Final Exam Hearing and Balance
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The frequency range for human hearing is
0.02 to 20 k Hz
The frequency range for human hearing is
200-20,000 hz
What proportion of the external auditory canal is osseous?
2/3
What is the dB SPL value for a sound pressure of 20 uPa?
0 dB SPL
The anatomical geometry of the pinna assists in providing a listener with auditory information regarding:
Front/back localization
The damping of a sine wave over time is due to
Loss of mechanical energy from friction
Audiology was not established as a separate discipline until after:
World War II
The force that restores an object to its resting position once it has been moved is:
Elasticity
Sounds that are associated with simple harmonic motion are called
Pure tones
Pressure is a measure of
Fore/area
The wavelength of a sine wave is
Inversely proportional to frequency
The x-axis of the waveform for a sinusoid is represented by:
Time
Who was the French mathematician who determined all complex periodic signals coasted of a sum of individual sinusoids?
Fourier
The area of increased density of air molecules surrounding vibrating objects is referred to as
Condensation
Currently, to practice audiology someone is required to a minimum of a
Doctoral degree
Psychometric functions discussed in class are utilized to
Relate an observer’s performance to the intensity of the auditory signal
If the frequency of a sine wave is 5000 Hz, the period of that sine wave would be:
0.0002 seconds
The ability for an object to remain in motion once it has started moving is referred to as:
Inertia
Another name fora sinusoid is:
