Chapter 12 Options
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
OPTION TERMINOLOGY
Is the buyer of an options contract long or short?
Does the buyer pay or receive the premium on a contract?
Is the premium the buyers max gain or max loss?
Long
Pay
Max loss
Is the seller of an options contract long or short?
Does the seller pay or receive the premium on a contract?
Is the premium the sellers max gain or max loss?
Short
Receive
Max gain
What does a call option provide?
It give the owner the right to purchase the security and the seller the obligation to deliver the security at the agreed upon strike price
What does a put option provide?
It give the owner the right to deliver the security and the seller the obligation to purchase the security at the agreed upon strike price
What does a class of options mean?
Provide an example?
What is a series?
Provide and example?
A class means they are all of the same underlying asset and direction
GE calls are one class and GE puts are another
Represents all options of the same class with the same expiration and price
GE Jan 140 calls is a single series while GE Jan 150 calls is a separate series
What is a covered versus an uncovered option?
Which is more risky?
If the seller of an option already owns the underlying asset they may need to deliver they are covered, if not then they are uncovered
Uncovered option writing is far more risky
Explain the following option listing?

Long: This means that the investor is the buyer of the contract
1: They bought 1 contract which is worth 100 underlying shares
XYZ: This is the underlying security
May: This is the month the option expires
30: This is the strike price the buyer is able to buy the underling asset at
Call: Signifies this is a call option
3: This is the “insurance fee” the investor is paying to have the rights to the contract, it is multiplied by 100 ($300)
What day of the month do options contracts expire?
What are the timelines for that day?
The 3rd Friday
At 4:00PM trading stops, 5:30PM the exercise instructions need to be issued, 11:59 the contract officially expires
When does an options contract have intrinsic value?
Is there ever negative intrinsic value?
When the options contract is in the money
No, the contract would just have no intrinsic value
What is time value?
When is there more time value?
This is the portion of an options premium that exceeds the intrinsic value
There is more time value when there is more time till its expiration
What is the options premium formula?
Option premium = Time Value + Intrinsic value
What is the main factor in determining if an option contract is in, at, or out of the money?
This is determined by the underlying securities market price, in relation to the strike price
For a call option when is the option…
In the money?
At the money?
Out of the money?
In the money: The stock’s market price is above the strike price
At the money: The stock’s market price is equal to the strike price
Out of the money: The stock’s market price if below the strike price
For a put option when is the option…
In the money?
At the money?
Out of the money?
In the money: The stock’s market price is below the strike price
At the money: The stock’s market price is equal to the strike price
Out of the money: The stock’s market price if above the strike price
If an options contract has a premium, but is out of the money, what kind of value does it have?
Only time value, there is no intrinsic value
Let’s assume the XYZ May 30 call has a premium of 3 at a time when the stock is trading at $32 per share, provide a breakdown of the value here?
There is $2 of intrinsic value and another $1 of time value
If there is intrinsic value, does this guarantee profitability?
No, there can be intrinsic value, but if it does not exceed the premium as well (past the breakeven), then it still is not profitable
BREAKEVEN
What is the breakeven point?
This is the point where the underlying stock must be trading so that the investor does not make or lose money, inclusive of the premium
What does the breakeven mean to the buyer?
What does it mean to the seller?
For the buyer, it is the the amount they need the underlying stock to move in their favor to make back the premium they paid
For the seller, it is the amount they can afford the underlying stock to move against them before they begin losing money
ADJUSTMENTS TO AN OPTION CONTRACT
What happens if a stock split or stock dividend occurs?
What if it is a cash dividend?
The number of options contracts or underlying shares is changed and the exercise prices adjusts proportionately
There is no change
What is an even stock split?
How does this effect the option ownership?
This is when the company does something for 1, could be 2 for 1 or 3 for 1
There would be an increase in the number of option contracts the investor owns and a decrease in the exercise price
Even Stock Split Example

What is an odd stock split?
How does this effect the option ownership?
This is when the company does an uneven stock split like 3 for 2 or 5 for 4
There will be an increase to the number of underlying stock per contract, and the exercise price will adjust proportionately
Odd Stock Split Example

What happens when a company does a reverse stock split?
