Light and sound - KS3
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
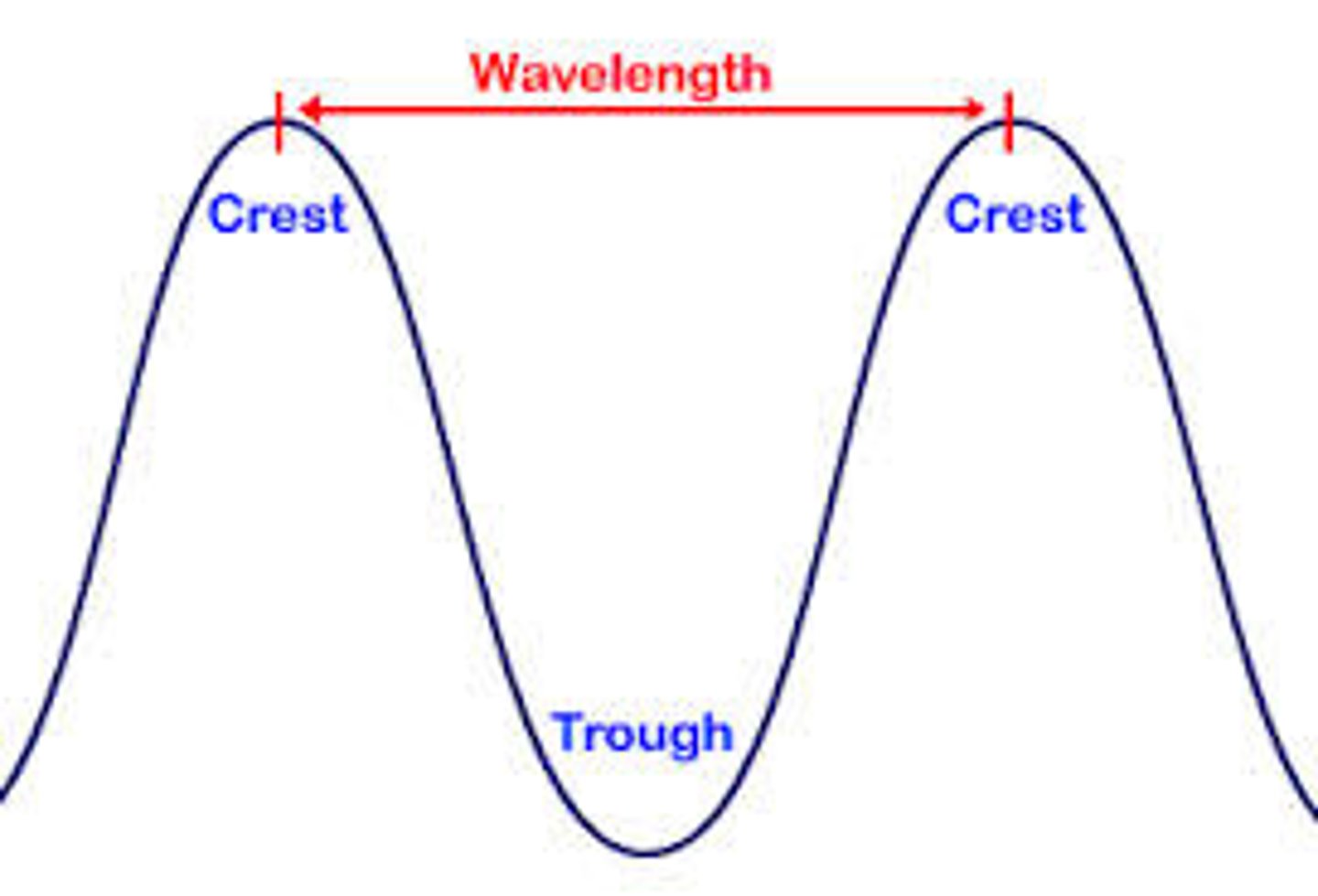
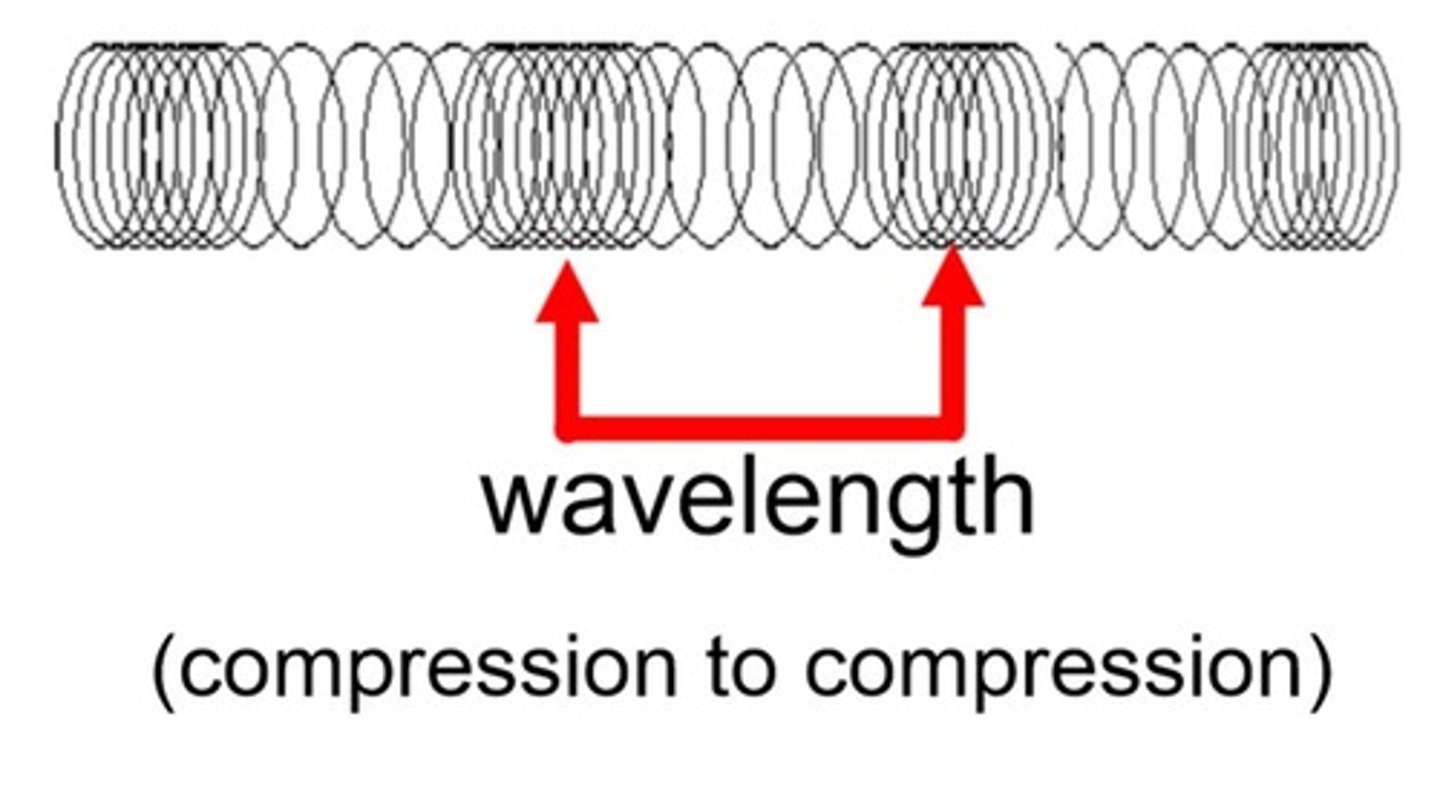
Wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
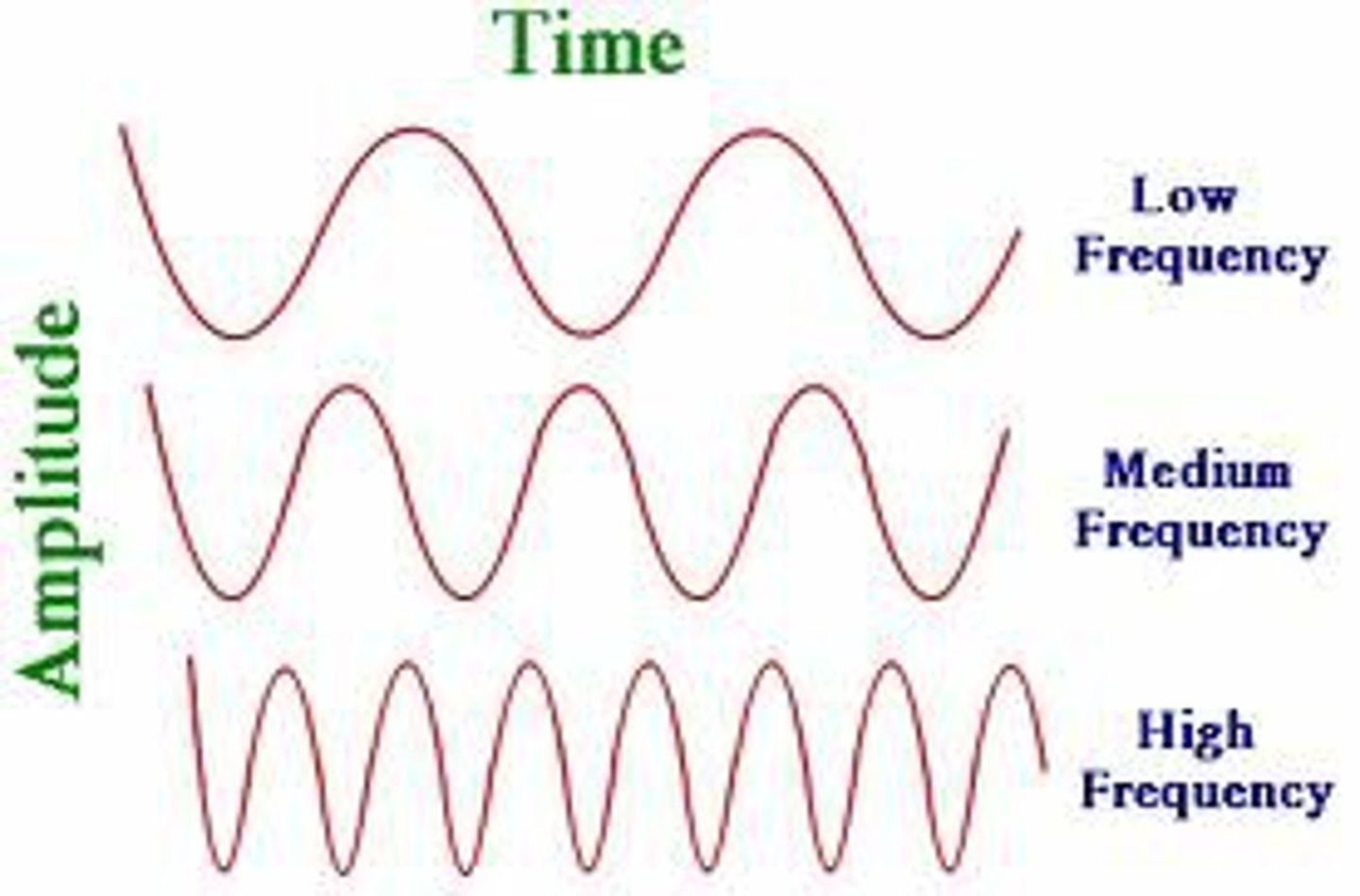
