CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 17: Inheritance
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
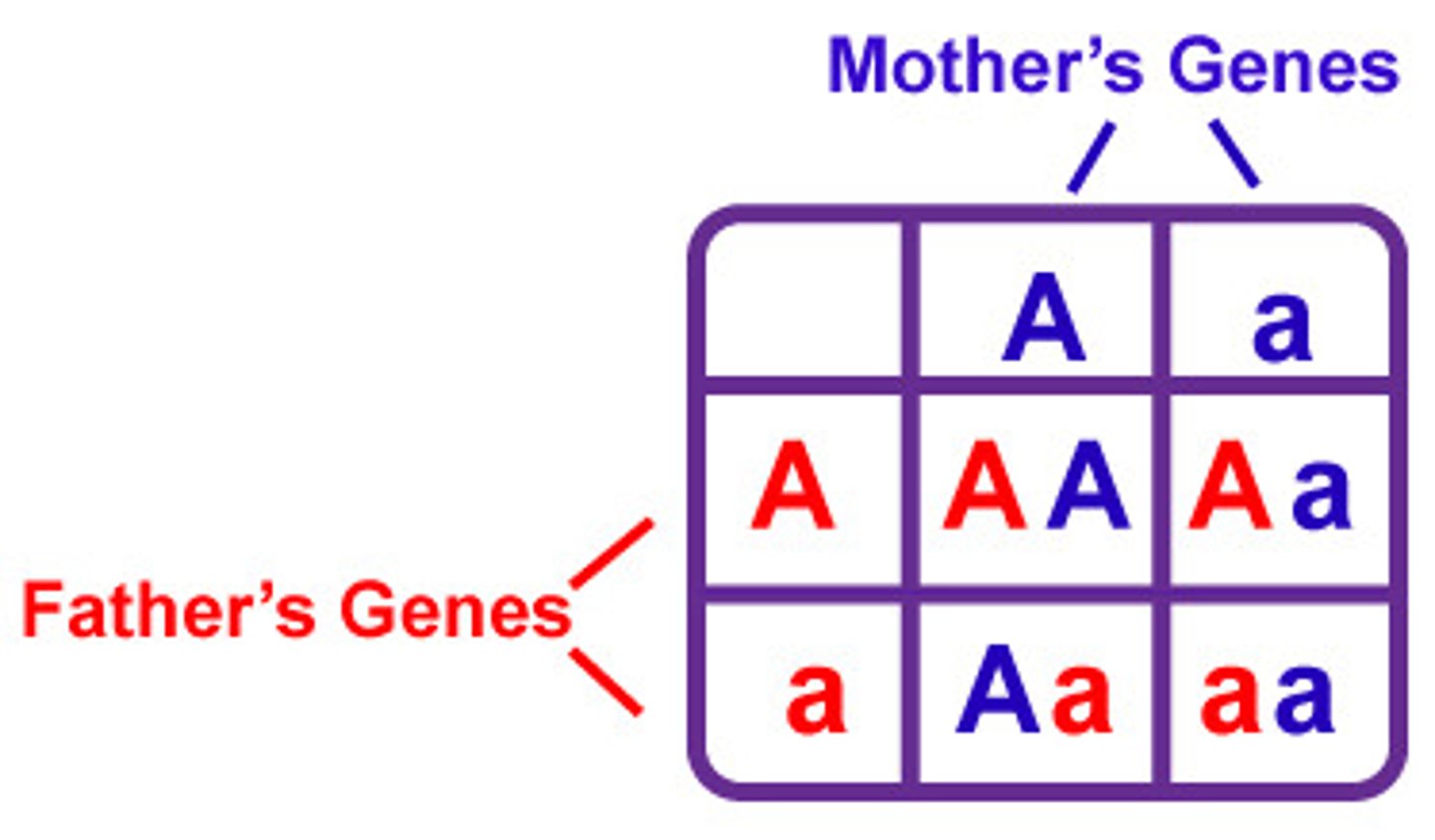
Punnett squares
inheritance
the transmission of genetic information from generation to generation
chromosome
a thread-like structure of DNA, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
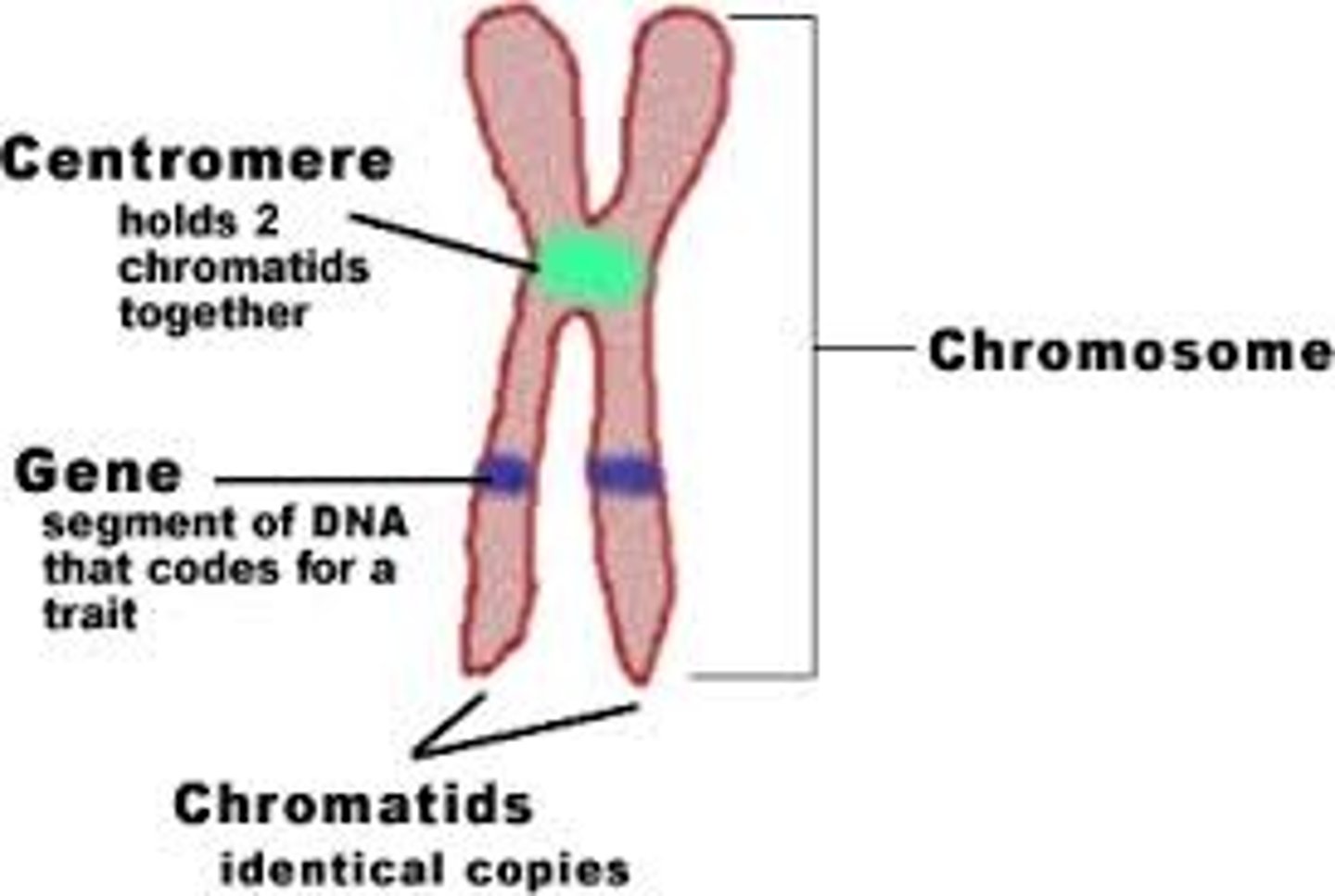
gene
a length of DNA that codes for a protein

allele
a version of a gene

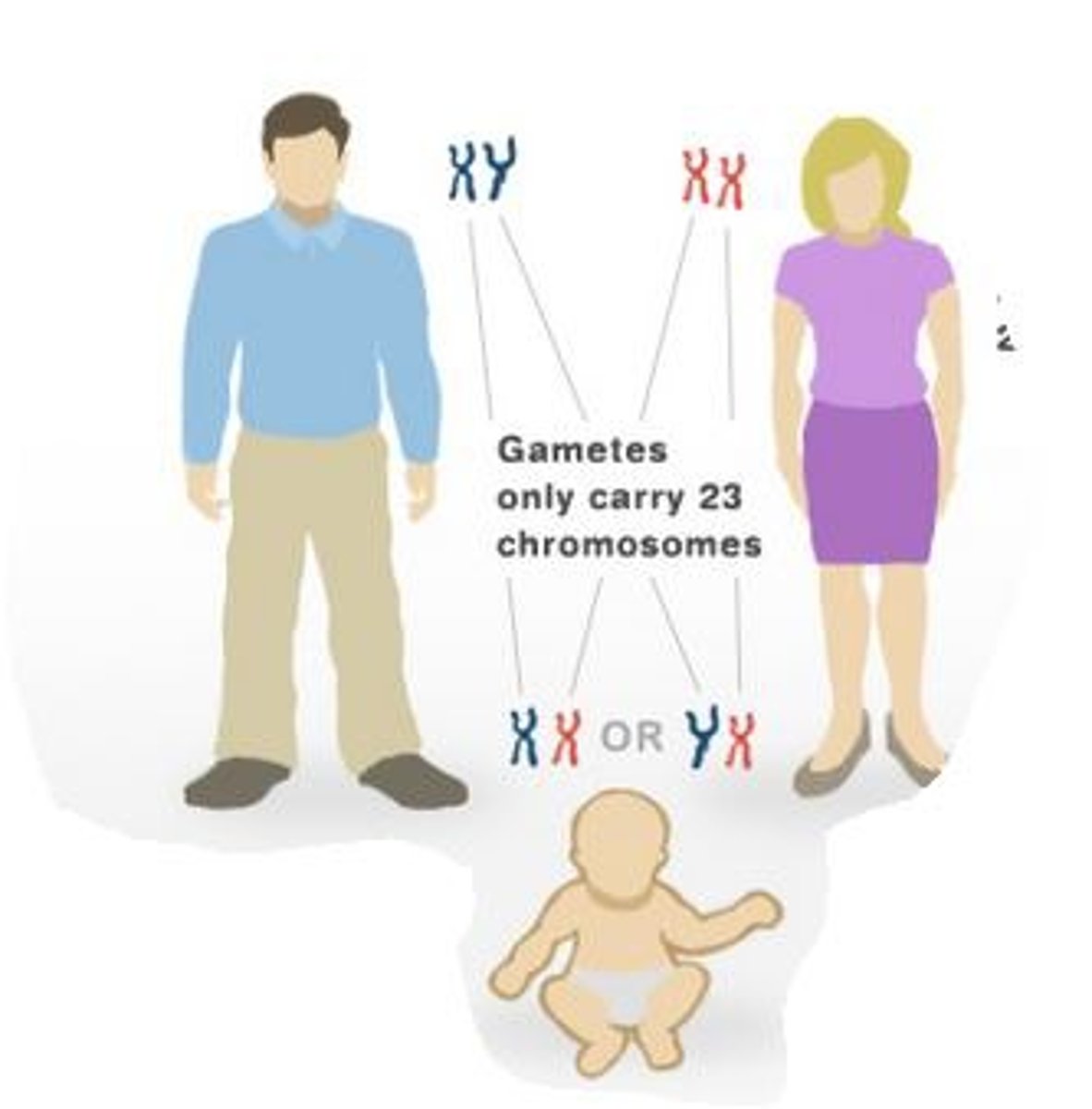