Pure tone
The area of decrease density air molecules surrounding vibrating objects is referred to as:
Rarefaction
What is the wavelength of a 6000 Hz sine wave in feet?
0.183 ft
The thresholds of audibility as plotted on the minimum audible pressure (MAP) curve defined:
The smallest amount of sound pressure in dB SPL to which the auditory system is sensitive while listing through earphones
Most of the structures of the auditory system are contained within the:
Temporal bone
When referring to decibel values expressed in dB SPL, the reference pressure is:
20 uPa
The log of 1 is:
0
If the wavelength of a sound is 0.08 meters, what is the period in seconds?
0.0002 seconds
A periodic waveform is one that:
Repeats at fixed intervals
The period of a sine wave is:
Inversely proportional to frequency
What is the matching anatomical orientation to anterior ?
Posterior
The matching anatomical orientation to medial?
Lateral
The matching anatomical orientation to inferior
Superior
The MAP curve suggests that for normal hearing adults
The lowest thresholds in dB SPL are obtained for the frequencies ranging between 1 and 4 k Hz
The functions of the outer ear include (3 things)
Protection, front/back localization, amplifier
What is the first part of sound transmission?
Sound source
What is the second part of sound transmission? (After sound source)
Medium (air)
What is the dB SPL equivalent of 550 uPa?
29 dB SPL
What is the dB SPL equivalent of 1,450 uPa?
37 db SPL
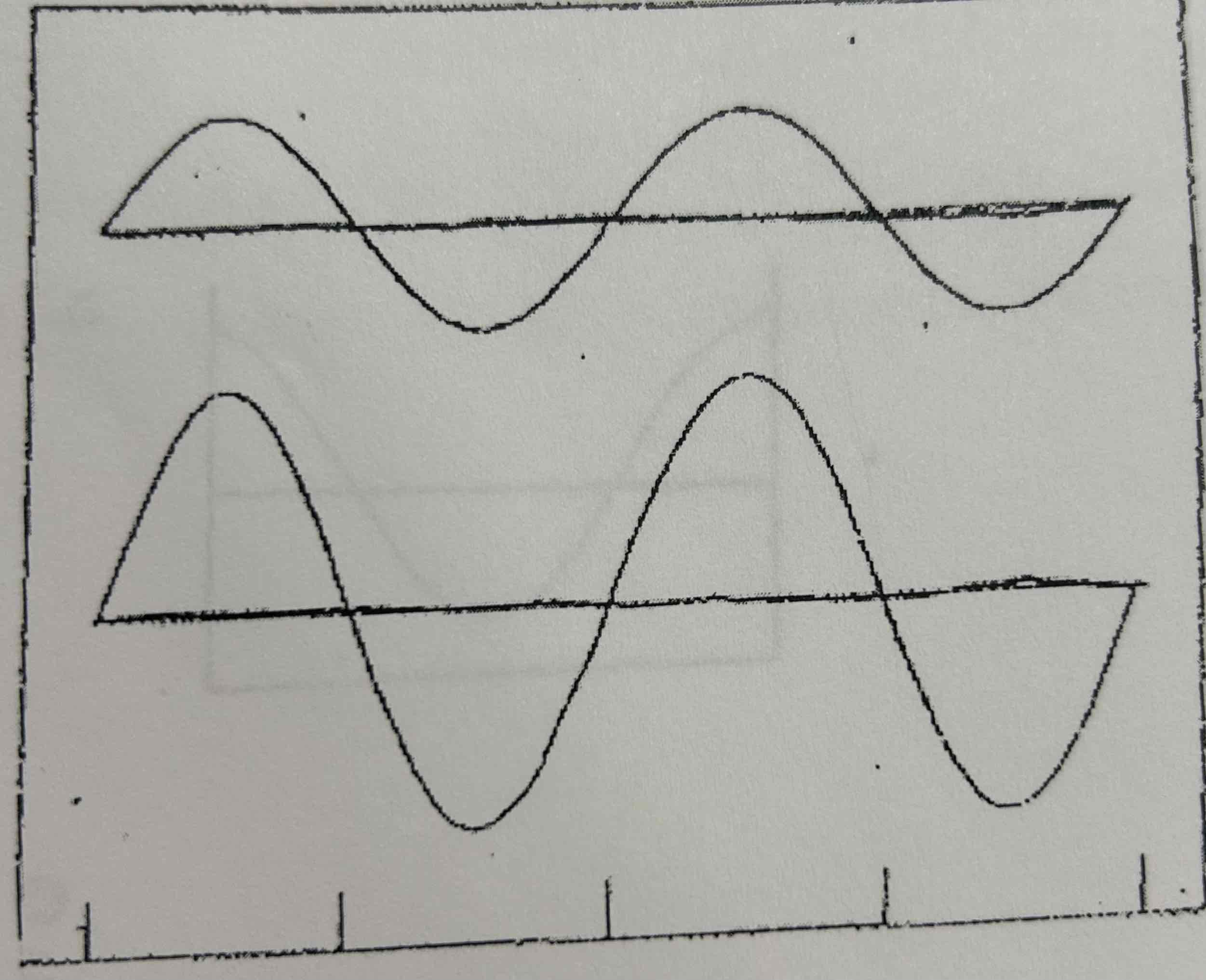
Are these two waveforms the same frequency?
Yes
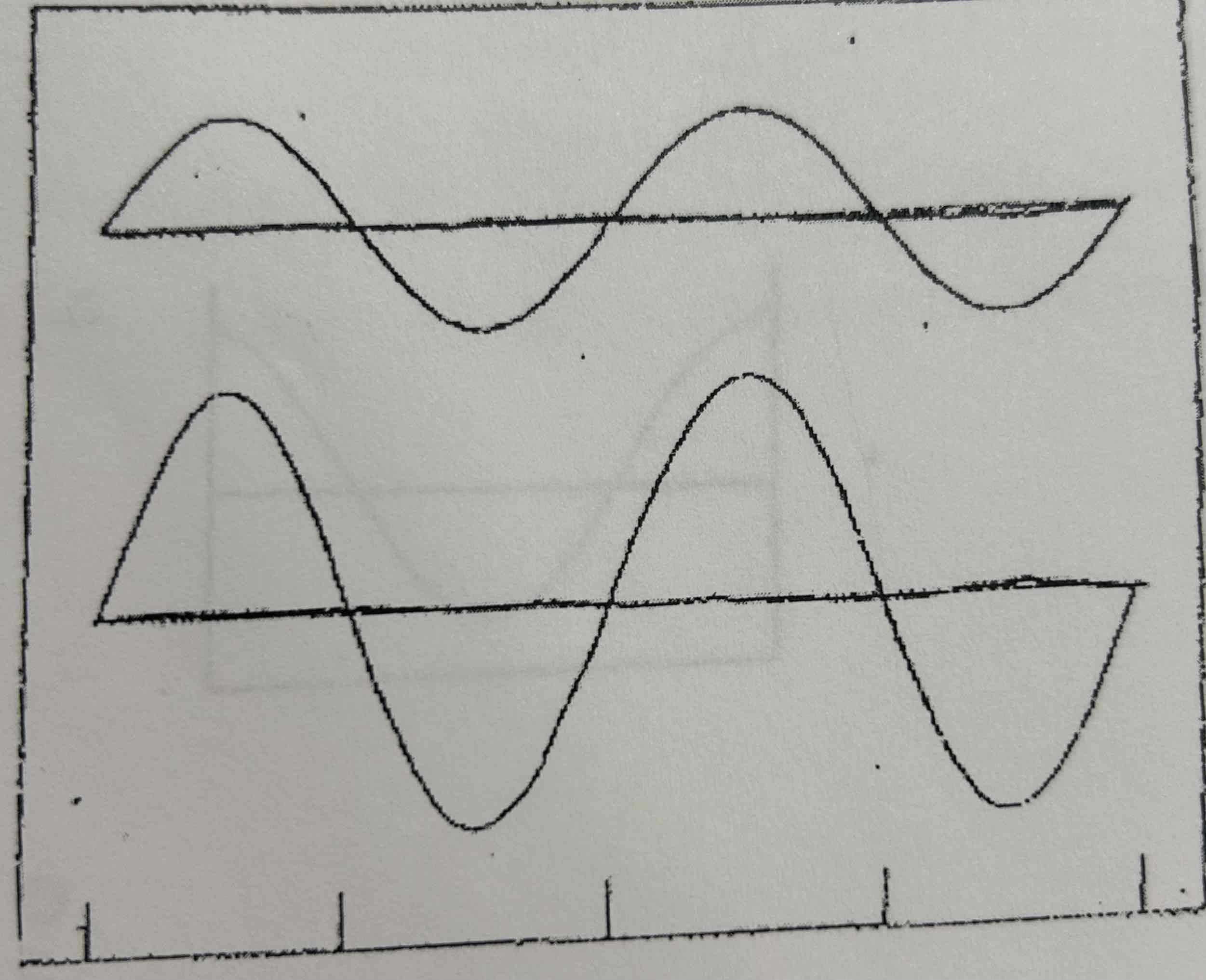
Why do these two waves have the same frequency?
