Lecture 13 & 14: infectious diseases of the hematopoietic system
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Bartonellaa henselae
•Short, fastidious Gram-negative rods; difficult to culture
•Facultative intracellular pathogens; infect CD34+ cells
•Transmitted by bites or scratches from infected cats or fleas
transmission of bartonella hensseae
-cutaneous lesion at site of inoculation---> regional lymphadenopatahy
presentation of bartonella henselae
bartonella henselae
________ can be a cause of culture nengative endocarditis
Bacillary angiomatosis
this complication of bartonella henselae primarily presents in AIDS pts
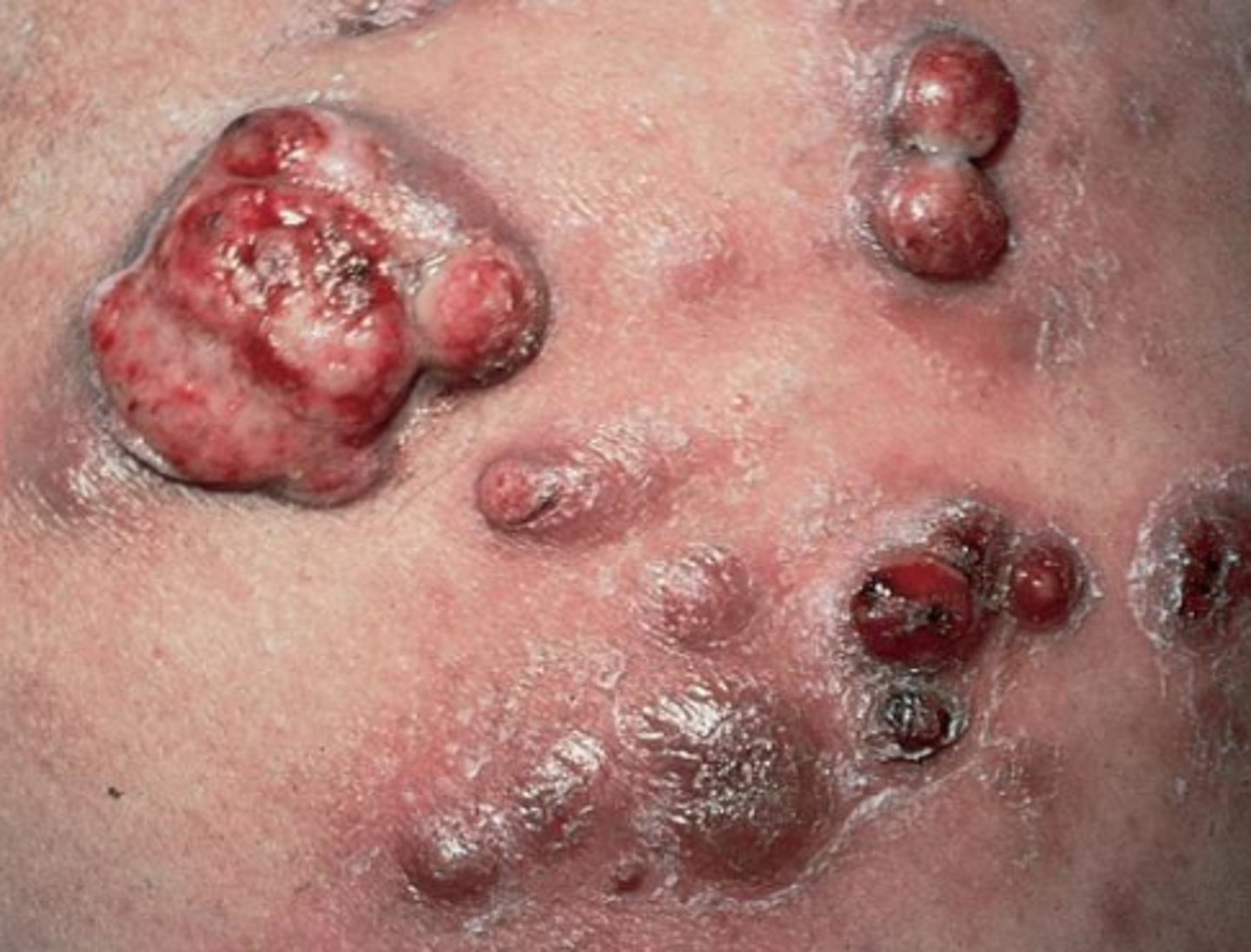
bacillary angiomatosis
angioproliferative cutaneous lesions associated with B. henselae
-bone lesiions
-peliosis
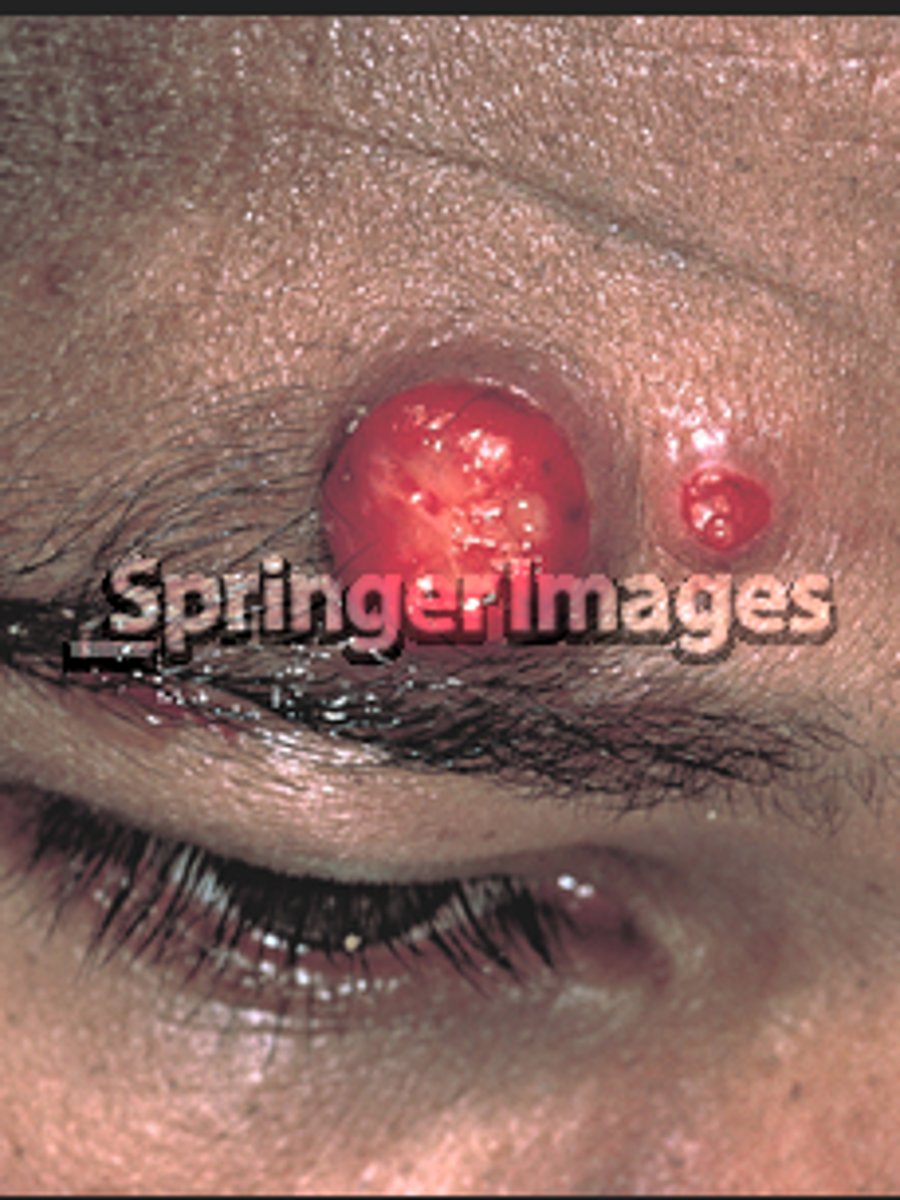
Bartonella bacilliformis
-bartonella endemic to the andes mountains
-transmitted by female sand fly
-most frequently in children
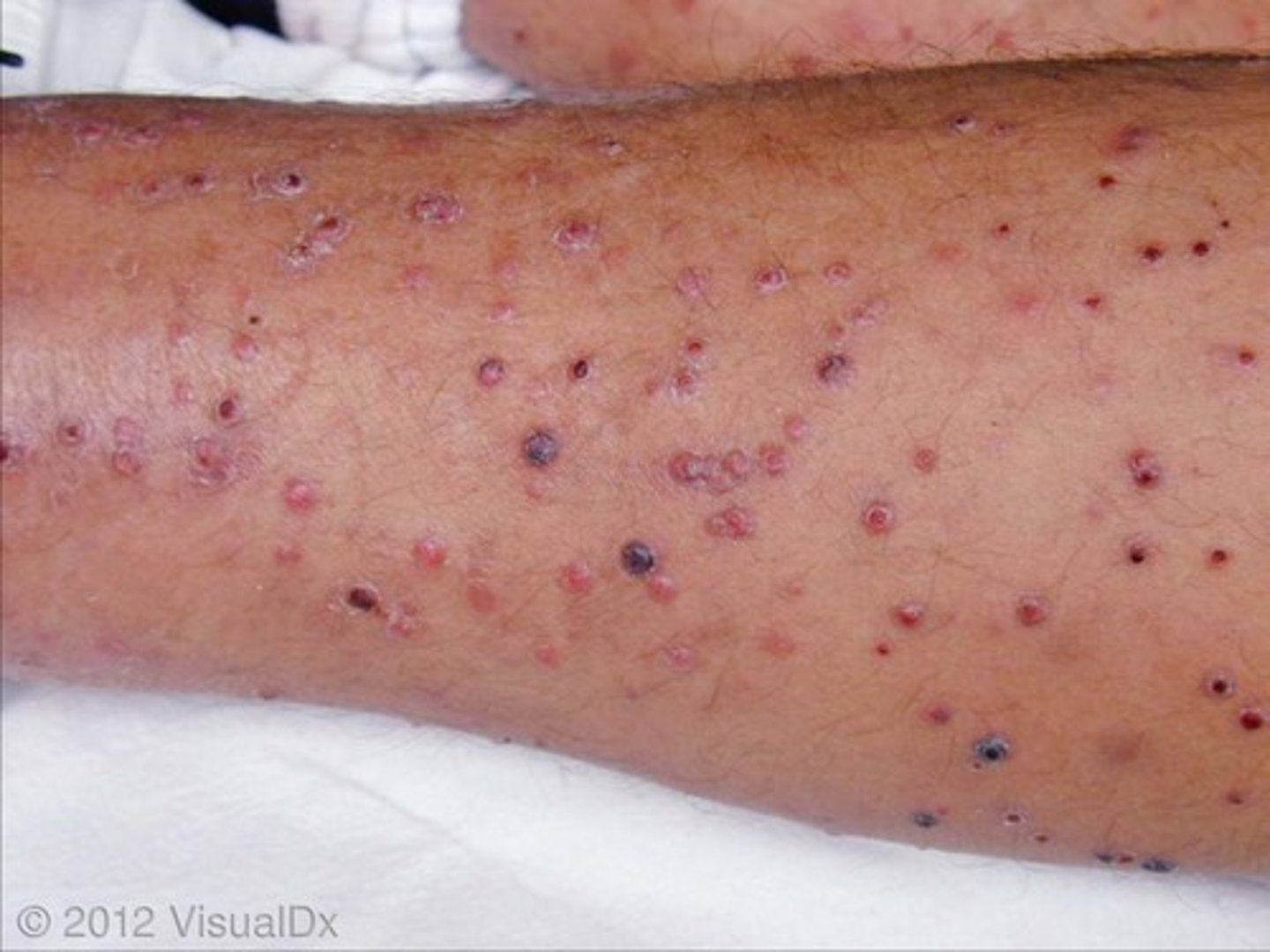
south american bartonellosis
AKA Carrionn's disease
-acute phase oroya fever to chronic phase verruga peruana with skin lesions