Describe the inheritance of sex in humans
The difference in sex chromosome between male and female leads to specific inheritance patterns for sex-linked genes
sequence of bases in a gene
the genetic code for putting together amino
acids in the correct order to make a specific
protein
How DNA controls cell functions
controls cell function by controlling the production of proteins (some of which are enzymes), antibodies and receptors for neurotransmitters
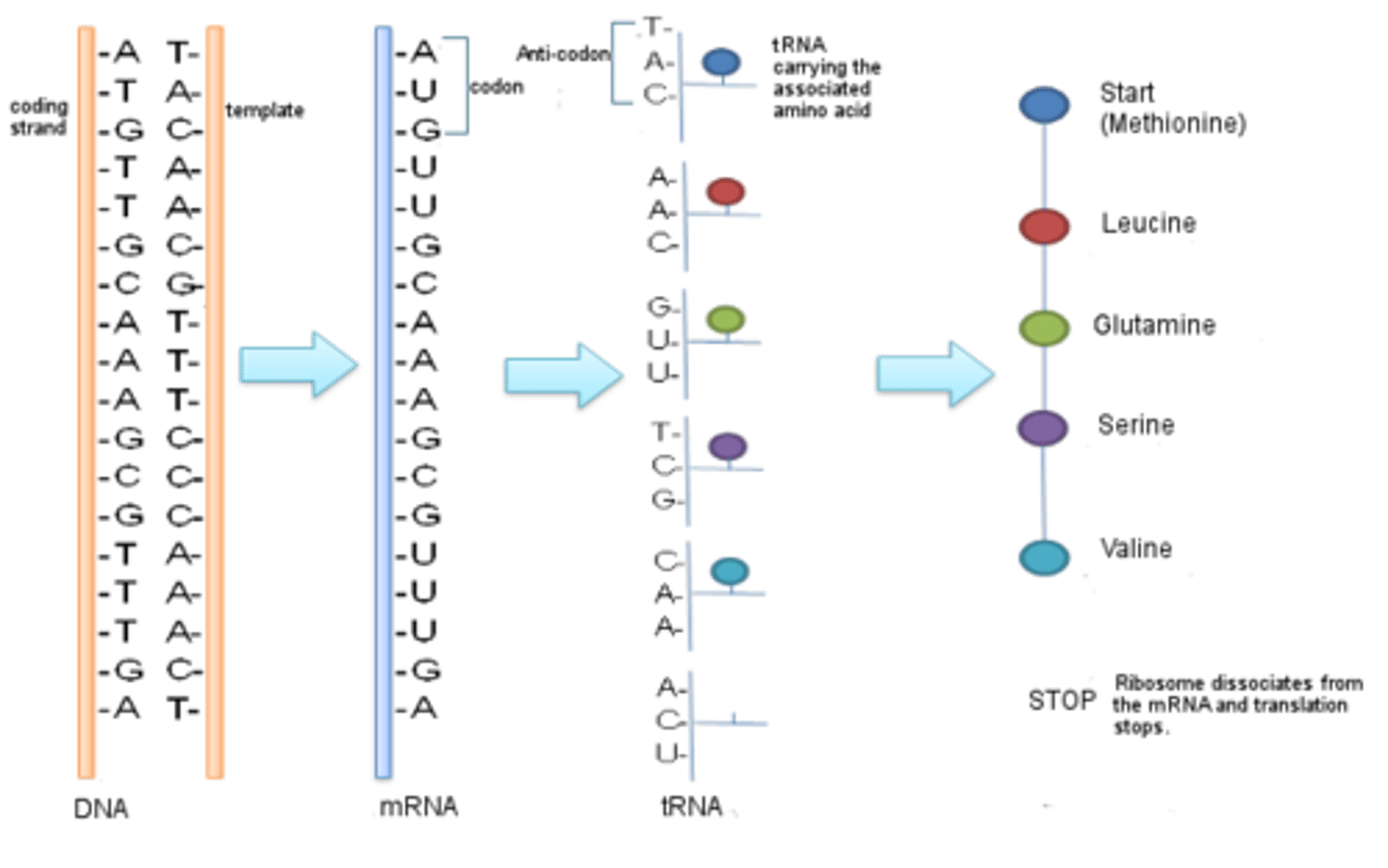
