Chapter 1 Mendelian Genetics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the basic unit of biological information?
A gene
A cross in which the pollen and egg come from the same plant is called____
Self-fertilization
Select all examples of discrete traits.
height
skin color
pea plant seeds can be either green or yellow
Dogs can have long or short hair
A rabbit can have white or black fur
A pea plant with white flowers is cross-fertilized with another pea plant with white flowers. All the offspring have white flowers. The cross is then repeated for 3 more generations and all offspring of all crosses have white flowers. These pea plants are most likely a _____- _____ line
pure-breeding
which of the following would be classified as the Parent (P) generation in a genetic cross?
Two true- breeding plants that are crossed
The ____ is the basic unit of biological information
gene
If a genetic study began with your grandparents, which generation would represent you and your siblings?
F2
______ - fertilization occurs when an egg is fertilized by pollen produced by the same plant
self
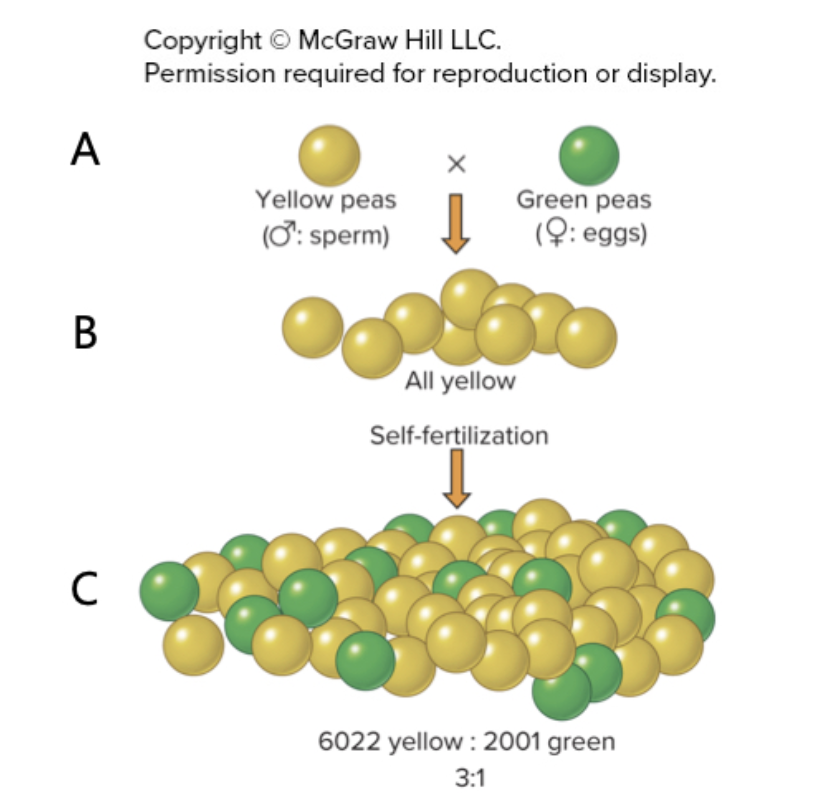
A pea plant can hav either yellow or green pods, If a true-breeding green-podded plant is crossed to a true-breeding yellow-podded plant, al of the offspring have green pods, however, if those hybrids are allowed to self-fertilized, both yellow-podded and green-podded offspring are produced. What conclusion can be drawn based on this information?
The yellow pod character is recessive to the green pod character.
Select all examples of continuous traits
amount of milk a cow produces in liters
measurements of human blood pressure
A line of peas that, when allowed to self-fertilize, produces the same type of offspring generation is called ____ _____ line
pure-breeding
Two plants have different forms of a gene that determines pea pod color. One plant has yellow pods, and the other green. What are the different forms of the pea pod color gene called?
Allele
In one of his experiments, Mendel started by crossing pure-breeding tall pea plants with pure- breeding short pea plants. These pure-breeding plants are considered the ____ generation.