Have the same # of cycles
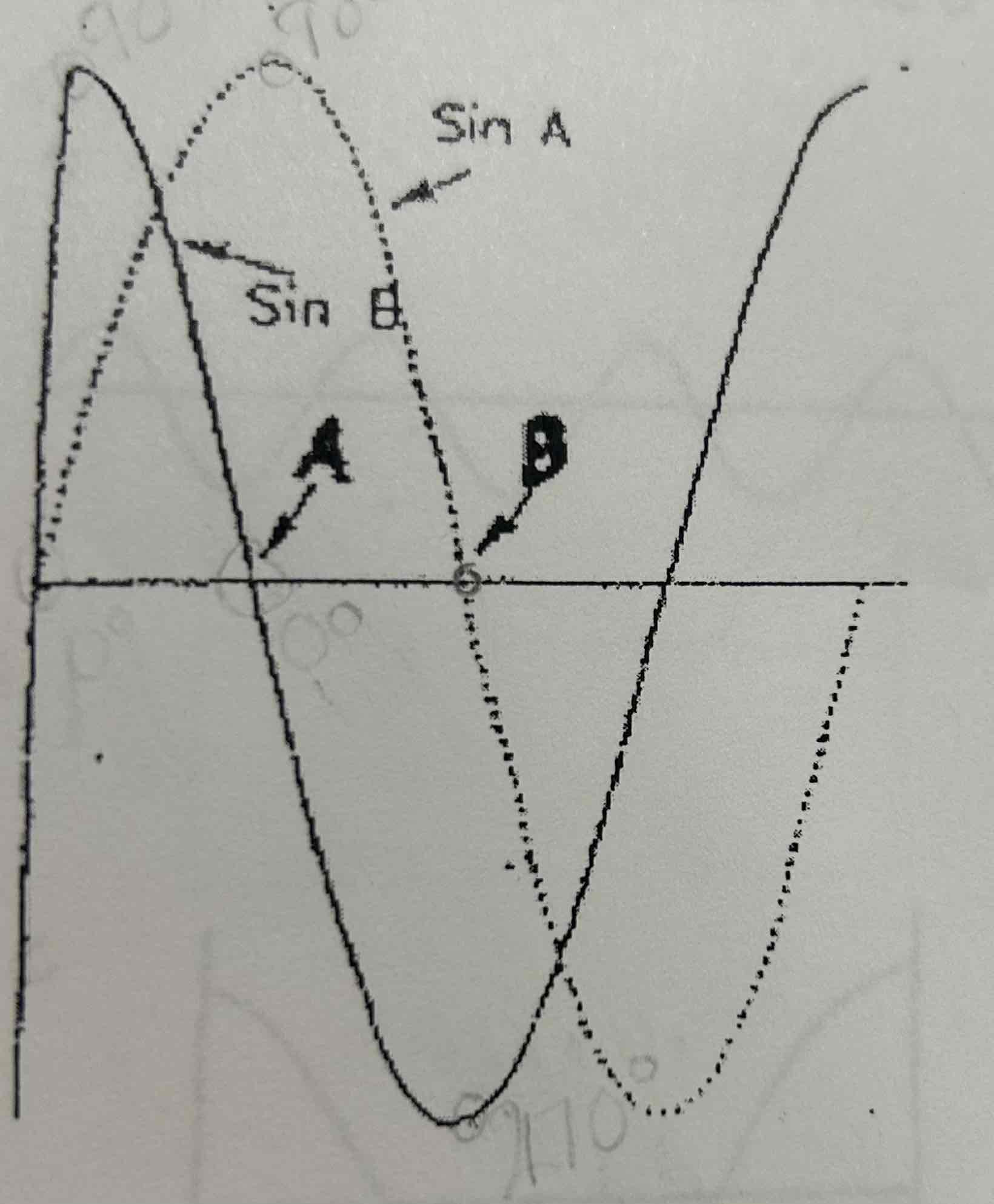
How far out of phase are the waveforms at point A?