Frequency
Number of cycles per second, measured in Hertz (Hz)
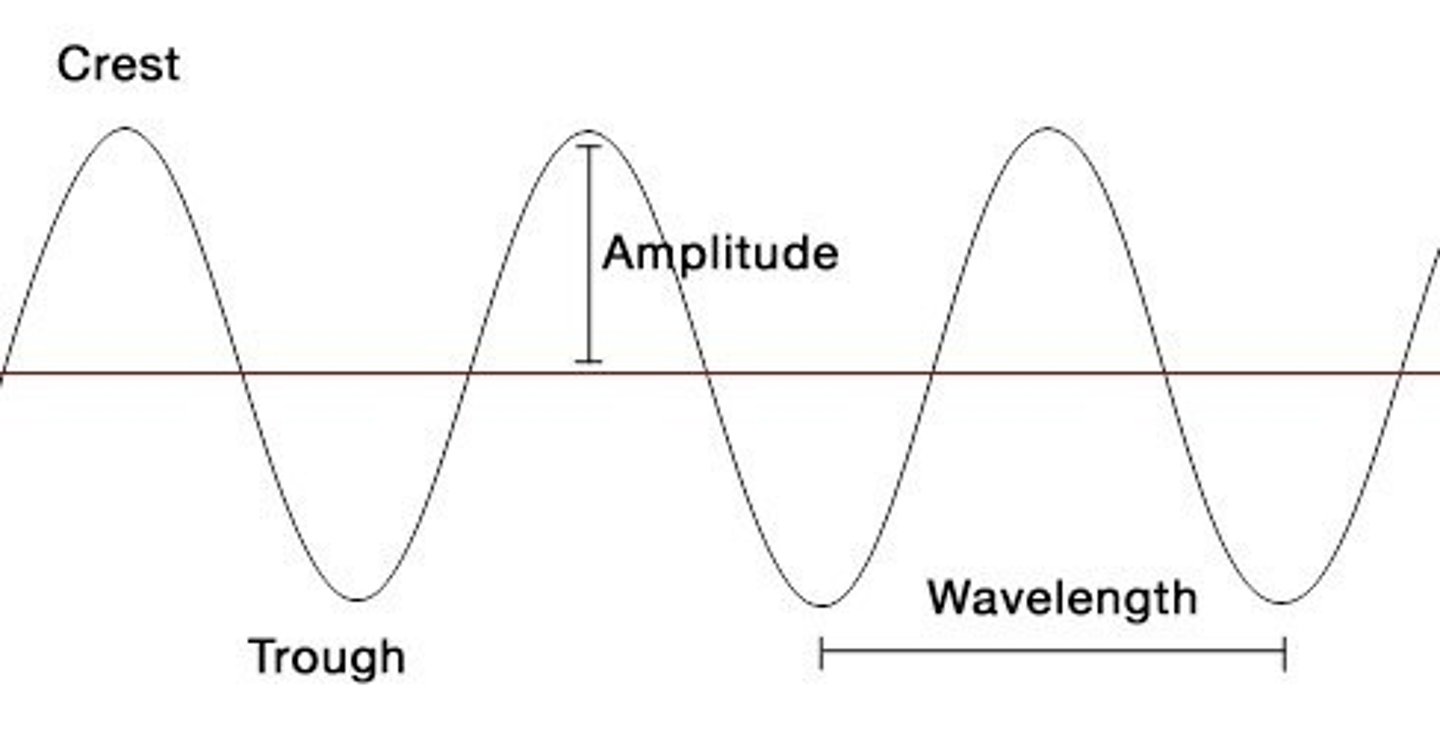
Amplitude
the maximum displacement of a periodic wave
Speed of a wave,c
High Frequency: Low wavelength
Low Frequency: High wavelength