How does this effect the option ownership?
The company tries to raise their price by merging shares
There will be a reduction in the number of underling shares per contract and an increase in the exercise price of the contract
Reverse Stock Split Example
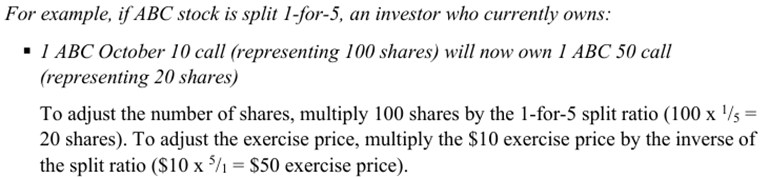
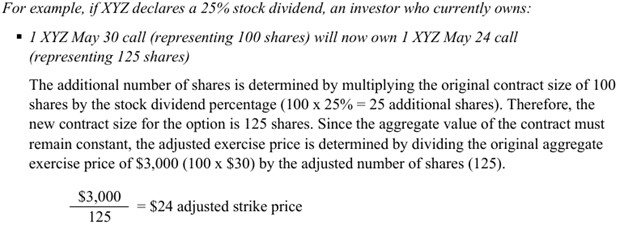
What happens when a company does a stock dividend?
How does this effect the option ownership?
Company issues additional stock to shareholders in the form of a dividend
There will be an increase to the number of underlying stock per contract, and the exercise price will adjust proportionately (same as odd stock split)
Stock Dividend Example
THE OPTIONS CLEARING CORPORATION
What does the Options Clearing Corporation do?
When a customer of a BD enters into an option contract, how long does the BD have to settle with the OCC?
They act similar to GSCC, they guarantee the other end of the transaction and eliminate counter party risk
Must be done within 1 business day
What is a position limit?
What is an exercise limit?
The OCC and the options exchanges limit the number of contracts a single investor or group of investors acting together can accumulate on the same underlying security
It is the max number of contracts that can be exercised within 5 consecutive business days
Do these limitations apply to trades that are on the same side on the market?
Yes
Bullish: Long calls and short puts
Bearish: Short puts and long calls
Long-Term Equity Anticipation Securities
What are LEAPS?
Long term options contracts with expirations up to 39 months
What are the advantages to these?
Lose time value slower
Provide a longer term horizon to participate in price changes
OPTION EVENTS
What does it mean to liquidate an options contract?
If I opened a long position what would need to be done?
If I opened a short position what would need to be done?
The buyer or the seller can liquidate a position by executing the opposing transaction
I would need to sell the equivalent contract
I would need to buy the equivalent contract
When liquidating a contract what needs to be marked on the ticket?
When trading in and out of option contracts, they need to be marked as “opening a new position” and “closing a previously opened position”
They may also be marked at buy or sell depending on the direction of the contract
Who has the right to exercise an option contract?
If a contract is exercised, how long does it take for the underlying stock settle?
The buyer of the contract
One business day
What is American option exercise?
What is European option exercise?
American: May be exercised at any time up to the day they expire
European: May only be exercised at a specified point in time, usually on expiration
Why would a contract owner let an option expire?
Who makes money when a contract expires?
If there is no value, there is no point in exercising
The seller receives the premium
OPTIONS STRATEGIES
Why might an investor buy a call?
What is the max profit?
What is the max loss?
How would you find the breakeven?
Allows for bullish speculation on a stock with leverage
Unlimited, stock could go to infinity
The premium paid to the seller
Take the strike price and add the premium
Why might an investor sell a call?
What is the max profit?
What is the max loss?
How would you find the breakeven?
They believe the stock price will remain the same or decrease (bearish)
The premium that is paid by the buyer
Could be infinite if the position is uncovered
Strike price plus premium, same as buying a call
Can selling calls uncovered be done in any account?
No, it is just as risk as taking a short position so they can only be done in margin accounts
Why might an investor buy a put?
What is the max profit?
What is the max loss?
How would you find the breakeven?