pattern of disease progression of Carrion Disease (bartonella baciilliformis)
Verruga peruana
-chronic form of Carrion's disease, present as skin lesion
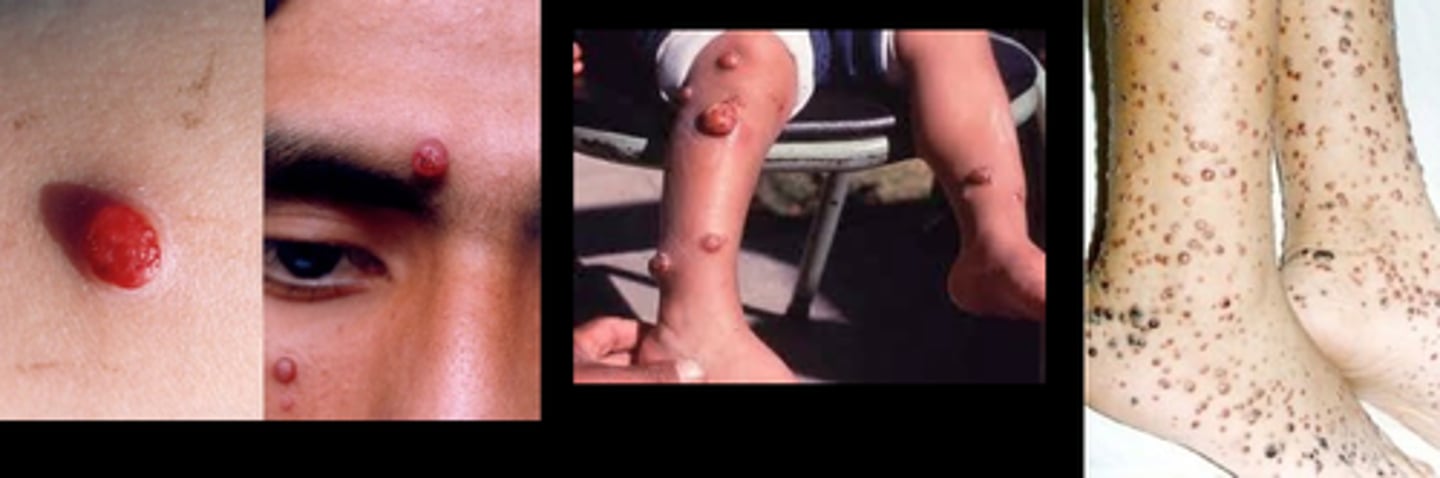
rocha-lima inclusions
characteristic lesions of verruga peruana on histology
toxin inactivating an inhibitory G protein, activates adenylate cyclase, increasing cAMP
Pertussis toxini causes lymphocytosis via
Bordatella pertussis
lymphocytosis indicating
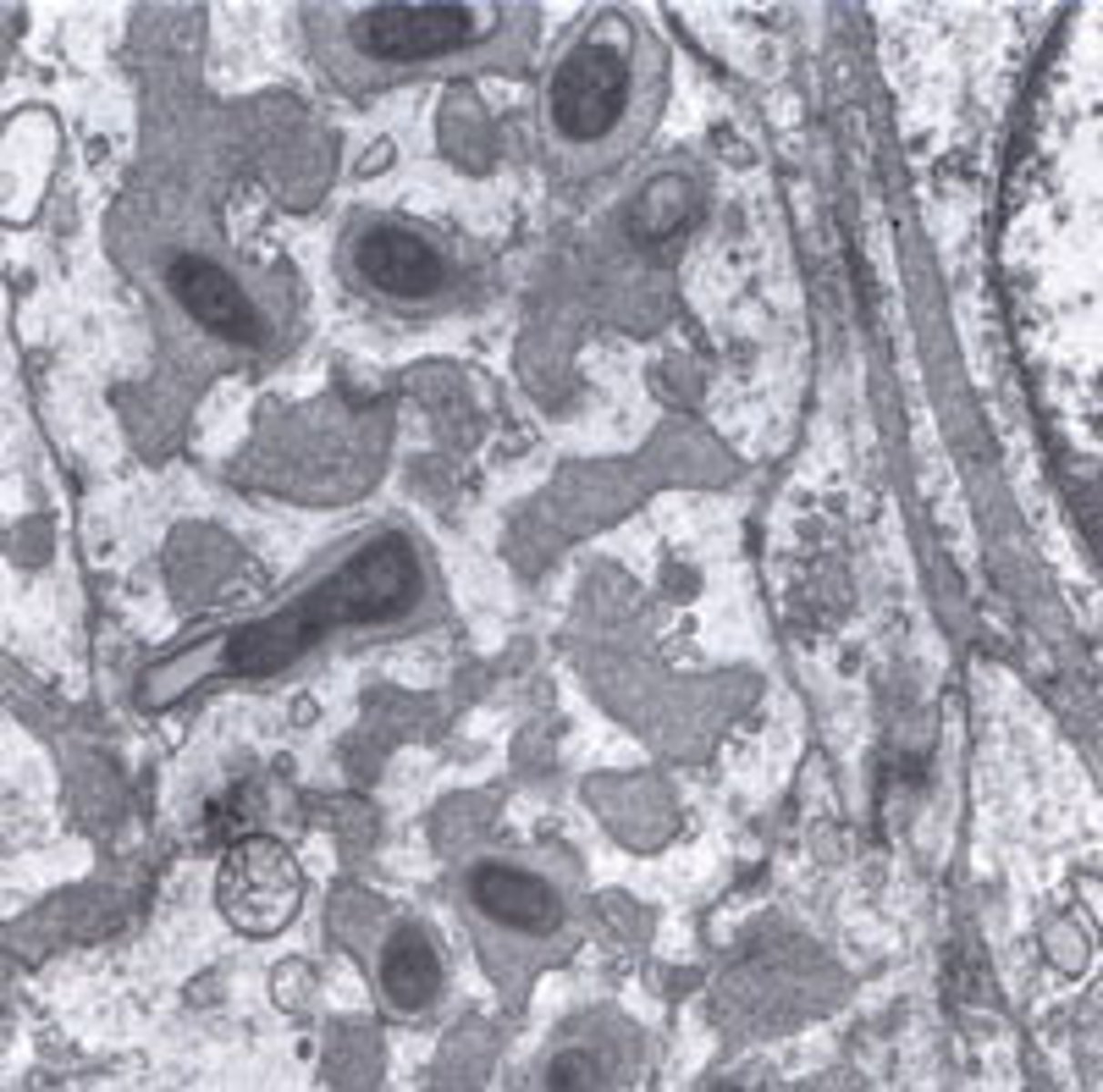
ananplasma phagocytophilum
an obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria, forms morulae
•Causes human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA)
new england, minnesota, wisconsin
geographic distribution of anaplasma phagocytophilum
Ixodes tick
principle vector of anaplasma phagocytophilum
-acute illness with flu-like symptoms
-•Usually less severe than E. chaffeensis infection
presentation of anaplasma phagocytophilum
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
•Obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria
•Causes human monocyte ehrlichiosis (HME)
•Amblyomma americana (lone star tick)
prinicipal vector of Ehrliichhia chaffeensis
Ehhrlichia chaffeensis
