Week 7_physiochemical properties
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Physical Property
A property that does not affect the chemical identity of a compound
Can be observed and measured without changing a compound’s composition of matter
– Any substance that has mass and can occupy space
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
2 Types of Physical property
INTRAmolecular forces
INTERmolecular forces
Molecular Forces 2 TYPES
INTRAmolecular forces
Strong Types of molecular forces
INTRAmolecular forces
within ATOM
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
INTRAmolecular forces 3 TYPES
Covalent
Weak type of INTRAmolecular forces
Metallic
Strong type of INTRAmolecular forces
INTERmolecular forces
Within MOLECULE
Vander waals
Ion-Dipole
Hydrogen bond
INTERmolecular forces 3 Types
Van der Waals
Weak type of INTERmolecular forces
Hydrogen Bonding
Strong type of INTERmolecular forces
Keesom
Debye
London dispersion
3 types of VAN DER WAALS
Dipole - Dipole
other term for KEESOM
Dipole - Induced Dipole
other term for DEBYE
Induced Dipole - Induced Dipole
other term for LONDON DISPERSION
London Dispersion
Weak type of Vander waals
DIPOLE
other term for POLAR
Homolytic Fission
The fission of a covalent bond with equal sharing of bonding electrons.
Heterolytic Fission
The fission of a covalent bond involving unequal sharing of bonding electrons
5-25 kJ/mol
what is the IMF’s range of HYDROGEN BONDING
5-10 kJ/mol
what is the IMF’s range of DIPOLE-DIPOLE
2-5 kJ/mol
what is the IMF’s range of LONDON DISPERION
FON
What are the elements connected in Hydrogen bonding that have a LONE PAIR e-
Hydrogen bonding
is a complex interaction that includes dipole-dipole, as well as orbital interactions and the transfer of electron density between molecules
Dipole-dipole forces
arise from the attraction of oppositely charged atoms (other than H) in molecules. These molecules may have a permanent dipole moment.
Generally in organic molecules they result from the presence of C-X bonds where X is more electronegative to that of C.
London dispersion
forces arise from the movement of electrons within a molecule. This natural motion can produce an uneven distribution of the electrons (polarization of the distribution) resulting in a temporary dipole moment in the molecule.
This will induce the movement of electrons in adjacent molecules producing a dipole moment in them.
alcohols, amines
Any functional group that can donate a hydrogen bond to water ——
will significantly contribute to water solubility.
ketones, aldehydes, ethers
Any functional group that can only accept a hydrogen bond from water ——
will have a somewhat smaller but still significant effect on water solubility
alkyl halides, thiols, sulfides
groups that contribute to polarity ——
will make a small contribution to water solubility.
Boiling and melting point
are processes in which noncovalent interactions between identical molecules in a pure sample are disrupted.
Methane
What is the lowest melting point with -182.5 c and
boiling points with -167.7 c
Triacontane
What is the heights melting point with 449.7 c and
boiling points with 65.8 c
chemical reaction
occurs when one substance is converted into another substance(s).
it is accompanied by breaking of some bonds and by making of some others.
Free radicals
are neutral but reactive species having an unpaired electron and these can also initiate a chemical reaction
carbocation
an ion which has a positive charge on the carbon atom, is known as the?
carbanion
an ion with a negative charge on the carbon atom is known as the?
Electrophiles:
is an electron deficient species and it may be positively charged or neutral.
• Examples are H+ , AlCl3 , Br2 , Cl2 , Ag+ , CH3+, BF3 etc. –
Nucleophiles
is negatively charged or electron rich neutral species.
• Examples are OH–, –NO2+ , H2O, :NH3 etc.
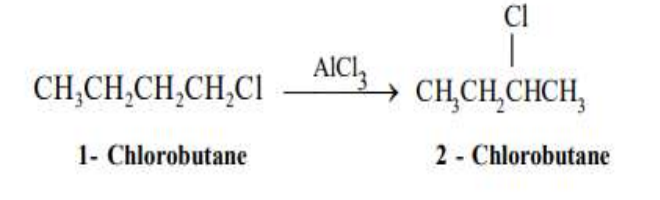
Elimination
characterized by the removal of a small molecule from adjacent carbon atoms and the formation of a double bond.
Addition
Unsaturated hydrocarbons such as alkenes and alkynes are extremely reactive towards a wide variety of reagents. The carbon-carbon double bond (–C=C–) of an alkene contains two types of bonds. In alkynes, three carbon-carbon bonds.
molecular Rearrangements
– proceeds with a fundamental change in the hydrocarbon skeleton of the molecule. During this reaction, an atom or group migrates from one position to another.
Elimination
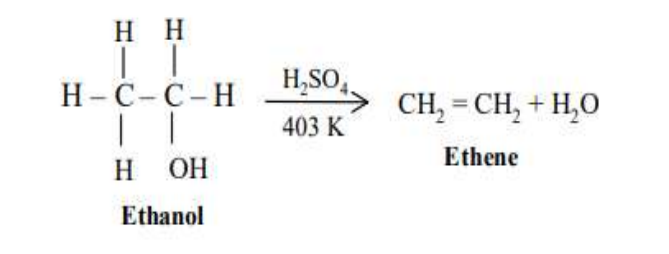
Addition
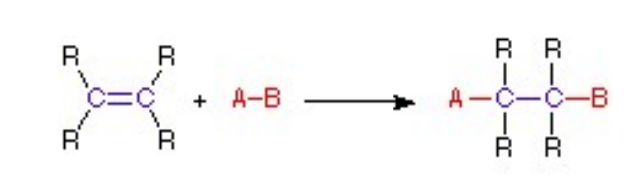
Molecular rearrangements