EBP After Midterm Material
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Diagnosis
A process that…
Labels patients
Classifies a problem
Determines prognosis
Determines intervention
Purpose of a Diagnosis
Focus the examination on a particular body region or symptom
Identify potential problems requiring referral to a physician or other specialist
Assist in the classification process
Test Threshold
“The probability below which a diagnostic test will not be ordered or performed because the possibility of the diagnosis is so remote”
Treatment Threshold
“The probability above which a diagnostic test will not be ordered or performed because the possibility of the diagnosis is so great that immediate treatment is indicated.”
meaning Probability is so high, I probably don’t need a diagnostic test bc I am very likely this happens
Sensitivity
Ability of the test to correctly identify (+ test result) in someone with the disorder
equation for sensitivity
patients with the disorder who test positive/ all patients with the disorder
true positive / (true positive +false negative)
Specificity
Ability of the test to correctly identify (- test result) in someone without the disorder
equation for Specificity
patients without the disorder who test negative / all patients without the disorder
true negative / (false positive + true negative)
Positive Predictive Value
Ability of the test to correctly determine the % of people with the disorder from all of the people with positive test results
equation for Positive predictive Value
Patients with the disorder who test positive
over
All patients who test positive
a/ a+b
Negative Predictive Value
Ability of the test to correctly determine the % of people without the disorder from all of the people with a negative test result
How many people who tested negative truly don’t have the condition
equation for Negative predictive Value
Patients without the disorder who test negative / All patients who test negative
true negative / (false negative + true negative)
Positive Likelihood Ratio
The likelihood that a positive test result was observed in a person with the disorder v. in a person without the disorder of interest
Ratio of True + : false +
Range from 0- infinity
Likely over 1
Want it to be high
equation for Positive Likelihood Ratio
Sensitivity / 1 - Specificity
Negative Likelihood Ratio
The likelihood that a negative test result is observed in a person with the disorder v. in a person without the disorder of interest
Ratio of False - : True –
equation for negative likelihood ratio
1 - Sensitivity
over
Specificity
what does it mean if LR+ > 10 or LR - < 0.10
large and conclusive change
what does it mean if LR+ = 5-10 or LR- = 0.10-0.20
moderate change
what does it mean if LR+ = 2-5 or LR- = 0.20-0.50
small, but sometimes important change
what does it mean if LR+ = 1-2 or LR- = 0.50-1.0
Negligible change in pre-test probability
How do you determine pre- test probability?
Prevalence (%)
Could get from history, collect from subjective
How do you determine pre-test odds?
What you think the odds are that the patient has the disorder before you conduct the diagnostic test
= pretest probability/ 1-pretest probablity
How do you determine post-test odds?
What you think the odds are that the patient has the disorder after you conduct the diagnostic test
= pretest odds x LR+/-
How do you determine post-test probability?
Probability of the disorder once the test results are obtained
= Posttest odds/ posttest odds + 1
p-value
the probability that the result (e.g., correlation coefficient, Sn, Sp, PPV, PNV, LR+, LR-) occurred due to chance
95% confidence interval
the range of values within which the true value is estimated to lie within a 95% probability
Considerations and clinical tests/ measures for diagnostic criteria
Reliability/Validity
Minimal Detectable Change (MDC)
Sn, Sp, LR, PV ?