•More likely to be severe compared with Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection
-may see rash and neuro symptoms
Ehrlichia ewingii
•Obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria
•Infects granulocytes and causes ehrlichiosis
Amblyomma americanum (lone star tick)
principle vector of Ehrlichiia ewiingii
•Large anaerobic, gram-positive, spore-forming rod
genome of Clostridium perfingens
C. perfringens
-present as myonecrosis, usually due to trauma
-gas in the soft tissue
•hemolysis and interferes with neutrophil differentiation
May lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute kidney injury
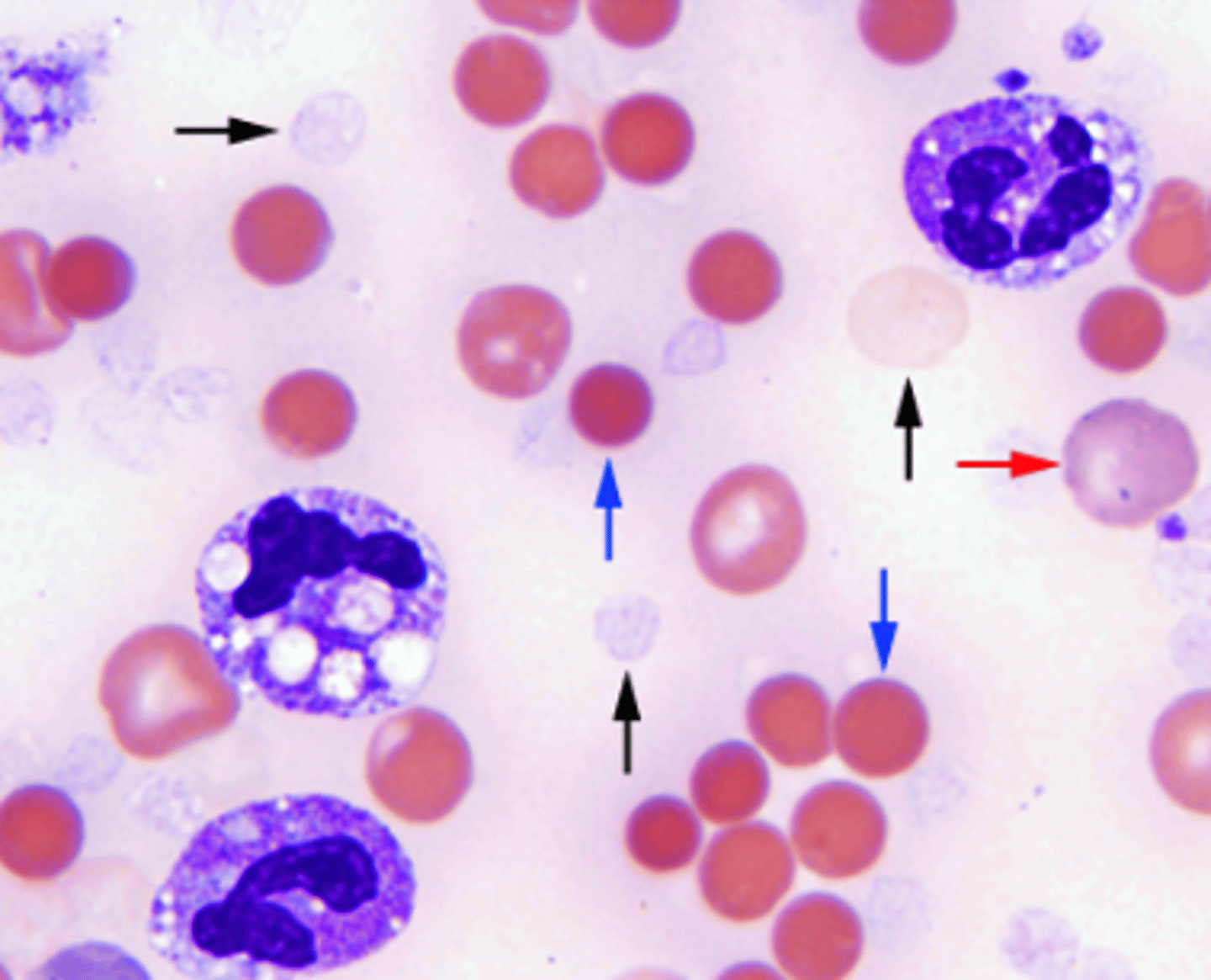
the alpha toxin of C. perfringens leads to
increased spherocytes and RBC ghosts (black arrow), and neutrophiils toxic granulation
blood smear of C. perfringens show
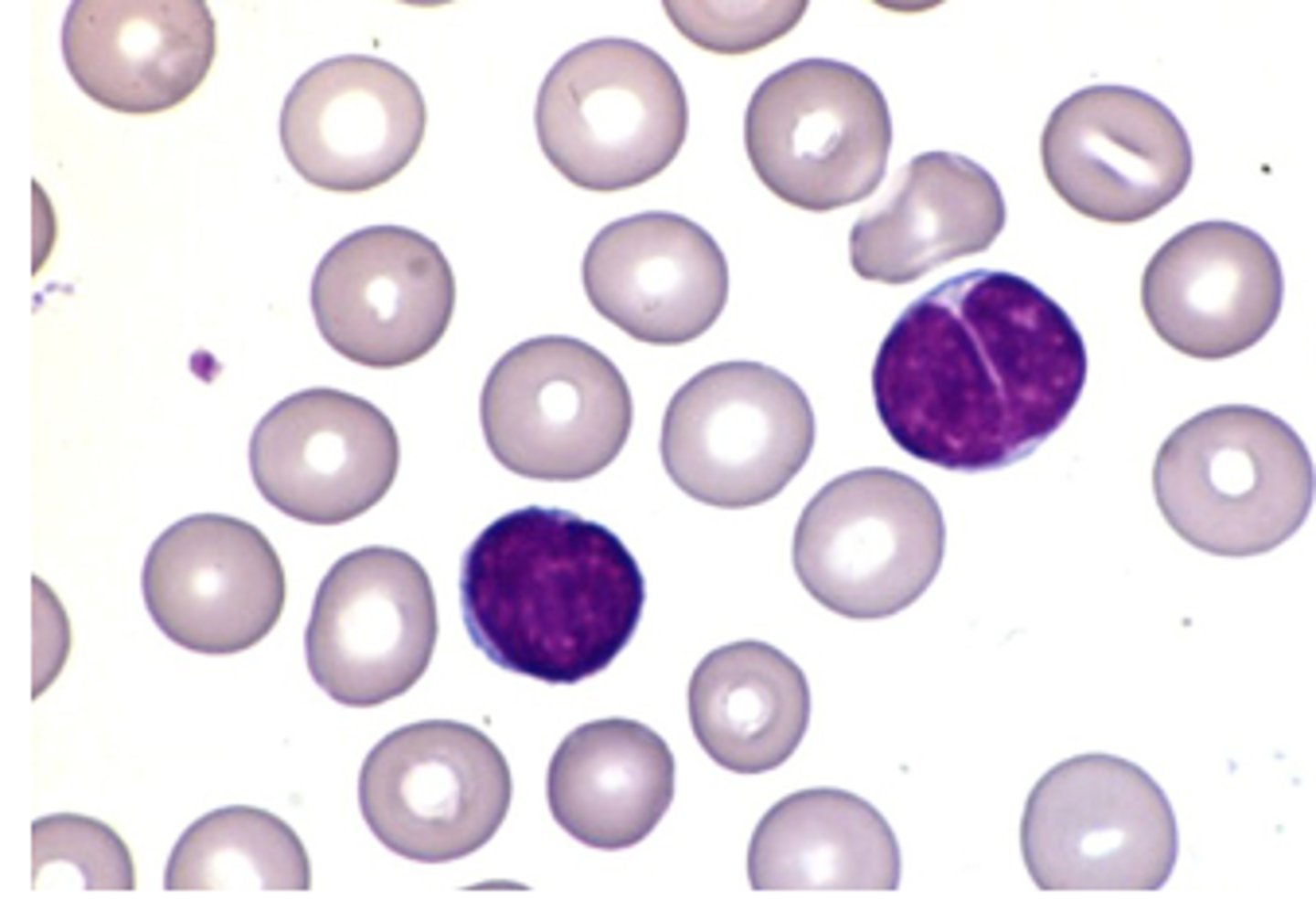
Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus
•Transmitted via breast-feeding, blood, or sexual contact
•Women 2x more likely to be infected
adult T cell leukemia-lymphoma
presents as:
•Widespread involvement of lymph nodes, peripheral blood, and/or skin
