BIOL 3030 Exam 1 Bernal
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Evolution
change in characteristics of a population through time
Anaximander (610-546 BC)
proposed that the sun, moon, and stars were physical objects, not deities
Aristotle (384-322 BC)
Presented logic and hypothesis testing.
Catastrophism
sudden events would change geological features and presence of species at a given time. Also thought the Earth was fairly young.
Xenophanes (570-470 BC)
questioned the date of the earth when he found marine fossils at the top of a mountain.
James Hutton
formally suggested the earth must be very old based on observations of sediment layer which he attributed to erosion, pressure, sedimentation, etc.
Charles Lyell
Wrote Principles of Geology; proposed uniformitariansim
Uniformitarianism
Geological features we see today are gradually changing through time; processes that cause change are happening today
Naturalism
explaining the world based on observable phenomena
Mundus Subterraneaus
Book that gave recipe for creating worms and flies by leaving out rotten food.
Empedocles
Proposed that all living things are made up of independent body parts that were running around alone and mixed together to make organisms. Only functional combinations persisted.
Francesco Reddi
Proved that life could not spawn from nonliving material
Scala Naturae
All species created in their perfect, unchanging form by a deity, as a link in a chain from most simple (worms) to complex (human).
Al jahiz
Ethiopian thinker, Wrote "Book of Animals" in 700s-800s , hinted at natural selection
George Louis Leclerq
Wrote Histoire Naturelle, said "Common morphological characteristics are an expression of close relationships between them."
Erasmus Darwin
Wrote Zoonomia: All life has evolved through a "single living filament", changing through time.
Wrote Temple of Nature: Noted struggle for existence
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
an organism's efforts during it's lifetime cause changes to it's phenotype, and these changes are passed to offspring
Lamarck
French guy who believed in IAC
Patrick Matthew
Proposed a similar idea to natural selection in the boat building book he wrote.
Charles Darwin
observed reason for atolls, credited with developing natural selection
Published Origin of Species
Alfred Wallace
Naturalist that studied in the Malyan archipelago
Observations gave rise to biogeography
Found that flora and fauna of Asia and Australia were distinct despite being close together.
Ali Wallace
Malayan assistant of Alfred Wallace
Origin of Species
Book by Darwin that covered:
Natural Selection
Artificial Selection
Evidence for Evolution
Artificial Selection
Humans choose which individuals to mate, to obtain desirable characteristics
Natural Selection
Differential survival
Differences in reproductive success.
Darwin's 2 main ideas
natural selection
Organisms have common descent
Variation in the population and a selective agent
Natural selection requires 2 components:
Thomas Malthus
Principles of Population: Human populations grow faster than the available food, so there would be overpopulation if it wasn't for war, famine, disease
Darwin borrowed heavily from this work
transformational, variational
Lamarck's process is ________, Darwin's process is _________
A hammer, a sifter
An example of a transformational process would be getting fine dust with __________, while variational is like using __________
Descent with modification
Darwin's other main idea:
- species split from common ancestor and slowly gain differences
- This is why closely related species are similar
Lamarck
_________ would claim that all species who acquired hair evolved independently.
Darwin
_________ would claim that all species are related by descent and it is possible to have similar structures/adaptations as the common ancestor
- How to account for complex structures with a slow process?
- Vestigial traits
- Why would variation persist?
- How are traits inherited?
Four key problem with Origin of Species
Adaptation
inherited trait that makes an organism more fit in its environment, as a result of natural selection
Can
Environment _____ cause phenotypic variation
genotype, phenotypes
The same _____ may produce different ________ under different environmental conditions
Norm of Reaction
both environment and genetics can play a big role in the phenotype
Life History
refers to how organisms invest their energy in reproduction over their lifetimes
Antagonistic pleiotropy
a trait that increases fitness in one condition can decrease fitness in another setting
structures to detect light
Eyes originated as ________ and progressively became more complex
Vestigial Traits
Traits that were useful in ancestors that are inherited today, but that have lost their original use.
