T/F MCQs FINAL Gen. Path.
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Is it true that: Disease is a significant disturbance of the homeostasis due to changes in the environment or disturbance in the rebound response of the individual.
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that: Disease is a significant disturbance of the homeostasis due to changes in the environment or disturbance in the rebound response of the individual.
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that: Health is a state of imbalance of the organism with the external environment which doesn’t allow it to realize its biological potential
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that: Health is a state of imbalance of the organism with the external environment which doesn’t allow it to realize its biological potential
a) yes
b) no
Is it correct that etiology studies the causes of the diseases?
a) yes
b) no
Is it correct that etiology studies the causes of the diseases?
a) yes
b) no
Is it correct that pathogenesis studies the mechanisms of healing from a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it correct that pathogenesis studies the mechanisms of healing from a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that morphogenesis studies the consequences of structural changes in the course of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that morphogenesis studies the consequences of structural changes in the course of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Morphogenesis -a series of local structural changes in the course of' a disease.
Is it true that sanogenesis studies the mechanisms of development of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that sanogenesis studies the mechanisms of development of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that tanatogenesis studies the changes which occur in the process of death?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that tanatogenesis studies the changes which occur in the process of death?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that pathomorphosis studies the microscopic and gross changes in the course of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that pathomorphosis studies the microscopic and gross changes in the course of a disease?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that cytology is a slow and very informative method?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that cytology is a slow and very informative method?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that biopsy is a slower method but gives maximum information and allows more tests to be done like genetics?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that biopsy is a slower method but gives maximum information and allows more tests to be done like genetics?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Van Gieson stain proves collagen fibres that stain in red.
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Van Gieson stain proves collagen fibres that stain in red.
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that PAS reaction is used to prove glycogen which stains in yellow?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that PAS reaction is used to prove glycogen which stains in yellow?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Sudan III is used to prove lipids and they stain in orange?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Sudan III is used to prove lipids and they stain in orange?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Sudan IV is used to prove lipids and they stain in red?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Sudan IV is used to prove lipids and they stain in red?
a) yes
b) no
Stainings to prove lipids are: Sudan llI. Oil red - red Scharlactor - in red; Sudan IV or with osmic acid - in black:
Is it true that Perls reaction is used to prove hemosiderin which stains in (Prussian) blue?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Perls reaction is used to prove hemosiderin which stains in (Prussian) blue?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Toluidine Bleu stain used to prove glucosaminoglycans and the tissue demonstrates metachromasia in pink-violet color?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Toluidine Bleu stain used to prove glucosaminoglycans and the tissue demonstrates metachromasia in pink-violet color?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Congo red is used to prove hyaline which stains in “brick red” and shines like “a green apple” on a polarized light?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that Congo red is used to prove hyaline which stains in “brick red” and shines like “a green apple” on a polarized light?
a) yes
b) no
Congo red is for AMYLOID staining, the description of the test results for it is as above but the question says hyaline!
Do intracellular accumulations depend on the type and intensity of the injurious stimuli?
a) yes
b) no
Do intracellular accumulations depend on the type and intensity of the injurious stimuli?
a) yes
b) no
Is it possible that a tattoo can lead to enlargement and inflammation of the local lymph nodes?
a) yes
b) no
Is it possible that a tattoo can lead to enlargement and inflammation of the local lymph nodes?
a) yes
b) no
Exogenous pigments are divided into organic and nonorganic.
a) yes
b) no
Exogenous pigments are divided into organic and nonorganic.
a) yes
b) no
Endogenous pigments are divided into hemoglobinogenous and non-hemoglobinogenous
a) yes
b) no
Endogenous pigments are divided into hemoglobinogenous and non-hemoglobinogenous
a) yes
b) no
Hemoglobinogenous pigments are divided into iron-containing and non-iron containing.
a) yes
b) no
Hemoglobinogenous pigments are divided into iron-containing and non-iron containing.
a) yes
b) no
Bilirubin is iron-containing pigment.
a) yes
b) no
Bilirubin is iron-containing pigment.
a) yes
b) no
Hemosiderin is non-iron-containing pigment.