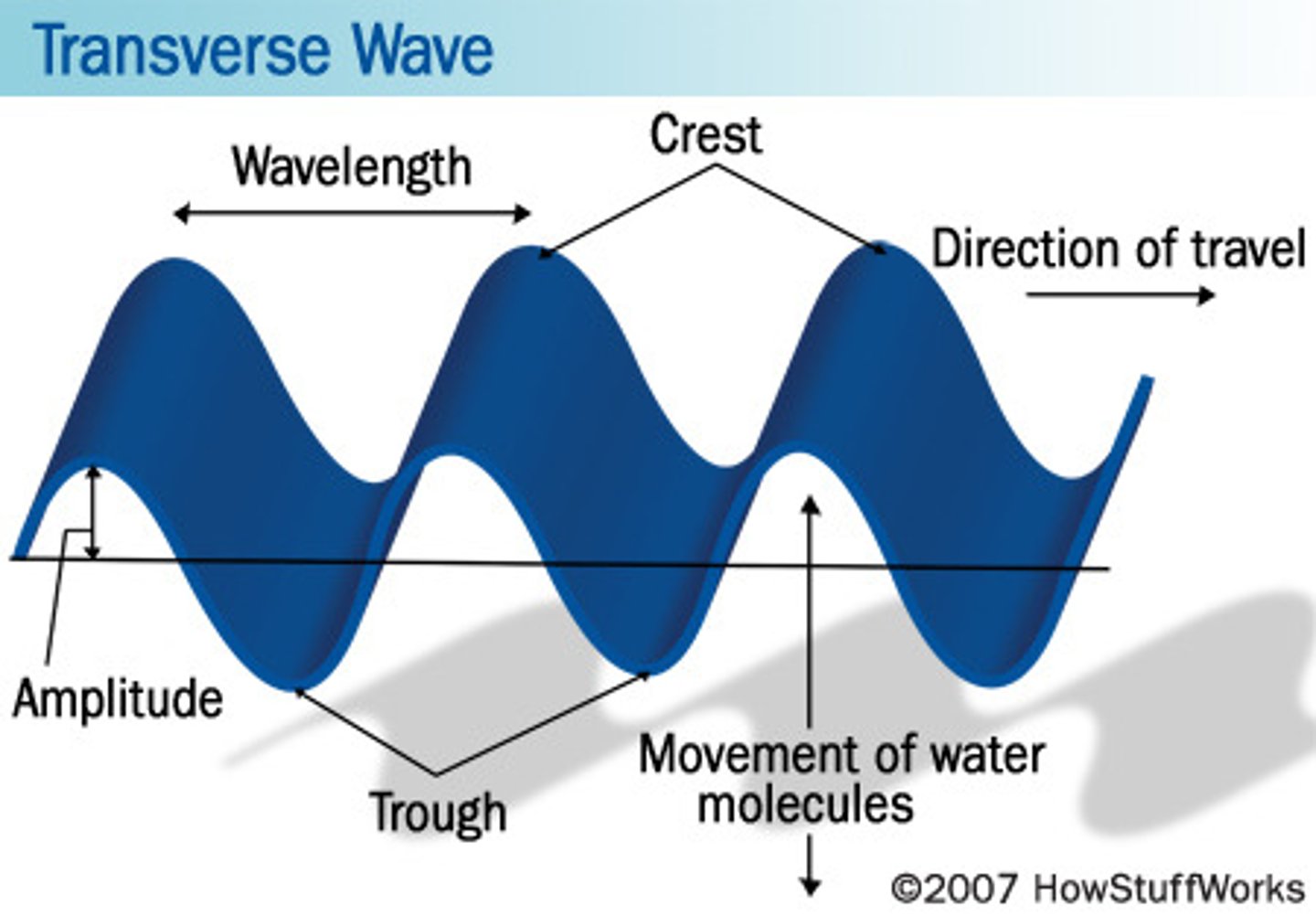
Transverse Wave
a wave vibrating at right angles to the direction of its propagation. Examples: Light, Water waves.
Longitudinal Waves
a wave in which the particles move parallel to the path of the wave. Sound.