90 degrees
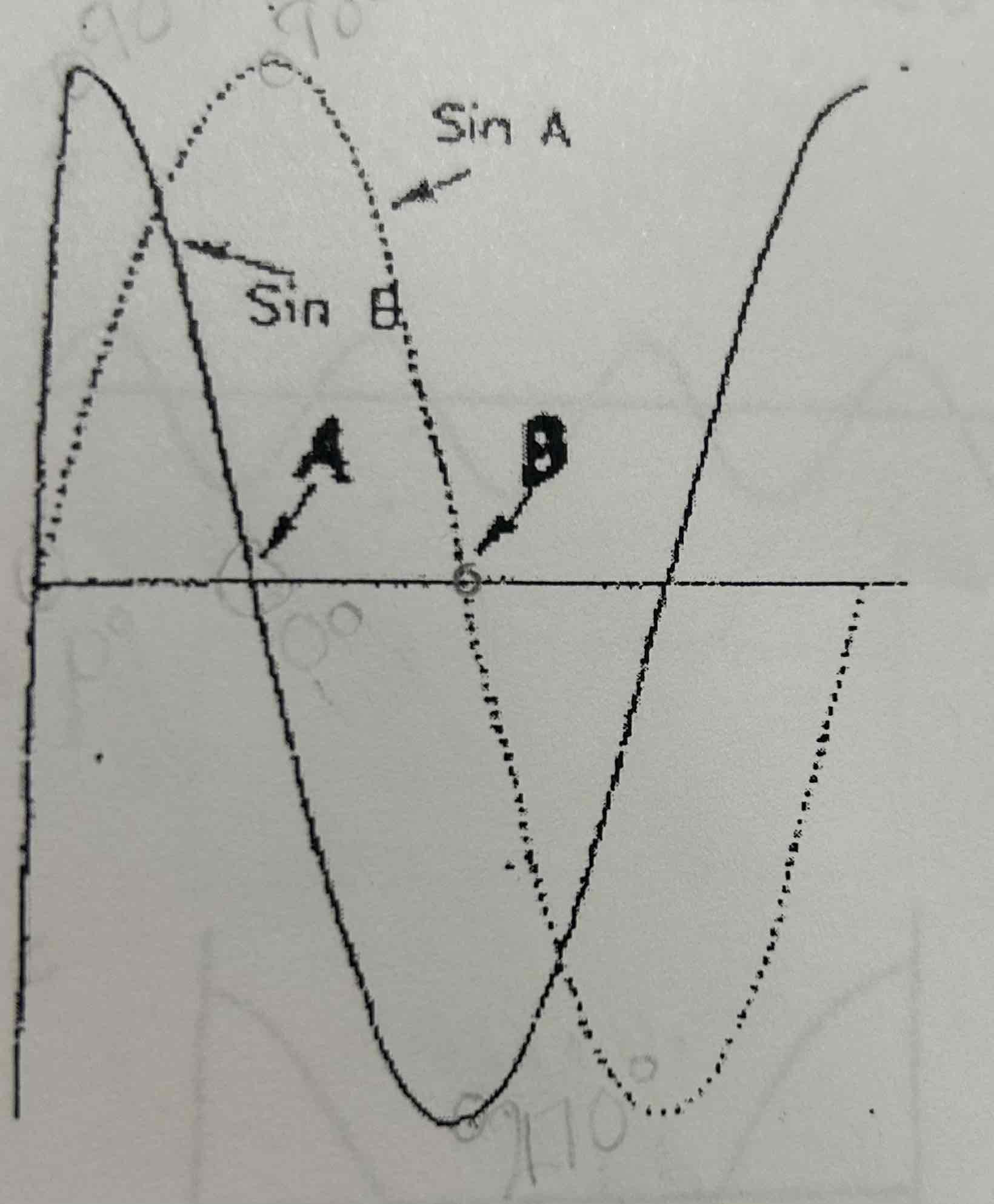
How far out of phase are the waveforms at point B?