Exaptation
a heritable trait that increases fitness in a certain environment that was originally selected for a different function but also advantageous
(ex. feathers)
Physical Constraints
Why can't elephants have long legs?
Why can't owls have 360 vision?
Nature of the Environment
NS problem: It is impossible to be a 'perfect' organism if the target is always moving
Abiotic environments always changing allowing for different species to thrive over time
Evolutionary Arms race
evolutionary forces that lead to the development of defenses on the host, and mechanisms to evade such defenses on pathogen/predator
Lack of Foresight
NS problem: Natural selection is not predictive, and it is unable to forecast the future. Selection can only happen on past and present events.
Carl Linnaeus
In his book: Systema Naturae, tried to classify all known species
Developed binomial nomenclature (father of taxonomy)
Ernst Haeckel
coined the term phylogeny;
famous idea was "embryology recapitulates phylogeny" which suggests that embryonic stages of organisms are represented in their ancestors
Phylogeny
branching relationships of species, as they give rise to descendant groups over time
Characters
any observable or measurable characteristic of an organism
Traits
represents the specific state of the character
Taxon
groups represented at tip of phylogeny
Nodes
sections where branches of phylogeny split. Represents common ancestor. Not alive today
Root
represents the common ancestor to all groups in the tree. base of the tree
Hypotheses
Phylogenies represent _________ about evolutionary history, and such they can be tested, challenged, and refuted.
