Antigens
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
An antigen is any substance that can ______ components of the immune system.
bind to
An immunogen is a substance that ______ products of the immune system.
reacts with
Adjuvants are added to vaccines to ______ the immune response.
enhance
A hapten is a low MW compound that can bind ______
antibody
A hapten-carrier compound causes ______.
immune response
What is an example of a hapten-carrier complex?
Urushiol and Langerhans cells
T-dependent antigens require processed antigens presented to ______.
T cells
T-dependent antigens are ______ antigens.
most
T-dependent antigens can undergo ______.
class switching
T-dependent antigens can have ______ response.
amnestic (recall)
T-dependent antigens are associated with _____ cells.
memory
T-independent antigens stimulate ______ without T cells.
antibody
T-independent antigens have ______ units.
repetitive
T-independent antigens involve ______.
bacterial polysaccharides
T-independent antigens are ______ only.
IgM
T-independent antigens trigger a ______ and ______ immune response.
rapid, initial
Epitopes recognized by B cells are ______ the molecule.
outside
They can be ______ or ______ in shape.
linear, nonlinear
Epitopes recognized by T cells are ______ the molecule.
inside
They are ______ in shape.
linear
They are produced by ______.
antigen processing
What are the factors of immunogenicity (antigenicity)?
- Genetic makeup
- Dose of antigen
- Route of immunization
- Primary vs. secondary immune response
Immunogenicity is the ability to induce an ______.
immune response
What are the 4 main characteristics of immunogenicity?
- Foreignness
- High MW
- Chemical complexity
- Degradability and interaction with host MHC
Antigenicity is the ability to ______ to a specific substance.
bind
Cross-reactivity occurs when two antigens share ______.
epitopes/shape
The higher the affinity, the more ______ the immune response.
affinity
Precipitation curve
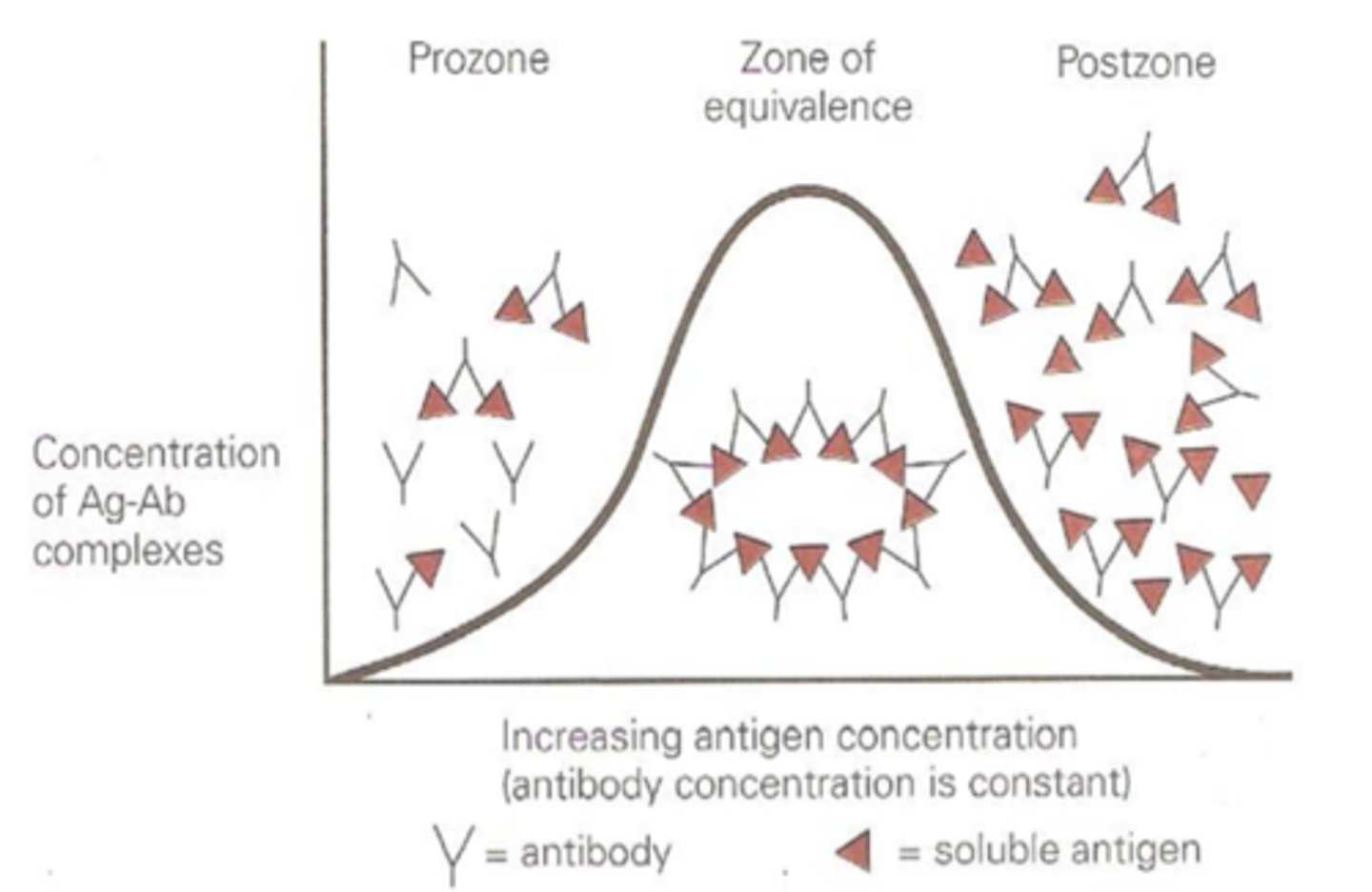
Affinity is the strength of binding that an Ab binding site has with its corresponding ______.
antigen/epitope
Avidity is the stability of the ______ complex.
antibody-antigen
Affinity is a property of the ______, while avidity is a property of the ______.
antigen, antibody
Low affinity antibodies don't ______ with the antigen.
bind strongly
High affinity antibodies are most ______ antibodies.
reagent (mAb)
Precipitation occurs when an Ag and Ab react and ______ occurs.
cross-linking
This reaction can be detected by ______ of the complex out of solution.
precipitation
Agglutination occurs when a surface Ag forms a visible ______ when bound by Ab.
aggregation
This most often happens with ______.
IgM
What are the types of agglutination?
Direct, passive, reverse passive
Direct agglutination occurs when the Ag is ______ on the surface of an RBC.
naturally coated
Passive agglutination
Antibodies or antigens attached to particles (latex beads)
Reverse passive agglutination
Antibody is attached to the carrier particle (instead of antigen)
Agglutination and precipitation are similar because they both crosslink Ab and Ag and form a ______.
precipitate
Precipitation has a ______ antigen.
soluble
Agglutination has an ______ antigen.
insoluble