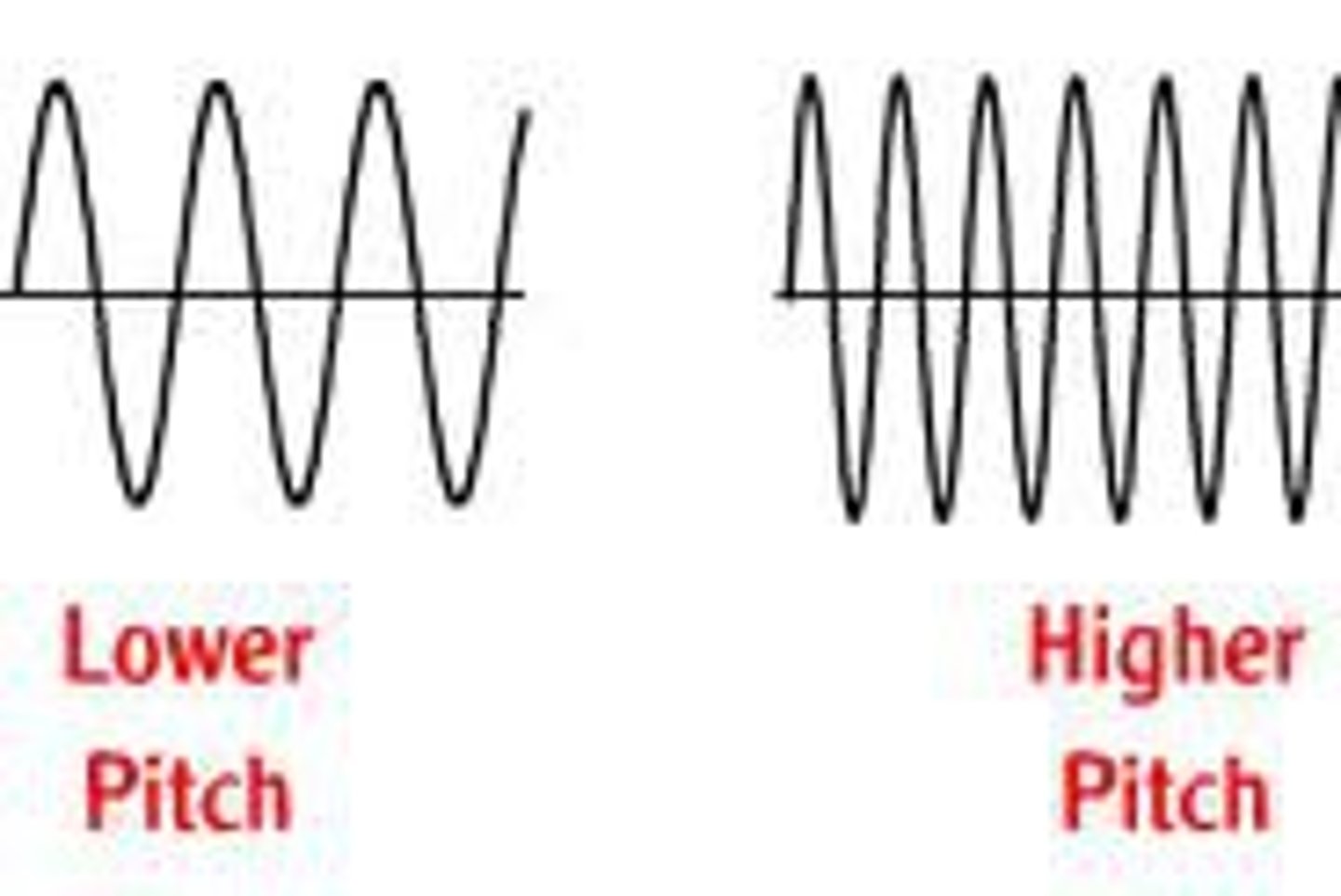
Pitch
Perception of the frequency of a sound. High pitch = High Frequency
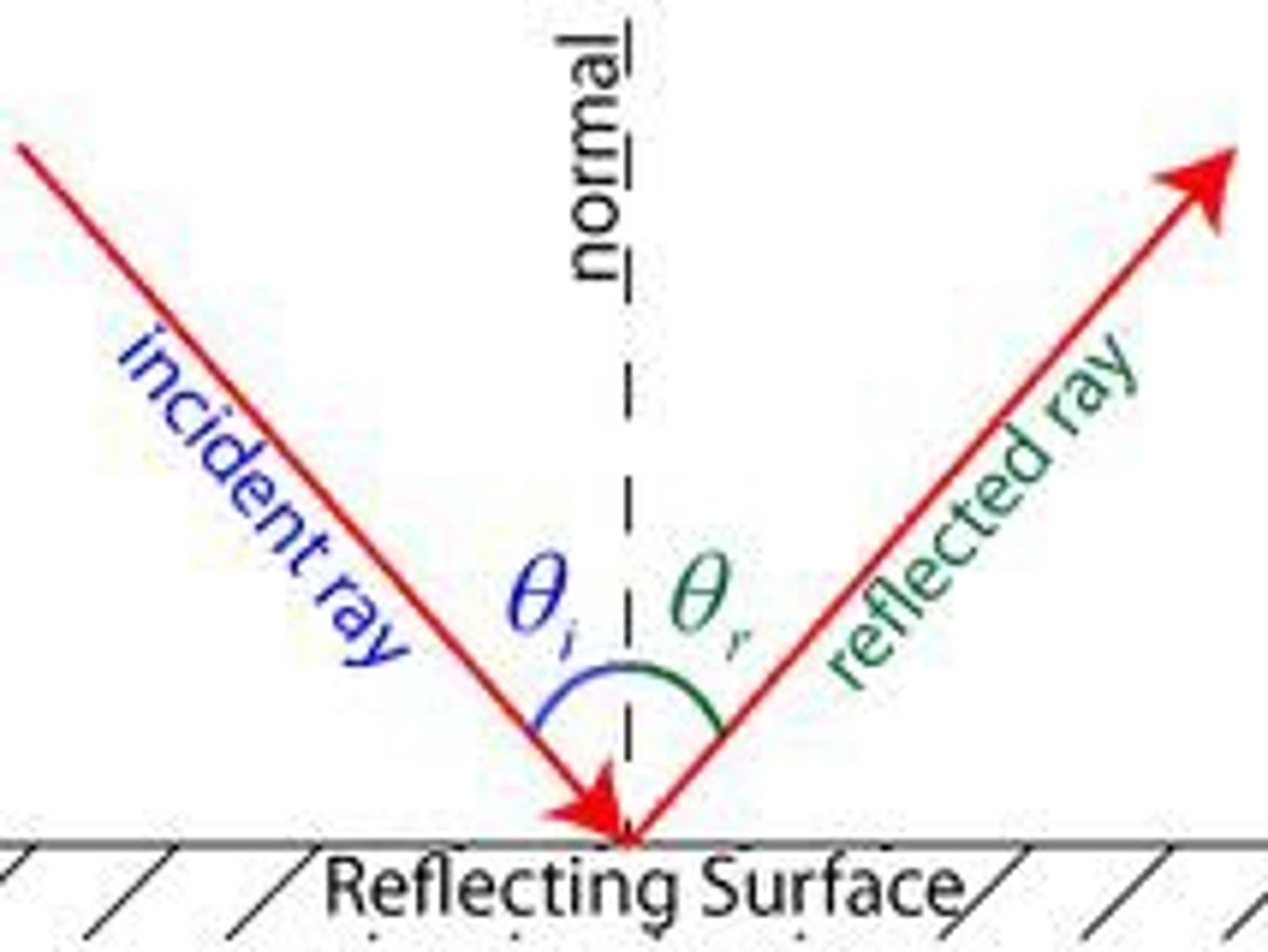
