Topic 1 - Cells
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is a Prokaryotic and a Eukaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic - Smaller simpler cells that don’t have a nucleus (Bacteria)
Eukaryotic- Complex cells with a nucleus (Plants or Animals)
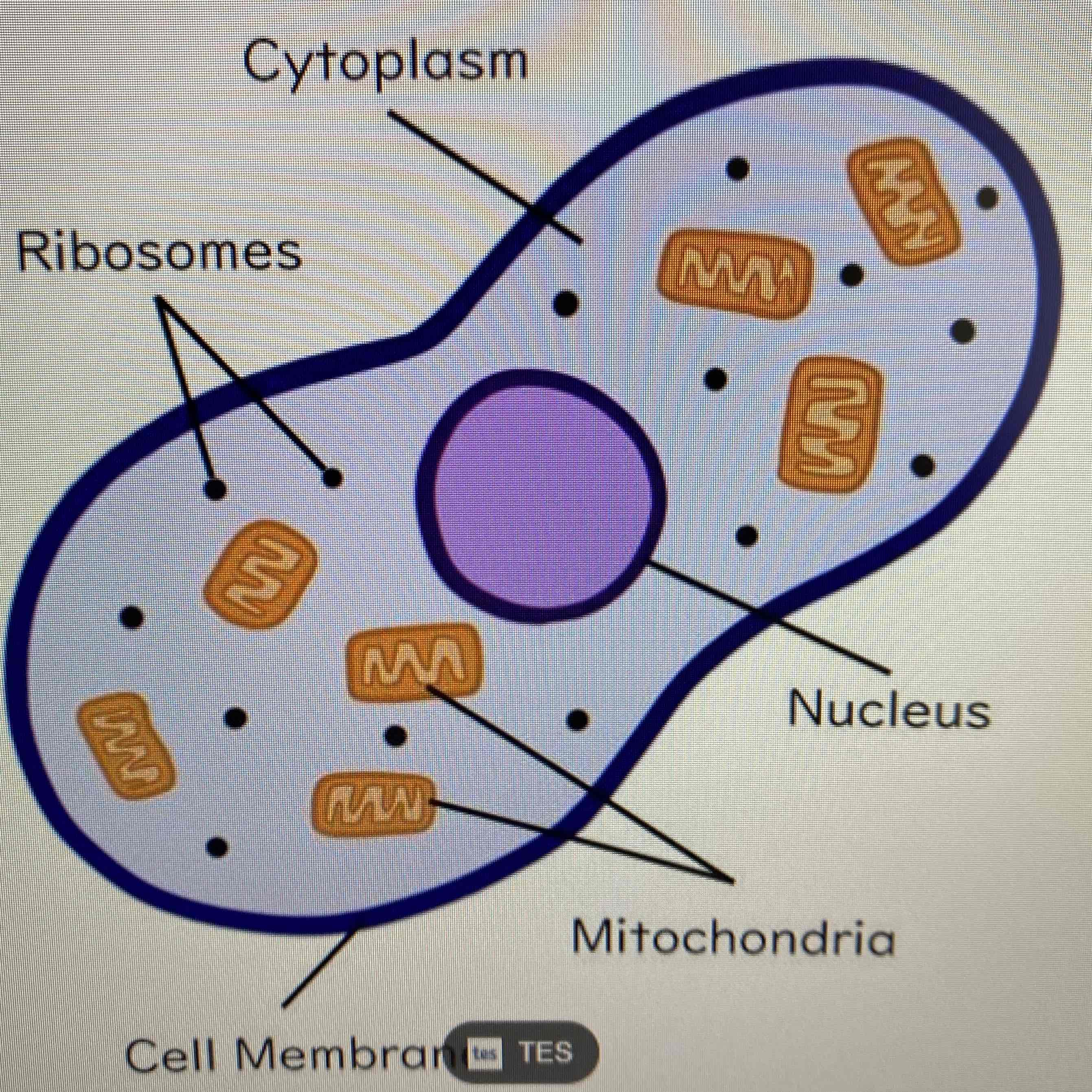
Describe and label the parts of a animal cell:
See Image
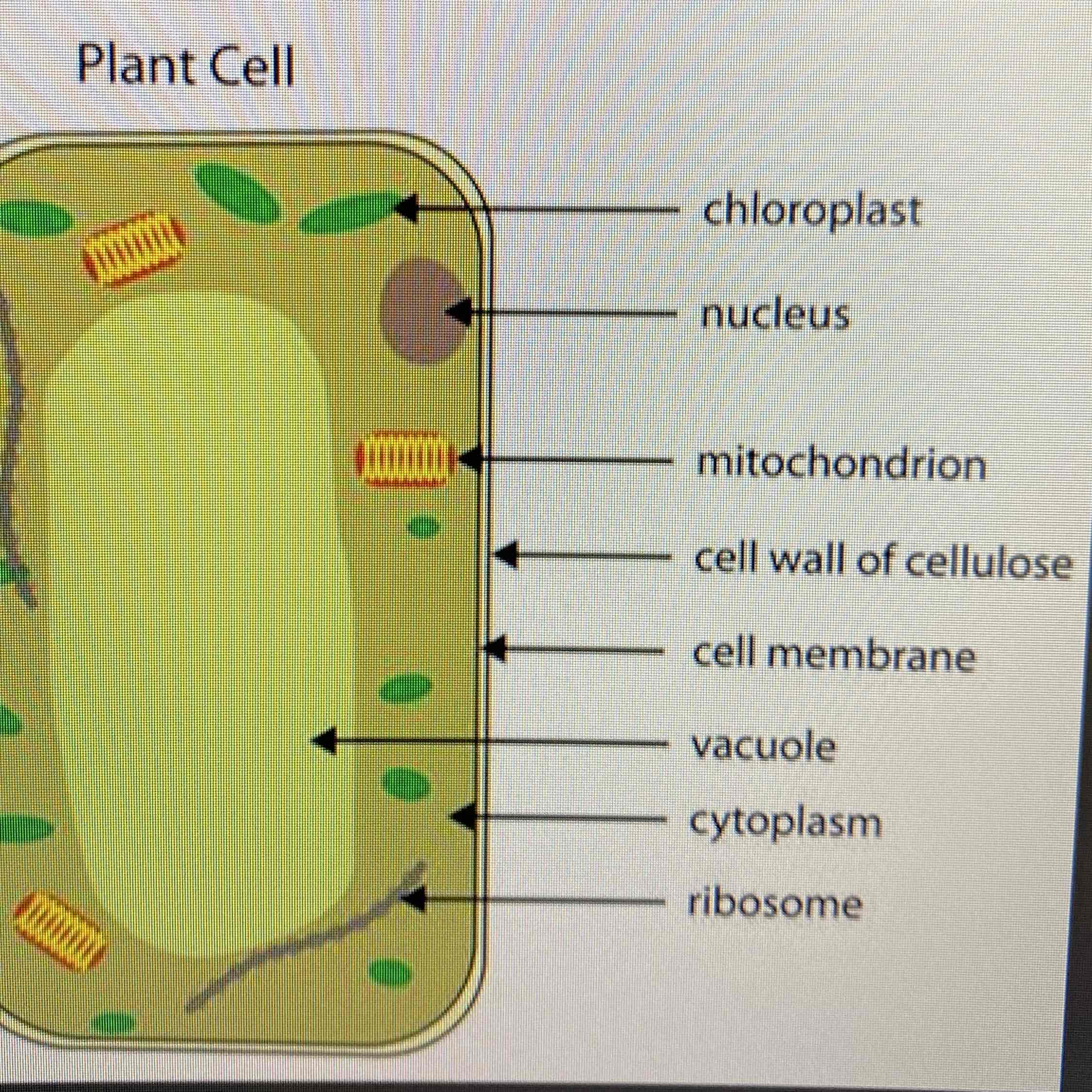
Describe and label the parts of a plant cell:
See Image
Explain the function of all the sub-cellular structures mentioned before:
Nucleus - Contains genetic material and controls the activities of the cell.
Cytoplasm - Gel-like substance that contains enzymes which control all the chemical reactions that happen there.
Cell Membrane - Holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out.
Mitochondria - Where aerobic respiration takes place.
Ribosomes - Where proteins are made.
Cell Wall - Made of cellulose, supports the cell and strengthens it.
Vacuole - Contains cell sap and a weak solution of sugars and salts.
Chloroplasts - Where photosynthesis takes place. It also contains chlorophyll which absorb light needed for photosynthesis.