a) yes
b) no
Hemosiderin is non-iron-containing pigment.
a) yes
b) no
Melanin, lipofuscin and adrenochromes are endogenous hemoglobinogenous pigments.
a) yes
b) no
Melanin, lipofuscin and adrenochromes are endogenous hemoglobinogenous pigments.
a) yes
b) no
Hepatocellular jaundice can be seen in malaria and some types of anemia.
a) yes
b) no
Hepatocellular jaundice can be seen in malaria and some types of anemia.
a) yes
b) no
Obstructive jaundice can be seen in cancer of the head of pancreas and in choledocholithiasis
a) yes
b) no
Obstructive jaundice can be seen in cancer of the head of pancreas and in choledocholithiasis
a) yes
b) no
Hemolytic jaundice is seen in acute hepatitis and in mushroom poisoning.
a) yes
b) no
Hemolytic jaundice is seen in acute hepatitis and in mushroom poisoning.
a) yes
b) no
Is sclerosis the end stage of fibrosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is sclerosis the end stage of fibrosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that cirrhosis doesn’t cause deformation of the affected organ?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that cirrhosis doesn’t cause deformation of the affected organ?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that fibrinoid necrosis damages the fibrillary structures of the extracellular matrix but also the cells in the focus?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that fibrinoid necrosis damages the fibrillary structures of the extracellular matrix but also the cells in the focus?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that fibrosis is only a physiological process and cannot lead to organ deformation and dysfunction?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that fibrosis is only a physiological process and cannot lead to organ deformation and dysfunction?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that grossly, uric acid crystals are white painful nodules on the skin, usually on the extensor surfaces on the extremities
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that grossly, uric acid crystals are white painful nodules on the skin, usually on the extensor surfaces on the extremities
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that the capacity of cell proliferation is the most important factor for the development of hypertrophy or hyperplasia?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that the capacity of cell proliferation is the most important factor for the development of hypertrophy or hyperplasia?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that dysplasia means that cancer has already developed?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that dysplasia means that cancer has already developed?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that dysplasia can be found together with cancer?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that dysplasia can be found together with cancer?
a) yes
b) no
Is thrombus formation possible in the heart cavities?
a) yes
b) no
Is thrombus formation possible in the heart cavities?
a) yes
b) no
Are thrombosis and coagulation in normal homeostasis one and the same process?
a) yes
b) no
Are thrombosis and coagulation in normal homeostasis one and the same process?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that inflammatory and immune reactions are completely independent reactions of the organism against pathological agents?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that inflammatory and immune reactions are completely independent reactions of the organism against pathological agents?
a) yes
b) no
immune reactions are part of inflammatory reactions, they overlap. think about how allergic reactions produce inflammatory reactions, despite being an immune response to things the antibodies have become sensitised to
Is it true that hypersensitivity of immediate type is related to chronic inflammatory reactions?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that hypersensitivity of immediate type is related to chronic inflammatory reactions?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true, that hypersensitivity of delayed type IV is related to chronic inflammatory reactions?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true, that hypersensitivity of delayed type IV is related to chronic inflammatory reactions?
a) yes
b) no
Are necrosis and hemorrhages typical findings in adenomas?
a) yes
b) no
Are necrosis and hemorrhages typical findings in adenomas?
a) yes
b) no
Is peritonitis possible complication of colon cancer?
a) no
b) yes
Is peritonitis possible complication of colon cancer?
a) no
b) yes
Is breast fibroadenoma a precancerous lesion?
a) yes
b) no
Is breast fibroadenoma a precancerous lesion?
a) yes
b) no
Is fibroadenoma a malignant tumor?
a) yes
b) no
Is fibroadenoma a malignant tumor?
a) yes
b) no
Do benign tumors arising from the smooth muscles have a capsule?
a) no
b) yes
Do benign tumors arising from the smooth muscles have a capsule?
a) no
b) yes
Leiomyomas, which are benign tumors arising from smooth muscle, do not have a true capsule but are typically surrounded by a pseudocapsule.
