AP Bio Unit 1 (1.3-1.7)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
monomers
chemical subunits used to create polymers
polymers
macromolecule made of many monomers
dehydration synthesis
used to create macromolecules, pulls out an H2O
hydrolysis reactions
polymers are broken down (hydrolyzed) into monomers, adding a water molecule to break a bond
monosaccharide
carbohydrate monomer, ex. glucose, ribose
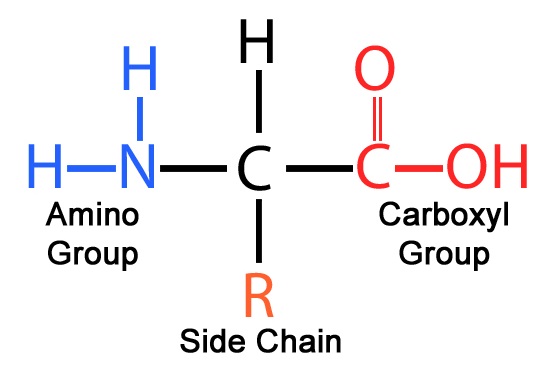
amino acid
protein monomer
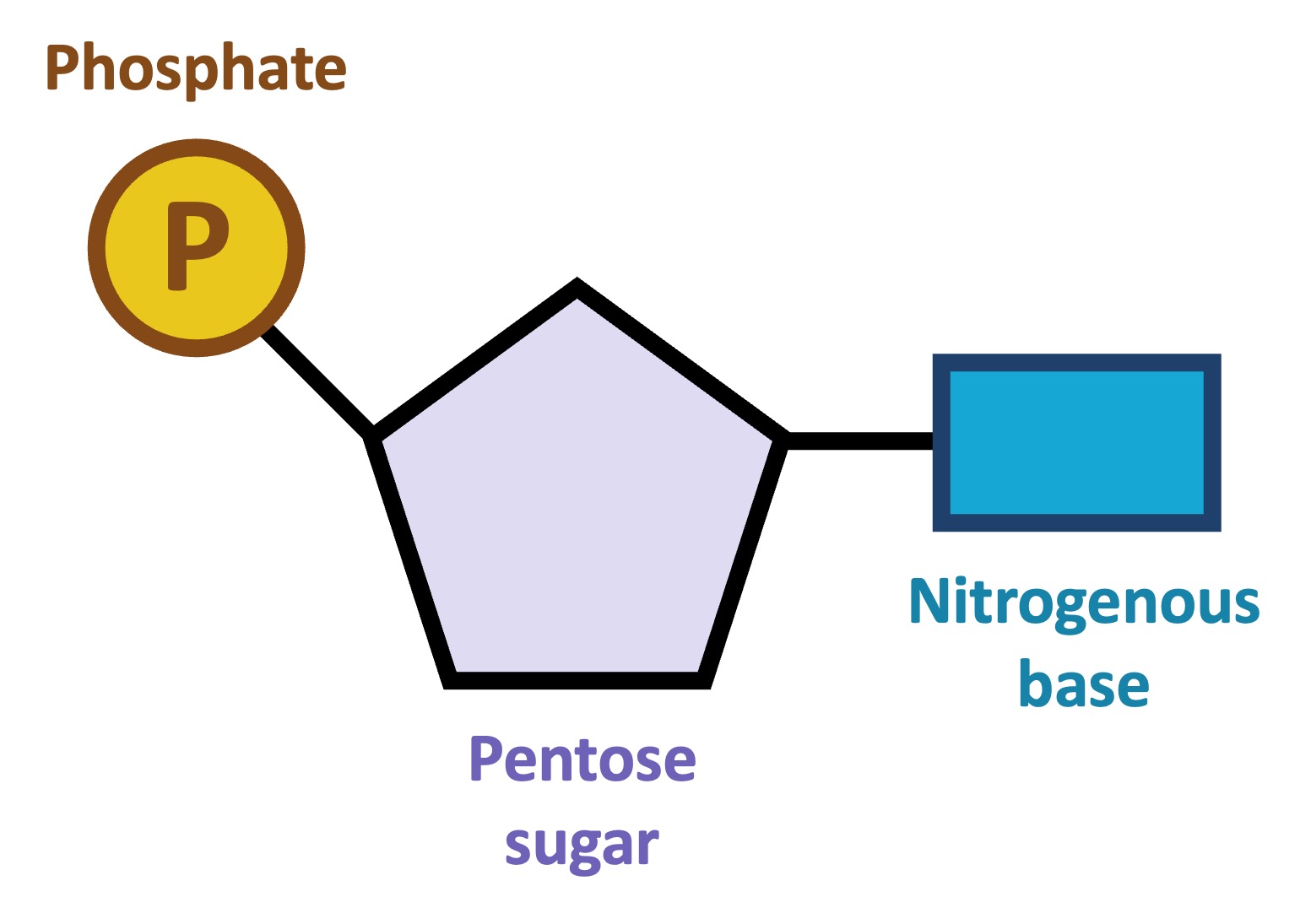
nucleotide
nucleic acid monomer - 5-carbon sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
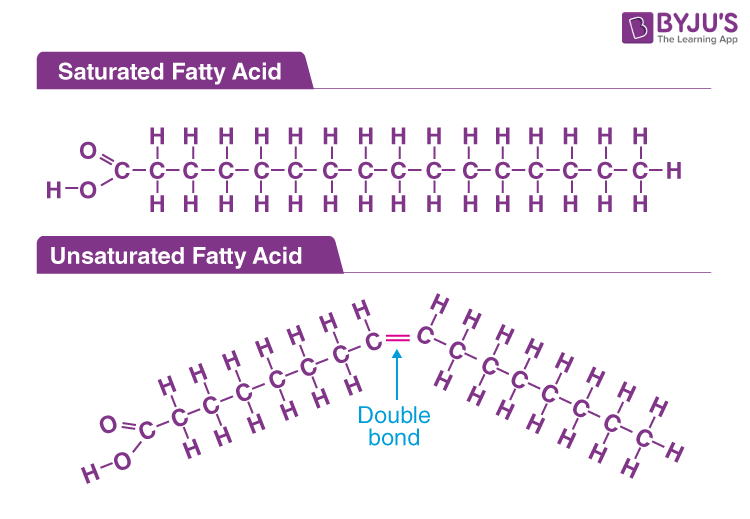
fatty acid*
foundation of lipids, not true monomers
isomer
same molecular formula w/ different atom arrangement
amino group, R-group/side chain, carboxyl group
parts of an amino acid
adenine, thymine (DNA), guanine, cytosine, uracil (RNA)
nitrogenous bases
store + transport hereditary info
function of nucleic acids
deoxyribose (DNA) and ribose (RNA)
DNA and RNA sugars
hydrophilic
polar, likes water
hydrophobic
non-polar, doesn’t like water
polysaccaride
complex carbohydrate, functions: storage (plants-starch, animals - glycogen), structure (plants - cellulose, arthropod, chitin)
saturated fatty acids
only single bonds between carbon atoms, solid at room temp, from animals
unsaturated fatty acids
at least 1 double bond between carbon atoms, results in a kink in the chain, liquid at room temp, from plants
fats
type of lipid that provides energy storage + supports cell function, some provide insulation