Additional Considerations for diagnostic testing credibility
Is there a detailed description of the:
Clinical Setting
Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
Protocol for test(s)
Prognosis
A process that tells us…
Which outcomes could happen
The likelihood that outcomes will happen
The timeframe for outcome development
Develop POC and set goals
prognostic indicator
may predict any type of event or outcome
risk factor
predicts adverse events or outcomes
Case control study
Retrospective comparison of two groups
1 group w/ disorder or outcome, 1 group w/o disorder or outcome
Look at proportion of each group who had the risk factor or prognostic indicator of interest
cohort study
Prospective comparison of two or more groups before they have the disorder or outcome
Monitor the groups to see who develops the disorder or outcome and identify what characteristics they have
predictive model
Can use retrospective or prospective data
Regression model determines which relevant factors predict the outcome of interest
survival rates
What is the rate of outcome development over time
relative risk
Ratio of risk for developing the adverse outcome in patients with the risk factor versus patients without the risk factor
With people who have the factor, which of them develop the outcome
Generally depends on being able to determine incidence of the outcome
Best for prospective studies
odds ratio
The likelihood that an individual with the prognostic or risk factor will develop the outcome of interest
Seen in prospective and retrospective, better for prospective
Likelihood of the event occurring in a specific group
Proportion of people who do have it to people who don't
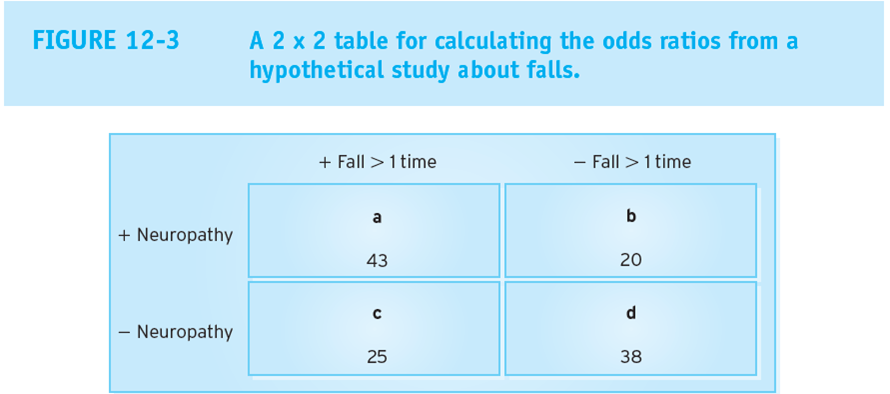
equation for Odds ratio
(a/b) / (c/d)
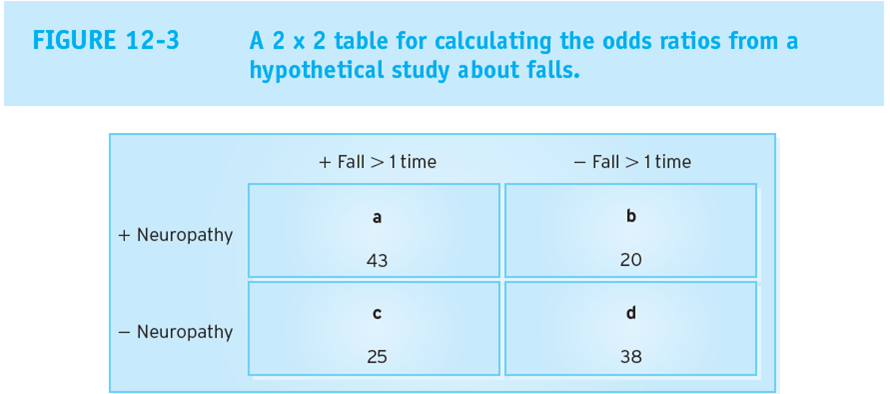
equation for relative risk
(a/a+b)/ (c/c+d)
what does a RR >1 mean?
increased risk of adverse outcome
what does a RR of <1 mean?
decreased risk of an adverse outcome
what does an OR >1 mean if the outcome is negative?
the odds are in favor of an adverse outcome
the problem will develop
what does an OR >1 mean if the outcome is positive?
the odds are in favor of a positive outcome
what does an OR <1 mean if the outcome is negative?
the odds are against an adverse outcome
the prognostic factor is protective against the problem
what does an OR <1 mean if the outcome is positive?
the odds are against a positive outcome
the prognostic factor is harmful
What should be considered about a regression analysis?
the more factors/ variables there are, the more people you need to have to power it
you should have 20 people per factor
what does an OR of 1 mean?
represents a 50:50 chance of increasing or decreasing the odds that the outcome will occur
what does a RR of 1 mean?
represents a 50:50 chance increasing or decreasing the risk that the outcome will occur
issues related to experimental designs
best for controlling bias, but excessive control may overshadow clinical relevance
issues with quasi experimental designs
more vulnerable to bias, but may be more clinically relevant
issues with non-experimental designs
most vulnerable to bias, but may be most clinically relevant
what is the outcome under ideal conditions?
efficacy
what is the outcome in the clinical scenario?
effectiveness
effect size
a statistical expression of the size of the difference between sample means”
Effect from pre to post / independent of sample size
equation for absolute effect size
mean score (experimental) - mean score (control)
equation for standardized effect size
mean score (experimental) - mean score (control) / pooled standard deviation
treat to effect size
not having enough power or big enough sample
weakness to effect size
doesn’t consider the roles of bias and doesn’t consider if it is normally distributed or not (skewed data can lead to large effect sizes)
Cohen’s D
most common equation to find pooled standard deviation
what is considered a large effect size / big effect?