90 degrees
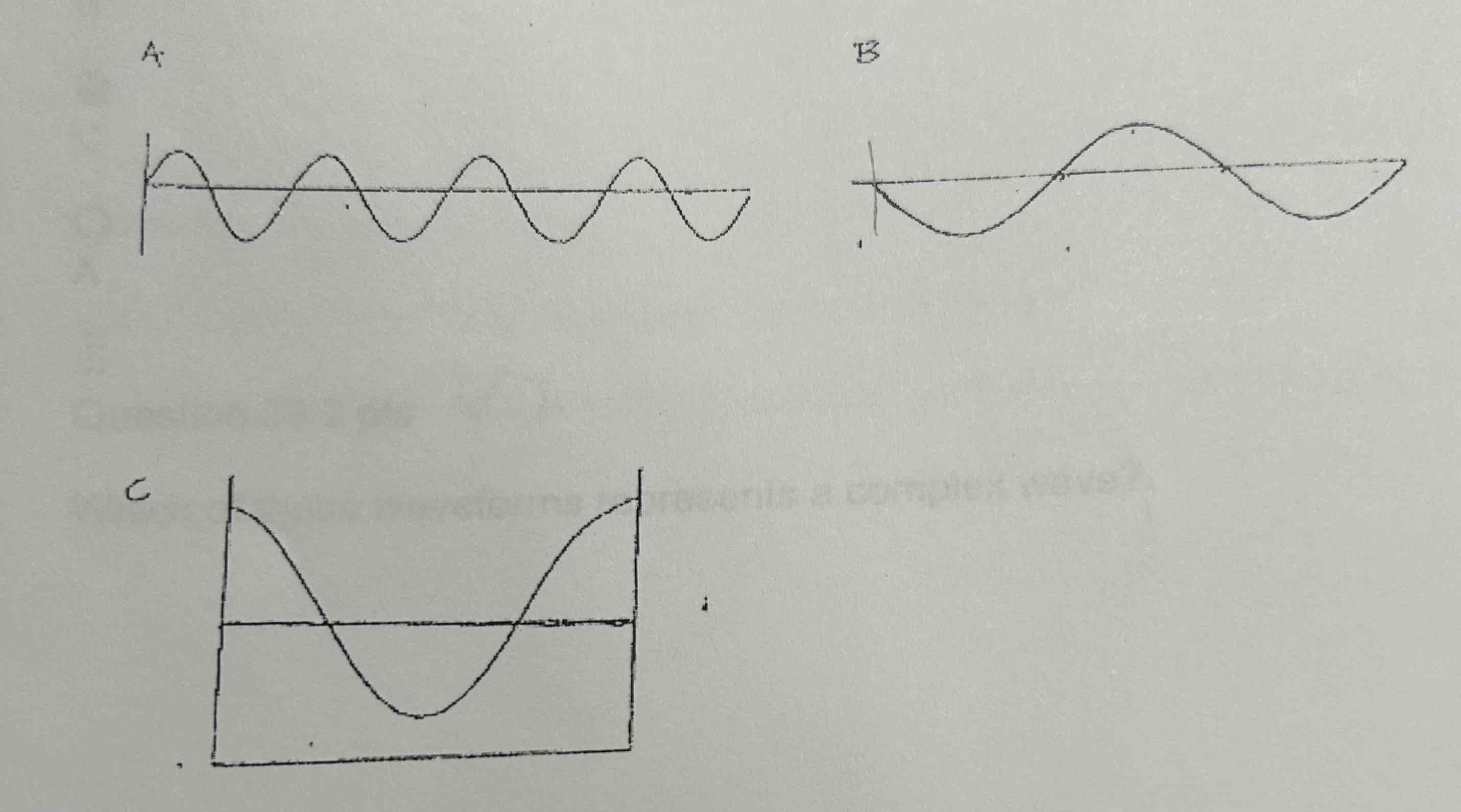
Which of these waveforms has a starting phase of 180 degrees: A, B, or C?