Polytomy
more than one branch coming out of one node
Monophyletic group
a common ancestor and all of its descendants
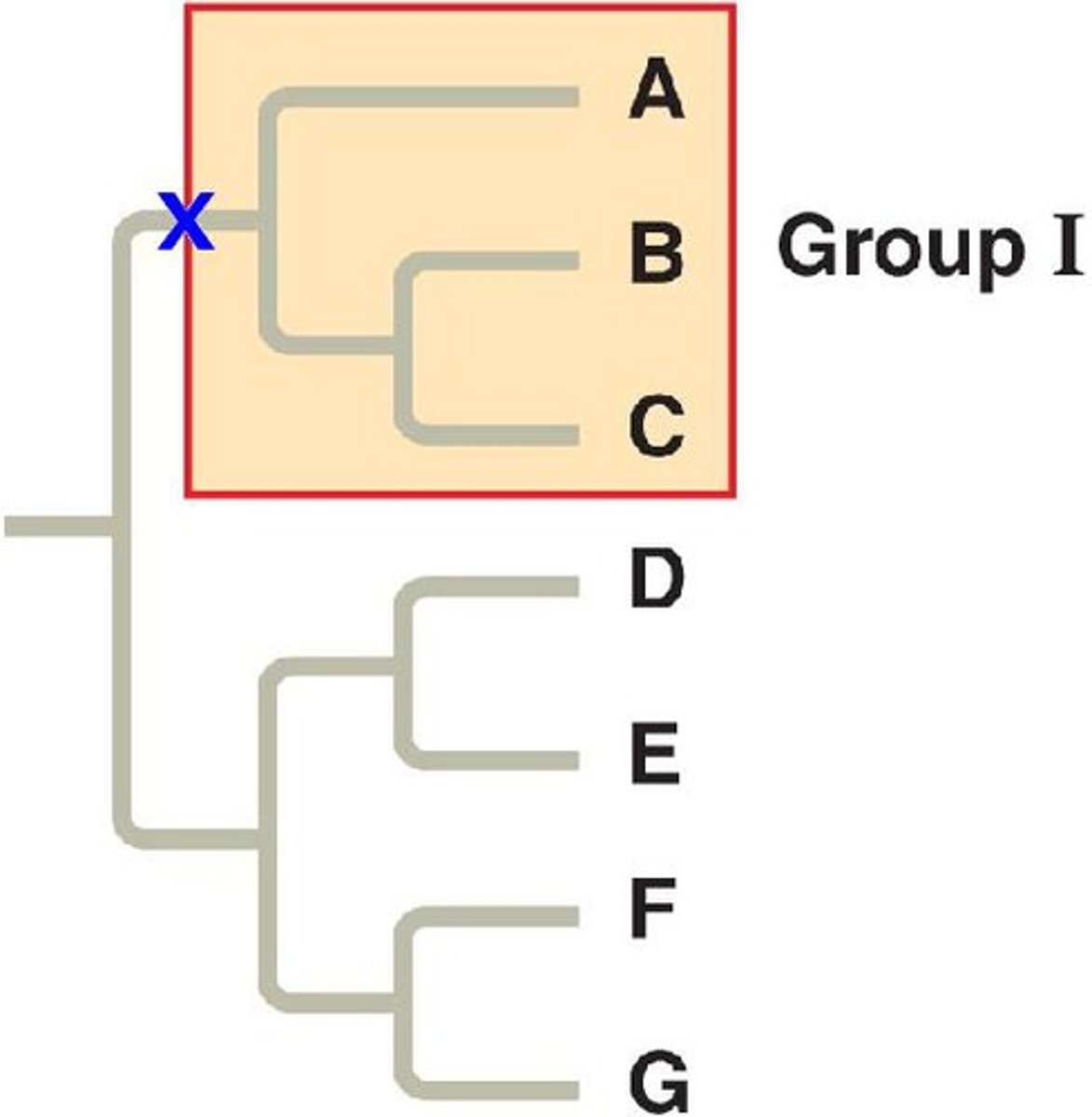
Clade
group of species that share a single common ancestor
Polyphyletic Group
when a group does not include common ancestor of all members, nor all descendants from that ancestor
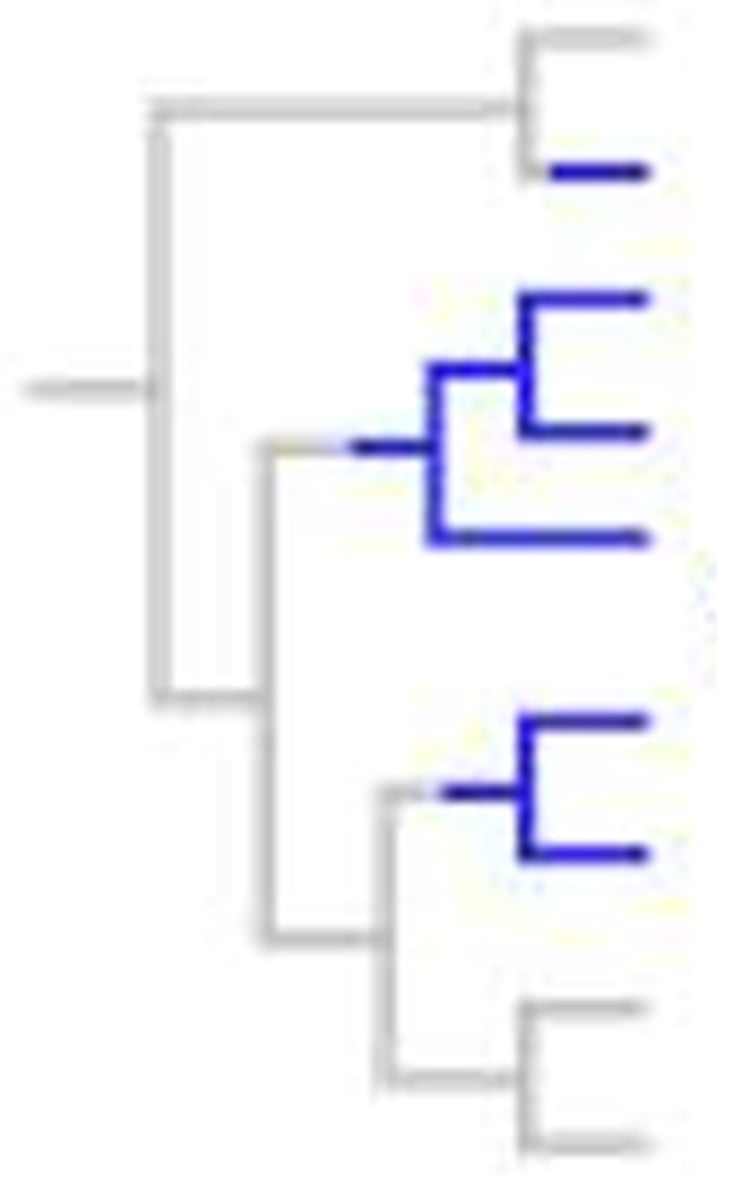
Paraphyletic group
contains the group's common ancestor, but not all descendants
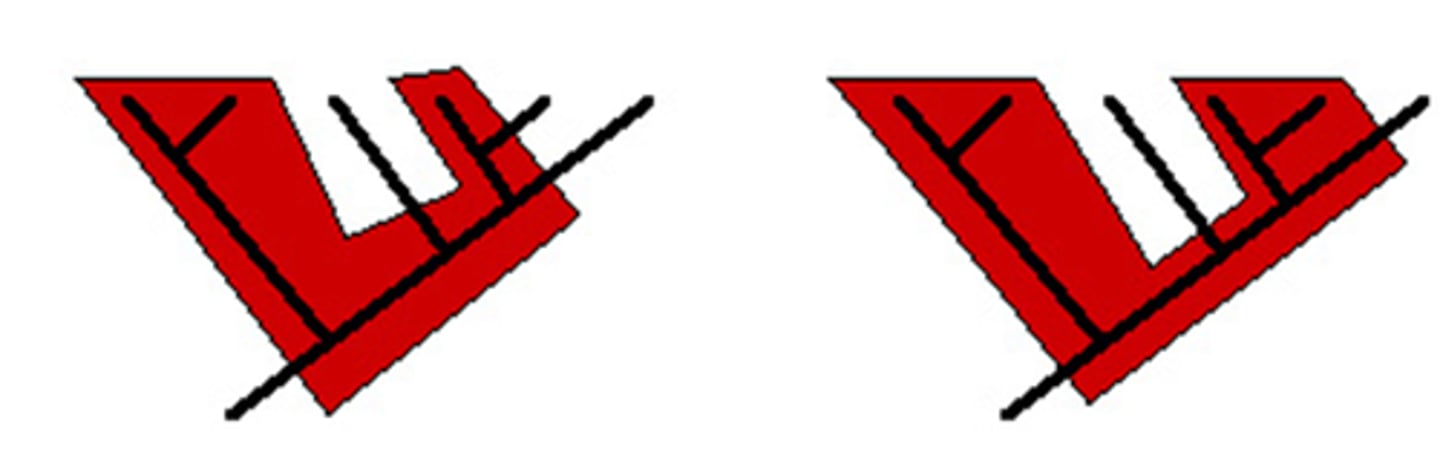
Rooted tree
ancestor from which all other lineages derive is included in the tree
Unrooted tree
tree not designed from the perspective of a single common ancestor
Cladogram
no branch lengths, just relationships
Phylogram
branch lengths indicating some sort of evolutionary change
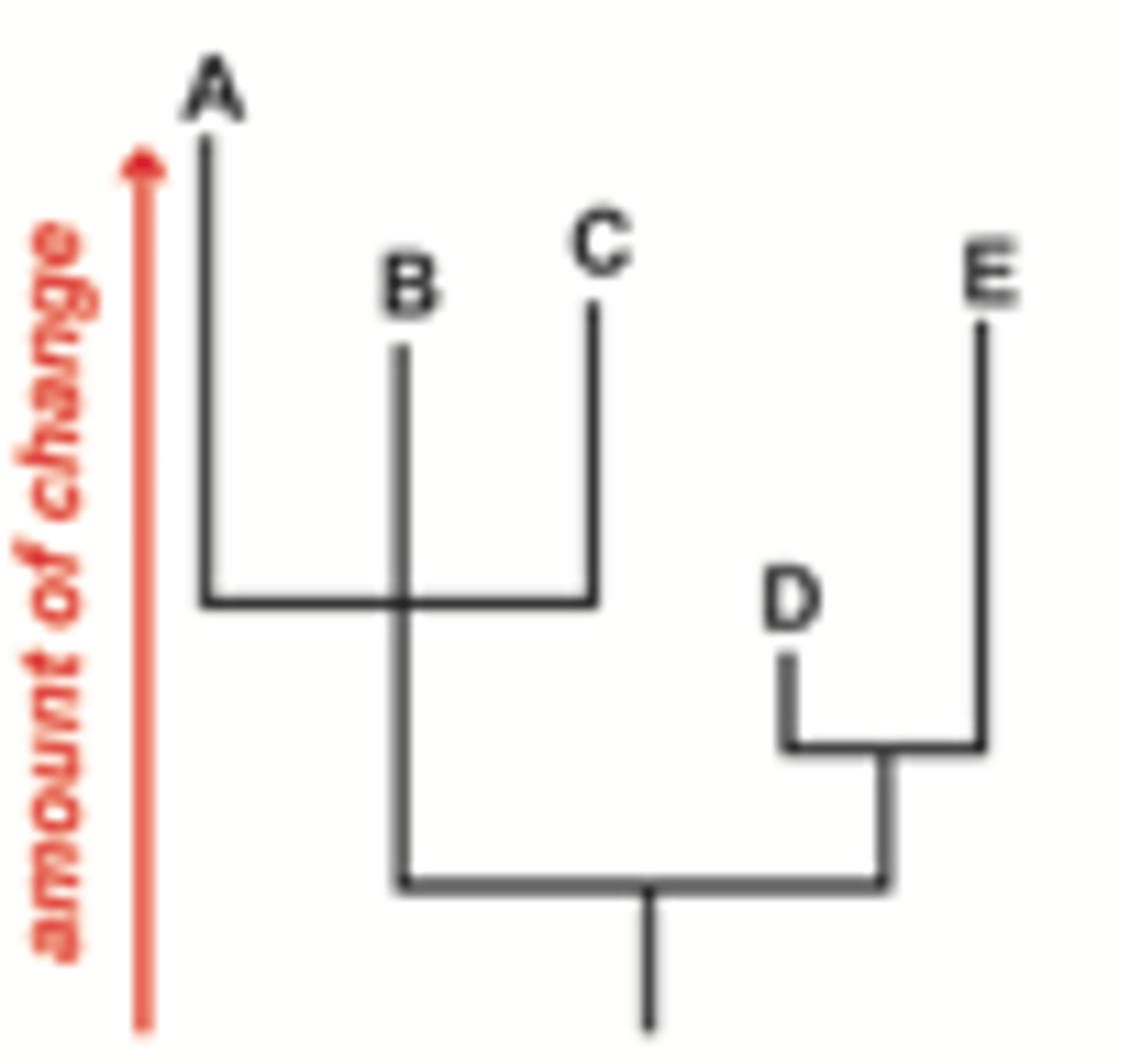