Protein synthesis
- the gene coding for the protein remains in
the nucleus
- mRNA molecules carry a copy of the gene
to the cytoplasm
- the mRNA passes through ribosomes
- the ribosome assembles amino acids into
protein molecules
- the specific order of amino acids is
determined by the sequence of bases in
the mRNA
genes not expressed
all body cells in an organism contain the same genes, but many genes in a particular cell are not expressed because the cell only makes the specific proteins it needs
haploid nucleus
a nucleus containing a single set of unpaired
chromosomes, e.g. in gametes
diploid nucleus
a nucleus containing two sets of chromosomes, e.g. in body cells. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a human diploid cell
mitosis
nuclear division giving rise to genetically identical cells
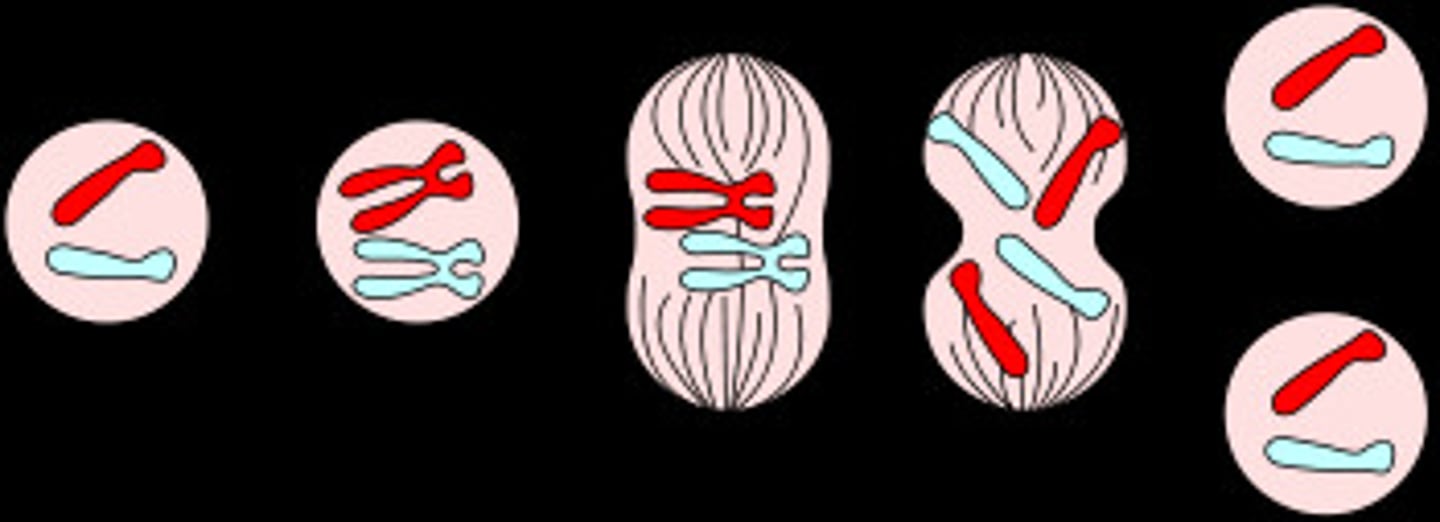
Process of mitosis
the exact duplication of chromosomes occurs before mitosis and the copies of chromosomes separate, maintaining the chromosome number