P
Different alleles of a single fly gene determine whether a fly has white or red eyes. A fruit fly that carries one allele for white eyes and one allele for red eyes is ___
a monohybrid
which letter denotes the F1 generation?
B
A ___ is a specialized cell that carries a single copy of each gene to the next generation
A gamete
When a true-breeding tall pea plants is crossed with a true-breeding dwarf pea plant, all the offspring are tall. This observation indicates that tall is ____ to dwarf.
dominant
A typical gamete will contain____
one allele of each gene
The genetic composition of an individual is the ____
genotype
The term that describes an alternative form of a gene is ____
allele
The color and pattern of fur is controlled by genes. A dog has fur that is white with black spots. Does this description refer to the dog’s genotype or phenotype?
Phenotype
An organism with one dominant and one recessive allele for a single trait is called ____
a monohybrid
A true-breeding tall pea plants with purple flowers is crossed with a true-breeding short pea plant with white flowers and the offspring are allowed to self-fertilize. The two characters of each trait are controlled by alternate alleles of the same gene. This type of cross is a ___ cross.
dihybrid
Which of the following are gametes?
eggs and sperms
In the F2 progeny of a dihybrid cross, some offspring look like the original individuals that were crossed to procedure the F1 hybrids and are known as ___ types, while other offspring exhibit new phenotypic combinations and are known as ____ types.
parental, recombinant
Consider one particular gene of a sexually reproducing organism. When gametes are formed, each receives ___.
one allele of the gene
What term describes an individual’s combination of alleles?
genotype
An organisms’s genotype is Rr Yy and it produces gametes with the genotypes R Y, Ry, rY, and ry with equal frequency. which of the mendel’s law explains this fact?
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
What term describes the observable characterisitcs that result from the expression of a gene?
phenotype
In an ___ cross, scientists mate the F1 progeny of true-breeding parents that differ in three or more traits.
multihybrid
what type of cross is performed when a true-breeding tall pea plant with yellow seeds is crossed with a true-breeding short pea plant that has green seeds, and the offspring are allowed to self-fertilize (the two characters of each trait are controlled by alternate alleles of the same gene)?
Dihybrid cross
A pea plant requires an enzyme to produce flowers that are purple. If this enzyme is not functional, the flowers will be white. Based on this information, which of the statements are true?
the allele for the white flower phenotype is most likely recessive to the normal allele.
The non-functional allele is most likely recessive to the normal allele.
Consider a dihybrid cross involving two traits, each with two characters controlled by alternate alleles of the same gene. The true breeding parents all tall pea plants that produce purple flowers, and short pea plants that produce white flowers. All of the F1 offspring are tall pea plants and produce purple flowers. Therefore, all of the F1 progeny are _____
Parental type
which statements accurately describe the inheritance of common human traits, such as hair color?
They arise through the interaction of several genes.
They do not exhibit Mendelian inheritance.
what information can be obtained from a human pedigree?
a family history of genetic traits
how a gene is inherited
The alleles of two different genes will be distributed randomly into gametes. This statement summarize which of Mendel's laws?