•Hypercalcemia, lytic bone lesions, skin lesions
CD4+
human T cell lymphotrophic viruss infect these cells
Tax proteini
in HTLV-1, this viral protein induces infeted cells to produce CCL22, which attracts CCR4-expressiinig CD4 cells
Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus
associated with flower cellss in peripheral blood
CD4+, CD25+, CD7-, CD8-
immunophenotypes of HTLV
-mono
-oral hairy leukoplakia, lymphoproliferative disorders, several malignancies
what are the various presentations of EBV
-EphA2 receptor of epithelial cells
-taragets B cells MHC class II protein, binds CD21
host cell receptor and target of EBV
heterophile antibodies, mostly IgM
antibodies produced by EBV infection of B cells
downey cells
-reactive lymphocytes that appear to hug RBC
-appear 1-3 weeks after onset of EBV
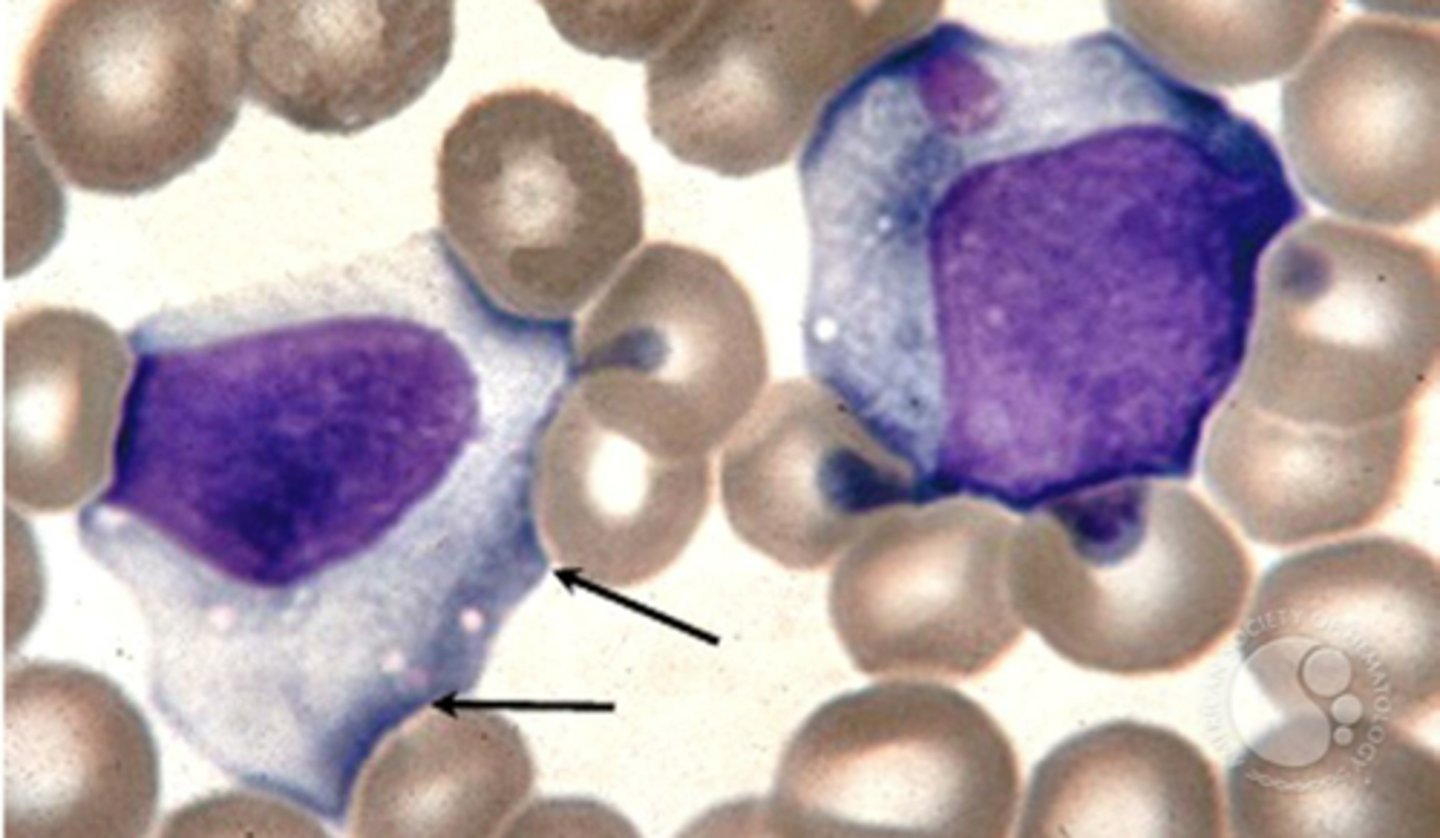
Lymphocytic infiltration
what causes the hepatosplenomegaly associated with EBV?
•lymphocytosis, atypical lymphocytes, elevated aminotransferases
hematologic findings associated with mononucleosis
Burkitt lymphoma
•Rapidly growing tumors in jaw or facial bones, primarily in children in malaria endemic regions