role of mitosis
growth, repair of damaged tissues, replacement of cells and asexual reproduction
stem cells
unspecialised cells that divide by mitosis to produce daughter cells that can become specialised for specific functions
meiosis
reduction division in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid
to haploid resulting in genetically different cells
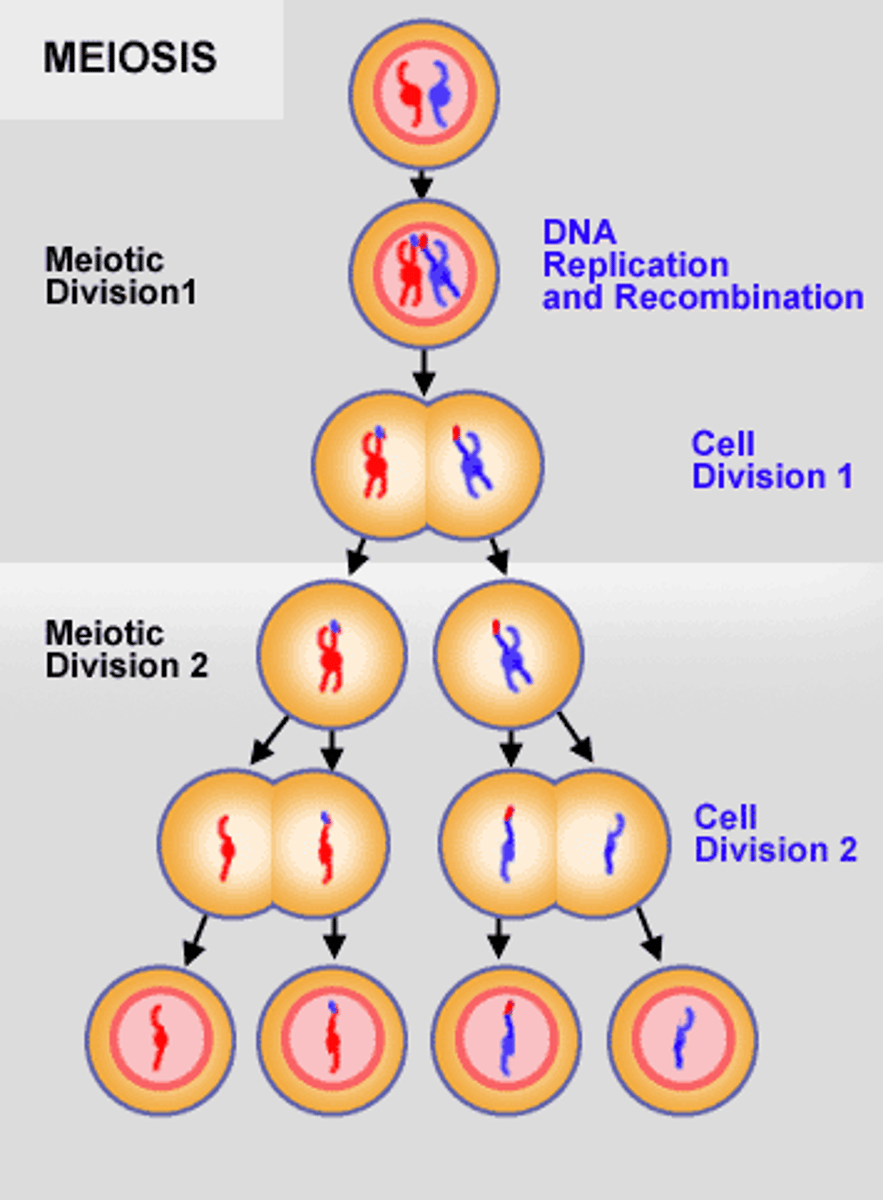
How meiosis produces variation
by forming new combinations of maternal and
paternal chromosomes