B
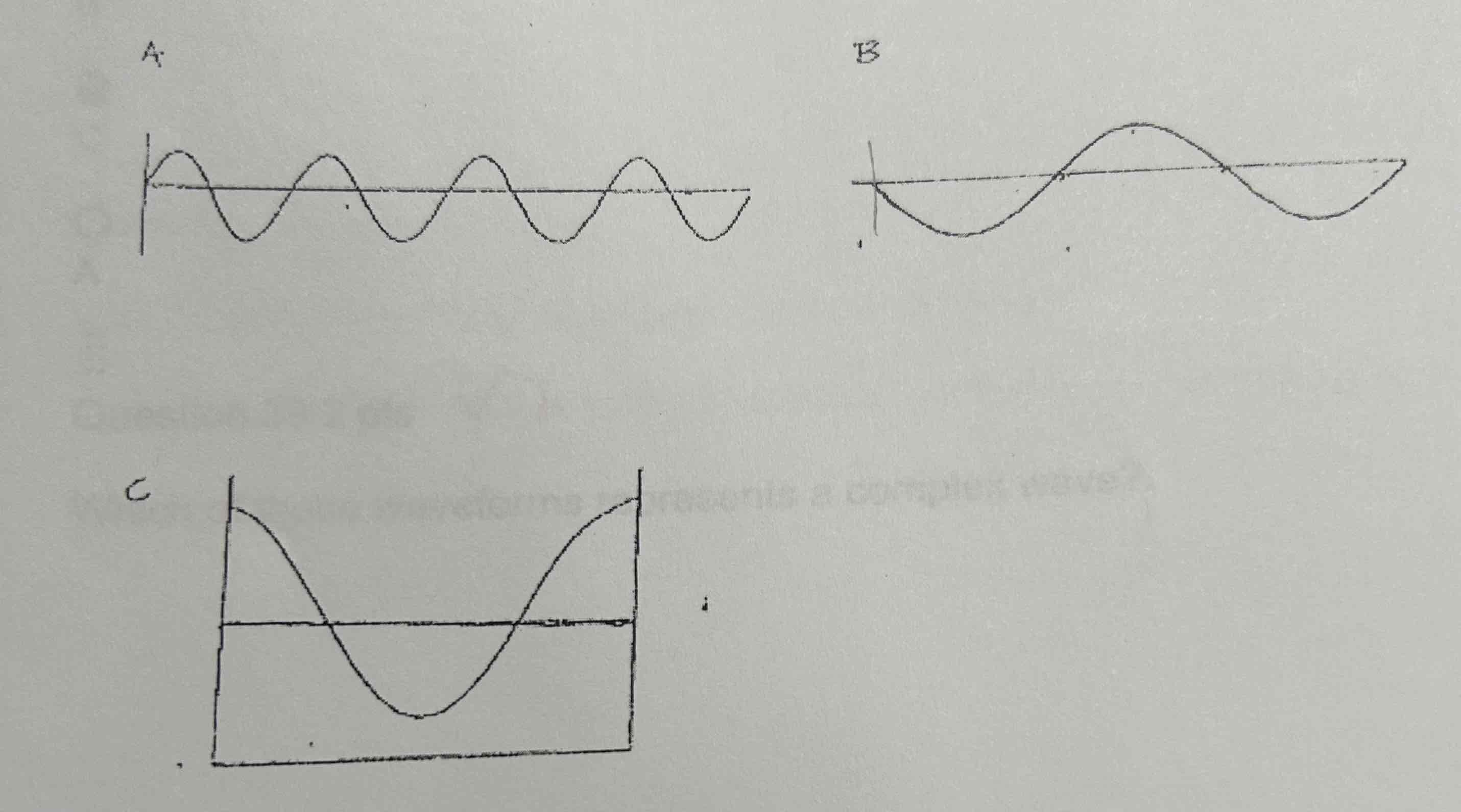
Which of these waveforms has a starting phase of 90 degrees?
C
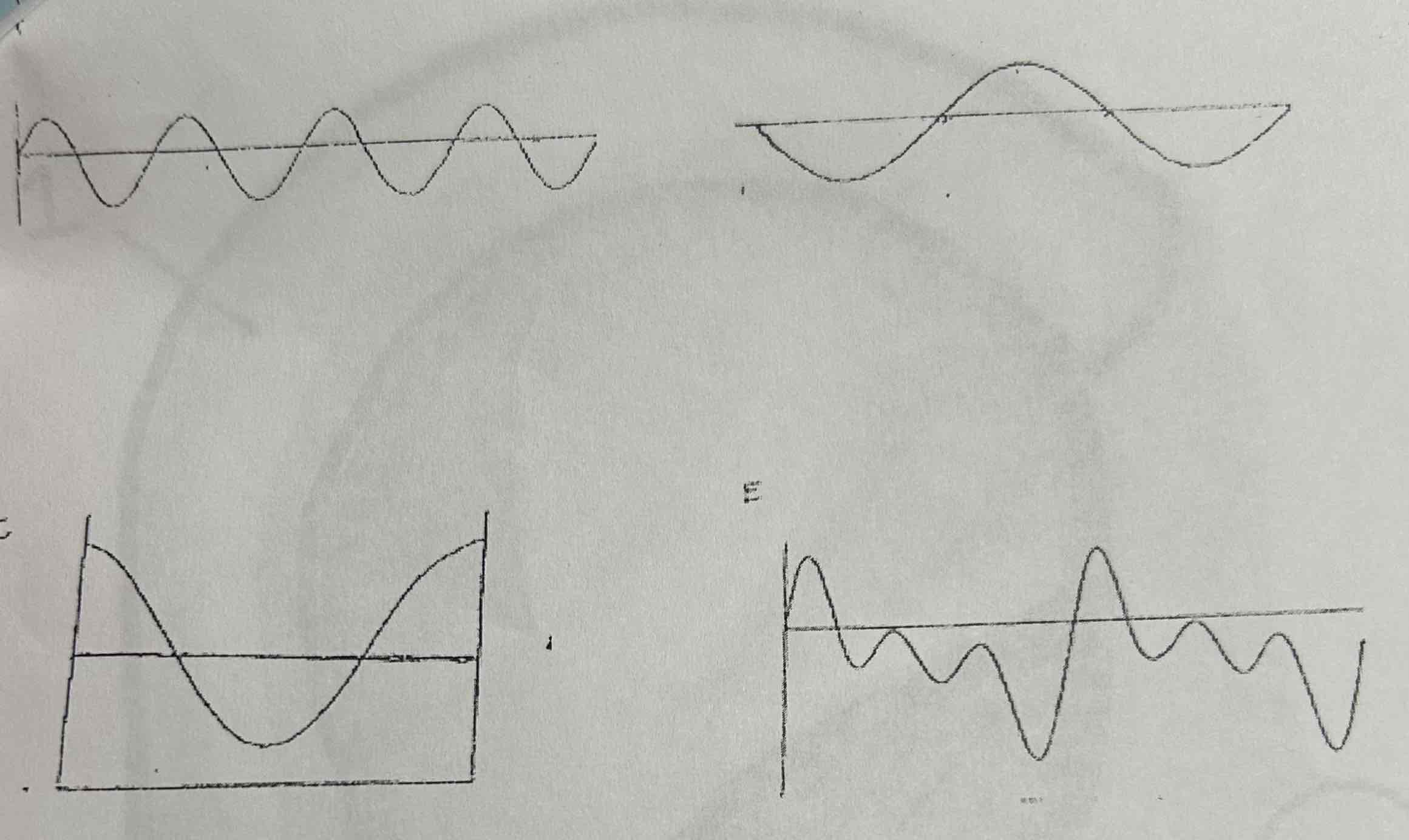