Burkitt lymphoma
histology shows starry sky pattern of histiocytes dispersed through basophilic tumor cells
•May include unexplained anemia, thrombocytopenia, or leukopenia
•Elevated LDH (tumor lysis syndrome)
•↑ EBV viral load
hematologic findings of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
CMV infection
presents like mono: cervical lymphadenopathy, tonsillitis less common than with EBV
•Heterophile antibody negative, owl's eye inclusions in infected cells, CMV IgM or IgG positive
hematologic findings associated with CMV
rocky mountain wood tick in mountains of western US and Canada
coltvirus is transmitted by
symptoms begin most commonly in May-July
most common season of coltvirus infection
•Biphasic fever, chills, headache, myalgia/arthralgia, fatigue, sometimes rash
•Leukopenia with both lymphocytes and neutrophils
presentation of coltivirus
parvovirus B19
the agent of erythema infectiosum
parvovirus B19
virus that can cause a transient aplastic crisis in pts with hematologic abnormalities--> severe anemia and related complications
lytic infection of erythroid precursors
cause of aplastic anemia in pts with parvo
parvovirus B19
-virus causing hydrops fetalis in pregnant women (abnormal fluid in fetal soft tissues)
-virus binds to P blood group antigen found on RBC and precursors
-viral replication leads to cell destruction, inhibiting erythropoiesis
pathogenesis of parvovirus B19
infected monocytes transport virus to muscle, joints, liver, and brain
pathogenesis of chikungunya virrus
Aedes mosquito
chikungunya virus is transmitted by
•Acute febrile illness, rash, arthralgia +/- swelling
•Some patients develop chronic arthritis
presentation of chikungunya virus
zika virus
virus infects neural cells and many other cell types
•Transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes, sex, maternal-fetal
transmission of zika virus
-most are asymptomatic
•Low grade fever, rash, arthralgia, conjunctivitis
•Strong association with Guillain-Barré syndrome
•Congenital infection can cause microcephaly and neurodevelopmental abnormalities
presentation of zika virus
anopheles mosquitoes
Plasmodium spp. is transmitted by
•Febrile illness with nonspecific flu-like symptoms
•Repeated bouts of chills and fever
•May have anemia and palpable spleen
presentation of plasmodium spp.