The investor would be bearish and believes the stock will decline in value
It is limited to if the stock plummets to $0
The premium paid
Strike price minus the premium paid
Why might an investor sell a put?
What is the max profit?
What is the max loss?
How would you find the breakeven?
An investor is bullish on the stock and wants to generate some income
The premium that was received from the buyer
If the stock price drops to $0 (would be the strike price minus the premium)
Strike price minus the premium amount
MULTIPLE OPTION STRATEGIES
What is an option straddle?
Involves simultaneously buying and selling a call/put together
Buying a call and put together
Selling a call and put together
What is a long straddle?
Why would an investor buy this?
This is buying a call and put together
They are speculating in a lot of price movement, direction doesn’t matter, just volatility
What needs to be accounted for in a long straddle in terms of premium and breakeven?
Provide an example?
There are now 2 premiums being paid and both will need to be recovered for the breakeven point
EX: If I buy a call with a premium of 3 and put with a premium of 2, my new break even is 5
What is the maximum gain for each leg of a long straddle?
What is the max loss of a long straddle?
If the stock moves in favor of the call it will be infinite
If the stock moves in favor with the put, it will be if the stock goes to $0
The premiums paid on both legs
What is a short straddle?
Why would an investor buy this?
The sale of a call and put simultaneously
They are expecting the stock to remain stable, not bullish or bearish
What needs to be accounted for in a short straddle in terms of premium and breakeven?
Provide an example?
There are now 2 premiums being received which gives the seller room in either direction
EX: If I buy a call with a premium of 3 and put with a premium of 2, my new break even is 5
What is the maximum gain for each leg of a short straddle?
What is the max loss of a short straddle?
The premium received for both legs
If the stock moves in favor of the call it will be infinite
If the stock moves in favor with the put, it will be if the stock goes to $0
What is a combination straddle?
A straddle where the two legs have different strikes and/or different expirations
SPREADS
What is a spread trade?
What is the point of a spread trade?
The purchase and sale of a call or put
Allows the minimization of losses but also profits
How do you identify the dominant leg?
When is an investor a buyer?
Seller?
It is the leg with the larger premium
The buy leg is dominant
The sell leg is dominant
What is a call spread?
What is a put spread?
Both legs are calls
Both legs are puts
What is a price spread?
Are these vertical or horizontal?
Both options have the same expirations but different strike prices
Vertical
What is a time spread?
Are these vertical or horizontal?
Both options have the same strike price but different expirations
Horizontal

What is a diagonal spread?
When both legs have different strikes and expiration months

NET CREDIT SPREADS
What is the net premium in a spread trade?
Since the investor is buying and selling options, they are both paying and receiving premiums so it is the difference between the two
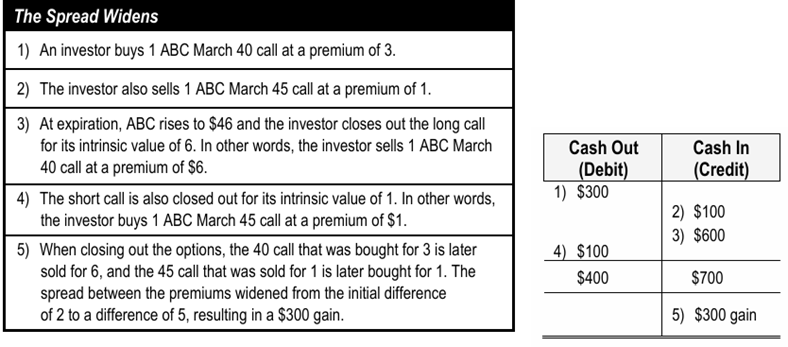
What is a net debit spread?
When does this occur?
This is when the investor pays more in premium then they receive
The buy leg is dominant (has larger premium)
In a net debit spread, does the investor want the spread to widen or narrow?
Why?
They want the spread to widen
Since I now own the leg i paid more for in the beginning, i would want the spread to increase, so the value foes up, then I could sell for a larger profit and make back my net debit from the initial transaction
How do you find the breakeven point for call spreads?
How do you find the breakeven point for put spreads?
