Rhetorical Terms Vocabulary
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms

Allusion
A reference to a well-known person, place, event, or work of literature to enhance meaning.

Anecdote
A short, personal story used to illustrate a point or engage the audience.

Antithesis
A rhetorical device that contrasts opposing ideas in a balanced structure.

Aphorism
A concise statement that expresses a general truth or principle.

Circumlocution
The use of unnecessarily wordy language to express an idea.

Connotation
The implied or suggested meaning of a word beyond its literal definition.

Denotation
The literal, dictionary definition of a word.

Digression
A temporary departure from the main topic in speech or writing.

Epiphany
A moment of sudden revelation or insight.

Epithet
A descriptive phrase expressing a quality or characteristic of a person or thing.

Euphemism
A mild or indirect word or expression used to replace one that may be considered harsh or blunt.
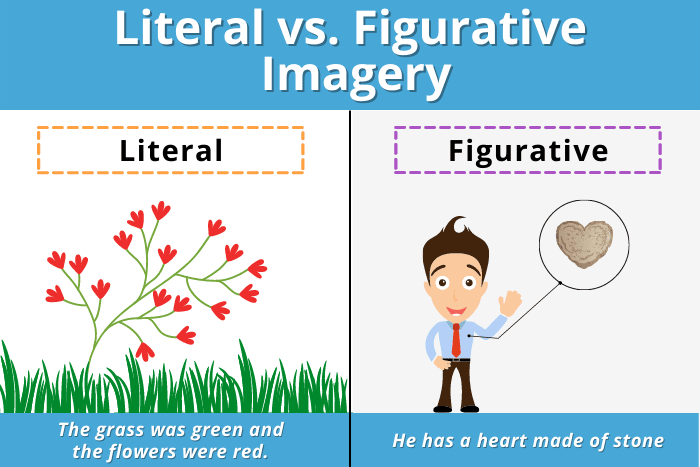
Imagery
Descriptive language that appeals to the senses and creates mental images.
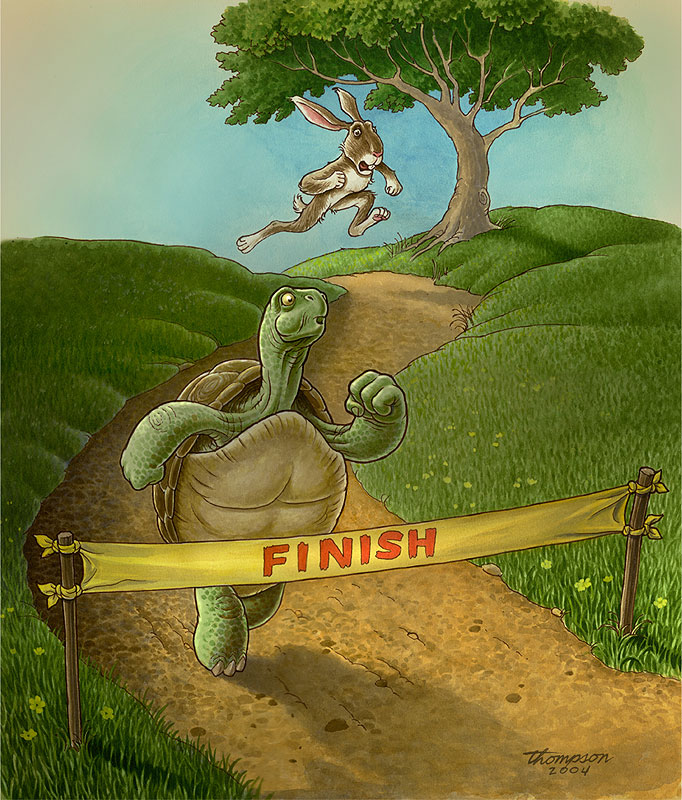

Juxtaposition
Placing two or more ideas, characters, or settings side by side to highlight their differences.