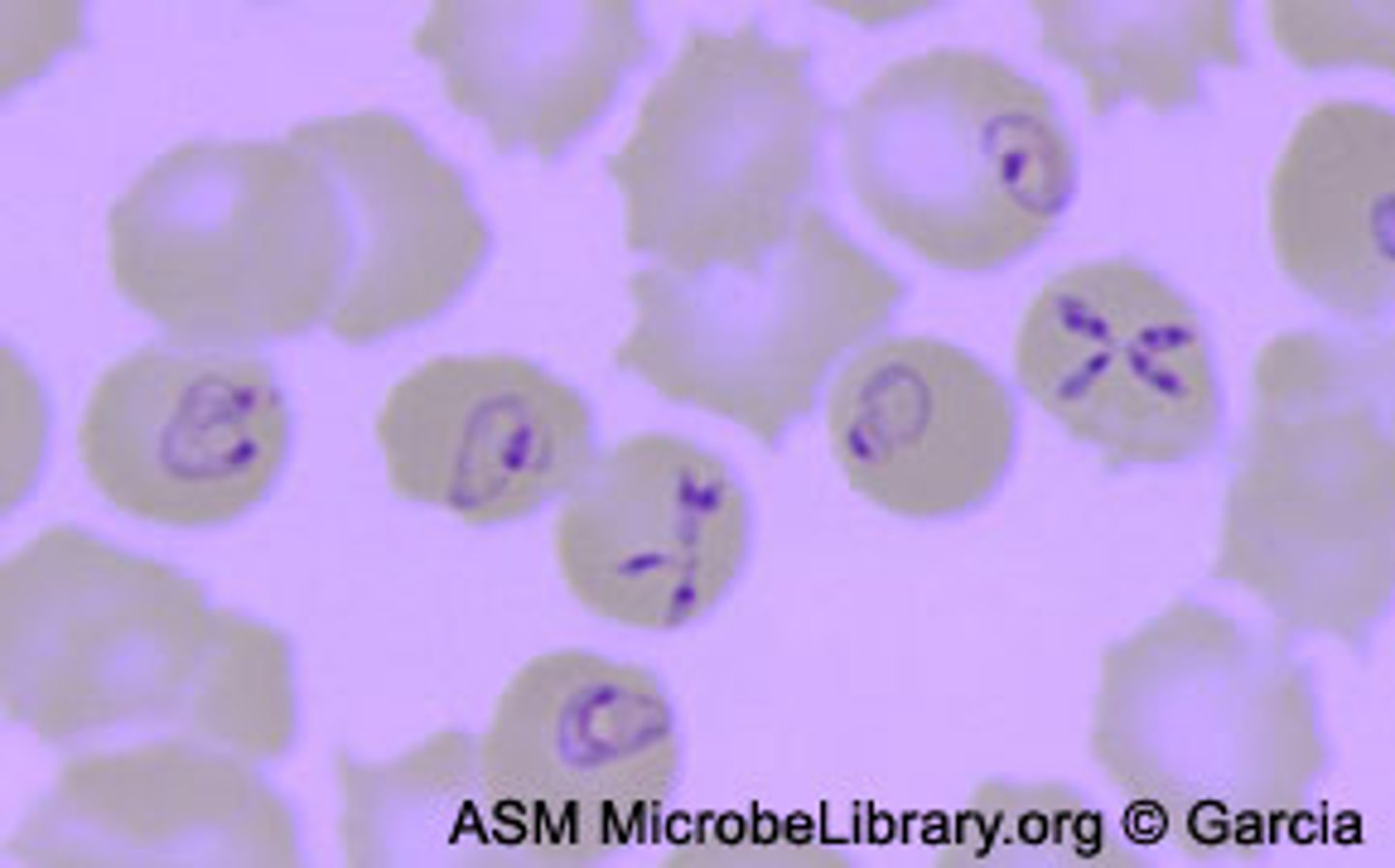
Hemozoin
plasmodium parasites make
when infected RBCs burst at the same time
what causes paroxysms in plasmodium inffection?
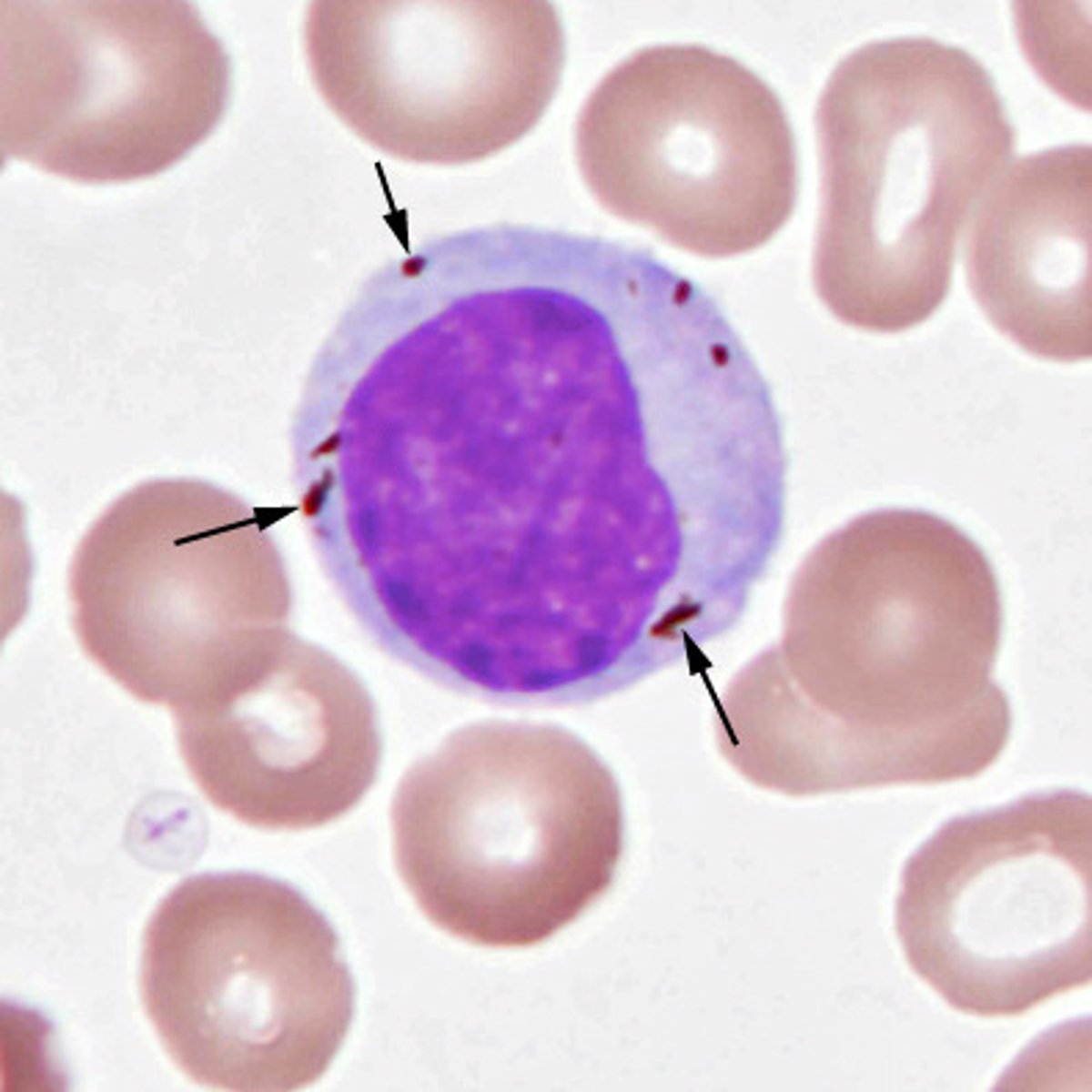
Babesia spp.
makes a maltese cross appearance of RBCs
ixodes ticks; most cases in the northeast
transmission of babesia
NO!
plasmodium does
do babesia deposit hemozoin in RBC?