(Same for Credit/Debit Spreads)
(Probably don’t need to memorize, just know how to do the math in an example to figure out)
Lower strike + the net premium
Higher strike - the net premium
What is the maximum gain?
What is the maximum loss?
(Probably don’t need to memorize, just know how to do the math in an example to figure out)
The max gain will be limited by the non-dominant leg, the investor will be profitable past the breakeven but only up until the strike of the non-dominant
The difference in strikes minus the net premium paid
The net premium paid
Net debit example?
NET CREDIT SPREADS
What is a net credit spread?
When does this occur?
This is when the investor receives more in premium then they pay
The sell leg is dominant (has larger premium)
In a net credit spread, does the investor want the spread to widen or narrow?
Why?
Narrow
If the spread narrows to zero where they are trading for the same premium, you can close out both positions and keep the initial premium received as profit
How do you find the breakeven point for call spreads?
How do you find the breakeven point for put spreads?
(Same for Credit/Debit Spreads)
(Probably don’t need to memorize, just know how to do the math in an example to figure out)
Lower strike + the net premium
Higher strike - the net premium
What is the maximum gain?
What is the maximum loss?
(Probably don’t need to memorize, just know how to do the math in an example to figure out)
The net premium
The difference between strike prices minus the net premium
SPREAD STRATEGIES/TIPS
What should be the first thing done when assessing a spread?
What is the dominant leg?
Identify the dominant leg
The leg with the higher premium
How could you find the dominant leg is the question does not mention premiums?
The lower strike price call spread will have a higher premium
The higher strike put spread will have a higher premium
BUTTERFLY SPREADS
What is a butterfly spread trade?
Which way do the legs face, bullish or bearish?
This is when two spreads are established simultaneously
One spread is bullish while the other is bearish
What is the point a butterfly trade?
The investor is looking for neutrality, they benefit if the stock price stays stable
What is the breakeven point?
There are two break even points since there are two spreads placed
What is a downside to the butterfly trade?
There can be high commissions due to the multiple positions that need to be placed
USING OPTIONS AS A HEDGE (PROTECTION)
What is the long stock + long put method?
What does it do?
This is when the investor has a long cash stock position and also purchases a put
It provides protection to the investor if the stock moves to the downside
How does buying a protective put effect the customer’s basis?
They are now not only paying for the stock but also the premium
What is the short stock + long call method?
What does it do?
This is when the investor has a short cash stock position and also purchases a call
It provides protection to the investor if the stock moves to the upside
How does buying a protective call effect the customer’s basis?
They need to account for the premium on the call when calculating net profits and loss
USING OPTIONS TO GENERATE INCOME
How are options used to generate income?
Investors may use their current long/short positions to sell calls against them to generate income off of the premiums
What is a Long Stock + Short Call method?
What is another name for this?
This involves owning the underlying stock cash position while simultaneously selling a call
Covered call writing
What is a limitation to covered call writing?
What does it do?
It limits the potential returns if the stock moves to the upside
As long as the stock price does not move above the breakeven during the option contracts life, the seller will get the premium
What is the breakeven for the seller of the covered call?
What is the maximum gain?
What is the maximum loss?
It is the price they bought the cash stock position at minus the premium they received
The capital gains up to the strike price of the contract plus the premium received
If the stock goes to $0 minus whatever they receive in premium
Is the covered call writer bullish or bearish?
They would be mildly bullish during the life of the option since they want the stock to go up but only to a certain point
What is ratio writing?
What is an advantage to this?
What is a disadvantage to this?
This is an aggressive covered call writing strategy where there is an unequal number of calls written against the long position
It give the seller the opportunity to double their income on premiums
The seller is now open to unlimited losses since both calls sold are not covered
How do you find the breakeven of a ratio?
What is the max gain?
What is the max loss?
Take the purchase price of the stock and subtract the premiums received
The difference between the strike price of the call sold and the price the securities were purchased at plus the premiums received
Since the investor is uncovered on one of the calls, it is unlimited
What is a Short Stock + Short Put method?
What is another name for this?
This is when an investor sell stock short and also sells a put
Covered put writing