Physics units 1 - 2 Flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
What is the definition of Physics as a mathematical science?
Physics is a mathematical science because its concepts and principles have a mathematical basis.
2
New cards
What are the two categories of quantities in physics?
Quantities in physics are categorized as either vectors or scalars.
3
New cards
Define a scalar quantity.
Scalars are quantities that are fully described by a magnitude (or numerical value) alone.
4
New cards
Define a vector quantity.
Vectors are quantities that are fully described by both a magnitude and a direction.
5
New cards
What are examples of scalar quantities?
Examples include distance and speed.
6
New cards
What are examples of vector quantities?
Examples include displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
7
New cards
Explain the difference between distance and displacement.
Distance refers to how much ground an object has covered, while displacement refers to how far out of place an object is overall, including direction.
8
New cards
How can the journey of a physics teacher walking 4m East, 2m South, 4m West, and 2m North illustrate distance and displacement?
The teacher covers a distance of 12m but has a displacement of 0m, as the starting and ending points coincide.
9
New cards
What is speed?
Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, defined as the rate at which an object covers distance.
10
New cards
What is velocity?
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate at which an object changes its position, including direction.
11
New cards
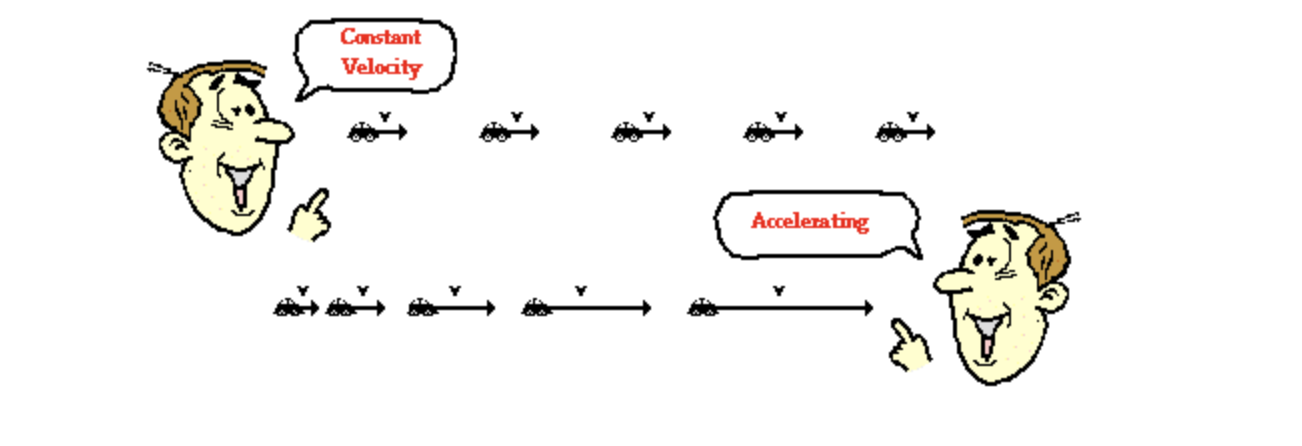
Describe the meaning of constant acceleration.
Constant acceleration occurs when an object’s acceleration remains the same over time.
12
New cards
What is average acceleration?
Average acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by the time it takes for that change to occur.
13
New cards
Why is distinguishing between speed and velocity important?
Speed does not provide information about direction, while velocity does, making it crucial for understanding motion in physics.
14
New cards
When is speed considered instantaneous?
Instantaneous speed refers to the speed of an object at a specific moment in time.
15
New cards
How do you calculate average speed?
Average speed can be calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
16
New cards
Explain the concept of instantaneous velocity.
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time, often determined through calculus.
17
New cards
What is the significance of the acceleration vector’s direction?
The direction of the acceleration vector indicates whether an object is speeding up or slowing down.
18
New cards
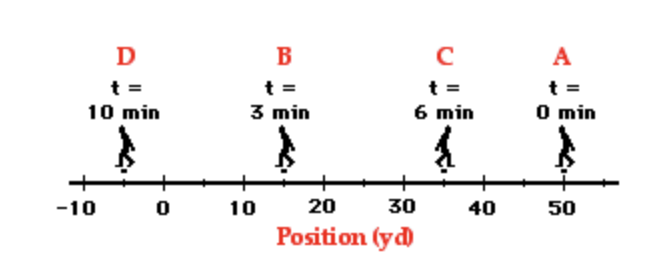
Illustrate a basic distance vs. displacement diagram
The distance is 95 while the displacement is -65
19
New cards
What does the slope of a position-time graph represent?
The slope of a position-time graph represents the velocity of an object.
20
New cards
In a velocity-time graph, what does the area under the graph represent?
The area under a velocity-time graph represents the displacement of the object.
21
New cards
What is a common misconception about acceleration?
A common misconception is that acceleration always means an object is speeding up; it can also mean slowing down or changing direction.
22
New cards
What is the formula for average acceleration?
Average acceleration is calculated using the formula
a_{avg}=\frac{\Delta v}{t}
or
a_{avg}=\frac{v_{f} - v_{i}}{t}
23
New cards
Why is direction important when discussing velocity and acceleration?
Direction is crucial as it affects whether the object is moving away from or toward a reference point.
24
New cards
How does one determine the direction of a velocity vector?
The direction of a velocity vector can be determined by its motion relative to a reference frame.
25
New cards
What happens to velocity when an object experiences negative acceleration?
When an object experiences negative acceleration, its velocity decreases.
26
New cards
How are speed and distance related mathematically?
Speed is defined as distance divided by time/
27
New cards
How are velocity and displacement related mathematically?
Velocity is defined as displacement divided by time.
28
New cards
What is the difference between total displacement and net displacement?
Total displacement refers to the straight-line distance from the starting point to the endpoint, while net displacement accounts for overall change in position including direction.
29
New cards
Provide a real-world example of constant acceleration.
A car accelerating from rest at a constant rate of 3 m/s².
30
New cards
How can you visually represent acceleration in a vector diagram?
An acceleration vector indicates the change in velocity over time, along with its direction.