Laws of reflection
1) angle of incidence= angle of reflection
•
2) Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie on the same plane
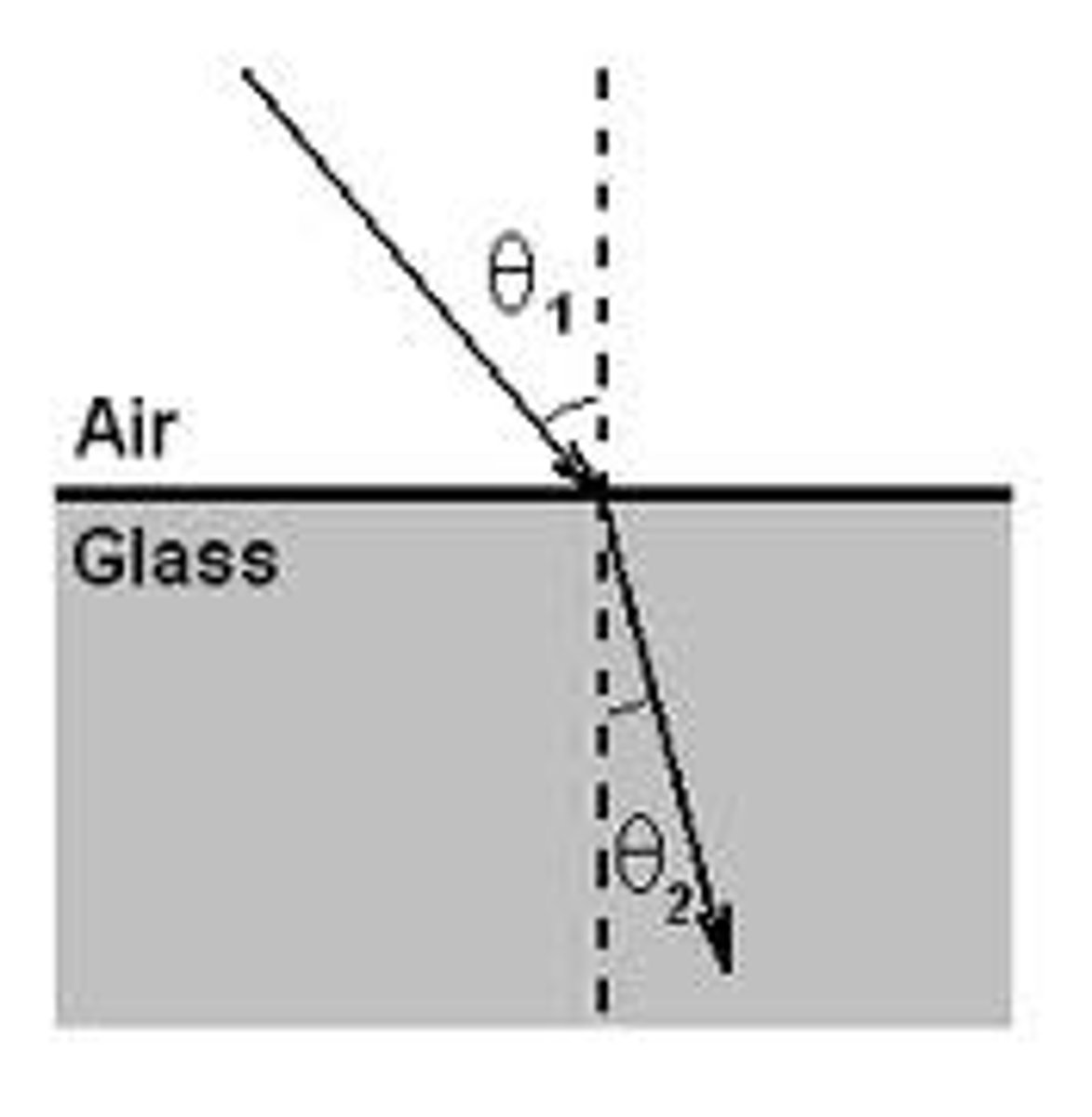
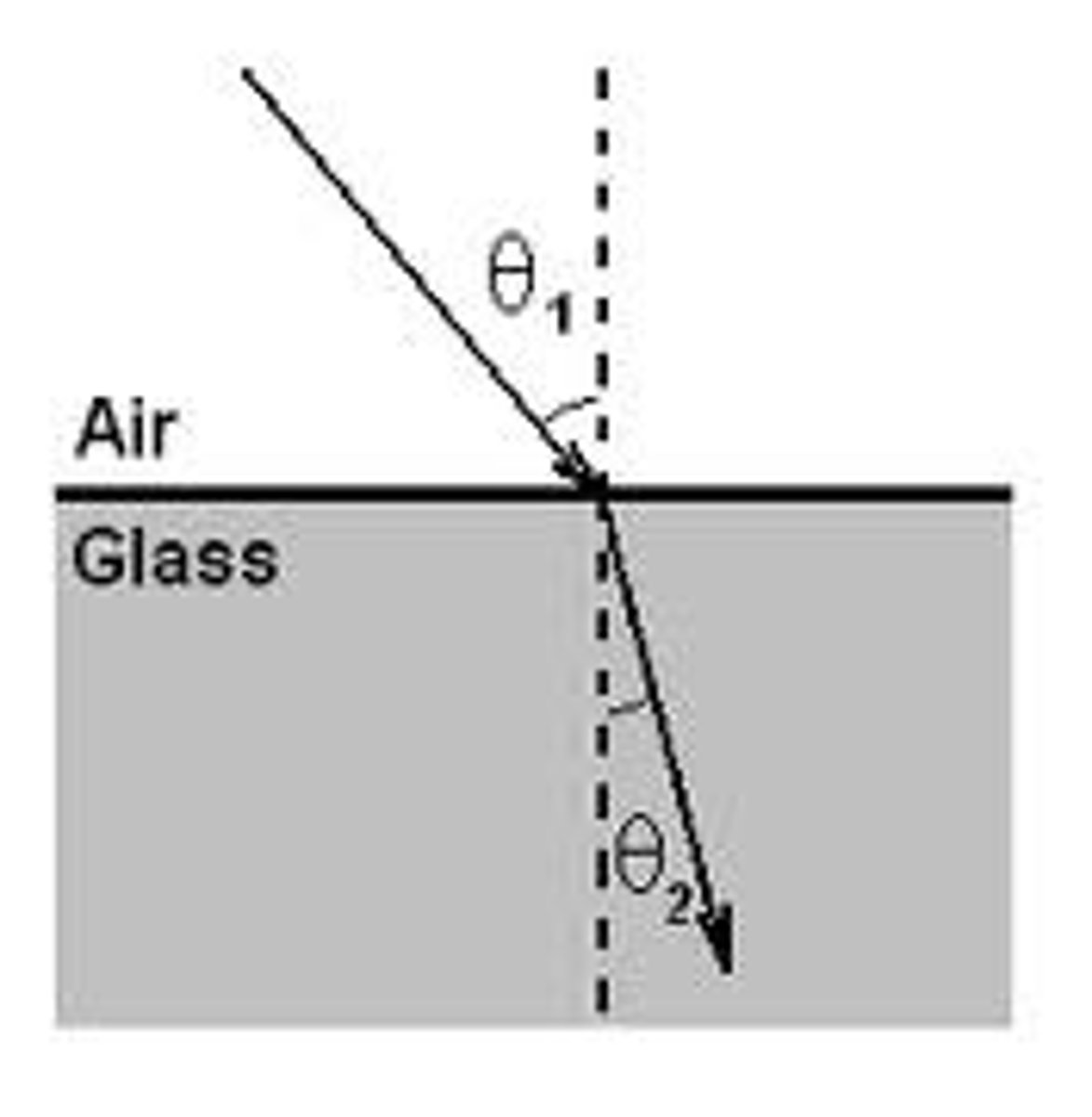
Laws of refraction
1. The incident, normal and