invasion and metastasis
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
metastasis definition
process by which tumour cells disseminate to distant sites to establish discontinuous secondary tumours
how is metastasis different to invasion
creating a distant, secondary tumour
invasion metastasis cascade
Breakaway from the primary tumor and breach the underlying basement membrane
Migrate through the surrounding stroma
Enter the blood flow by crossing the endothelial cell layer
In order to travel through the blood/lymph vessel the have to survive in this “strange” environment
extravasate into distant tissue
establish a new colony of cells - colonisation
requirement for invasion metastasis cascade
cell migration
ability to invade and remodel the ECM
intravasation
dissemination through the circulation
extravasation
survival in inappropriate tissue contexts
acquisition of local invasiveness
Reduced cell-cell adhesion
Down-regulation of E-cadherin
Proteolytic degradation of the basement membrane
Invadopodia are specialized subcellular structures which perform this role
Acquisition of a motile phenotype
Adhesion to the stromal ECM
Cytoskeletal reorganisation
Propulsive force
actomyosin contraction and actin
polymerisation
Proteolytic degradation of the stromal ECM
prominent role for matrix metalloproteinases
How are motility and invasiveness acquired?
induction of oncogenes such as ras
stimulation of TNF alpha and HGF - induce JNK, NF-kB, Erk cascades
HGF activation leads to activation of cmet, tyrosine kinase receptor, ras → migratory machinery
pro migratory growth factors released by cancer cells or fibroblasts, immune cells
spindle morphology - mobility
EMT
which cadherin is lost through EMT
E
invadopodia
like drills
actin rich protrusions with metalloproteases
allow degradation of laminin and collagen, degrading BM
which receptor is upregulated for invasion
alpha v beta 6 fibronectin receptor
injections of RGD
interfere with integrin binding to ECM
effective in mice but not in humans
cell migration through actin cytoskeletal reorganisation
actin polymerisation at front and myosin contraction at the rear end of the cell
extension of front of cell creates new attachments, focal contacts contain integrins
lamellipodia
lamellipodia - actin based, at the leading edge
filopodia
thin protrusions which help the cell to explore the surroundings of the cell, allowing polarisation, detecting stiffness and gradients
Rho GTPases 3 families
Rac
Rho
Cdc42
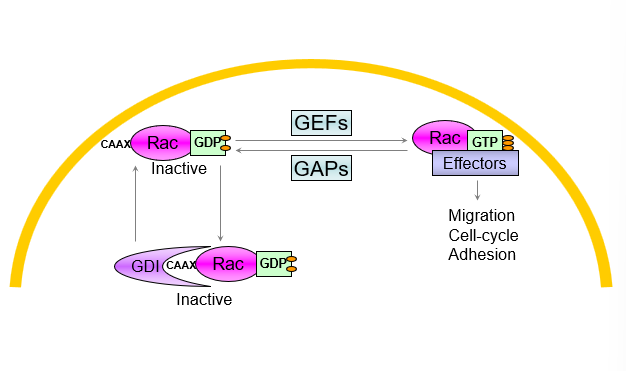
Regulation of GTPase activity
GEFs promote binding to GTP leading to activation
GAPS stimulate hydrolysis of GDP leading to deactivation
Rho GDI binding leads to inactivation
rho induction of lamellipodia and focal contacts
leads to reorganisation of actin cytoskeleton leading to lamellipodia
cdc42 induction of filopodia
cdc42 activation leads to reorganisation of the actin cytoskeleton to form filopodia
cells use the filopodia to detect chemical changes and direct migration
vinculin distribution changes but still coinicdes with organised actin at filopodia
rho and stress fibres
when rho is activated the cells form stress fibres which act as cables to retract the cell and after lamellipodia formation create net movement
Proteases role in invasiveness
matrix metallopases are the most important
also include serine proteinases, cysteine cathepsins etc
which matrix is more tightly organised than collagen I
basal membranes
alternatives to mesencyhmal invasion
amoeboid
high contractility Rho-ROCK, squeezes through without breakdown of ECM
collective cell invasion
brute force, cells retain many of the cell-cell adhesions, so no lack of e cadherin
may be reason why integrin inhibitors dont always work
survival of metastases in circulation
intravasation degrades blood vessel membrane
tumour cells need to resist apoptosis
vast majority perish
can get stuck in first capillary bed
why are micrometastases hard to treat
tend to be resilient and hard to find, cannot focus radiation
many are not clinically significant
mostly become dormant and form micrometastases due to hypoxia and angiogenic switch
can create residual disease after main tumour is treated
What determines sites of metastases
pattern of blood flow - passive
tissue ‘tropism’ - selection
homing signals - active
mechanism of circulation examples for metastasis
eg colon and liver
blood from intestines pass through the liver before entering the venous system
hepatic portal circulatory system before liver
eg breast cancer to lymph nodes to main circulation and then from heart to lungs
seed and soil hypothesis
only certain tissues will have similar trophic signals
chemokines drive a homing response - trigger chemostatic and invasive responses
metastatic cells create a niche to establish a tumour
what is the pre metatsatic niche?
inflammation
immune supression
angiogenesis
ECM remodelling
antimetastatic compounds
trigger measurable responses where treatment is initiated prior to the formation of primary tumours or metastases
display efficacy in preventative models to impair metastasis only after formation of small micrometastases
dastinib MPA
inhibit the metastatic outgrowth of already disseminated tumour cells in intervention assays
what have no effect on metastases
MMP inhibitors - lack of specificity
ras leads to which acquired capabilities
apoptosis
evasion
mitogenic independence
angiogenesis
metastasis invasion
breast cancer invasion and feedback loop
breast cancer invasiveness can be stimulated through IL-6
secretion of IL-4 by breast cancer cells can trigger cathespin protease activity, increasing the carcinoma cell invasiveness
shows bi directional interactions between tumour cells and nearby stroma
carcinoma cells stimulate formation of inflamed stroma, and the stroma enhances the malignant traits of the carcinoma cells
self amplifying pos feedback loop
vimentin
intermediate filament protein of the cytoskeleton of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts
TGF Beta role
leads to progressive loss of epithelial morphology
reduction in epithelial markers - cytokeratins and e cadherins
induction of EMT
signals which induce EMT programs?
TGF beta
cytokines
stiff extracellular matrix
absence of epithelial neighbours
collagen type I
Interactions between macrophage and carcinoma cell
carcinoma cell produces CSF-1 which binds to receptor on macrophage
stimulates macrophage to release EGF which binds to EGF receptor on carcinoma cell
What leads to proteolytic degradation of E cadherin?
cathepsin B protease