Pseudocapsule:
A leiomyoma is usually well-circumscribed and enclosed by a layer of compressed smooth muscle fibers and connective tissue that forms as the tumor grows and displaces surrounding tissue. This structure gives the appearance of a capsule but is not a true capsule derived from the tumor itself.
True Capsule:
A true capsule is a fibrous layer that is part of the tumor's structure and distinctly separates the tumor from adjacent tissues. Leiomyomas lack this feature.
Do hemangiomas have a capsule?
a) yes
b) no
Do hemangiomas have a capsule?
a) yes
b) no
Hemangiomas, which are benign tumors composed of blood vessels, typically do not have a true capsule. However, they are often well-demarcated from the surrounding tissues
Are hemorrhages and necrosis in the smooth muscle tumors of uterus a typical sign for malignancy?
a) yes
b) no
Are hemorrhages and necrosis in the smooth muscle tumors of uterus a typical sign for malignancy?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that lymphomas are benign tumors?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that lymphomas are benign tumors?
a) yes
b) no
Are there benign tumors arising from the hemopoetic tissues?
a) yes
b) no
Are there benign tumors arising from the hemopoetic tissues?
a) yes
b) no
Can hydropic degeneration lead to necrosis of the cells?
a) yes
b) no
Can hydropic degeneration lead to necrosis of the cells?
a) yes
b) no
Does PAS-reaction identifies glycogen in the cells?
a) yes
b) no
Does PAS-reaction identifies glycogen in the cells?
a) yes
b) no
Is hypoxia an important factor for the development of fatty degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is hypoxia an important factor for the development of fatty degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Can gall bladder contain uric acid crystals?
a) yes
b) no
Can gall bladder contain uric acid crystals?
a) yes
b) no
Is a hypoxia an important factor for development of the fatty degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is a hypoxia an important factor for development of the fatty degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is uric acid infarction related to a circulatory disorder?
a) yes
b) no
Is uric acid infarction related to a circulatory disorder?
a) yes
b) no
Is a deposition of the glycogen in the epithelium of the renal tubules a feature of diabetes?
a) yes
b) no
Is a deposition of the glycogen in the epithelium of the renal tubules a feature of diabetes?
a) yes
b) no
Does plasma leakage play an important role in the development of hyalinosis?
a) yes
b) no
Does plasma leakage play an important role in the development of hyalinosis?
a) yes
b) no
Are lysosomal enzymes important in the inflammatory processes?
a) yes
b) no
Are lysosomal enzymes important in the inflammatory processes?
a) yes
b) no
Is endothelial injury important for thrombosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is endothelial injury important for thrombosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is formalin a suitable fixative for demonstration of neutral lipids?
a) yes
b) no
Is formalin a suitable fixative for demonstration of neutral lipids?
a) yes
but paraffin materials we can’t as they are easily soluble in them. We CAN study them in formalin if tissue is fixed afte cut on freezing microtome or unfixed tissues. don’t confuse the 2!!
b) no

Perls’ reaction is used for demonstrating hemosiderin:
a) yes
b) no
Perls’ reaction is used for demonstrating hemosiderin:
a) yes
b) no
perl’s stain is used to produce the prussian blue reaction - giving a deep blue colour when potassium ferrocynaide reacts with ferric (Fe2+) ions of hemosiderin

Could hemolytic jaundice be seen in the newborn?
a) yes
b) no
Could hemolytic jaundice be seen in the newborn?
a) yes
b) no
Is the development of amyloidosis possible in systemic diseases of the connective tissue?
a) yes
b) no
Is the development of amyloidosis possible in systemic diseases of the connective tissue?
a) yes
b) no
this can be primary amyloidosis
e.g. multiple myeloma, B cell lymphomas (AL protein)
and secondary
e.g. complications of chronic infections e.g. TB
and familial amyloidosis
e.g. familial mediterranena fever
Can thrombosis lead to the embolism?
a) yes
b) no
Can thrombosis lead to the embolism?
a) yes
b) no
Is coagulative necrosis seen in cerebral infarction?
a) yes
b) no
Is coagulative necrosis seen in cerebral infarction?
