Biol 3130 Lecture 9
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Flow of Genetic Information
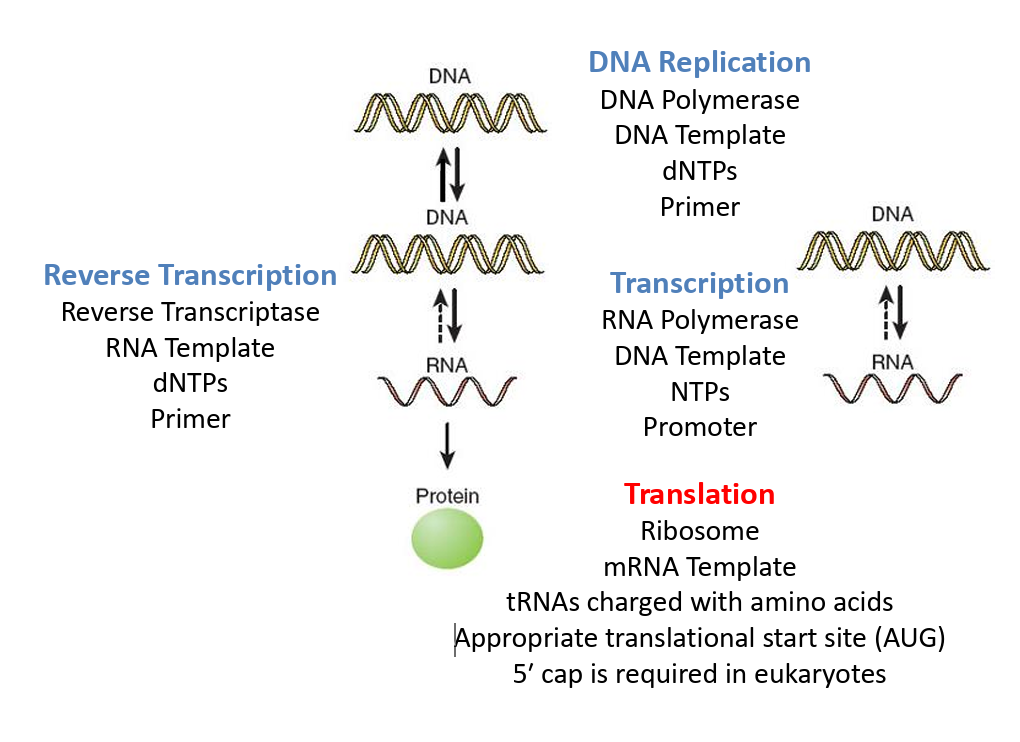

Translation
tRNA charging (attaching amino acids to appropriate tRNA)
Incorporation of the initiator tRNA with small ribosomal subunit
Locating the translational start site on the mRNA
Assembly of full ribosome
Synthesis of the first peptide bond
Translocation and elongation
Termination and release
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
Adaptor molecules
Transfer RNAs convert the genetic code found on mRNA codons to amino acids
read the codon sequence through their anticodon
anticodon sequence corresponds to the amino acid attached to the tRNA
anticodon: Triplet nucleotide sequence on tRNA molecules that base-pairs with a corresponding mRNA codon within the ribosome during translation
