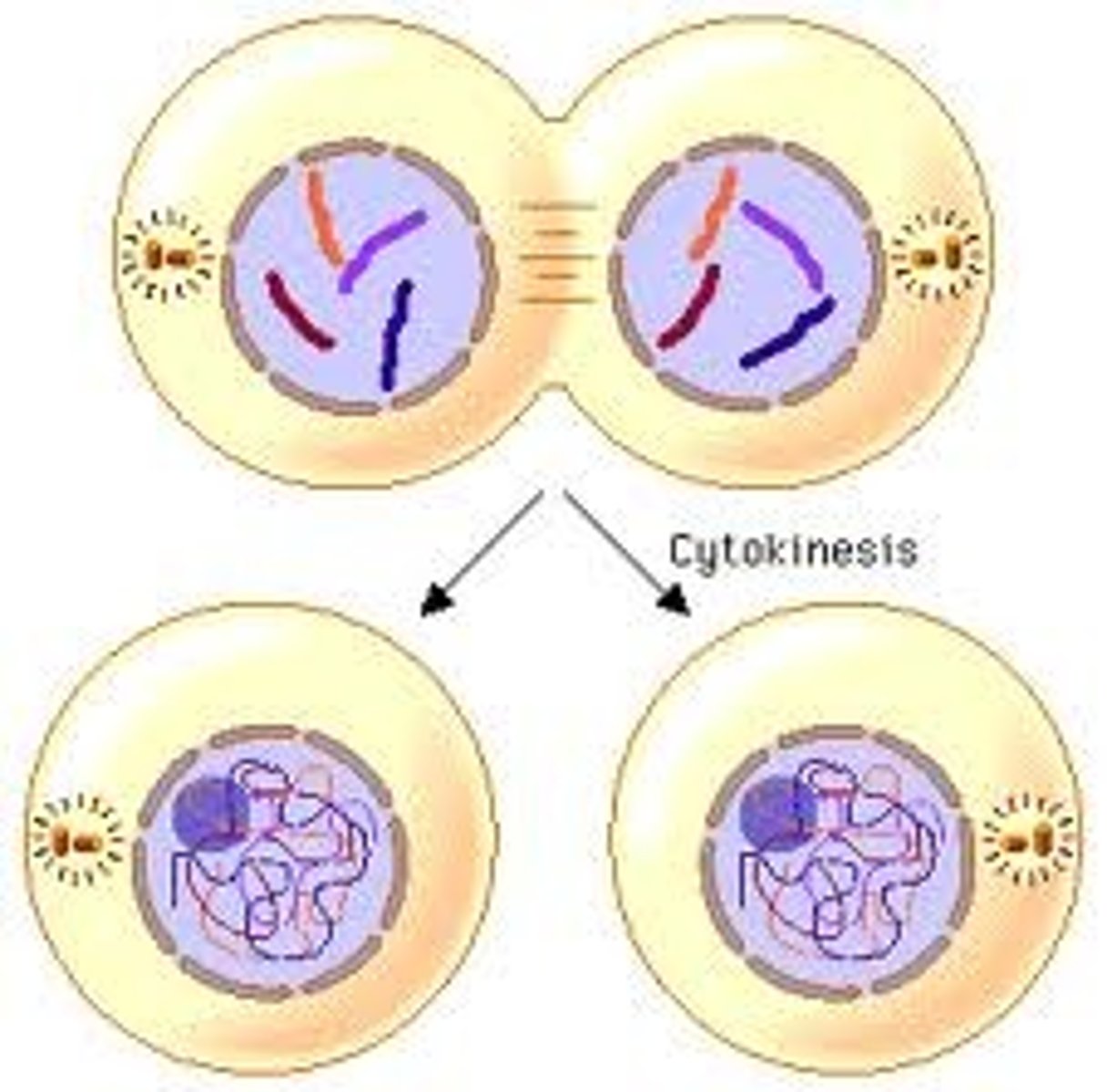
mitosis cytokinesis
splitting of cells
animals have a ring splitting the cells (cleavage furrow)
plants grow in size and then are split by cell wall
Template strand
Provides a template for ordering the sequence of complementary nucleotides in an RNA transcript
will be 3' to 5'
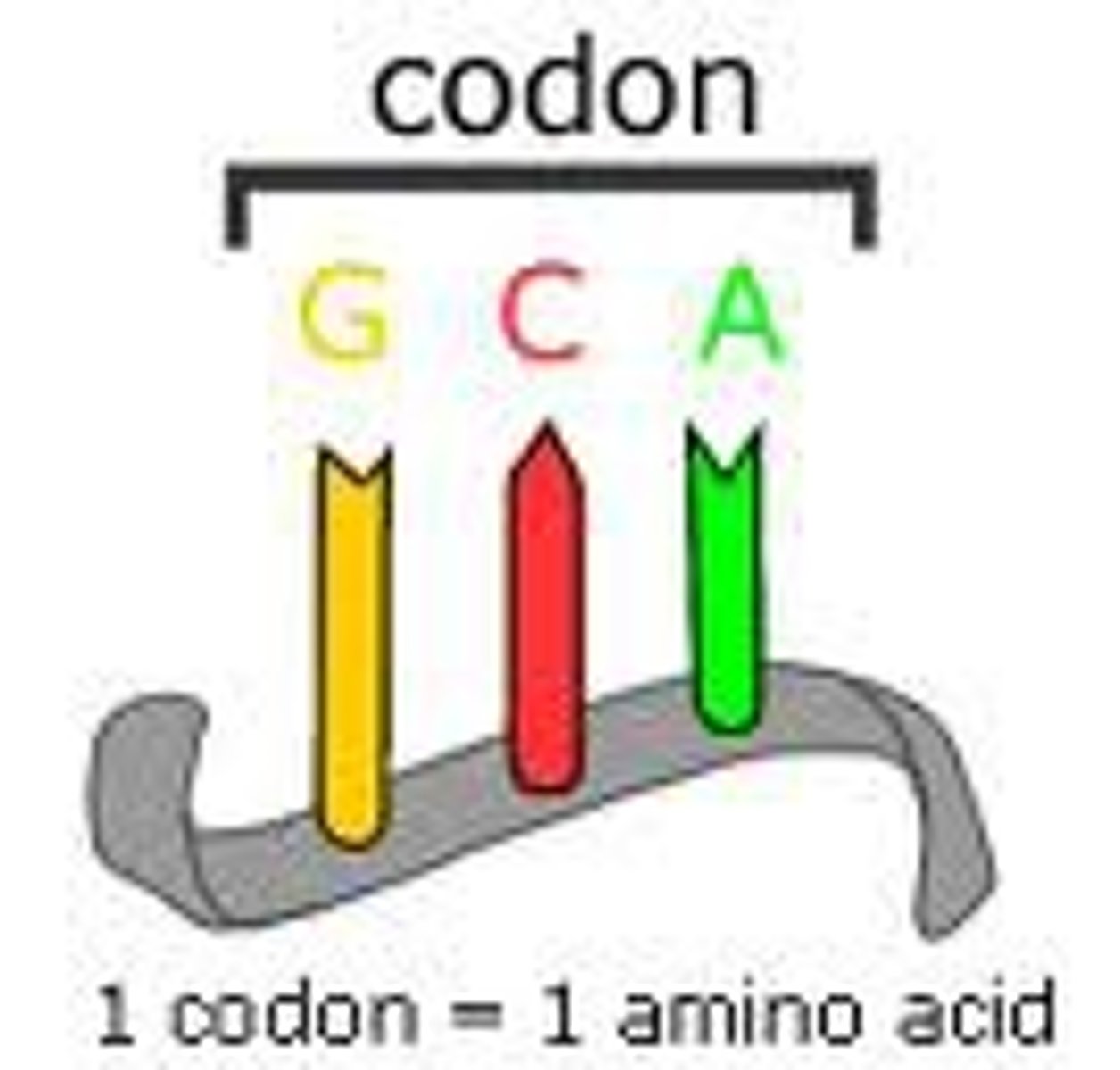
Codon
mRNA base triplets that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid (position on polypeptide)