genotype
the genetic make-up of an organism in terms of the alleles present
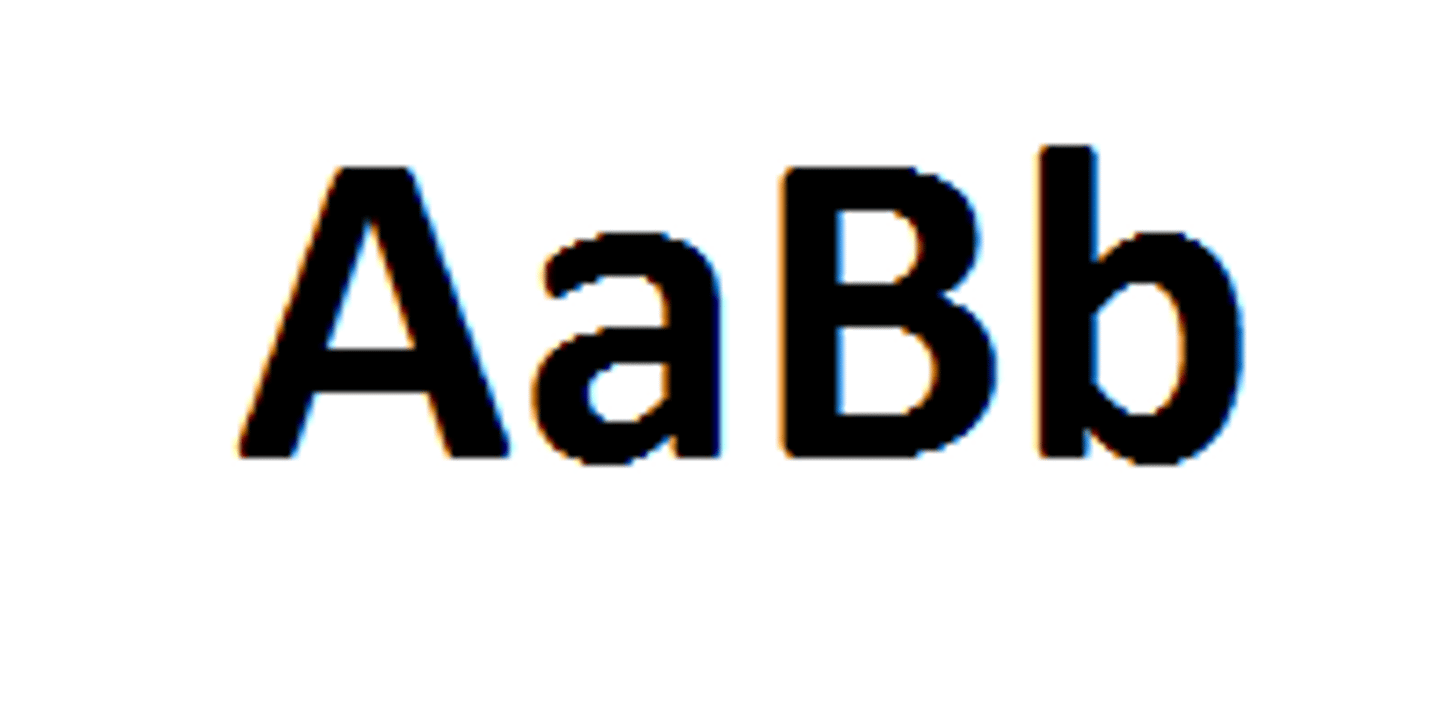
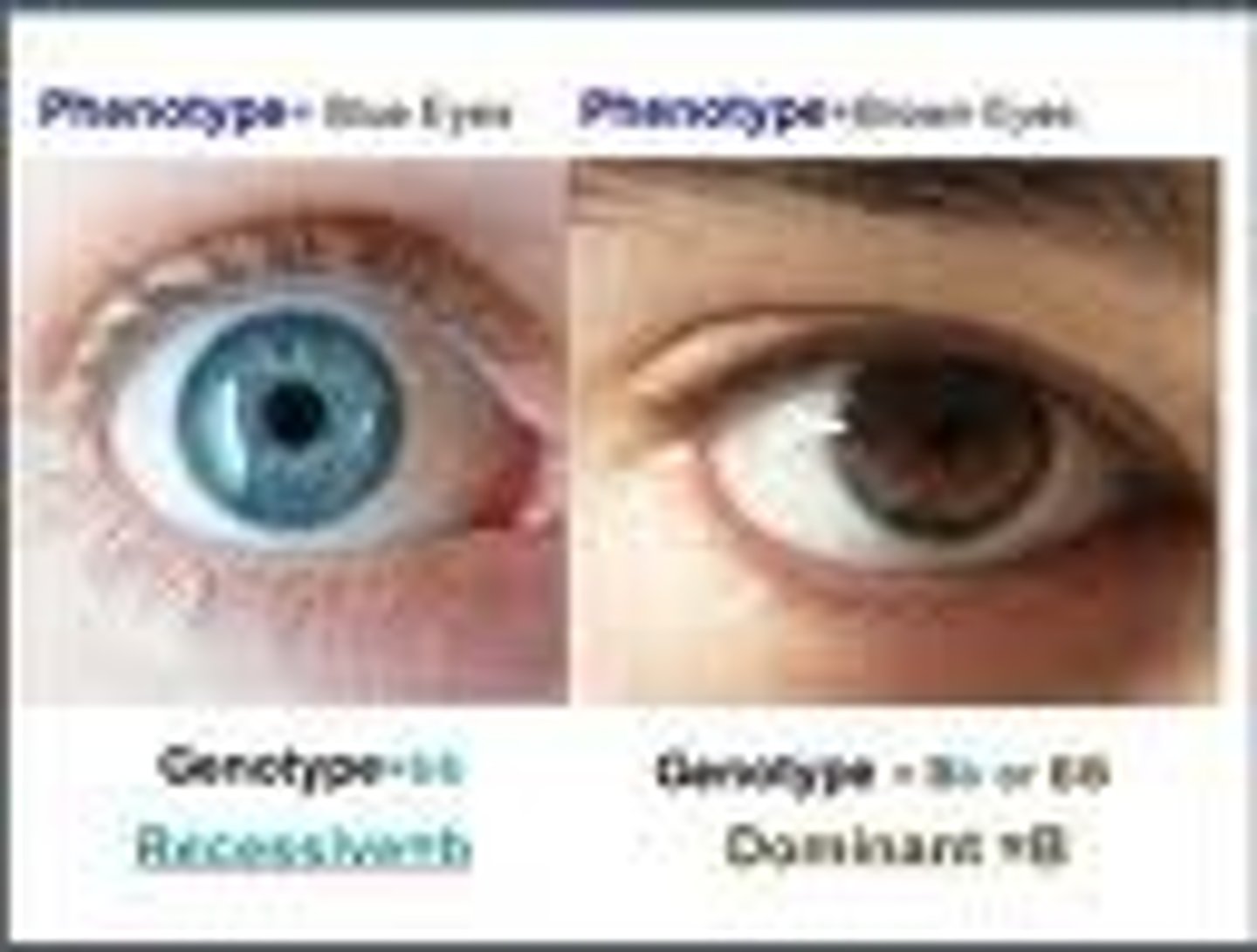
phenotype
the observable features of an organism
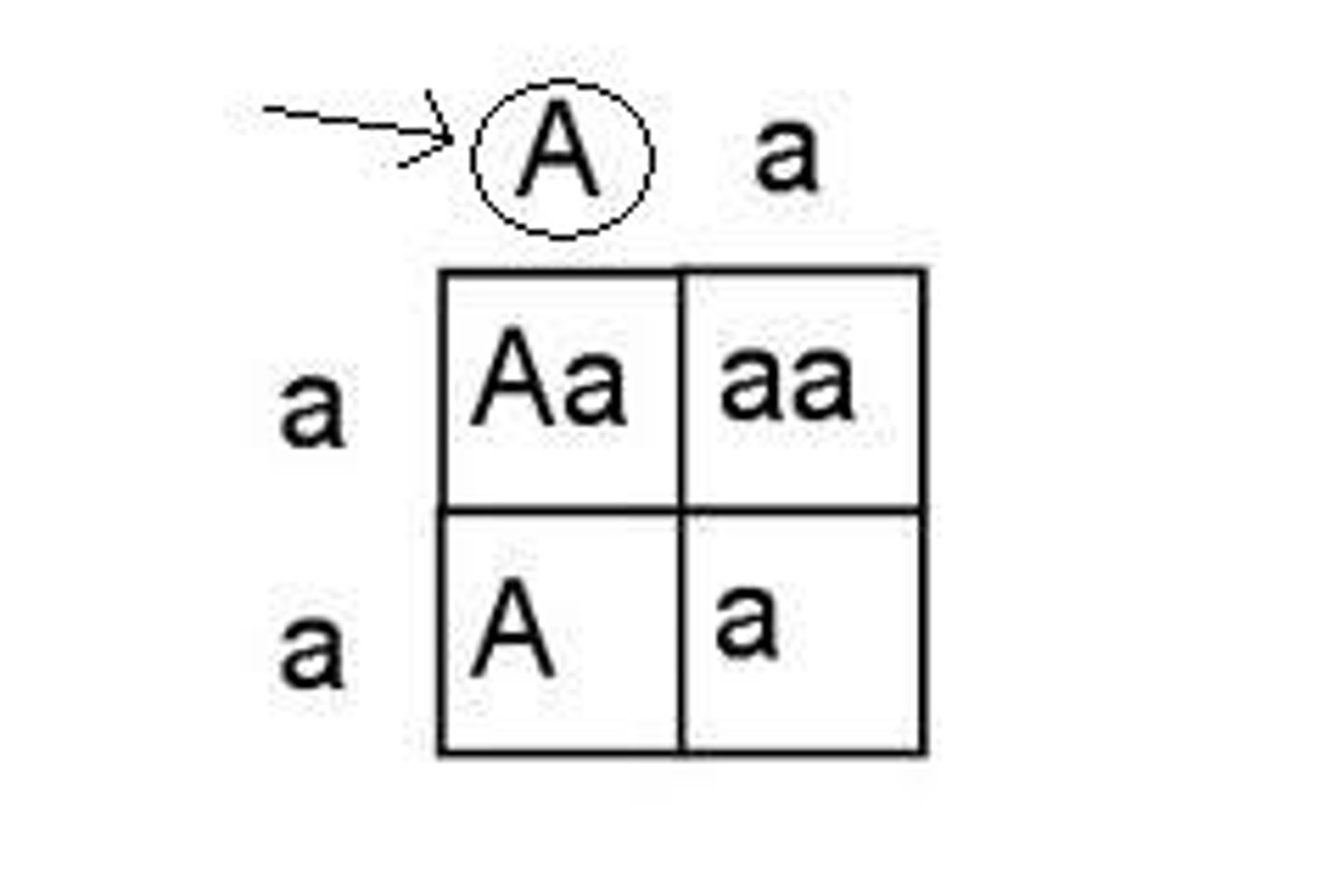
homozygous
having two identical alleles of a particular gene, two identical homozygous individuals that breed together will be pure-breeding

heterozygous
having two different alleles of a particular gene, will not be pure-breeding

dominant