Which of these waveforms represents a complex wave?
E
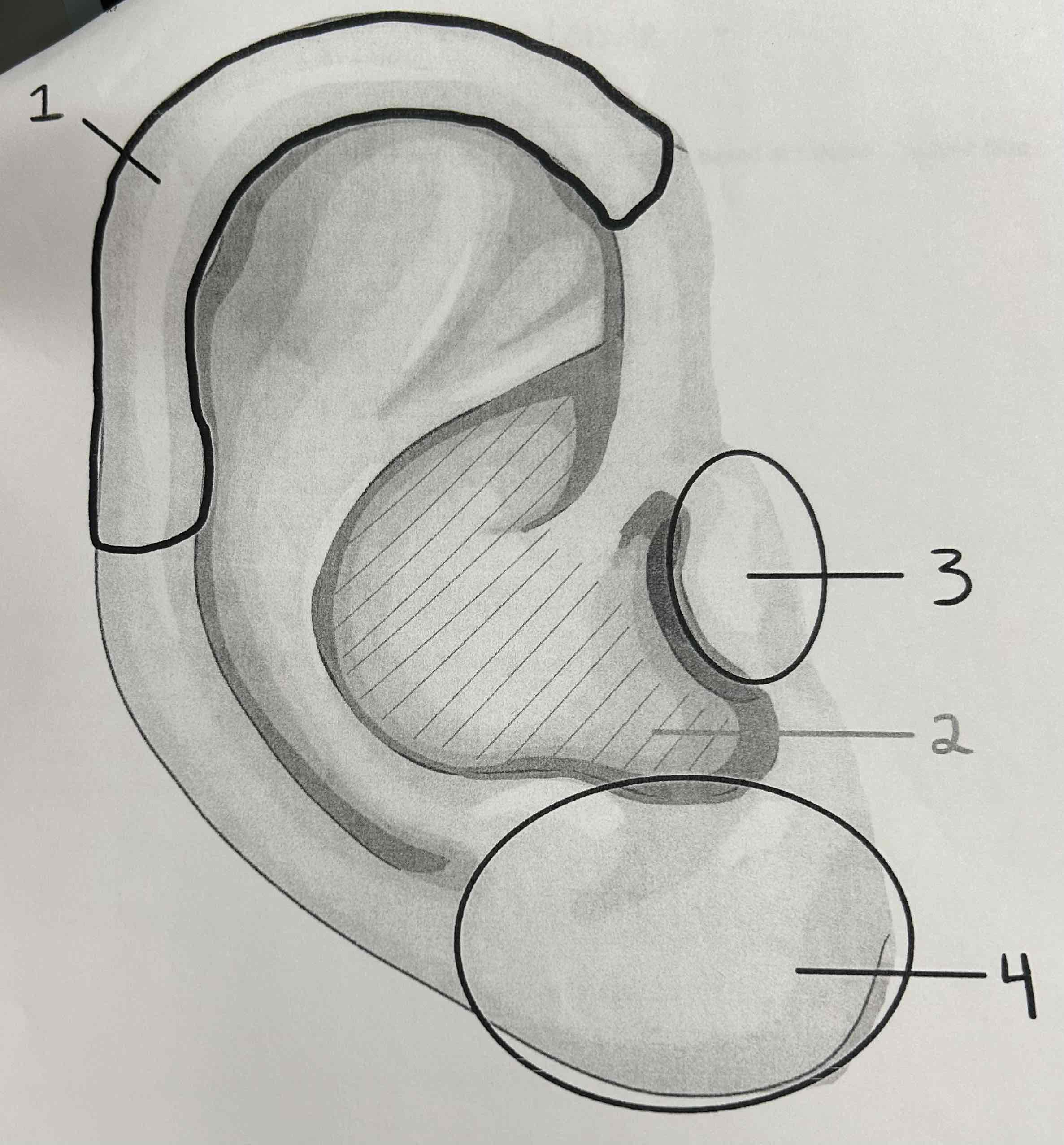
What is number 1 pointing to?