a) yes
liquefactive is seen
b) no
Does apoptosis affect a large group of cells?
a) yes
b) no
Does apoptosis affect a large group of cells?
a) yes
only selected groups that are programmed for death
b) no
Does necrosis affect the cells and extracellular matrix?
a) yes
b) no
Does necrosis affect the cells and extracellular matrix?
a) yes
b) no
Is hemosiderin an iron-containing pigment?
a) yes
b) no
Is hemosiderin an iron-containing pigment?
a) yes
b) no
Do tumors reverse spontaneously and return to normal structures?
a) yes
b) no
Do tumors reverse spontaneously and return to normal structures?
a) yes
DO NOT CONFUSE WITH Q89 which talks about precancerous lesions - these are not necessary tumours - they can be dysplasias, just showing signs of cellular atypia.. whereas tumours have proliferated enough to become a mass.
b) no
Could serous inflammation be seen in myocardium?
a) yes
b) no
Could serous inflammation be seen in myocardium?
a) yes
b) no
because it has serous producing membrane -
Is there a central necrosis in syphilitic granuloma?
a) yes
b) no
Is there a central necrosis in syphilitic granuloma?
a) yes
b) no
histologically, the gumma is a granuloma [1]. Syphilitic gummas have central necrosis, similar to caseous necrosis
Are benign tumors encapsulated?
a) yes
b) no
Are benign tumors encapsulated?
a) yes
b) no
Is serous inflammation a type of exudative inflammation?
a) yes
b) no
Is serous inflammation a type of exudative inflammation?
a) yes
b) no
Is a glomus angioma a vascular tumor?
a) yes
b) no
Is a glomus angioma a vascular tumor?
a) yes
b) no
A glomus tumor or glomangioma is a rare, benign growth of blood vessels which can develop in both adults and children. Glomus tumors can develop as a solitary glomangioma (one growth of blood vessels) or as multiple glomuvenous formations (multiple groupings of blood vessels)
Is metachromasia stained with toluidine blue characteristic for mucoid swelling?
a) yes
b) no
Is metachromasia stained with toluidine blue characteristic for mucoid swelling?
a) yes
b) no
Is there a serous inflammation in the myocardium?
a) yes
b) no
Is there a serous inflammation in the myocardium?
a) yes
b) no
it ocurs seldom in internal organs (serous pneumonia)

Can benign tumors lack capsule:
a) yes
b) no
Can benign tumors lack capsule:
a) yes
b) no
Is metachromasia characteristic for the mucoid degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is metachromasia characteristic for the mucoid degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
hence why tuloiduine blue works for it
Blood vessels are present in the tubercle granuloma?
a) yes
b) no
Blood vessels are present in the tubercle granuloma?
a) yes
TB granulomas are called tubercle and they have a central caseous necrosis surrounding by epitheloid cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells and giant Langhans cells.
central is caseous, fluid - not blood vessels!
b) no

Glomus-tumor belongs to endothelial tumors.
a) yes
b) no
Glomus-tumor belongs to endothelial tumors.
a) yes
glomus cells - present in atriovenosus shunts (mostly found in fingers or toe nail beds)
they arise from pericytes surrounding endothelial cells - so yes?
b) no

Benign tumors may not have a capsule:
a) yes
b) no
Benign tumors may not have a capsule:
a) yes
b) no
such as pseudocapsules of leiyomyomas
Are the plasma cells characteristic for tubercle granuloma?
a) yes
b) no
Are the plasma cells characteristic for tubercle granuloma?
a) yes
because plasma cells occur in tuberculoid leprosy, rhinoscleroma, gumma of syphyllitic granuloma as well as the non-specific granulomas like echinococcosus
b) no
Is there a coagulative necrosis in brain infarction?
a) yes
b) no
Is there a coagulative necrosis in brain infarction?
a) yes
liquefactive necrosis - where autocatalytic enzymes released from dead brain cells completely dissolves the tissue whereas coagulative necrosis is the opposite, lytic enzymes are inhibited, cells don’t lyse
b) no
Can thrombus in v. portae cause arterial emboli in art. pulmonalis?
a) yes
b) no
Can thrombus in v. portae cause arterial emboli in art. pulmonalis?
a) yes
so since the emboli would get stuck in the liver first (as the portal vein → liver → inferior VC) but to get to the inferior vena cava the embolus would get stuck in the smaller venous vessels in liver first before it can make it out to the IVC → RA → Pulmonary artery
A thrombus in the portal vein is confined to the venous system, specifically the splanchnic venous circulation, which drains blood from the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, and pancreas into the liver.