steroids
type of lipid - hormones that support physiological functions including growth and development, energy metabolism, and homeostasis
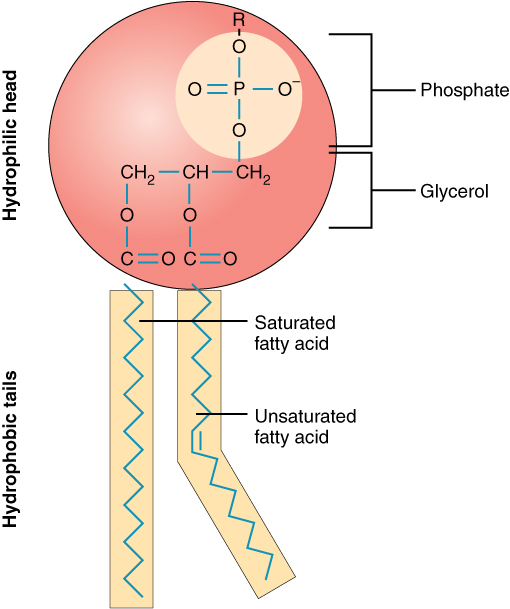
phospholipids
hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail, group together to form the lipid bilayers in plasma and cell membranes
adenine-thymine
held together by 2 hydrogen bonds in DNA
guanine-cytosine
held together by 3 hydrogen bonds in DNA
3 prime end
which end can nucleotides be added to?
peptide bonds
name for covalent bonds in proteins
R-group
part of amino acid that can be/have hydrophobic/non-polar, ionic, disulfide bridges, or hydrophilic/polar
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids held together by peptide (covalent) bonds
secondary structure of protein
arises through local folding of the amino acid chain into elements such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets bc of hydrogen bonding
tertiary structure of protein
3D shape of protein - various types of bonds and interactions stabilize at this level
quaternary structure of protein
arises from interactions between multiple polypeptide units
phosphodiester bond
phosphate-sugar backbone in a nucleotide
purine
nucleic acids - adenine and guanine, 2 carbon/nitrogen rings
pyrimidine
nucleic acids - thymine + cytosine, 1 carbon/nitrogen ring
enzymes, defense, storage, transport, hormones, receptors, movement, structure
functions of proteins
chaperonins
assist in proper folding of proteins