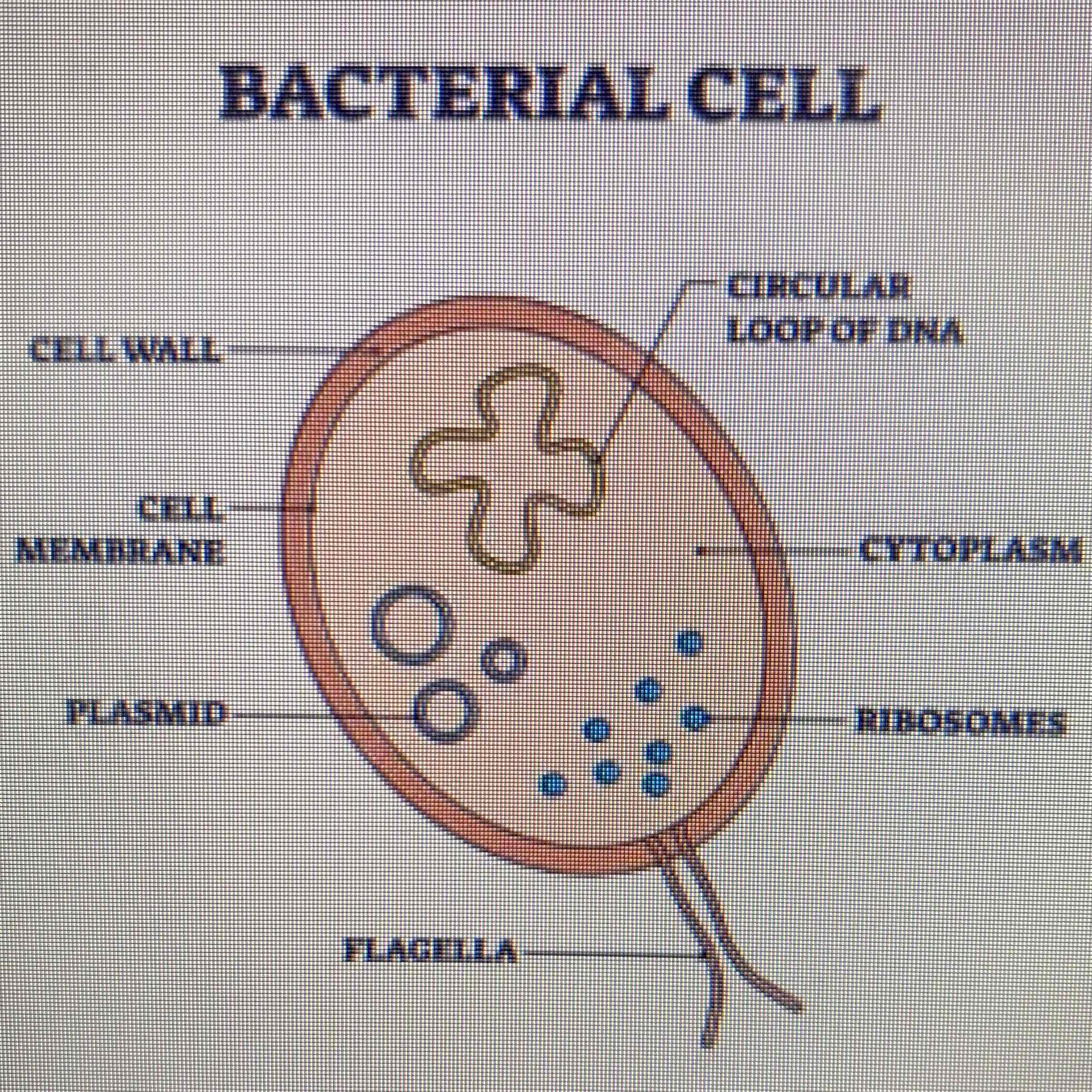
Describe and label a bacteria cell:
See Image:
Loop of DNA - Genetic Material - They don’t have a proper nucleus so it floats freely.
Plasmids - Small rings of DNA.
Flagella - Used to move the bacteria.
What are the properties of a light microscope and an electron microscope?
Light Microscope:
They use light and lenses to form in image
Can be used to view a living cell
In Colour
Electron Microscope:
Use a beam of electrons to examine it
Higher magnification and resolution
A 3D image is produced
What is the formula for magnification?