From the portal vein, blood flows through the liver and into the hepatic veins, which then drain into the inferior vena cava and ultimately return to the right atrium of the heart.
b) no
Is it true that gross changes of the organs are important for the diagnosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that gross changes of the organs are important for the diagnosis?
a) yes
b) no
Is brown induration of lungs a reversible change if the mitral stenosis, which cause it, is corrected by a mitral valve prosthesis?
a) yes
b) no
Is brown induration of lungs a reversible change if the mitral stenosis, which cause it, is corrected by a mitral valve prosthesis?
a) yes
couldn’t tell in the lecture course, not enough information. will just take it as
brown induration of lungs - process of venous plethora (congestion) that leads to the lungs looking dark and rusty brown, due to hemorrage of alveolar blood, Hb → hemosiderin → phagocytosis by “heart failure cells” macrophages - full of brown pigment giving the name of the colour.
b) no
Is it true that amyloid is an abnormal protein that accumulates in the extracellular space and lead to hypertrophy of the parenchymal cells and increased function of the organ?
a) yes
b) no
Is it true that amyloid is an abnormal protein that accumulates in the extracellular space and lead to hypertrophy of the parenchymal cells and increased function of the organ?
a) yes
DECREASES function of the organ
b) no
Precancerous lesions may have a reverse development (back to normal tissue):
a) yes
b) no
Precancerous lesions may have a reverse development (back to normal tissue):
a) yes
CONTRADICTION with Q77?? - no, but can be confused - that talks about tumours, this talks about precancerous lesions which can literally be a few atypical/dysplasic cells that could be removed/correct by the body when the causative agent is removed.
b) no
Yes, it is true that precancerous lesions may regress or revert to normal tissue in some cases. This process, called reverse development or regression, can occur due to various factors, including the removal of the underlying cause, improvements in immune function, or lifestyle changes. Here are some examples and contributing factors:
Examples of Regression:
Cervical Dysplasia:
Mild cervical dysplasia (CIN1), caused by HPV infection, often regresses on its own, especially in younger individuals. The body's immune system clears the virus, leading to normal tissue restoration.
Barrett's Esophagus:
In some cases, early interventions like addressing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) through medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery may lead to regression of Barrett's esophagus.
Oral Leukoplakia:
Stopping smoking or eliminating other irritants can lead to the resolution of leukoplakic patches, a common precancerous lesion in the mouth.
Colorectal Adenomas:
Small adenomas in the colon may regress with dietary changes, anti-inflammatory medications, or removal of other risk factors.
Factors Influencing Regression:
Immune System: A healthy immune response can help clear abnormal cells.
Elimination of Risk Factors: Stopping smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, or treating infections (e.g., HPV, H. pylori) can promote regression.
Medical Interventions: Topical treatments, vaccinations, or medications may reverse certain lesions.
Lifestyle Modifications: Improved diet, exercise, and weight management can help.
However, not all precancerous lesions regress. Some may persist or progress to cancer if not monitored or treated. Regular follo
Is there a characteristic macroscopic appearance in organs with hyaline degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is there a characteristic macroscopic appearance in organs with hyaline degeneration?
a) yes
b) no
Is it possible to find lymphocytes in the focus of acute inflammation?
a) no, lymphocytes are chronic inflammatory cells only
b) yes, they can be seen in the focus of acute inflammation when the etiologic agents are viruses
Is it possible to find lymphocytes in the focus of acute inflammation?
a) no, lymphocytes are chronic inflammatory cells only
b) yes, they can be seen in the focus of acute inflammation when the etiologic agents are viruses
Is it possible to find neutrophils in the focus of chronic inflammation?