Helix
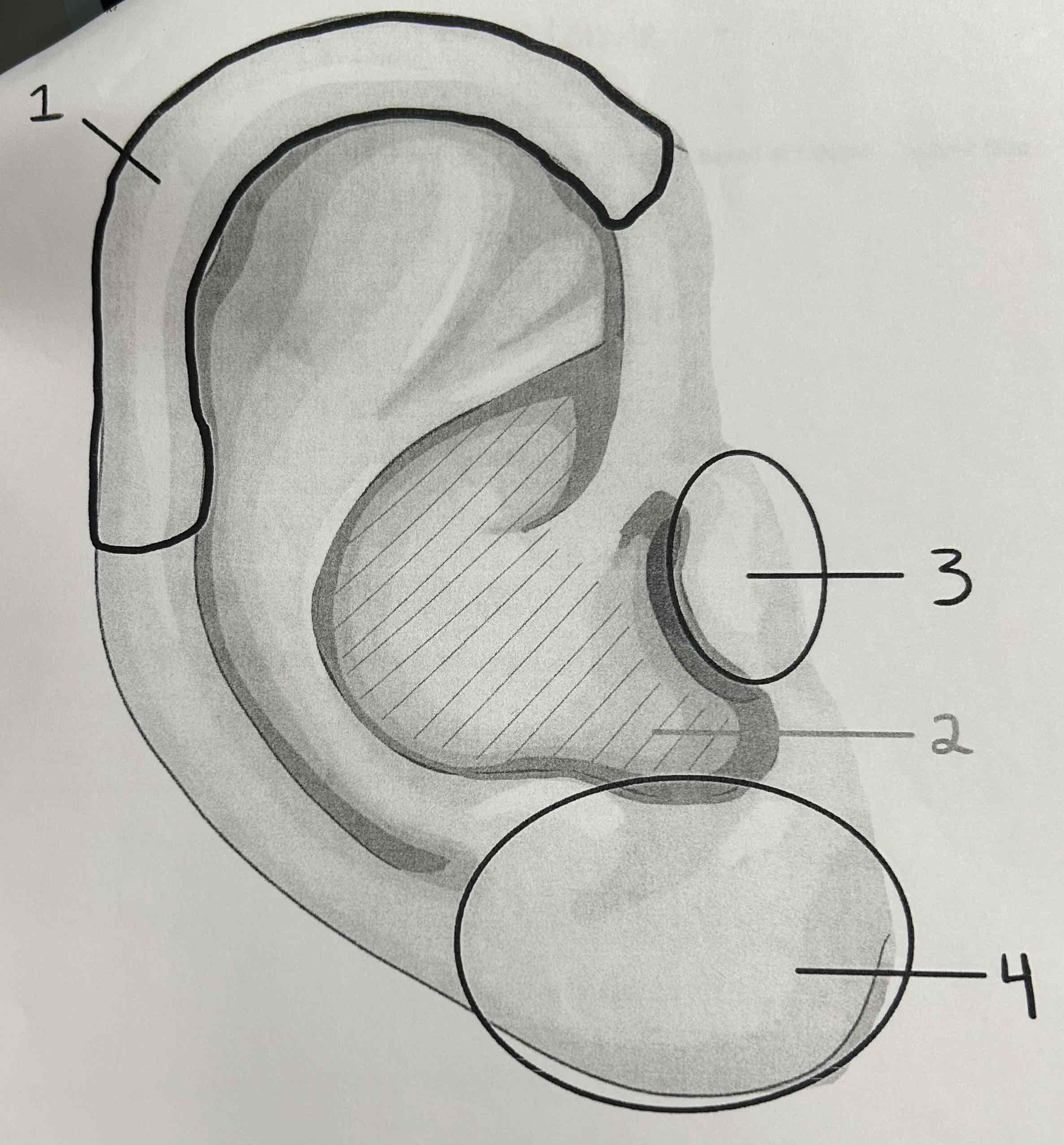
What is #2 pointing to?
Concha