water quality 🌊
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
science olympiad water quality :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
turbidity
measures the clarity or haziness of the water in a given body of water
NTU’s (nephelometric turbidity units)
comparison of the amount of light scattered by the suspended particles in the water
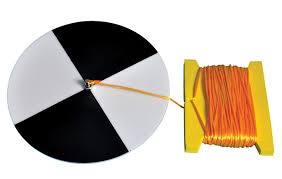
secchi disk
used to measure turbidity in a lake
DO (dissolved oxygen)
measures amount of gaseous oxygen dissolved in an aqueous solution
BOD (biochemical oxygen demand)
measures how fast organisms use up the oxygen in the water
phosphates
stimulate growth of water plants, too much causes excess algae and aquatic weeds using up large amounts of oxygen and causing aquatic organisms and fish to die
phosphorous cycle
recycles phosphorous in the form of phosphates for most life forms
total phosphorous test
measures all the forms of phosphorous in the sample (orthophosphate, condensed phosphate, and organic phosphate)
nitrogen
required for building proteins by all living plants and animals; inorganic forms include ammonia, nitrates, and nitrites
nitrates
stimulate growth of plants and algae in the water allowing for increased food, excess amounts cause algae to bloom wildly reduce oxygen levels for fish, usable form for acquatic plant growth, get into waterways from fertilizer and runoff
total solids
measures the suspended and dissolved solids in water
suspended solids
can be retained on a water filter and will settle to the bottom of a water column and include silt, clay, plankton, organic wastes, and inorganic precipitates; high concentration can reduce water clarity, impact turbidity, reduce light
dissolved solids
pass through a water filter and include calcium, bicarbonate, nitrogen, phosphorous, iron, and sulfur and other ions in the water; determines the flow of water in and out of the cells of aquatic organisms; many are essential nutrients
fecal coliform
live in the intestines of warm-blooded animals, found in feces excreted from humans, high numbers mean the water has received fecal matter from a source, may indicate presence of a disease
salinity
measures amount of salt in the water, high levels can adversely affect plant growth and water quality, sources include seawater intrusion, animal wastes, industrial wastes
biodegradable waste pollution
cause: humans, animals; symptoms: decreasing fish and acquatic life, increase in bacteria; effect: more bacteria, decreased oxygen; source: runoff, improperly treated effluent
nutrients pollution
cause: nitrates and phosphates; symptoms: green, cloudy, slimy, pungent water; effect: algae blooms, eutrophication of water source; source: over use of fertilizers, run-off from fields, improper disposal of containers
heat pollution
cause: increased water temperature; symptoms! warmer water, less oxygen, fewer aquatic organisms; effect: decrease in oxygen levels, death of fish and plants; source: industrial run-off, wastewater treatment
sedimentation pollution
cause: suspended particles settling out of water; symptoms: cloudy water, increased amount of bottom; effect: warms up water, decreases depth of water source, deposits toxins; source: construction sites, farming and livestock operations, logging, flooding, city runoff, dams
chemical pollution
cause: toxic and hazardous chemicals; symptoms: water color changes, develops and odor, aquatic life dies out; effect: kills aquatic life, can enter human food chain, birth defects, infertility, cancer, other diseases; source: human-made, improper disposal, runoff, dams, landfill leachate, acid rain
radioactive pollutants
cause: radioactive isotopes; symptoms: increased birth defects and cancer; effect: kills aquatic species and leads to cancer and death; source: waste water discharges from factories, hospitals, and uranium mines
medical pollution
cause: medicines, antibiotics; symptoms: infertility in aquatic organisms, unknown symptoms; effect: unknown; source: humans dumping medicines into water systems, wastewater treatment