Macroeconomics Chapter 8: The Federal Reserve System
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Federal Reserve System (the Fed)
Central bank of the US
Central bank
public authority that regulates a nation’s depository institutions and controls the quantity of money
Fed’s goals:
To moderate the business cycle and contribute toward achieving long-tern growth by keeping inflation in check and maintaining full employment
In pursuit of its goals, the Fed pays close attention to
Federal funds rate
Federal funds rate
the interest rate that banks charge each other on overnight loans of reserves
Key elements in the structure of the Fed
The Board of Governors - 7 members, The 12 regional Federal Reserve banks, The Federal Open Market Committee
The Board of Governors (pt.1)
7 members appointed by the president of the US and confirmed by the Senate, board terms are for 14 years and terms are staggered so that one position becomes vacant every 2 years
The Board of Governors (pt.2)
The president appoints one member to a renewable four-year term as chairman, each of the 12 Federal Reserve Regional Banks has a 9 board of directors and a president
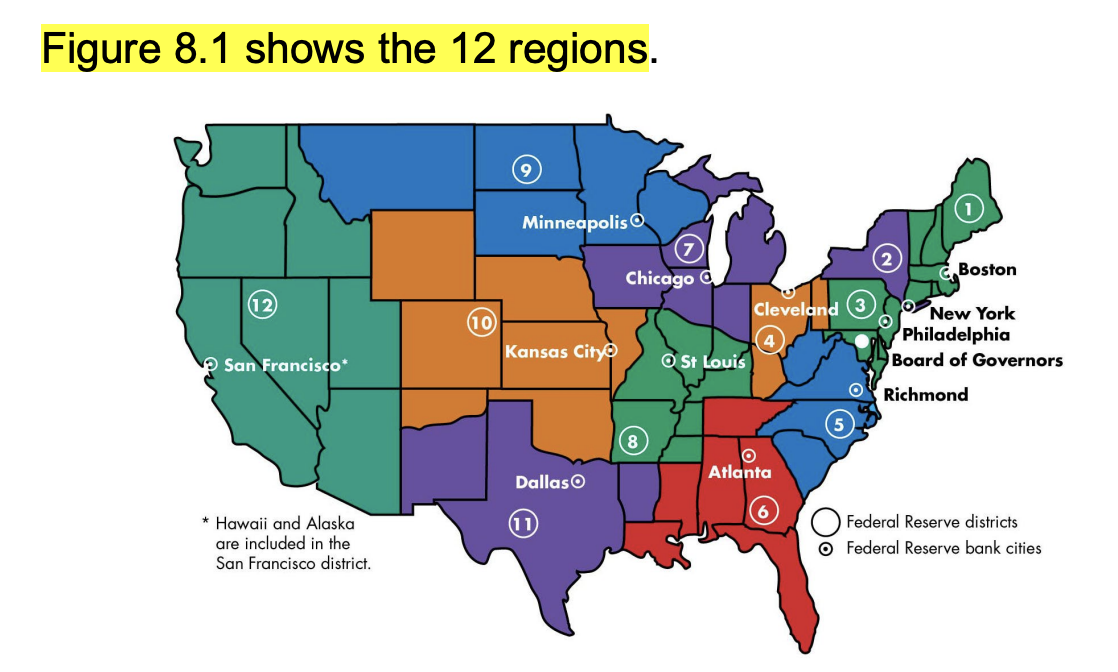
The 12 regions
The Federal Open Market Commitee (FOMC)
the main policy-making group in the Federal Reserve System
FOMC consists
members of Board of Governors, president of Fed Reserve bank of NY, 11 presidents of other regional Fed reserve banks of whom (on a rotating basis) 4 are voting members,
FOMC meets
every 6 weeks to formula monetary policy
Chair of the Board of Governors
Jerome Powell who has the largest influence on the Fed’s policy
Jerome Powell controls
the agenda of the Board and is the Fed’s spokesperson and point of contact with federal government and with foreign central banks and governments
The Fed influences the economy
through the size and composition of its balance sheet
Balance sheet
the assets that the Fed owns and the liabilities that it owes
The Fed’s two main assets
U.S. government securities and mortgage-backed securities
The Fed’s two liabiltiies
Currency and reserves of depository insitutions
Monetary base
The Fed’s total liabilities (currency and depository institutions’ deposits at the Fed)
Fed’s three main policy tools
Open market operations, last resort loans, required reserve ratios