refracted ray all lie on the same plane.
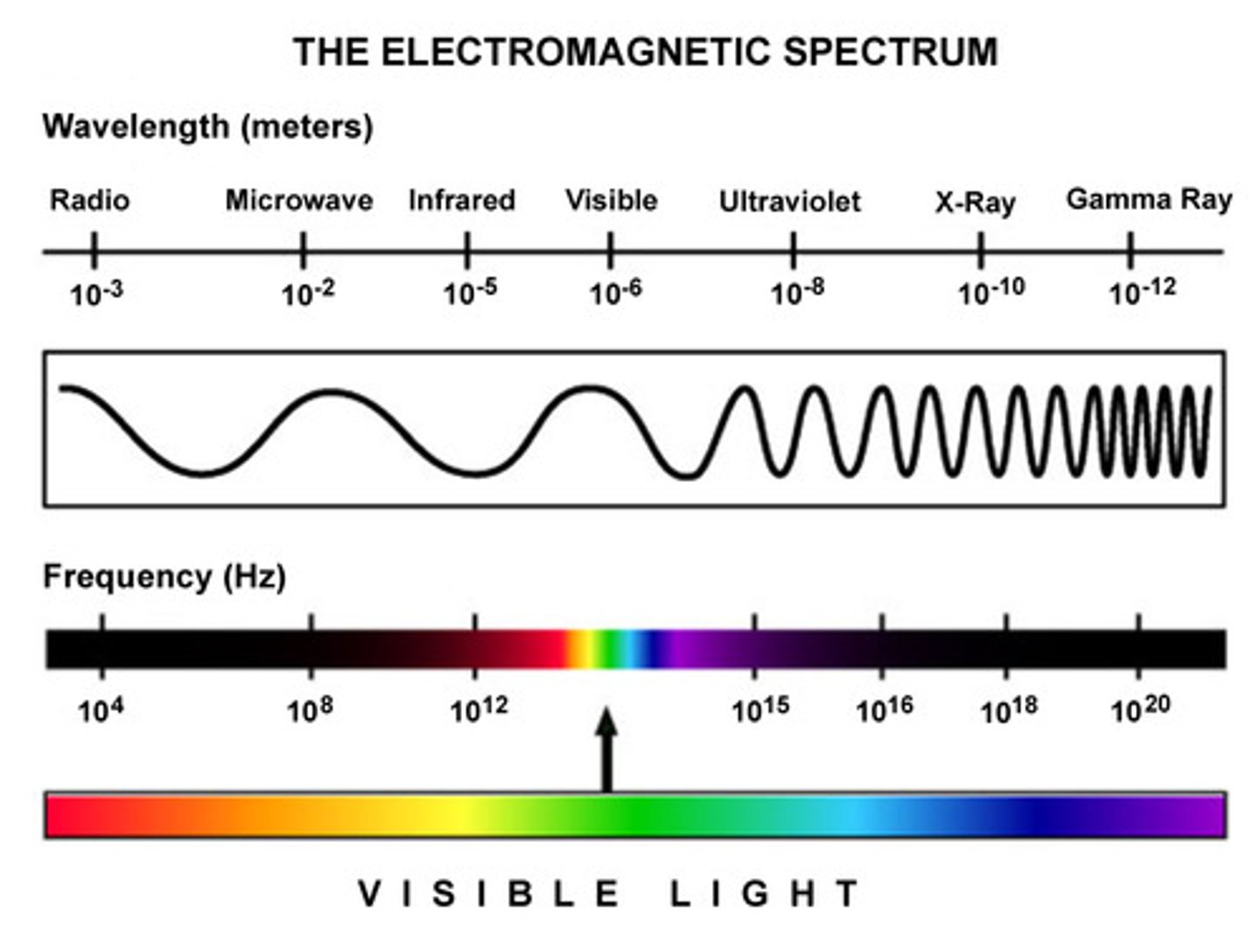
EM Wave
A type of wave, such as a light wave or radio wave.