ARDS
most common complication of babesia
sandflies
Leishmania donovani is transmitted by
-cutaneous leismaniasiis: painless ulcer
-mucocutaneous
-visceral/black fever
presentation of Leishmania donovanii
macrophages
leishmania replicate inside host __________
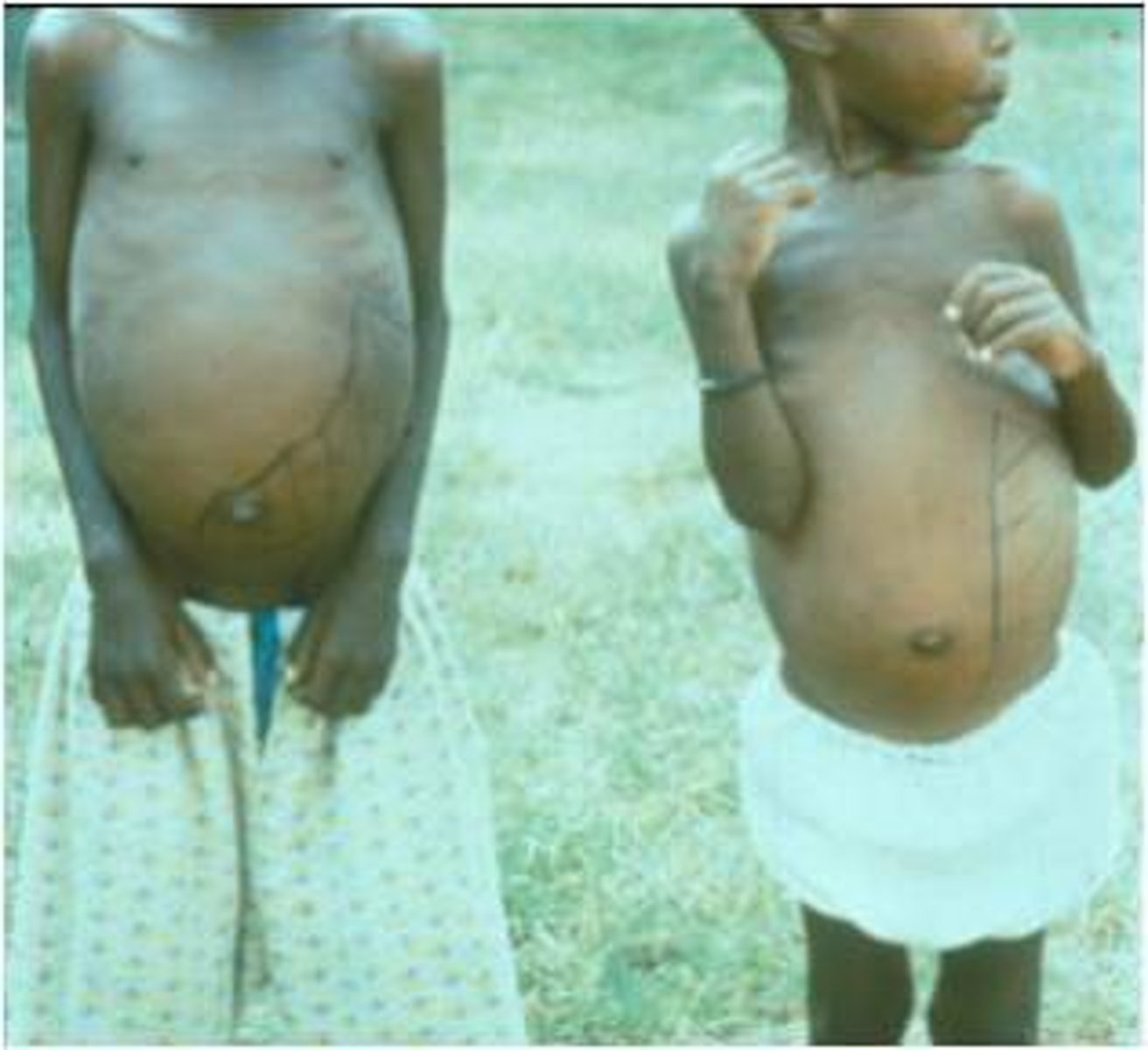
Visceral Leishmaniasis
•Parasites spread hematogenously to cells in liver, spleen, bone marrow, intestinal lymph nodes
Bartonella henselae
•cat scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis
Bartonella bacilliformis
•Oroya fever, verruga peruana
bartonella quintana
trench fever
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
•human granulocytic anaplasmosis
Ehrlichia chaffeensis
•human monocyte ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichia ewingii
ehrlichiosis
Clostridium perfringens
•foodborne illness, myonecrosis
HTLV1
•adult T cell leukemia-lymphoma, tropical spastic paraparesis
parvovirus B19
•erythema infectiosum, hydrops fetalis, transient aplastic crisis
zika virus
•milder dengue-like illness, congenital infection causes microcephaly
chikungunya viruss
•flu-like illness with rash and joint pain
hemolytic anemia
infections causing

lymphocytosis
infections causing

ehrichial/anaplasma
infections causing leukopenia
granulocyte
infected host cell off a. phagocytophilum
anaplasmosis: ixodes tick
ehrlichiosis: amblyomma americanum (lone star tick)
vector of Anaplasmosis vs ehrlichiosis
monocytes, macrophages
infected host cell of E. chaaffeensis
chikungunya
virus associated with SEVERE joint pain mainly in arms and legs, high ffeverr
zika virus
virus associated with red and white patchy skin rash
dengue viirus
virus associated with higher fever and more severe muscle pain