Metaphor (extended)
A comparison between two unlike things that continues throughout a piece of writing.
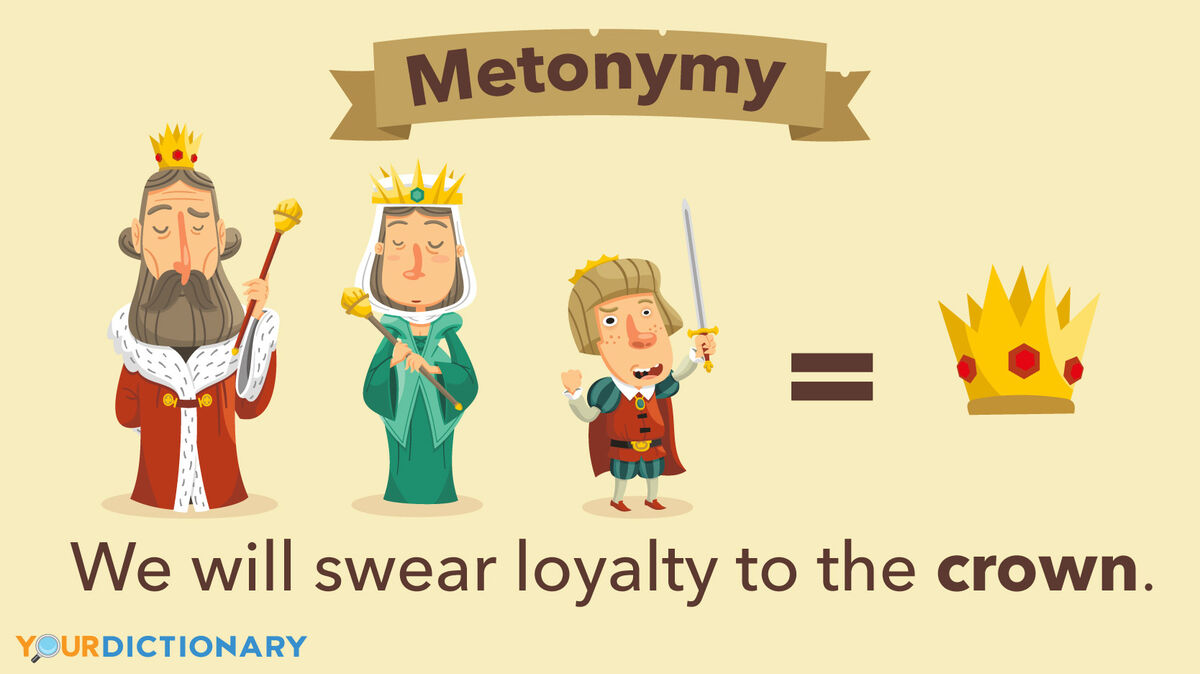
Metonymy
A figure of speech in which one word or phrase is substituted for another with which it is closely associated.

Non-sequitur
A statement that does not logically follow from the previous argument or statement.

Oxymoron
A figure of speech that combines contradictory terms.

Paradox
A statement that seems contradictory but reveals a deeper truth.

Parenthesis
An insertion of material that interrupts the typical flow of a sentence.

Satire
A genre that uses humor, irony, or exaggeration to criticize or mock.

Sardonic
A form of humor that is grimly mocking or cynical.

Synecdoche
A figure of speech in which a part is used to represent the whole or vice versa.

Understatement
A figure of speech that intentionally makes a situation seem less important than it is.

Anaphora
The repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses or sentences.

Asyndeton
The omission of conjunctions between parts of a sentence.
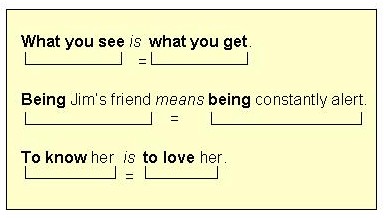
Parallelism
The use of similar structures in two or more phrases or clauses.

Polysyndeton
The use of multiple conjunctions in close succession for emphasis.
Accommodation
Adjusting one's argument or position to consider opposing views.
Apology
A defense or justification of an idea or action.
Authority
The credibility or expertise of a source in supporting an argument.
Claims/Warrants
Assertions made in an argument and the reasoning that supports them.

Concession
Acknowledging a point made by the opposing side.
Deduction
Reasoning from general principles to specific cases.
Ethos/Ethical Appeal
An appeal to credibility or character in persuasion.
Generalization
A broad statement or conclusion based on specific cases.
Induction
Reasoning from specific cases to form a general conclusion.
Logos/Logical Appeal
An appeal to logic and reason in argumentation.
Paradigm
A typical example or pattern of something; a model.
Pathos/Emotional Appeal
An appeal to the audience's emotions in persuasion.
Refutation
The act of disproving an argument or claim.
Syllogism
A form of reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn from two premises.
Testimonial
A statement in support of a particular truth or fact, often from a credible source.
Ad Hominem
An argument that attacks a person's character rather than addressing the issue.
Begging the Question
A logical fallacy in which the conclusion is assumed in the premises.
Equivocation
Using ambiguous language to mislead or misrepresent the truth.
Red Herring
A distraction from the main issue in an argument.
Scare Tactic
A strategy that uses fear to influence an audience's response.
Slippery Slope
A fallacy that suggests a minor action will lead to major consequences.
Straw Man
Misrepresenting an opponent's argument to make it easier to attack.
Grammar & Syntax
The rules and structure governing the composition of sentences.
Antecedent
The word, phrase, or clause referred to by a pronoun.
Appositive
A noun or noun phrase that renames another noun right beside it.
Clause
A group of words containing a subject and a predicate.
Cumulative Sentence
A sentence that begins