an allele that is expressed if it is present
recessive
an allele that is only expressed when there is no dominant allele of the gene present

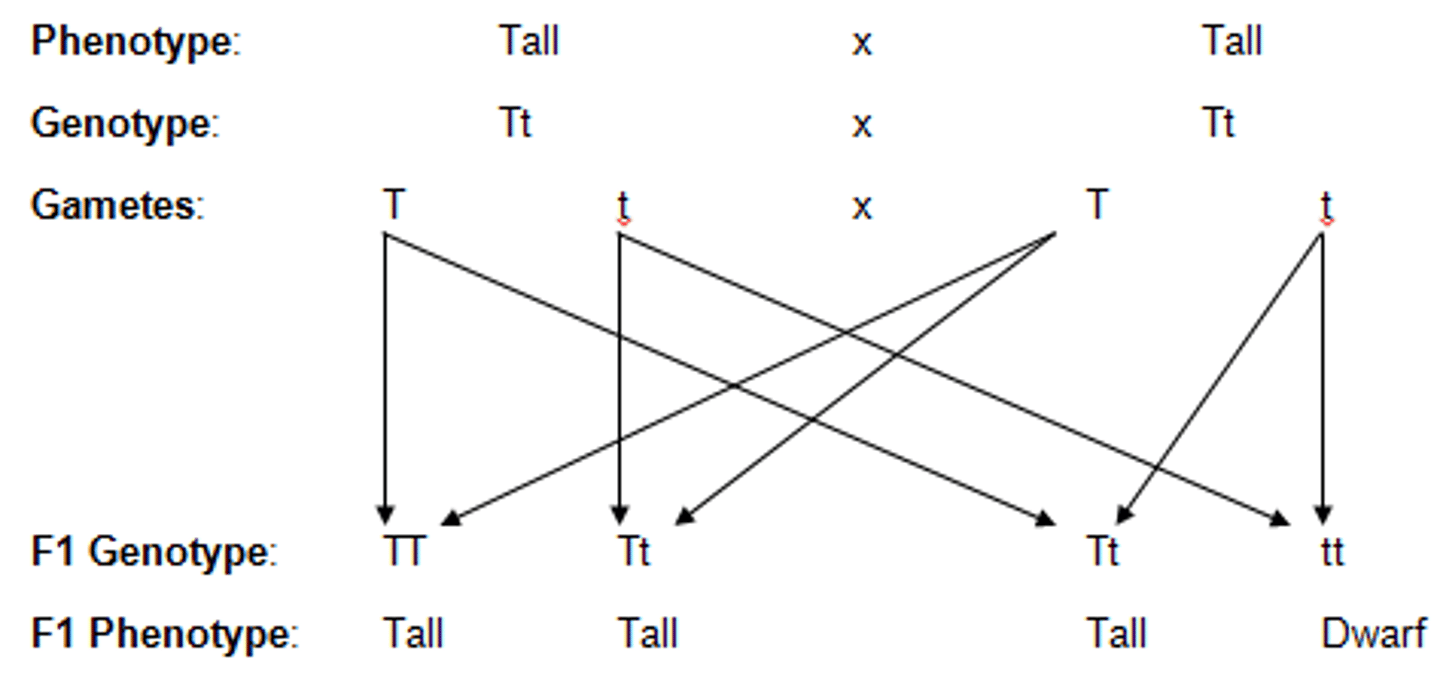
genetic diagrams
Finding the possible phenotypic ratio for offsprings
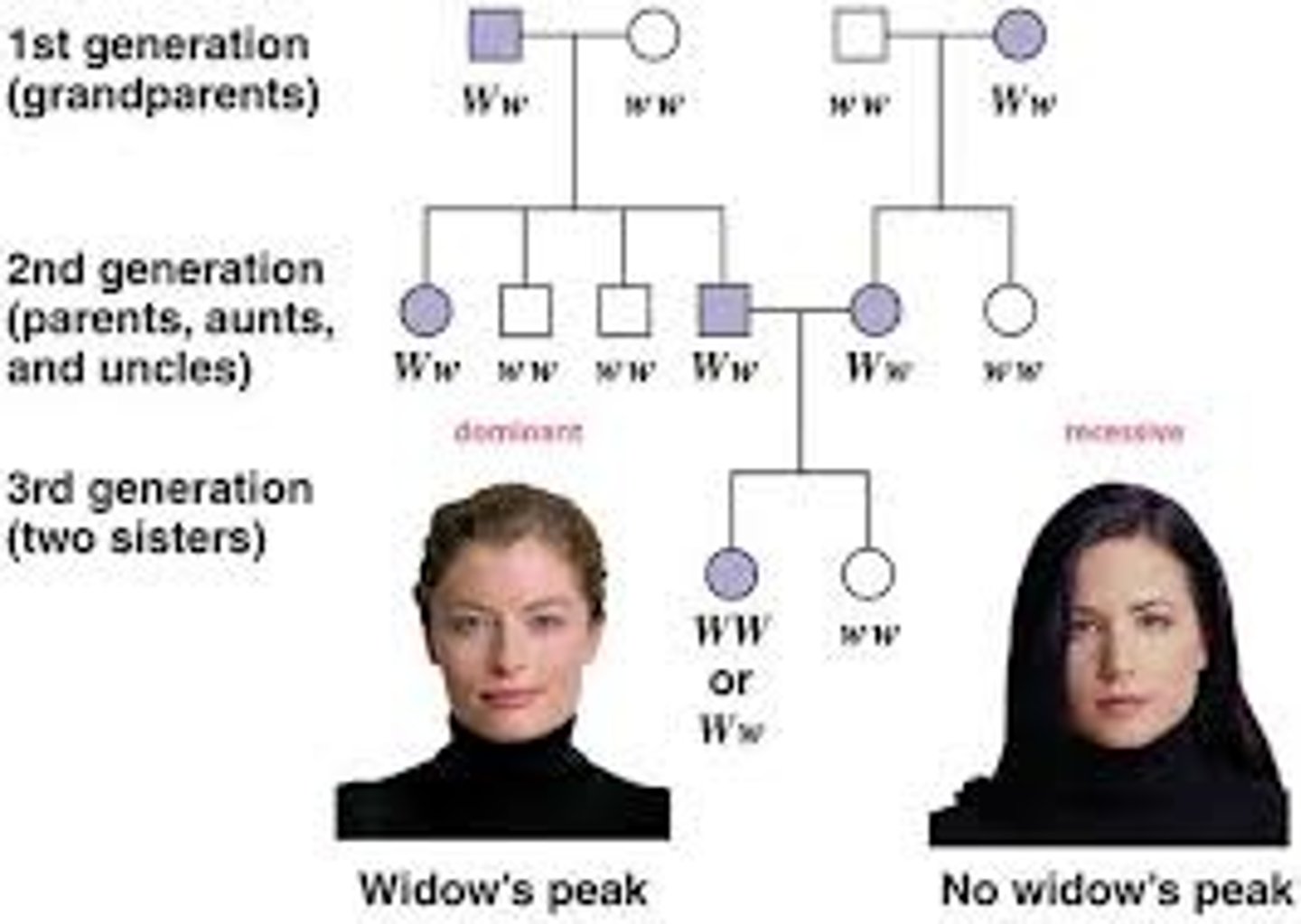
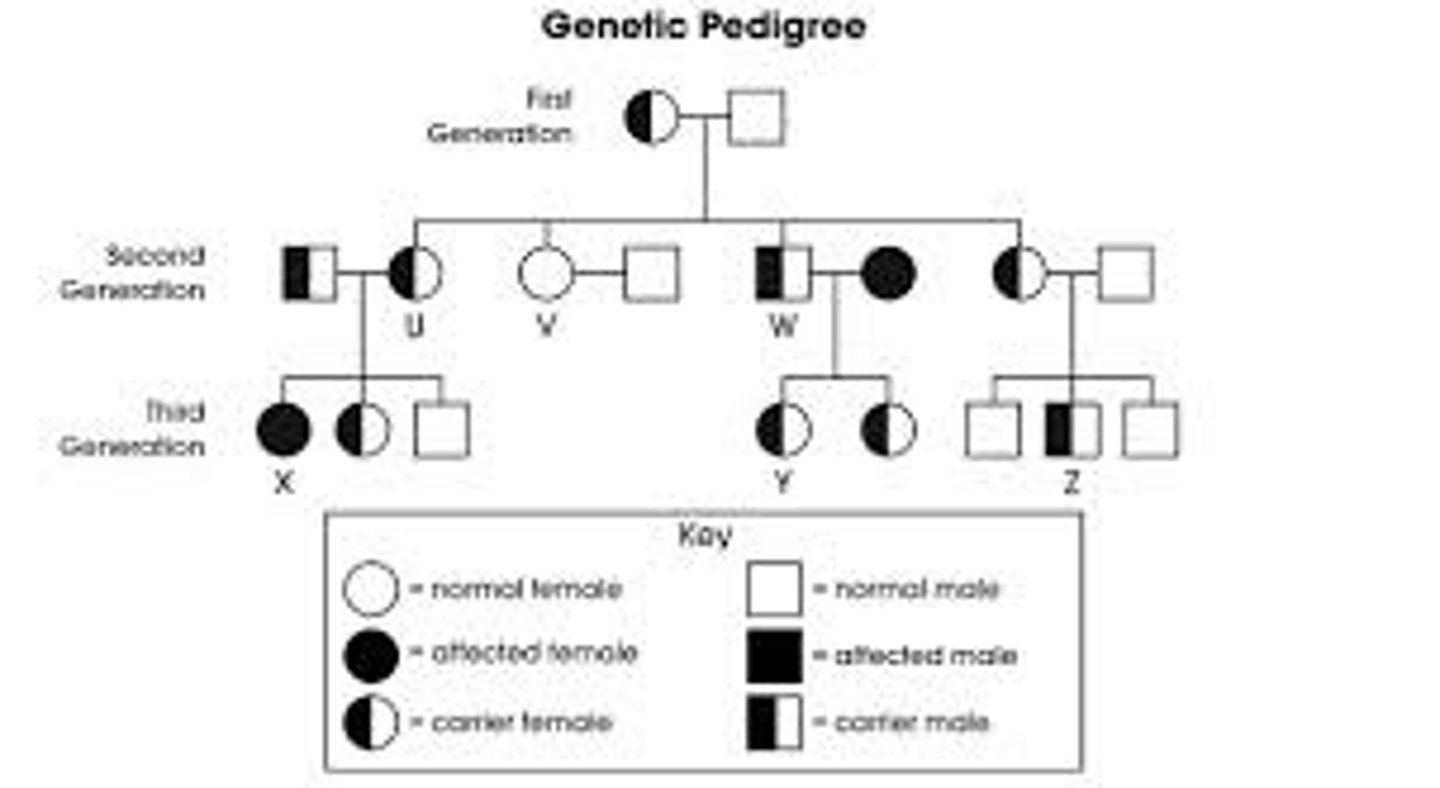
pedigree diagrams
A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance or phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next
punnet square
Finding the possible phenotypic ratio for offsprings