Law of independent assortment
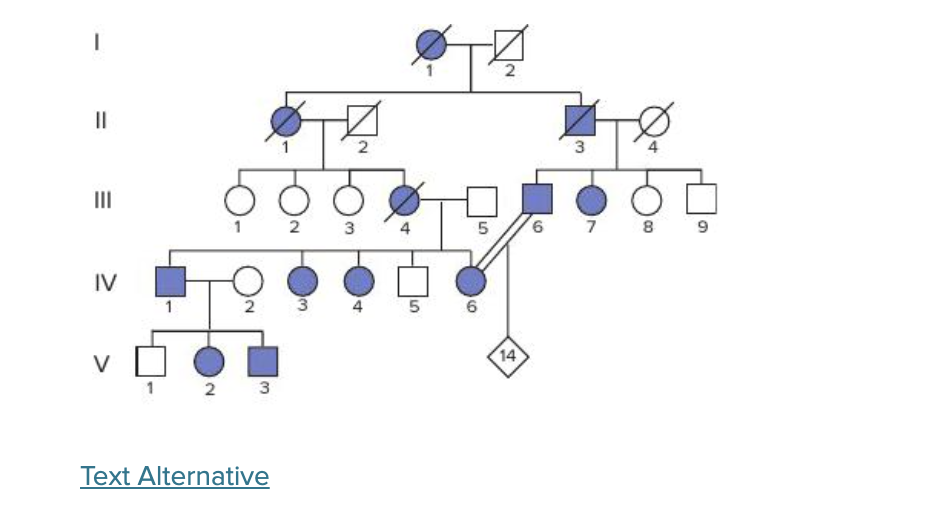
this pedigree shows a family with disease caused by a rare allele. What pattern of inheritance does this pedigree suggest?
dominant
How do scientists refer to crosses that involve matings between F1 progeny fo true-breeding parents that differ in three or more traits?
multihybrid crosses
When a preexisting allele is changed to a version that no longer codes for a functional protein, the new allele is likely to be ___ to a normal allele.
recessive
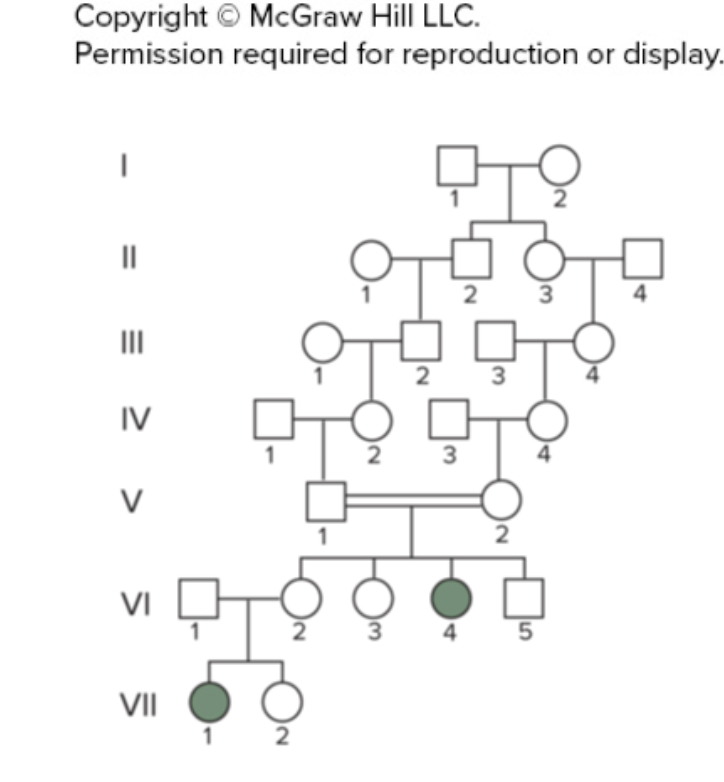
Based on this pedigree in Fig 1.20 of a rare disease cause by a recessive allele, we can conclude that individuals V-1 and V-2 are both ____.
heterozygous
Many common traits in humans (for example, eye or hair color) are controlled through the interaction of more than one ___.
gene
To determine inheritance patterns in human, researchers use a chart called a ___ that represents family relationships.
pedigree
You are studying a rare genetic disease using pedigree analysis and notice thta the every affected person has at least one affected person, and the disease is present in every generation. This suggests that the allele causing the disease is ___ to the normal allele.
dominant
As seen on this pedigree of a rare disease, two unaffected parents (V-1 and V-2) have three unaffected children and one affected child (v-14). What can we conclude from this?
This disease is caused by a recessive allele
The two parents (v-1 and V-2) are carriers