Magnification = Image Size / Real Size
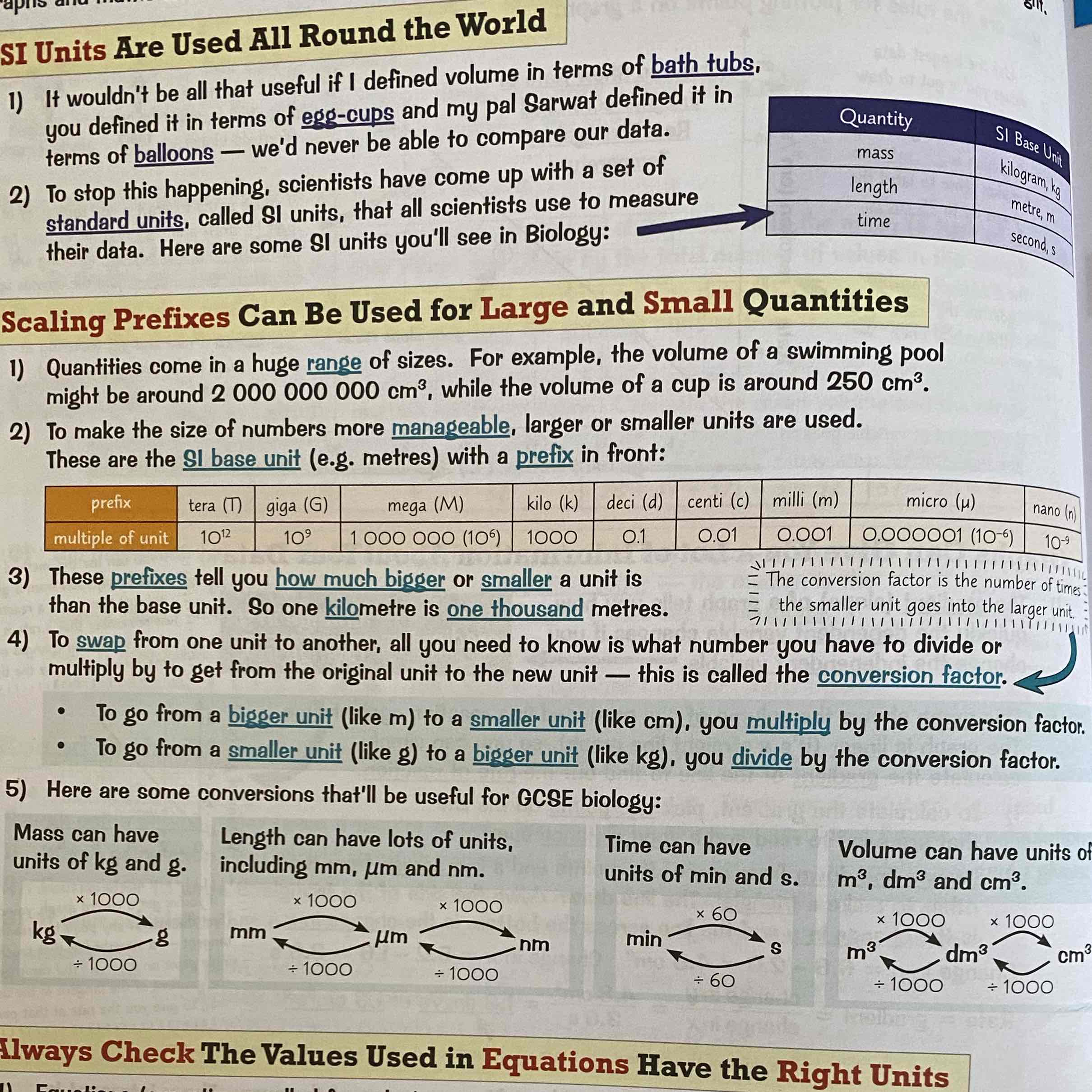
Remember to know conversion of units, for reference see image:
What is differentiation?
The process by which a cell changes to become specialised for its job. Most animal cells can’t differentiate after an early stage but plants never lose the ability.
Learn more about this in Stem Cells later.