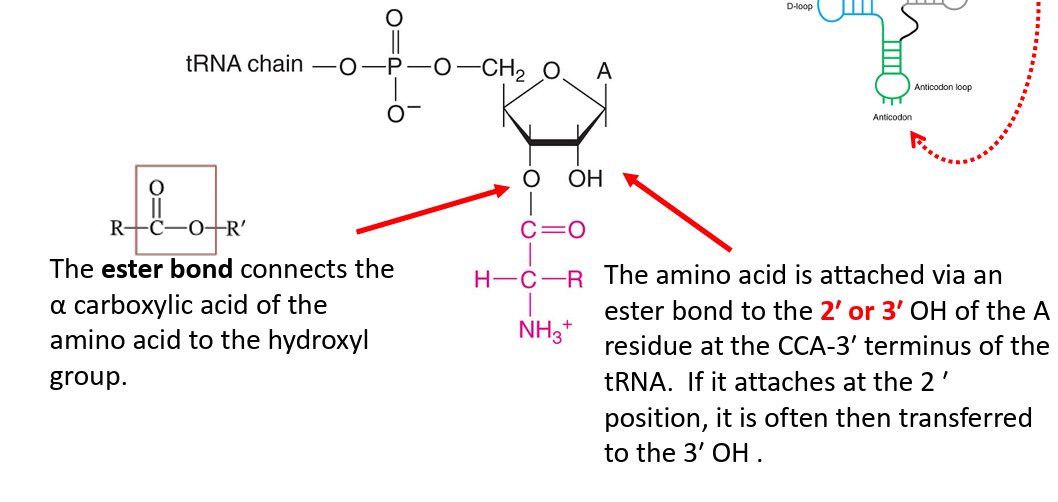
amino acid (technically, an aminoacyl when attached) is attached to the 3′ end of the tRNA, at a CCA-3′ sequence
2′ or 3′ OH of the 3′ A residue covalently attaches to the amino acid group
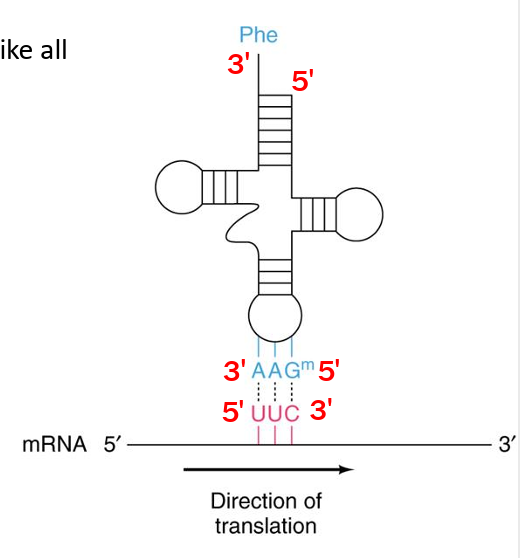
Anticodon-Codon Base-pairing
When the anticodon and the codon base pair, just like all types of base-pairing, strands are antiparallel.
In the example shown for a Phe tRNA:
The codon sequence is: 5′-UUC-3′
The anticodon sequence is: 5′-GAA-3′
tRNA Charging
refers to the attachment of an amino acid to the appropriate tRNA
correct amino acid needs to be attached to the tRNA with the corresponding anticodon
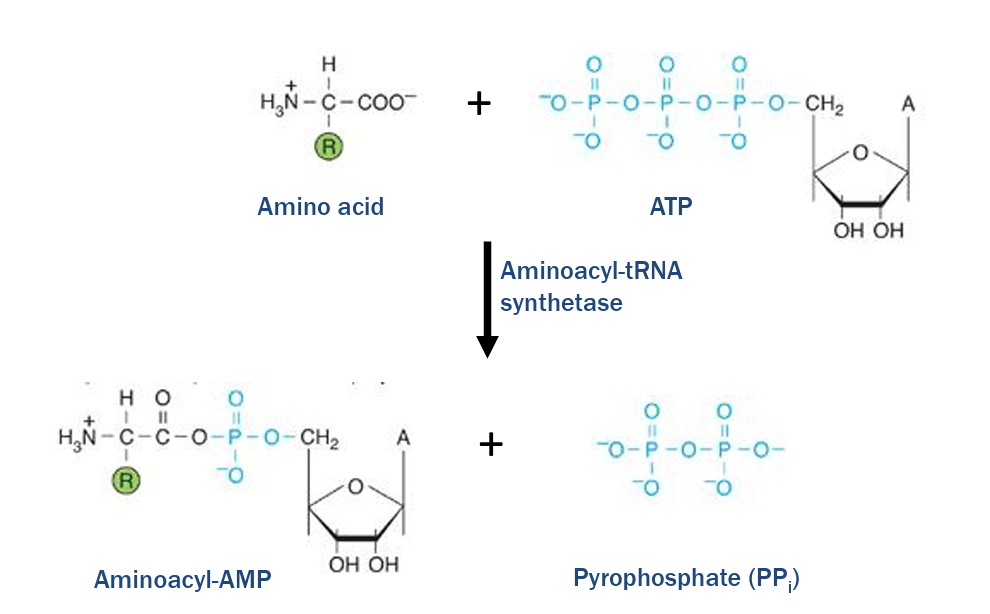
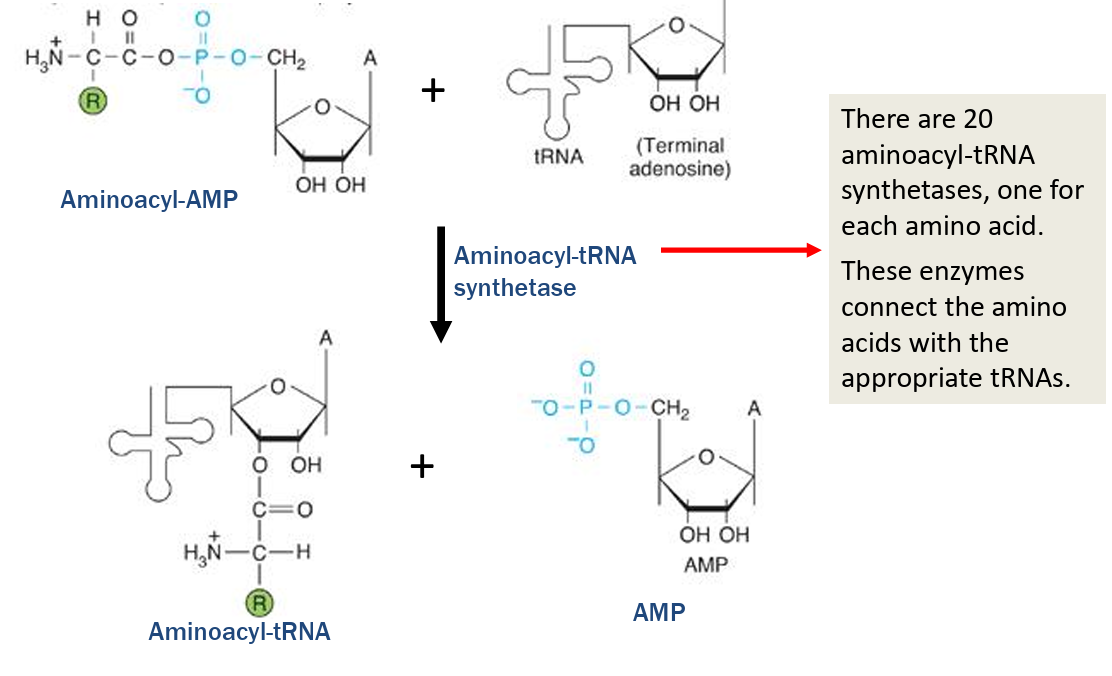
tRNA charging is a two-step process that is catalyzed by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
tRNA Charging Steps
Step 1
activation of amino acid
an amino acid is activated by displacing the diphosphate on ATP
powered by energy released by breaking a phosphoanyhdride bond
Aminoacyl-AMP is formed and pyrophosphate is released
Step 2
transfer to the tRNA
the aminoacyl group is transferred to the tRNA
E. coli Ribosome
Ribosomes are composed of a large subunit + a small subunit
subunit components are named according to their sedimentation coefficient: (how far they travel through a solution when spun in an ultracentrifuge)
Sedimentation coefficients depend on mass, density, and shape of the particles
E. coli ribosome (70S) is composed of a 50S large subunit, and a 30S small subunit
Each subunit is composed of rRNAs, and many proteins