a) yes, in case of chronic abscess
b) no, neutrophiles are seen in case of acute inflammation only
Is it possible to find neutrophils in the focus of chronic inflammation?
a) yes, in case of chronic abscess
b) no, neutrophiles are seen in case of acute inflammation only
Lipoma is a benign tumor from:
a) epithelial
b) mesenchymal origin
Lipoma is a benign tumor from:
a) epithelial
b) mesenchymal origin
so fat cells are of a mesenchymal origin
extra info:
Parenchyme
Definition: The functional tissue of an organ, as opposed to the supportive or structural tissue (stroma).
Function: Performs the primary work of the organ (e.g., hepatocytes in the liver for metabolism, alveolar cells in the lungs for gas exchange).
Example: In the kidney, the nephrons form the parenchyme.
Mesenchyme
Definition: A type of loosely organized, embryonic connective tissue that gives rise to many structures, including connective tissue, bone, cartilage, and blood.
Origin: Derived from the mesoderm during embryogenesis.
Function: Plays a key role in the development and repair of structural and connective tissues.
Example: Mesenchymal stem cells give rise to osteoblasts (bone cells), fibroblasts (connective tissue), and adipocytes (fat cells).
Epithelial
Definition: A type of tissue composed of tightly packed cells that form protective barriers, line surfaces, and perform absorption, secretion, or sensory functions.
Origin: Derived from ectoderm, mesoderm, or endoderm, depending on location.
Function: Protects underlying structures, facilitates selective permeability, secretes substances, and absorbs nutrients.
Example: Skin epidermis, lining of the digestive tract, and glandular tissue.
Specify the characteristic localization of intracellular hyaline degeneration:
a) liver cells
b) vascular endothelium
Specify the characteristic localization of intracellular hyaline degeneration:
a) liver cells
b) vascular endothelium
When is death possibly reversible?
a) clinical features of death
b) biological death
When is death possibly reversible?
a) clinical features of death
b) biological death
Indicate which cells are found in the granuloma "foreign body” type:
a) giant cells Langhans type
b) macrophages
Indicate which cells are found in the granuloma "foreign body” type:
a) giant cells Langhans type
b) macrophages
as the Langhans giant cells are horseshoe shaped and found in TB tubercles, gumma (in low amounts)
What may be the ultimate outcome of chronic venous congestion in the liver:
a) cardiac cirrhosis
b) brown induration
What may be the ultimate outcome of chronic venous congestion in the liver:
a) cardiac cirrhosis
b) brown induration
What kind of jaundice develops in cancer of the papilla Vateri?
a) mechanic
b) hemolytic
What kind of jaundice develops in cancer of the papilla Vateri?
a) mechanic
as post-hepatic
b) hemolytic
Basal cell cancer is localized most frequently:
a) forearm skin
b) facial skin
Basal cell cancer is localized most frequently:
a) forearm skin
b) facial skin
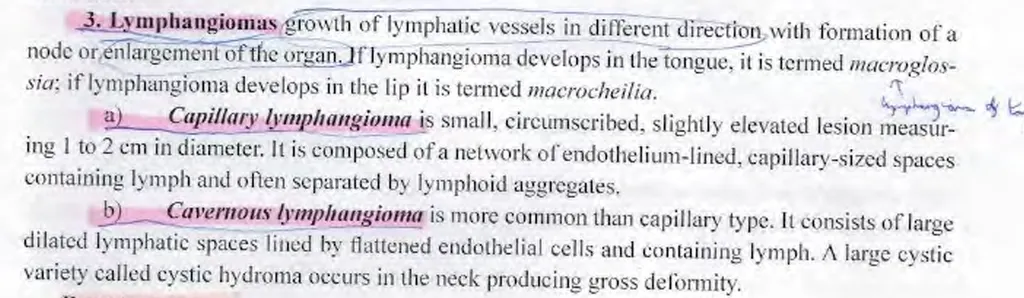
Lymphangiomas locate most often:
a) on the face
b) on lips, tongue
Lymphangiomas locate most often:
a) on the face
b) on lips, tongue