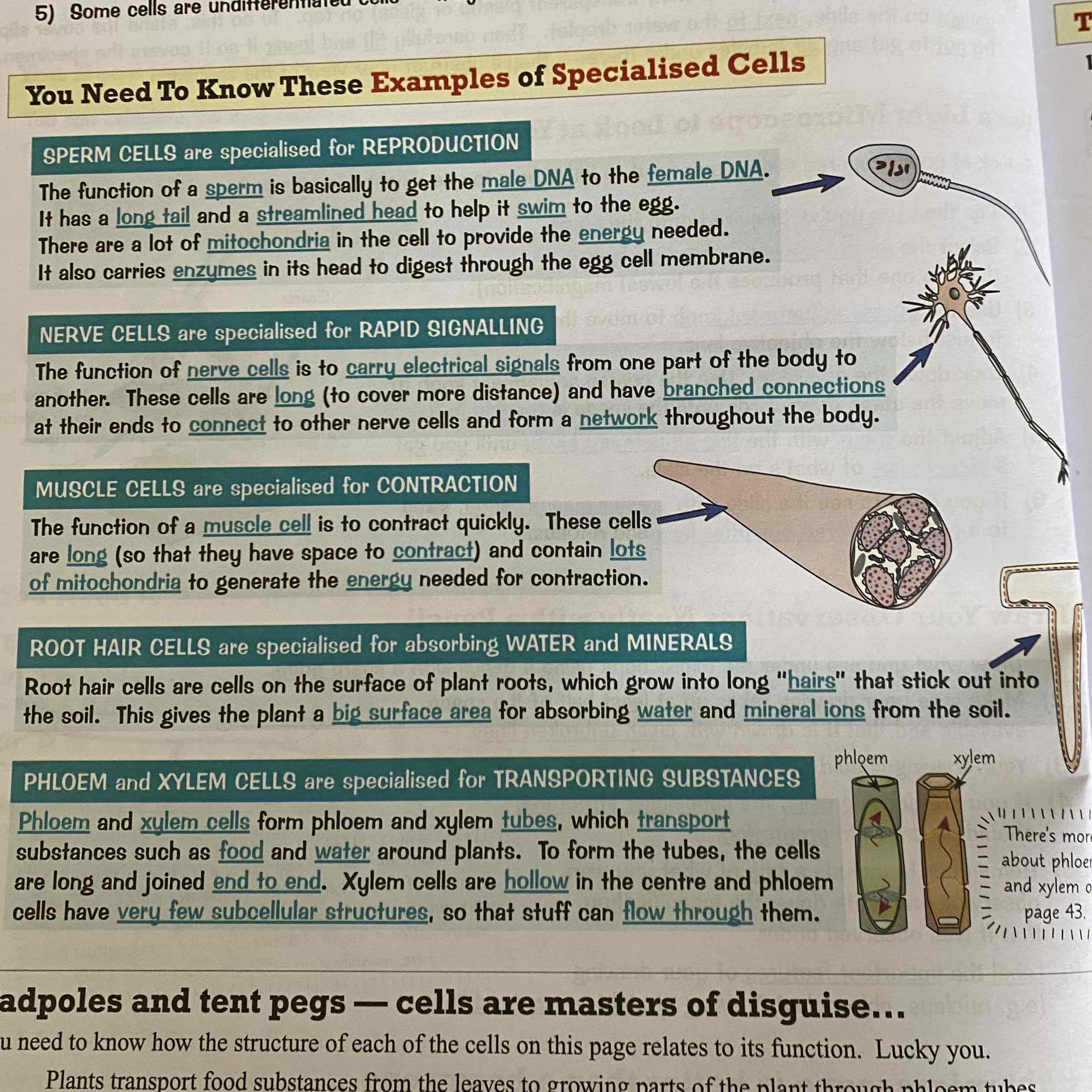
Examples and functions of specialised cells:
See Image and learn all of them:
What is a chromosome?
They are coiled up lengths of DNA found in the nucleus. In our body we have two pairs of 23 chromosomes made with one from each parent.
What is the cell cycle?
The process body cells go through for growth, repair and development. It goes through three stages: Interphase (Growth and DNA replication), Mitosis (Division of DNA) and cytokinesis (Division of cytoplasm).
For more information on Interphase and Mitosis see image:

What is Binary Fission?
The process by which Prokaryotic Cells replicate. See Image for explanation:

What are Stem Cells?
Stem Cells divide to produce more stem cells and differentiate into any type of cell. They are found in early human embryos. They can also be found in bone marrow but they can’t turn into any cell but only certain ones.
How can stem cells help in medicine?
They can be used to cure disease by replacing faulty or damaged cells.
However some people are against them as when using human embryos each one is a potential human life.
What is diffusion?
The spreading out of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
What is Osmosis?
The movement of water molecules from an area of higher water concentration to lower concentration across a partially permeable membrane.
What is Hypotonic, Hypertonic and Isotonic?
Hypotonic - A high water concentration with a low solute concentration.
Hypertonic - A low water concentration with a high solute concentration.
Isotonic- There is the same concentration of water on each side if the cell membrane.