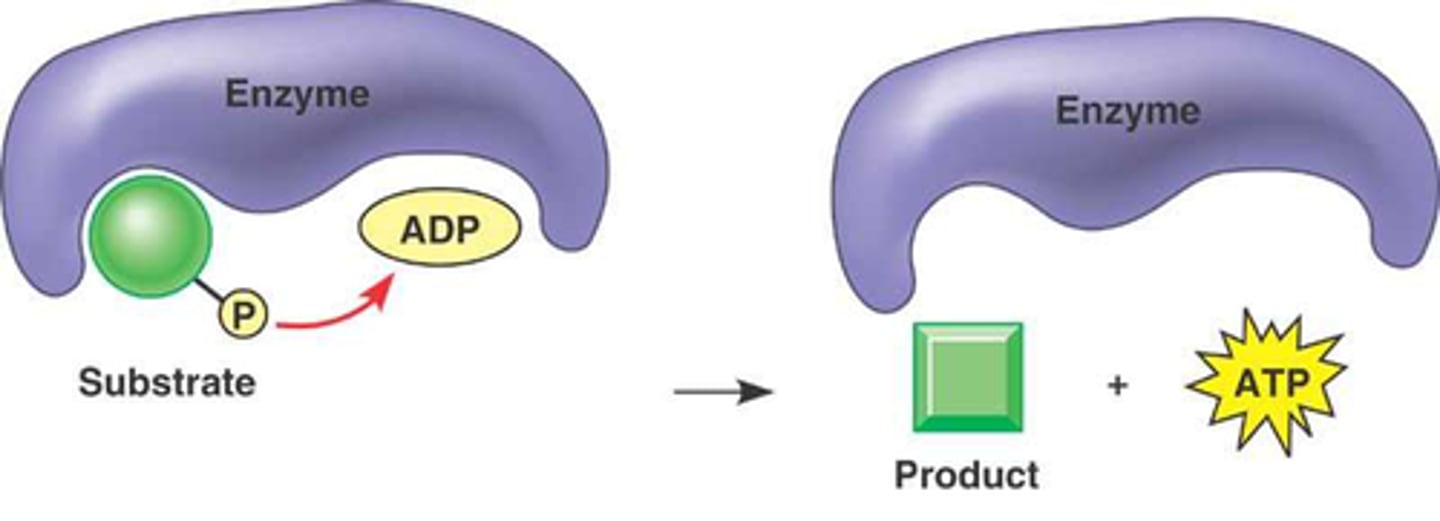
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
When an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule.
How many condons are there?
64
61 for amino acids and 3 are stop signals to end translation
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
potential energy
stored energy
What are the 3 stages of transcription?
1) Initiation
2) Elongation
3) Termination