0.8
what is considered a big enough effect from treatment that we can see it with the naked eye?
0.5-0.8
what is considered an effect size where the treatment effect is small enough that we cannot see it with the naked eye?
0.2-0.49
what is considered no treatment effect using effect size?
<0.2
Minimally clinically important difference
The minimal level of change REQUIRED in response to an intervention before the outcome would be considered worthwhile
Should at least exceed the standard error of measurement (SEM) for the outcome of interest
absolute benefit increase
There was x % difference in positive outcomes between experimental and control groups
Percent of people that would benefit from the treatment
% therapy group w/ outcome - % control group w/ outcome
equation for Number needed to treat
1/ ABI
Number needed to treat
for every “x” number of individuals, 1 will have the positive outcome
relative benefit increase
Absolute difference in positive outcome relative to everyone with the outcome
Those who receive the treatment improve by x% relative to those who didn’t receive the treatment
the more people in the control that get better, this value would be lower
equation for relative benefit increase
(% therapy group w/ outcome - % controls w/ outcome) /
(% of controls w/ outcome)
equation for relative risk reduction
(% controls group w/ outcome - % therapy group w/ outcome) /
(% of controls w/ outcome)
equation for absolute risk reduction
% controls w/ problem - % therapy group w/ problem
Absolute risk reduction
By how much does the intervention reduce the risk of an unwanted “event” (i.e., injury)?
outcome measures
measures taken to asses the impact of a disease or disorder ont he patient
test retest
reproducibility (stability) of a score when a measure is repeated under the same conditions at the same point in time
internal consistency
relationship between items in a questionnaire
(going to look at all the items and if they are related to each other and the change in the overall measure)
tests used to determine test-retest
ICC and Kappa
Tests used to determine internal consistency
Chronbach’s alpha
what is an appropriate range for chronbach’s alpha
0.7-0.9
Why do we not want a range of 0.9-1.0 for a chronbach’s alpha value?
the questions the measure is asking may be redundant, so we may need to ask different things
what is an appropriate ICC value?
>0.75
What is an appropriate kappa value?
>0.51
what do regression equations determine?
Predictive validity- if they fall below a score, are they more likely to have a good or poor outcome with therapy
Sources of measurement error
Instrument
Person collecting measure
Environment
Patient
Standard Error of Measurement
error at a single point in time
equation for standardized response mean
mean of change scores / standard deviation of change scores
"good” standard response mean value
> 1.0
equation to find effect size
mean of change scores / standard deviation of initial scores
“large” effect size value
> 0.8
Clinical Prediction Rule
Cluster of s/s to provide meaningful info or predictions of an outcome of interest that are:
Systematically derived
Statistically tested
what does the derivation step of CPR do?
identifies of factors with predictive power
what level of evidence is derivation
4
what does the narrow validation step of CPR do
applies the rule in a similar clinical setting and population as the derivation process
what does the Broad validation step of CPR do
applies the rule to multiple clinical settings with varying prevalence and outcomes of the condition
what does the impact analysis step of CPR do
identifies that a rule changes physician behavior and improves patient outcomes / reduces costs
what level of evidence is narrow validation?
3
What level of evidence is broad validation?
2
What level of evidence is impact analysis?
1
Clinical prediction Guidelines
Statements to assist practitioner and patient decisions in specific circumstances
Systematically developed
Have some component of a systematic review associated w them
what do CPG’s reflect?
Current best evidence
Expert clinical judgment
Patient opinion/perspective
Should be a good representation of evidence based practice
Who were CPG’s developed by?
Government agencies
Professional societies