What is Active Transport?
The movement of particles against a concentration gradient using energy.
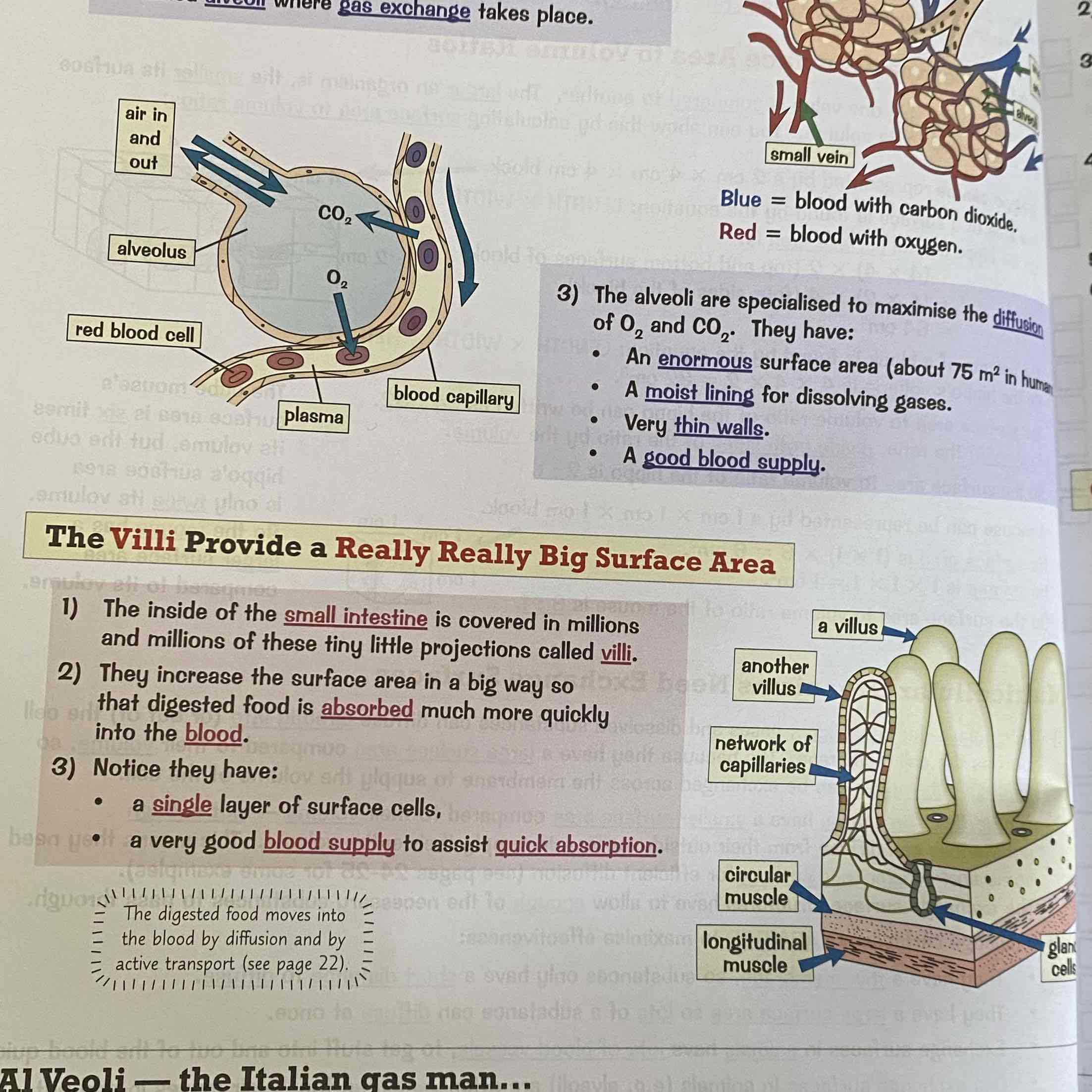
Where does exchanging substances happen in the body?
The Alveoli and the Villi.
See image for more:
Describe the potato and salt concentration experiment?
Cut a potato into three similar sized pieces
Then measure the mass of each piece
Measure out a volume of 0.1mold/dm³ of concentrated salt solution into a beaker.
Then place all your potato pieces into the beaker
After your chosen time remove each potato and dry the surface with a paper towel and measure the masses
The calculate the percentage change for each mass and work out the mean
Then repeat this with different concentrations of salt solution