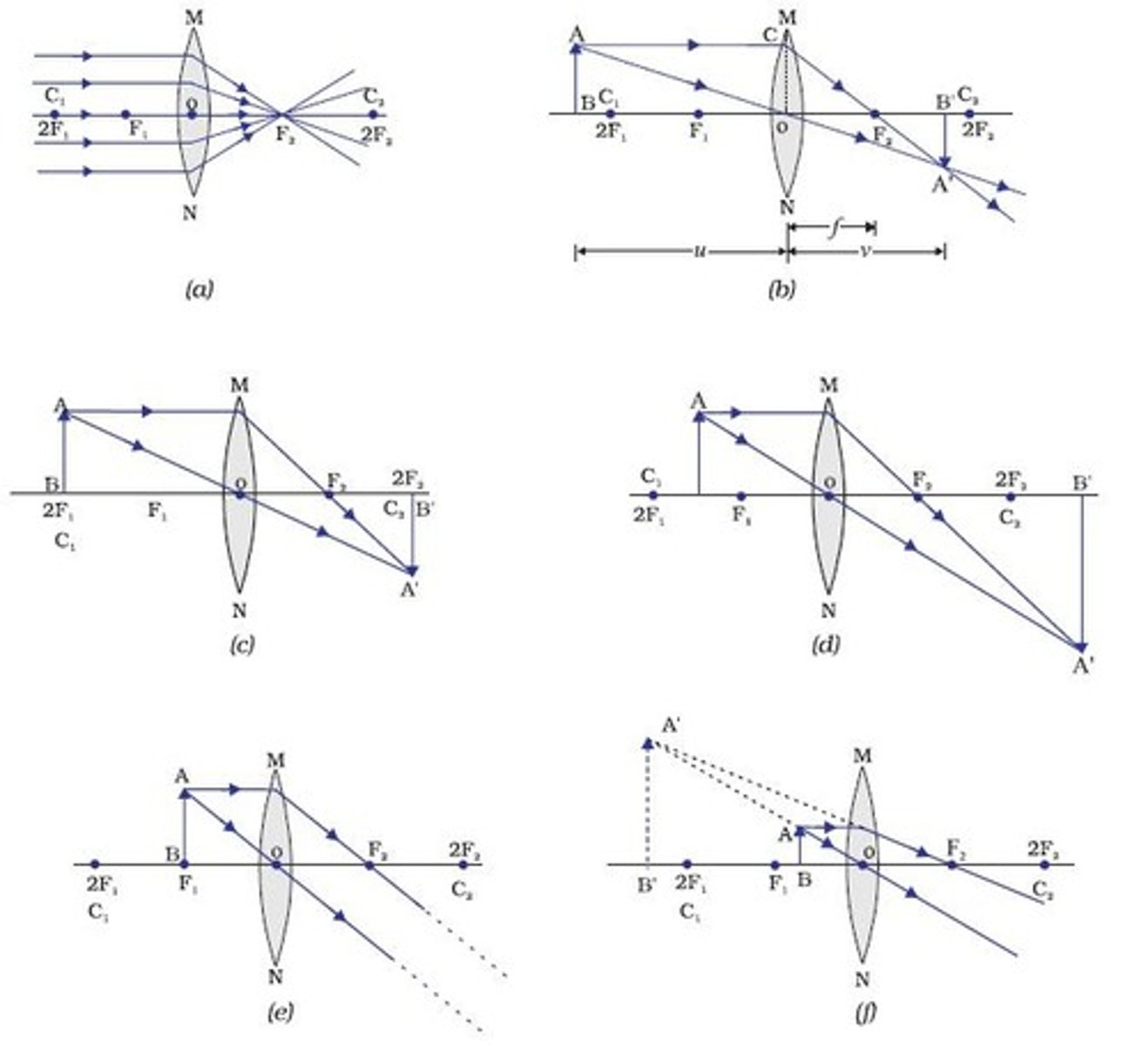
ray diagram
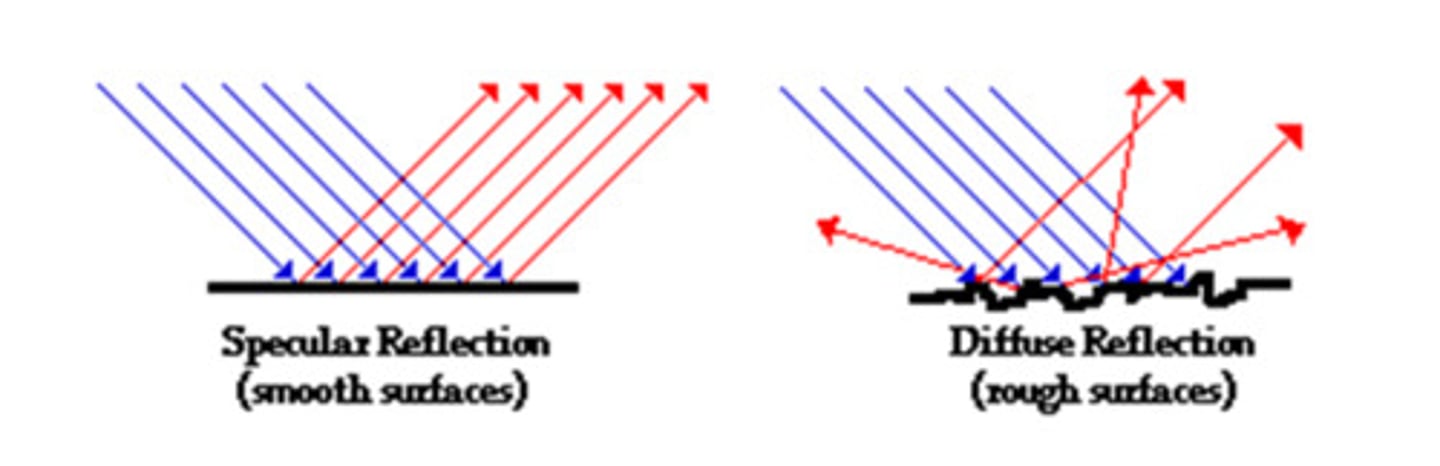
Diffuse reflection
A reflection that occurs when light bounces off an object at different angles. The result is a fuzzy image.
Refraction
The change in speed and direction of light when it passes from one kind of material to another.
period of a wave
Time taken for one complete oscillation. T = 1/f. Units: seconds or s
sound intensity
the energy of the sound wave
Differences between light and sound waves:
1. Light is a transverse wave sound is a longitudinal wave.
2. The speed of Light is much faster than sound. light 300,000,000 m per s. Sound 340 m per s.
3. Sound requires a medium to travel through.