Chronograms
trees that provide information about the time of split between different groups
Taxonomy
area of biology that is associated with describing, classifying, identifying and naming organisms
Systematics
the field associated with the classification of organisms based on their similarities, and their evolutionary history
Analogy
similarity in function or position between organs that have DIFFERENT evolutionary origin
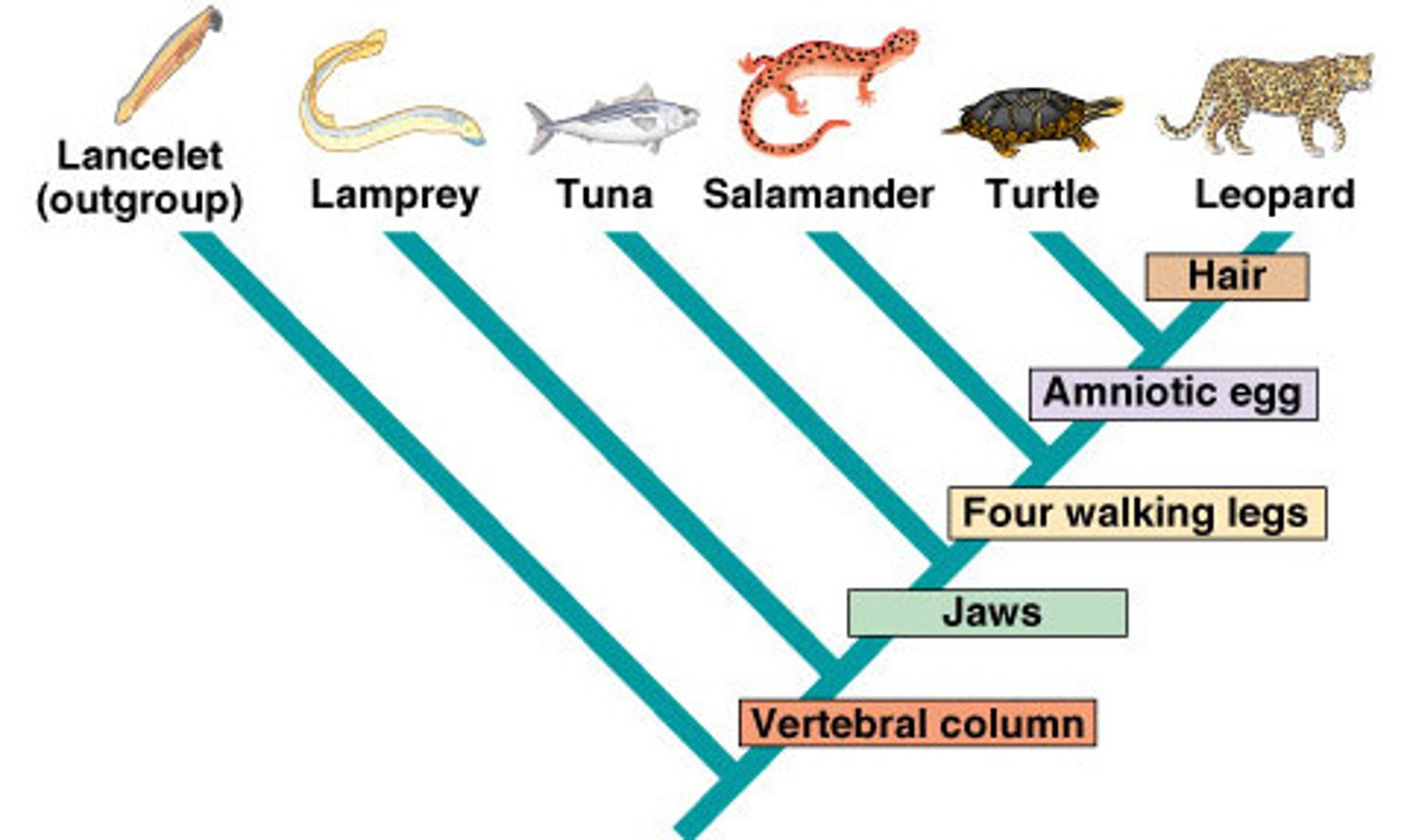
Homology
Structures that have same evolutionary origin, even if they have a different function
Synapomorphy
shared derived characteristic (homology);
defines clade
Homoplasy
represents a trait that is similar between two species, but these two species do not share a common ancestor (analogy)
Symplesiomorphy
shared primitive characteristic that is not present or different in one of the species in the group
Maximum Parsimony
Among competing hypotheses, the tree with the fewest number of changes should be selected
Disadvantage of Maximum Parsimony
based on the same information, you can end up with multiple trees that show different relationships
Distance Based Methods
Phylogenies based on the pairwise distances between species or populations
Limitations of distance based methods
Group species according to similarity regardless of true evolutionary history
Likelihood based methods
evaluates different trees and determines their likelihood or probability based on a chosen evolutionary model
Bootstrap Resampling
"sampling with replacement"
Can be used for all methods
Does not represent the probability of the whole tree, but rather the confidence in branching events