Chapter 10: Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
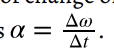
angular acceleration
the rate of change of angular velocity with time
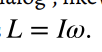
angular momentum
the product of moment of inertia and angular velocity
change in angular velocity
the difference between final and initial values of angular velocity
kinematics of rotational motion
describes the relationships among rotation angle, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and time
law of conservation of angular momentum
angular momentum is conserved, i.e., the initial angular momentum is equal to the final angular momentum when no external torque is applied to the system
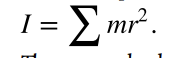
moment of inertia
mass times the square of perpendicular distance from the rotation axis; for a point mass, it is I=mr2 and, because any object can be built up from a collection of point masses, this relationship is the basis for all other moments of inertia
right-hand rule
direction of angular velocity ω and angular momentum L in which the thumb of your right hand points when you curl your fingers in the direction of the disk’s rotation
rotational inertia
resistance to change of rotation. The more rotational inertia an object has, the harder it is to rotate
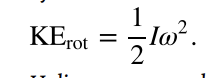
rotational kinetic energy
the kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object. This is part of its total kinetic energy
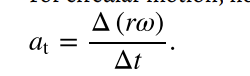
tangential acceleration
the acceleration in a direction tangent to the circle at the point of interest in circular motion
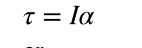
torque
the turning effectiveness of a force
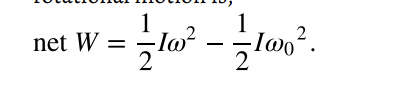
work-energy theorem
if one or more external forces act upon a rigid object, causing its kinetic energy to change from KE(1) to KE(2) , then the work W done by the net force is equal to the change in kinetic energy