co-dominance
reference to the inheritance of ABO blood groups - phenotypes being A, B, AB and O blood groups and alleles being IA IB and Io
sex-linked characteristic
a characteristic in which the gene responsible
is located on a sex chromosome and that this
makes it more common in one sex than in the
other
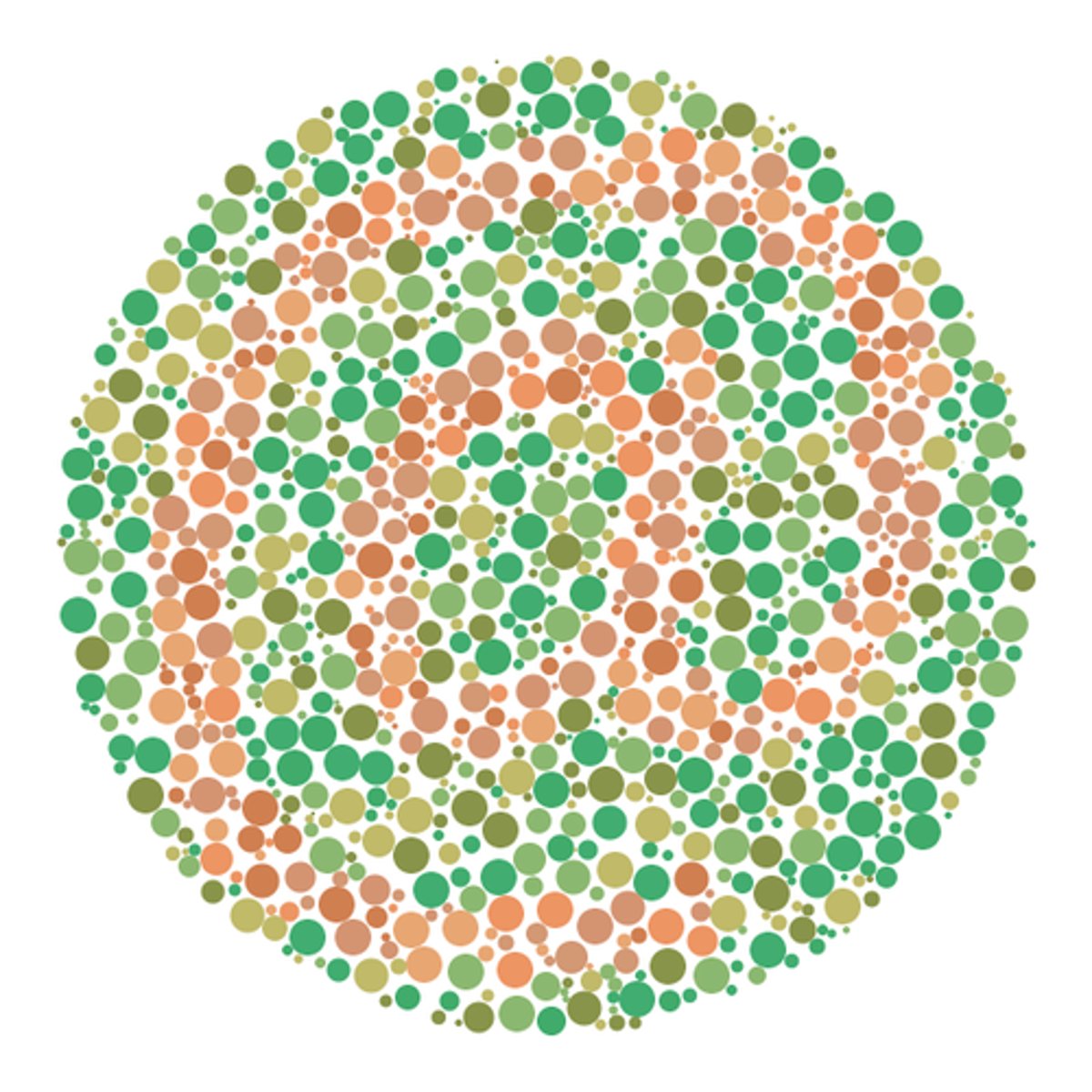
colour blindness
An inherited condition in which one or more of the three type of cone cell are unable to respond to coloured light.
